01369849fffb088e606b1ae8f87ad591.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Thick GEM-like multipliers: a simple solution for large area UV-RICH detectors R. Chechik, A. Breskin and C. Shalem Dept. of Particle Physics, The Weizmann Institute of Science, 76100 Rehovot, Israel R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 1
Thick GEM-like multipliers: a simple solution for large area UV-RICH detectors R. Chechik, A. Breskin and C. Shalem Dept. of Particle Physics, The Weizmann Institute of Science, 76100 Rehovot, Israel R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 1
 30 years of “Hole-multiplication” history: • Breskin, Charpak NIM 108(1973)427 discharge in glass capillaries • Lum et al. IEEE NS 27(1980)157, Del Guerra et al. NIMA 257(1987)609 Avalanches in holes • Bartol, Lemonnier et al. J. Phys. III France 6(1996)337 • Sakurai et al. NIMA 374(1996)341, Peskov et al. NIMA 433(1999)492 • Sauli NIMA 386(1997)531 CAT Glass Capillary Plates GEM • Ostling, Peskov et al, IEEE NS 50(2003)809 G-10 “Capillary plates ” R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 2
30 years of “Hole-multiplication” history: • Breskin, Charpak NIM 108(1973)427 discharge in glass capillaries • Lum et al. IEEE NS 27(1980)157, Del Guerra et al. NIMA 257(1987)609 Avalanches in holes • Bartol, Lemonnier et al. J. Phys. III France 6(1996)337 • Sakurai et al. NIMA 374(1996)341, Peskov et al. NIMA 433(1999)492 • Sauli NIMA 386(1997)531 CAT Glass Capillary Plates GEM • Ostling, Peskov et al, IEEE NS 50(2003)809 G-10 “Capillary plates ” R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 2
![Expanding the standard GEM… Standard GEM TGEM Geometry: similar to “Optimized GEM” [Peskov] But: Expanding the standard GEM… Standard GEM TGEM Geometry: similar to “Optimized GEM” [Peskov] But:](https://present5.com/presentation/01369849fffb088e606b1ae8f87ad591/image-3.jpg) Expanding the standard GEM… Standard GEM TGEM Geometry: similar to “Optimized GEM” [Peskov] But: etched rim 1 mm • 50 holes/mm 2 • Microlithography + etching • High Spatial resolution (tens of microns) • VGEM~400 V • >103 gain in single GEM • 106 gain in cascaded GEMs • Fast (ns) • Low pressure – gain~30 • • • 1 -2 holes/mm 2 PCB tech. of etching + drilling Simple and robust Sub-mm to mm spatial resolution VTGEM~2 KV (at atm. pressure) 105 gain in single-TGEM, 107 gain in double-TGEM • Fast (few ns) • Low pressure (<1 Torr) gain 104 Torr R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 3
