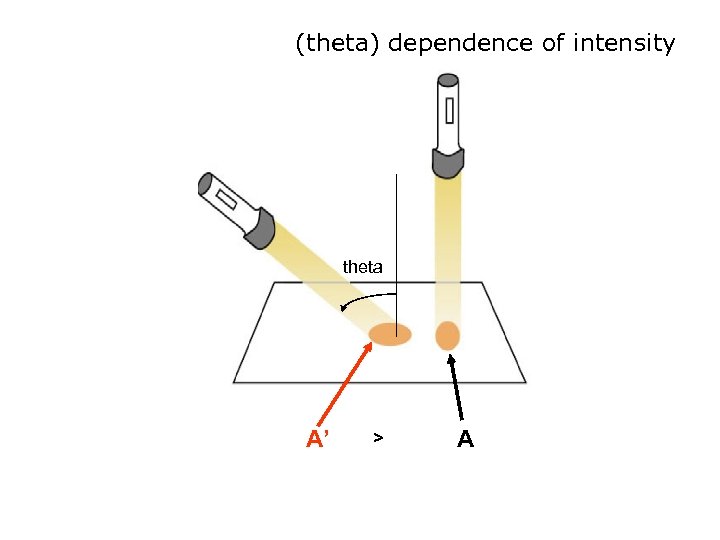
 (theta) dependence of intensity theta A’ > A
(theta) dependence of intensity theta A’ > A
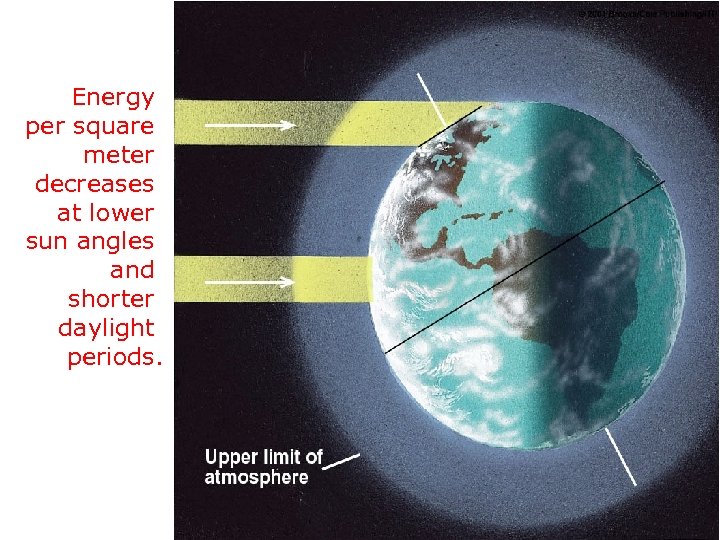 Energy per square meter decreases at lower sun angles and shorter daylight periods.
Energy per square meter decreases at lower sun angles and shorter daylight periods.
 Q 0 Which curve correctly describes the solar panel output power during a day?
Q 0 Which curve correctly describes the solar panel output power during a day?
 Goal: why the earth temperature is around 300 C? --- a simple energy balance model
Goal: why the earth temperature is around 300 C? --- a simple energy balance model
 Q 1 The earth will be a warmer place if A) it is further away from the sun; B) the surface temperature of the sun is lower; C) the solar constant is bigger; D) none of above.
Q 1 The earth will be a warmer place if A) it is further away from the sun; B) the surface temperature of the sun is lower; C) the solar constant is bigger; D) none of above.
 Q 2 Solar constant (1367 W/m^2) near the earth increases if A) the earth is closer to the sun; B) The surface temperature increases; C) Both a) and b) are true. D) None is true.
Q 2 Solar constant (1367 W/m^2) near the earth increases if A) the earth is closer to the sun; B) The surface temperature increases; C) Both a) and b) are true. D) None is true.
