4c8b23c666dd161f0449f161c93ee10c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

Thin Ice in the Cyber World Presented by Dr. Bill Hancock, CISSP, CISM Vice President, Security & Chief Security Officer bill. hancock@savvis. net 972 -740 -7347
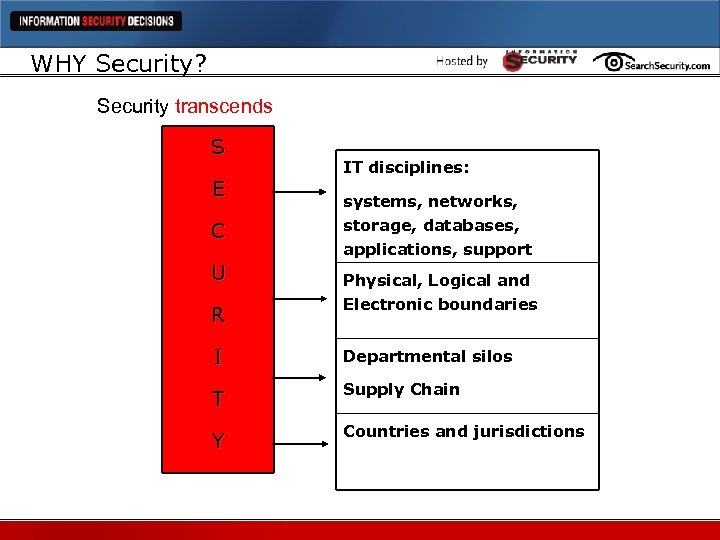
WHY Security? Security transcends S E C U R IT disciplines: systems, networks, storage, databases, applications, support Physical, Logical and Electronic boundaries I Departmental silos T Supply Chain Y Countries and jurisdictions

The Classic Reasons l Protect assets l PR fears l Management edict l Corporate policies l Fear of attacks l Customer info l Legal reasons l Was breached…
The Past
The Present Source: http: //cm. bell-labs. com/who/ches/map/gallery/index. html

Software Is Too Complex 50 l Sources of Complexity: Applications and operating systems 3 4 0 WINDOWS XP (2001) IP stacks in cell phones, PDAs, gaming consoles, refrigerators, thermostats 10 WINDOWS 2000 (2000) Always-on connections 16. 5 WINDOWS 98 (1998) Complex Web sites 15 WINDOWS NT 4. 0 (1996) • • • New Internet services § XML, SOAP, Vo. IP 18 20 WINDOWS 95 (1995) • 30 WINDOWS NT (1992) Data mixed with programs 35 WINDOWS 3. 1 (1992) • 40 MILLIONS • 45
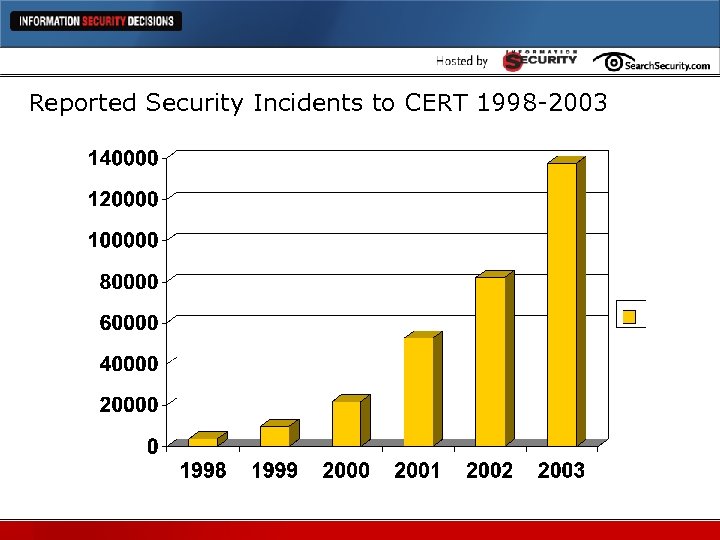
Reported Security Incidents to CERT 1998 -2003
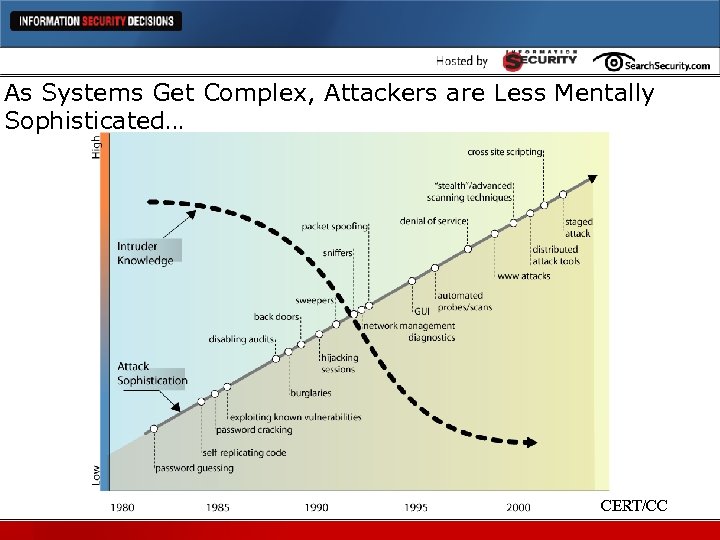
As Systems Get Complex, Attackers are Less Mentally Sophisticated… CERT/CC