Expanding the standard GEM… Standard GEM TGEM Geometry: similar to “Optimized GEM” [Peskov] But: etched rim 1 mm • 50 holes/mm 2 • Microlithography + etching • High Spatial resolution (tens of microns) • VGEM~400 V • >103 gain in single GEM • 106 gain in cascaded GEMs • Fast (ns) • Low pressure – gain~30 • • • 1 -2 holes/mm 2 PCB tech. of etching + drilling Simple and robust Sub-mm to mm spatial resolution VTGEM~2 KV (at atm. pressure) 105 gain in single-TGEM, 107 gain in double-TGEM • Fast (few ns) • Low pressure (<1 Torr) gain 104 Torr R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 3
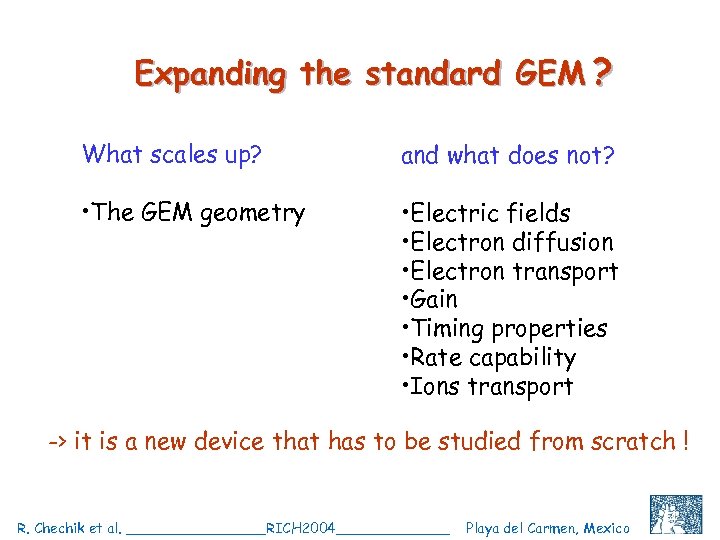 Expanding the standard GEM ? What scales up? and what does not? • The GEM geometry • Electric fields • Electron diffusion • Electron transport • Gain • Timing properties • Rate capability • Ions transport -> it is a new device that has to be studied from scratch ! R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 4
Expanding the standard GEM ? What scales up? and what does not? • The GEM geometry • Electric fields • Electron diffusion • Electron transport • Gain • Timing properties • Rate capability • Ions transport -> it is a new device that has to be studied from scratch ! R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 4
 The TGEMs: A TGEM costs ~4$ /unit. With minimum order of 400$ ~120 TGEMs. >10 times cheaper than standard GEM from CERN. R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 5
The TGEMs: A TGEM costs ~4$ /unit. With minimum order of 400$ ~120 TGEMs. >10 times cheaper than standard GEM from CERN. R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 5
 Various TGEMs studied at WIS Manufactured by standard PCB techniques of precise drilling in G-10 (+ other materials) and Cu etching Typical Atm. pressure geometry Low pressure geometry Hole diameter d=0. 3 mm Hole diameter d=1 mm Distance between holes a=0. 7 mm Distance between holes a=1. 5 mm 3 cm Thickness t=0. 4 mm Thickness t=1. 6 mm Cu G-10 0. 1 mm rim to prevent discharges 0. 1 mm Important for high gains! R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 6
Various TGEMs studied at WIS Manufactured by standard PCB techniques of precise drilling in G-10 (+ other materials) and Cu etching Typical Atm. pressure geometry Low pressure geometry Hole diameter d=0. 3 mm Hole diameter d=1 mm Distance between holes a=0. 7 mm Distance between holes a=1. 5 mm 3 cm Thickness t=0. 4 mm Thickness t=1. 6 mm Cu G-10 0. 1 mm rim to prevent discharges 0. 1 mm Important for high gains! R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 6
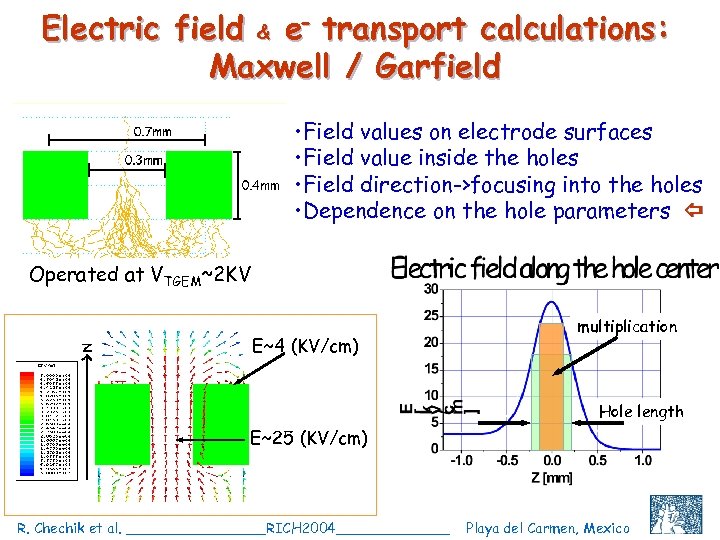 Electric field & e- transport calculations: Maxwell / Garfield • Field values on electrode surfaces • Field value inside the holes • Field direction->focusing into the holes • Dependence on the hole parameters Operated at VTGEM~2 KV E~4 (KV/cm) multiplication Hole length E~25 (KV/cm) R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 7
Electric field & e- transport calculations: Maxwell / Garfield • Field values on electrode surfaces • Field value inside the holes • Field direction->focusing into the holes • Dependence on the hole parameters Operated at VTGEM~2 KV E~4 (KV/cm) multiplication Hole length E~25 (KV/cm) R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 7
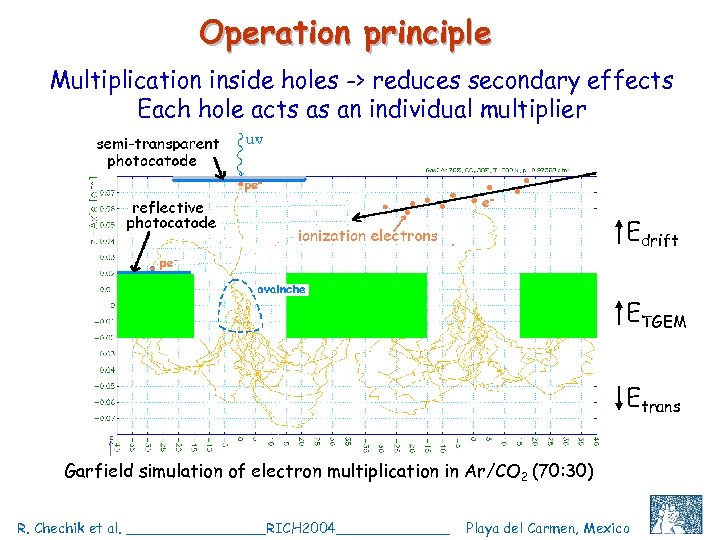 Operation principle Multiplication inside holes -> reduces secondary effects Each hole acts as an individual multiplier Edrift ETGEM Etrans Garfield simulation of electron multiplication in Ar/CO 2 (70: 30) R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 8
Operation principle Multiplication inside holes -> reduces secondary effects Each hole acts as an individual multiplier Edrift ETGEM Etrans Garfield simulation of electron multiplication in Ar/CO 2 (70: 30) R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 8
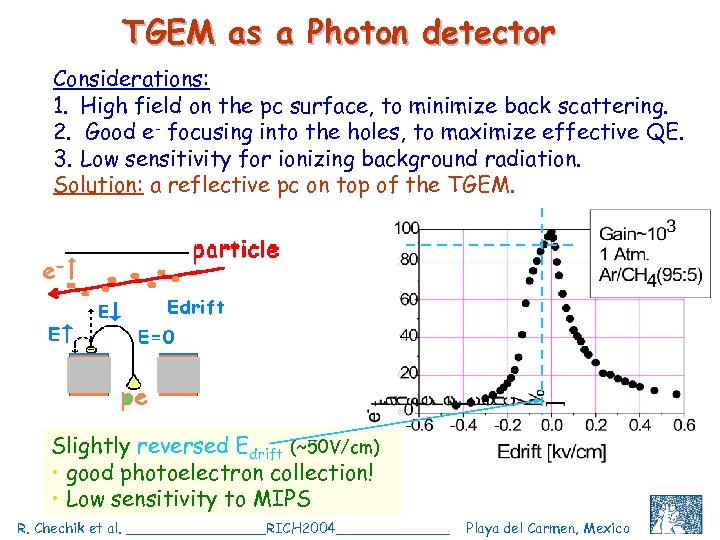 TGEM as a Photon detector Considerations: 1. High field on the pc surface, to minimize back scattering. 2. Good e- focusing into the holes, to maximize effective QE. 3. Low sensitivity for ionizing background radiation. Solution: a reflective pc on top of the TGEM. Slightly reversed Edrift (~50 V/cm) • good photoelectron collection! • Low sensitivity to MIPS R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 9