Attacker Diversity l Script kiddies l Social misfits l Internal attackers l Hacking “gangs” l Organized crime l Nation-state sponsored entities l Terrorist entities
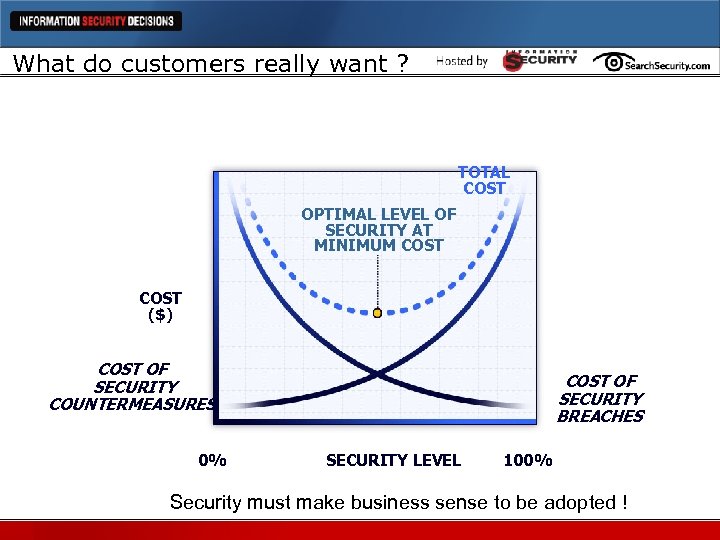
What do customers really want ? TOTAL COST OPTIMAL LEVEL OF SECURITY AT MINIMUM COST ($) COST OF SECURITY COUNTERMEASURES 0% COST OF SECURITY BREACHES SECURITY LEVEL 100% Security must make business sense to be adopted !

Security Biz Case Drivers The PAL Method l PAL – PR, assets/IP, law l Public Relations Issues • Costs for bad PR almost always exceed good security implementation l Asset Protection and Intellectual Property • • Intellectual property Customers Employees Data stores l The Law • Each country has compulsory compliance laws about security that most companies violate and don’t realize it

Purpose of the following section l Goal here is not to hit everything, just items that are either very timely or a bit outside the normal reporting of security events we see everyday
Classic Current IT Security Risks l DNS attacks l DDo. S, etc. l Virii, worms, etc. l Spoofs and redirects l Social engineering l Router table attacks l OS holes, bugs l Application code problems l Insider attacks l Others…

Upcoming Security Threats l Geographic location l China is major concern • Legislation in other countries l New hacker methods and tools l Vo. IP l IP-VPN (MPLS) l ASN. 1 and derivatives l Hacker “gangs” l Complexity of application solutions make it easier to disrupt them (Active Directory, Vo. IP, etc. ) l Industrial espionage from competition l Covert sampling l Covert interception

Threats - Infrastructure l Core (critical) • Routing infrastructure • DNS • Cryptographic key mgt. • PBX and voice methods • E-mail • Siebel database

Threats – Infrastructure, II l Essential • Financial systems • Customer console management systems • Access management to Exodus critical resources • Intellectual property protection methods • Privacy control methods • Internal firewalls and related management • HR systems

Routing Infrastructure l No router-to-router authentication • Router table poisoning • Vector dissolution • Hop count disruption • Path inaccuracies • Immediate effect • Redundancy has no effect on repair/recovery l Edge routers/switches do not use strong access authentication methods

Routing Infrastructure, II l No CW-wide internal network IDS/monitoring l No internal network security monitoring for anomalies or stress methods l No effective flooding defense or monitoring

DNS Security Assessment l Grossly inadequate security methods against attacks l No distributed method for attack segmentation recovery l No IDS or active alarms on DNS to even see if they are up or down l Geographic distribution inadequate and easy to kill due to replication l Zone replication allows poisoning of DNS dbms l DNS servers around the company do not implement solid security architecture

Mobile Technology Security l Most corporate mobile technology when removed from the internal network or premises is WIDE OPEN to data theft, intrusion, AML, etc. • Laptops (no FW, IDS, VPN, virus killers, email crypto, file crypto, theft prevention/management, cyber tracking, remote data destruct, remote logging, AML cleaning, etc. • Palm Pilots, etc, - no security • 3 G and data cells – no security • No operational security over wireless methods

Cyberterrorism l It’s real l It’s a major problem l Most sites have no clue on how to deal with it or what all is involved l Many sites have already been used for temporary storage of terrorist operational data (micro web sites, FTP buffer sites, steganography transfer, etc. ) l If not on your radar, put it there now