TGEM as a Photon detector Considerations: 1. High field on the pc surface, to minimize back scattering. 2. Good e- focusing into the holes, to maximize effective QE. 3. Low sensitivity for ionizing background radiation. Solution: a reflective pc on top of the TGEM. Slightly reversed Edrift (~50 V/cm) • good photoelectron collection! • Low sensitivity to MIPS R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 9
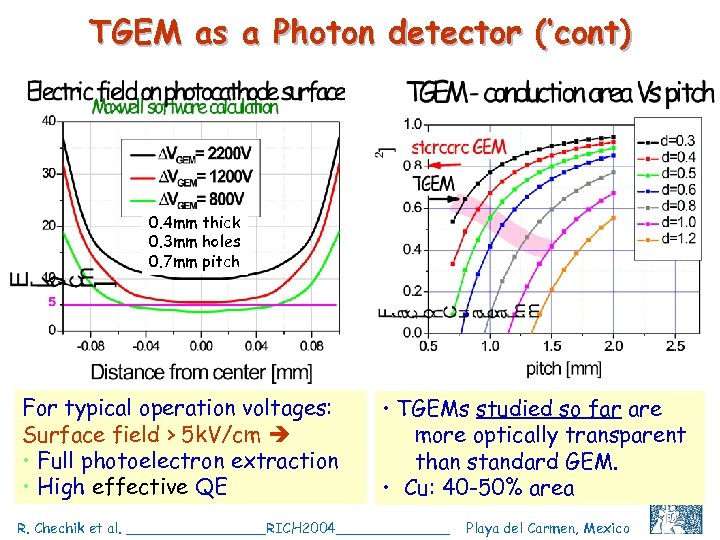 TGEM as a Photon detector (‘cont) 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch For typical operation voltages: Surface field > 5 k. V/cm • Full photoelectron extraction • High effective QE • TGEMs studied so far are more optically transparent than standard GEM. • Cu: 40 -50% area R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 10
TGEM as a Photon detector (‘cont) 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch For typical operation voltages: Surface field > 5 k. V/cm • Full photoelectron extraction • High effective QE • TGEMs studied so far are more optically transparent than standard GEM. • Cu: 40 -50% area R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 10
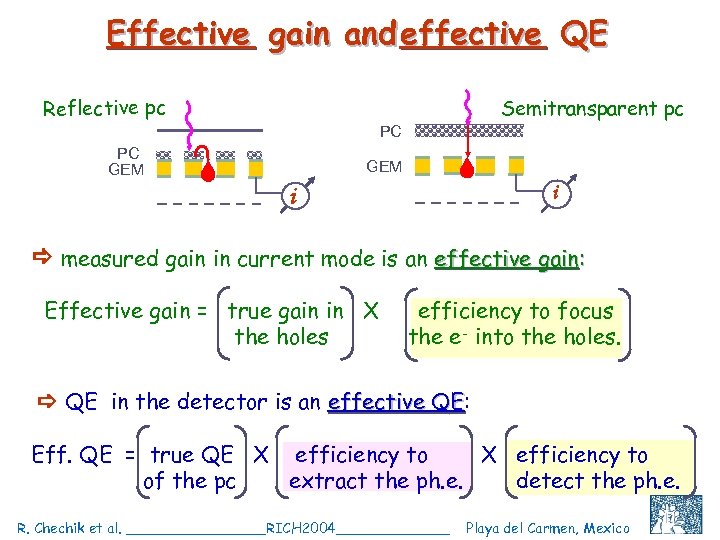 Effective gain and effective QE Reflective pc Semitransparent pc PC PC GEM i i measured gain in current mode is an effective gain: Effective gain = true gain in X the holes efficiency to focus the e - into the holes. QE in the detector is an effective QE: QE Eff. QE = true QE X efficiency to of the pc extract the ph. e. detect the ph. e. R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 11
Effective gain and effective QE Reflective pc Semitransparent pc PC PC GEM i i measured gain in current mode is an effective gain: Effective gain = true gain in X the holes efficiency to focus the e - into the holes. QE in the detector is an effective QE: QE Eff. QE = true QE X efficiency to of the pc extract the ph. e. detect the ph. e. R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 11
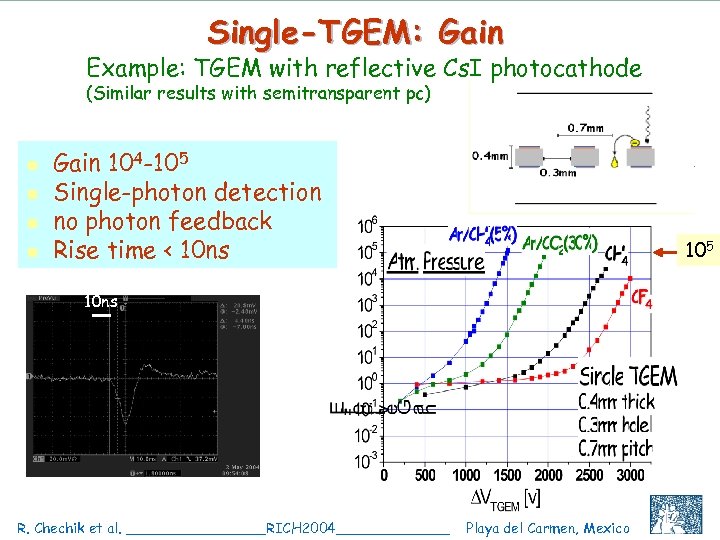 Single-TGEM: Gain Example: TGEM with reflective Cs. I photocathode (Similar results with semitransparent pc) n n Gain 104 -105 Single-photon detection no photon feedback Rise time < 10 ns 105 10 ns R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 12
Single-TGEM: Gain Example: TGEM with reflective Cs. I photocathode (Similar results with semitransparent pc) n n Gain 104 -105 Single-photon detection no photon feedback Rise time < 10 ns 105 10 ns R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 12
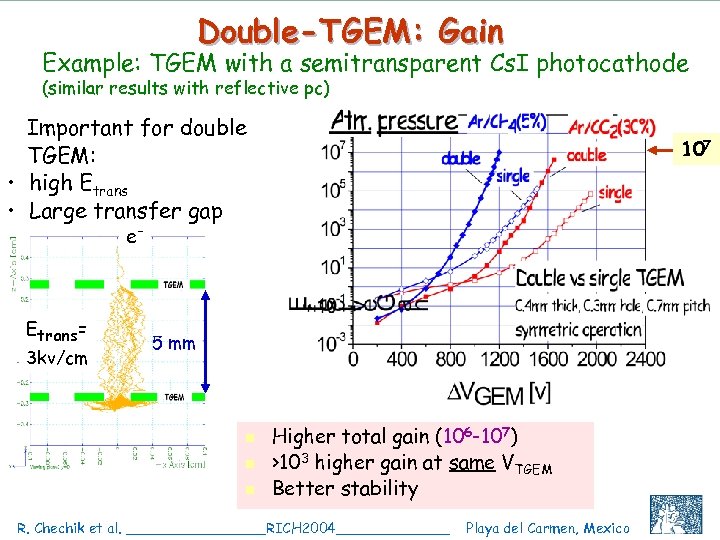 Double-TGEM: Gain Example: TGEM with a semitransparent Cs. I photocathode (similar results with reflective pc) Important for double TGEM: • high Etrans • Large transfer gap 107 e- Etrans = 3 kv/cm 5 mm n n n Higher total gain (106 -107) >103 higher gain at same VTGEM Better stability R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 13
Double-TGEM: Gain Example: TGEM with a semitransparent Cs. I photocathode (similar results with reflective pc) Important for double TGEM: • high Etrans • Large transfer gap 107 e- Etrans = 3 kv/cm 5 mm n n n Higher total gain (106 -107) >103 higher gain at same VTGEM Better stability R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 13
 Operation in CF 4 Problem: • Requires high TGEM voltage. • Damage due to sparks is fatal: after a spark the TGEM deteriorates continuously. (We suspect effects of etching to the Si. O 2 fibers). • Fatal spark damage was also observed in standard GEMs operating in CF 4, due to the high operating voltages. Solutions: • Segment the TGEM • Cascade several TGEMs. • Test other materials: Kevlar, Teflon, etc. R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 14
Operation in CF 4 Problem: • Requires high TGEM voltage. • Damage due to sparks is fatal: after a spark the TGEM deteriorates continuously. (We suspect effects of etching to the Si. O 2 fibers). • Fatal spark damage was also observed in standard GEMs operating in CF 4, due to the high operating voltages. Solutions: • Segment the TGEM • Cascade several TGEMs. • Test other materials: Kevlar, Teflon, etc. R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 14
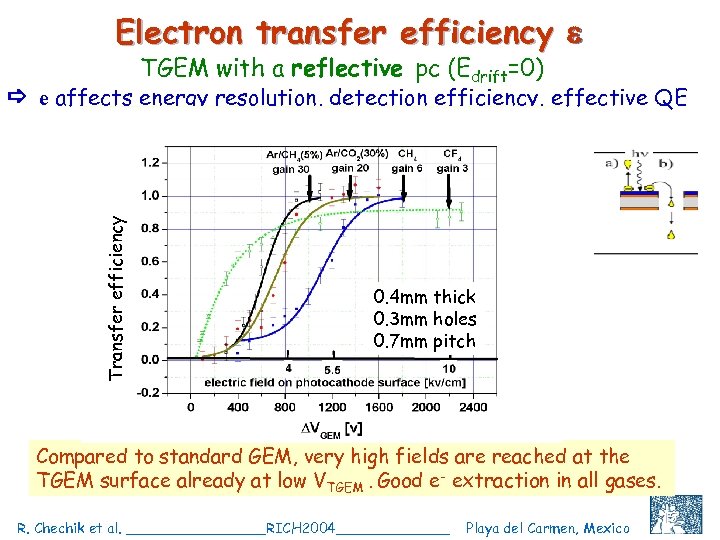 Electron transfer efficiency TGEM with a reflective pc (Edrift=0) Transfer efficiency e affects energy resolution, detection efficiency, effective QE F f 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch Compared to standard GEM, very high fields are reached at the TGEM surface already at low VTGEM. Good e- extraction in all gases. R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 15
Electron transfer efficiency TGEM with a reflective pc (Edrift=0) Transfer efficiency e affects energy resolution, detection efficiency, effective QE F f 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch Compared to standard GEM, very high fields are reached at the TGEM surface already at low VTGEM. Good e- extraction in all gases. R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 15