Autonomous Malicious Logic l Worms, which increase with complexity and capabilities with each iteration l Increasing body of hostile code l Scans large blocks if IP addresses for vulnerabilities • • Target agnostic Large or small, powerful or not l No specific attack rationale means that anyone is vulnerable l Sharp increase in number seen in last year and growing

Buffer Overflows l Concept is not new, but there a lot of new ones appearing daily l Due to underlying problems with core protocol language issues, such as ASN. 1, the same buffer overflow attack packet type for a specific protocol can affect many different entities in different ways: • SNMP OID buffer overflow in February 2002 affected practically every instantiation of SNMP that used ASN. 1 as the base definitional metalanguage • What it did to one vendor was radically different than what it did to a second vendor for the same type of packet attack

Password Crackers l Sharp rise in availability of password cracking programs l Bulk of them use brute force methods or known dictionary attack methods l Some are taking advantage of exploits of a known password hashing method l Commercial products starting to appear in the industry

Default Passwords l Still a popular exploit method: • • • Wireless access point admin Operating systems Broadband cable modems Routers out-of-the-box Databases out-of-the-box Simple exploits § Laser printer passwords § SCADA components § Embedded systems

Vendor Distributed Malware l Due to lack of care in preparing distribution kits, many vendors are starting to distribute their products with malware in it • Recent gaming company distributed NIMDA with a CD distribution • Others have shipped virii and other malicious code infestations l Perimeter malware checking is not enough anymore

Insiders l Still a major threat l Responsible for over 90% of actual financial losses to companies l Most sites do not have enforceable internal security controls or capabilities • • • Legacy system Hyperhrowth of systems/networks Lack of care and planning in security as the growth has happened
Cryptographic Key Management l None l What is available is all manual l Changing keys on some technologies takes MONTHS (e. g. TACACS+) l Keys are weak in some areas and easily broken l No “jamming” defenses for key exchange methods l Little internal knowledge on key mgt and cryptographic methods

PBX and Voice Methods l No assessment of toll fraud and PBX misuse l Cell phones used continually for sensitive conversations l No conference call monitoring for illicit connections or listening l No videoconferencing security methods

PBX and Voice Methods, II l No voicemail protection or auditing efforts trans company l Easy to social engineer PBX access and redirection l Redundancy of main switching systems questionable (e. g. May 2002 CWA OC-12 disruption)

E-Mail Security Issues l Employees in trusted positions reading e-mail l E-mail security methods take a long time to implement l Lack of use of encryption methods for confidential e-mail l Lack of keyserver for cryptographic methods (this is due to power) l Newly devised security methods not implemented yet l Use of active directory and LDAP in future a major concern

E-Mail Security Issues, II l Wireless e-mail a concern l No filters for SPAM l No keyword filter searching methods for potential IP “leakage” l Ex employees retain access information for their and other accounts

Hyperpatching l The need to quickly patch vulnerabilities is becoming a major security pain point l Protocol exploits such as SNMP will accelerate and require additional patching and fixes l Customers should stop with “old think” change control and start considering using hyperpatching and mass roll-out systems (push technology) to start solving hyperpatching problems

Employee Extortion l At least 5 different extortion methodologies have appeared that affect employee web surfers l Latest one involves persons who surf known child pornography web sites or hit on chat rooms on the subject • A link is e-mailed to the person and they threatened with being turned over to officials and employers unless they pay to keep the information about their surfing habits secret l This is a growing business…

Old Code Liabilities l. Software vendors are trying to figure out how to decommission older versions and older code quickly due to patch/fix and general liability issues l. Old code does not have security controls that are compatible with today’s problems and security systems

Wireless l Continues to be a problem l Mostly due to lack of implementation of controls l War driving is easy to do for most sites and to get on most networks l Illegal connection to a wireless network violates FCC regs l Need intrusion detection for wireless to detect who is associated to the LAN and doesn’t belong l Best short-term solution are peer-to-peer VPNs (desktop, site-to-site, etc. ) l New threats with upcoming 3 G products

Data Retention l BIG push for data retention in many parts of the world l With retention comes liabilities for retained information l U. S. has no specific retention laws except in specific financial and healthcare areas l EU and Asian countries recently enacted serious retention laws

M&A and Partnership Security l We often know nothing about the security of a non-corporate solution l After examination, most are very bad l We need procedures for evaluation of partners and M&A for security issues and corrective action l We also need to have as part of the diligence process proper security oversight on acquisitions • We often do not know about an M&A target until the press announcement

Blended Attacks l Biological and Cyber • Smallpox infection and DDo. S against infrastructure l Multiphasic Cyber Attack • DDo. S against routers, DNS poisoning attacks and defacement attacks at the same time l Sympathetic hacking group attacks l Upstream infrastructure attack • • IXC disruption Power grid disruption Peering point disruption Supply-chain vendor disruption

Questions? Dr. Bill Hancock, CISSP, CISM Vice President, Security & Chief Security Officer Email: bill. hancock@savvis. net Phone: 972 -740 -7347
4c8b23c666dd161f0449f161c93ee10c.ppt