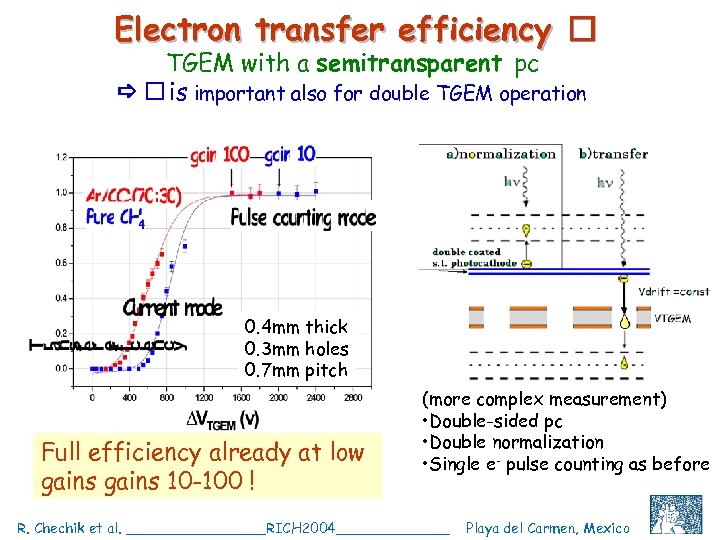 Electron transfer efficiency TGEM with a semitransparent pc is important also for double TGEM operation 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch Full efficiency already at low gains 10 -100 ! (more complex measurement) • Double-sided pc • Double normalization • Single e- pulse counting as before R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 16
Electron transfer efficiency TGEM with a semitransparent pc is important also for double TGEM operation 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch Full efficiency already at low gains 10 -100 ! (more complex measurement) • Double-sided pc • Double normalization • Single e- pulse counting as before R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 16
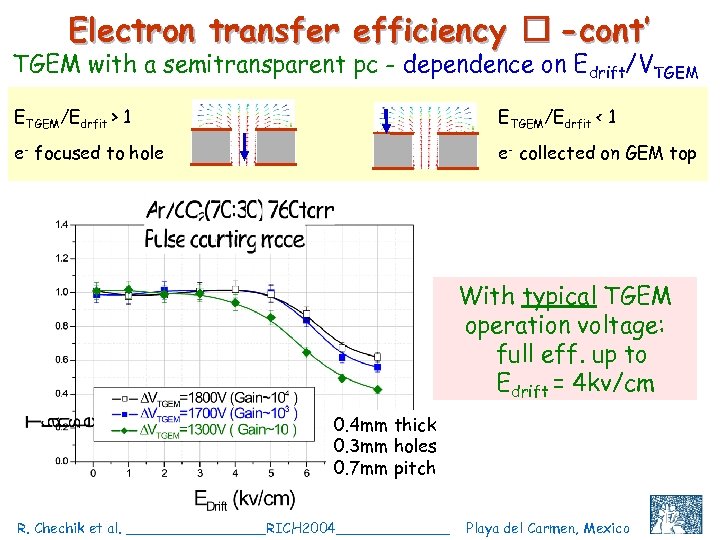 Electron transfer efficiency -cont’ TGEM with a semitransparent pc - dependence on Edrift/VTGEM ETGEM/Edrfit > 1 ETGEM/Edrfit < 1 e- focused to hole e- collected on GEM top With typical TGEM operation voltage: full eff. up to Edrift = 4 kv/cm 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 17
Electron transfer efficiency -cont’ TGEM with a semitransparent pc - dependence on Edrift/VTGEM ETGEM/Edrfit > 1 ETGEM/Edrfit < 1 e- focused to hole e- collected on GEM top With typical TGEM operation voltage: full eff. up to Edrift = 4 kv/cm 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 17
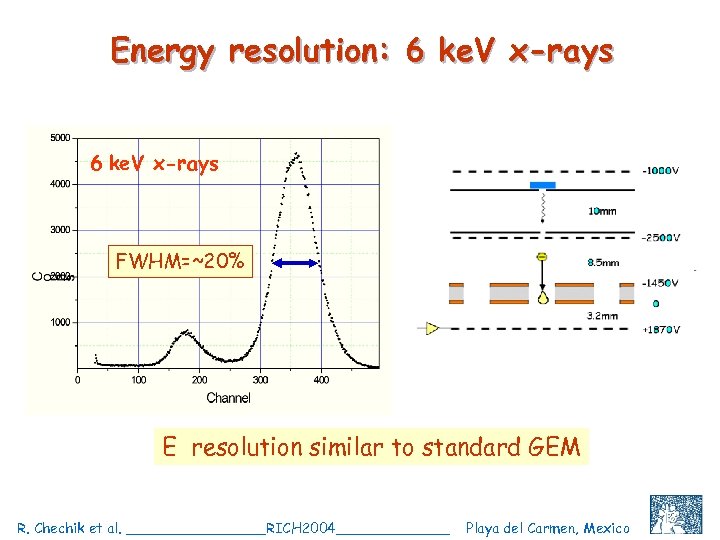 Energy resolution: 6 ke. V x-rays FWHM=~20% E resolution similar to standard GEM R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18
Energy resolution: 6 ke. V x-rays FWHM=~20% E resolution similar to standard GEM R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18
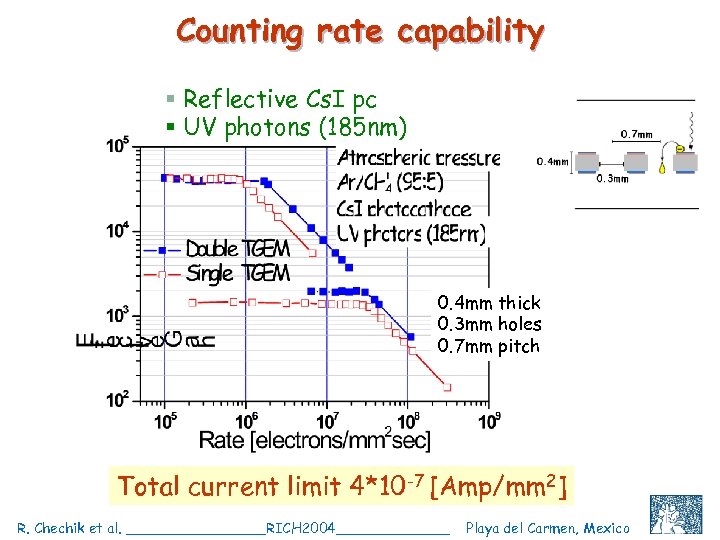 Counting rate capability § Reflective Cs. I pc § UV photons (185 nm) 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch Total current limit 4*10 -7 [Amp/mm 2] R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 19
Counting rate capability § Reflective Cs. I pc § UV photons (185 nm) 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch Total current limit 4*10 -7 [Amp/mm 2] R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 19
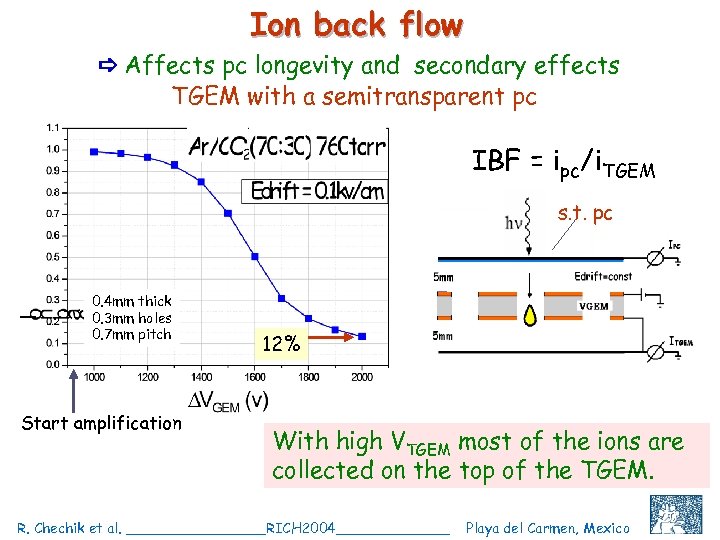 Ion back flow Affects pc longevity and secondary effects TGEM with a semitransparent pc IBF = ipc/i. TGEM s. t. pc 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch Start amplification 12% With high VTGEM most of the ions are collected on the top of the TGEM. R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 20
Ion back flow Affects pc longevity and secondary effects TGEM with a semitransparent pc IBF = ipc/i. TGEM s. t. pc 0. 4 mm thick 0. 3 mm holes 0. 7 mm pitch Start amplification 12% With high VTGEM most of the ions are collected on the top of the TGEM. R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 20
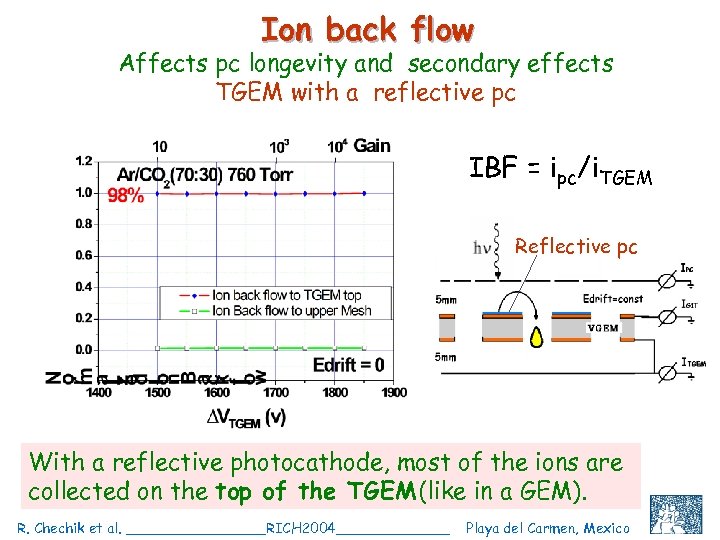 Ion back flow Affects pc longevity and secondary effects TGEM with a reflective pc IBF = ipc/i. TGEM Reflective pc With a reflective photocathode, most of the ions are collected on the top of the TGEM (like in a GEM). R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 21
Ion back flow Affects pc longevity and secondary effects TGEM with a reflective pc IBF = ipc/i. TGEM Reflective pc With a reflective photocathode, most of the ions are collected on the top of the TGEM (like in a GEM). R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 21
 Summary 1. G-10 TGEMs tested with several gases. 2. Gains: 105 with a single TGEM; 107 with cascaded double TGEM 3. Fast signals: r. t. <10 ns. 4. The e- transfer efficiency (into the holes) is well understood. 5. Counting rate capability: ~ 106 avalnches/sec x mm 2 @ gain 4 x 104 6. Ion backflow: study in course 7. In TPC-like conditions: IBF with a single TGEM is 12%. 8. In GPM/reflective pc: IBF with a single TGEM is 98%. 9. A cascade + other “tricks” (see GEM/MHSP) should reduce IBF . 10. 8. TGEMs of different materials (e. g. Kevlar, Teflon…) for CF 4 ? . 11. 9. Will study TGEM of lower optical transparency (higher eff. QE) R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 22
Summary 1. G-10 TGEMs tested with several gases. 2. Gains: 105 with a single TGEM; 107 with cascaded double TGEM 3. Fast signals: r. t. <10 ns. 4. The e- transfer efficiency (into the holes) is well understood. 5. Counting rate capability: ~ 106 avalnches/sec x mm 2 @ gain 4 x 104 6. Ion backflow: study in course 7. In TPC-like conditions: IBF with a single TGEM is 12%. 8. In GPM/reflective pc: IBF with a single TGEM is 98%. 9. A cascade + other “tricks” (see GEM/MHSP) should reduce IBF . 10. 8. TGEMs of different materials (e. g. Kevlar, Teflon…) for CF 4 ? . 11. 9. Will study TGEM of lower optical transparency (higher eff. QE) R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 22
 The end R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 23
The end R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 23
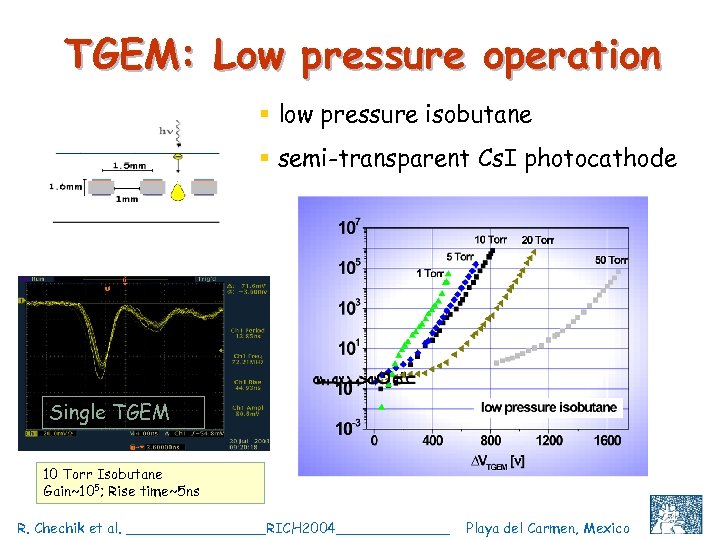 TGEM: Low pressure operation § low pressure isobutane § semi-transparent Cs. I photocathode Single TGEM 10 Torr Isobutane Gain~105; Rise time~5 ns R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 24
TGEM: Low pressure operation § low pressure isobutane § semi-transparent Cs. I photocathode Single TGEM 10 Torr Isobutane Gain~105; Rise time~5 ns R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 24
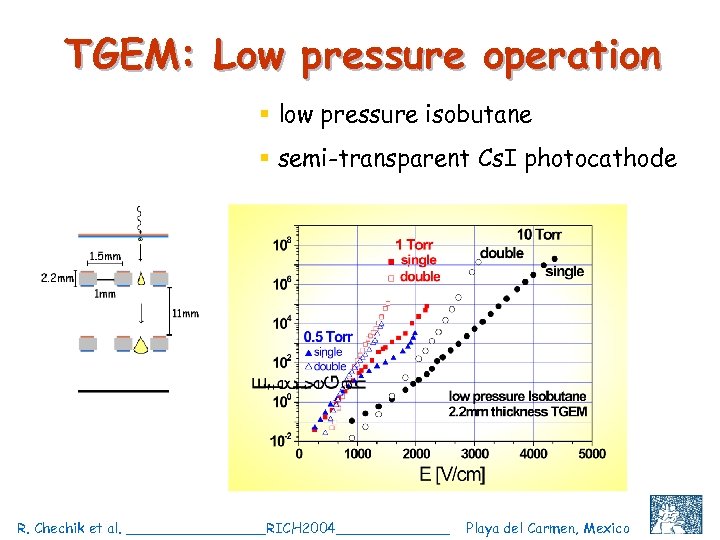 TGEM: Low pressure operation § low pressure isobutane § semi-transparent Cs. I photocathode R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 25
TGEM: Low pressure operation § low pressure isobutane § semi-transparent Cs. I photocathode R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 25
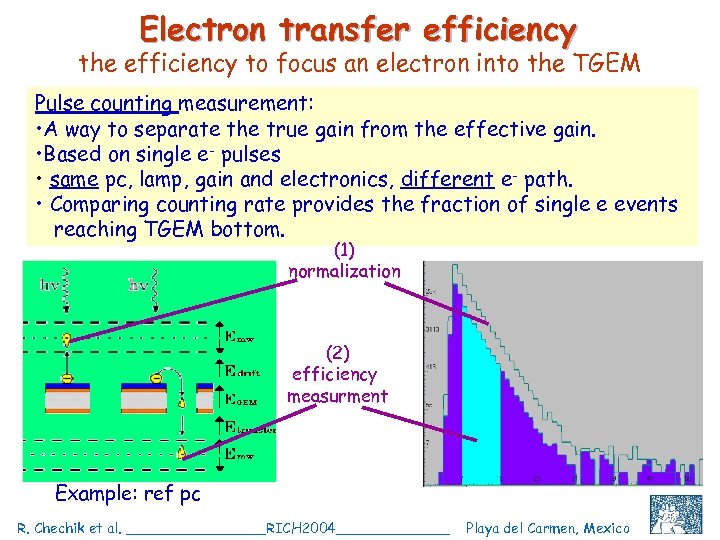 Electron transfer efficiency the efficiency to focus an electron into the TGEM Pulse counting measurement: • A way to separate the true gain from the effective gain. • Based on single e- pulses • same pc, lamp, gain and electronics, different e- path. • Comparing counting rate provides the fraction of single e events reaching TGEM bottom. (1) normalization (2) efficiency measurment Example: ref pc R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 26
Electron transfer efficiency the efficiency to focus an electron into the TGEM Pulse counting measurement: • A way to separate the true gain from the effective gain. • Based on single e- pulses • same pc, lamp, gain and electronics, different e- path. • Comparing counting rate provides the fraction of single e events reaching TGEM bottom. (1) normalization (2) efficiency measurment Example: ref pc R. Chechik et al. ________RICH 2004_______ Playa del Carmen, Mexico C. Shalem et al, IEEE 2004, Rome, October 18 26