 Q 3 (survey question) The earth surface temperature is about 15 C mainly because A) Solar constant is 1367 W/m^2; B) Green house gases; C) Thermal heat from the core of the earth; D) Both A) and B)
Q 3 (survey question) The earth surface temperature is about 15 C mainly because A) Solar constant is 1367 W/m^2; B) Green house gases; C) Thermal heat from the core of the earth; D) Both A) and B)
 Energy Balance Incoming solar radiation power (depends on the value of solar constant, or how far the earth is from the Sun) = Outgoing radiation emitted by the earth (depends on the earth temperature)
Energy Balance Incoming solar radiation power (depends on the value of solar constant, or how far the earth is from the Sun) = Outgoing radiation emitted by the earth (depends on the earth temperature)
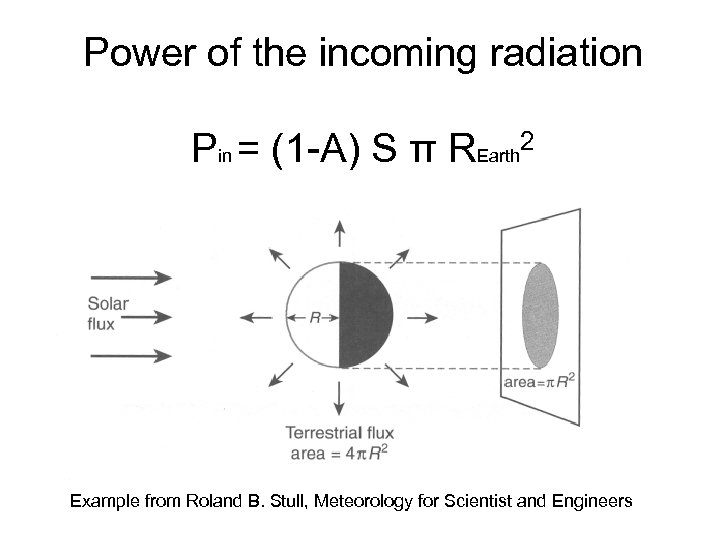 Power of the incoming radiation Pin = (1 -A) S π REarth 2 Example from Roland B. Stull, Meteorology for Scientist and Engineers
Power of the incoming radiation Pin = (1 -A) S π REarth 2 Example from Roland B. Stull, Meteorology for Scientist and Engineers
 Reflection coefficients or Albedo • Overall average reflection coefficient of an object: Albedo • Albedo of the Earth is about A = 0. 3 which means that the Earth as a whole reflects 30% of solar radiation.
Reflection coefficients or Albedo • Overall average reflection coefficient of an object: Albedo • Albedo of the Earth is about A = 0. 3 which means that the Earth as a whole reflects 30% of solar radiation.
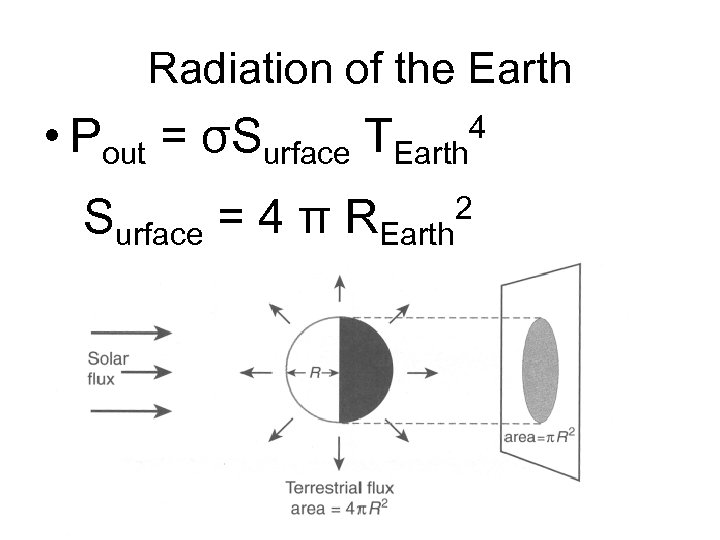 Radiation of the Earth • Pout = σSurface TEarth Surface = 4 π REarth 4 2
Radiation of the Earth • Pout = σSurface TEarth Surface = 4 π REarth 4 2
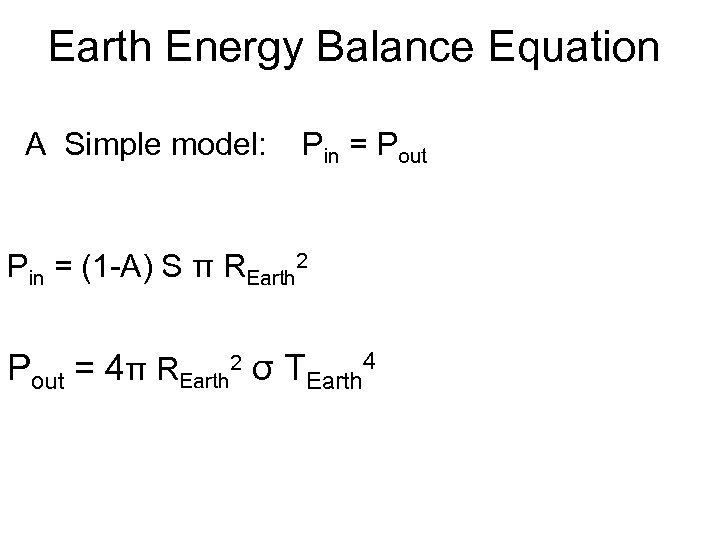 Earth Energy Balance Equation A Simple model: Pin = Pout Pin = (1 -A) S π REarth 2 Pout = 4π REarth 2 σ TEarth 4
Earth Energy Balance Equation A Simple model: Pin = Pout Pin = (1 -A) S π REarth 2 Pout = 4π REarth 2 σ TEarth 4
 Q 1 T 4 Earth = (1 -A) S /4 σ = (1 - 0. 3) 1367 W/m 2/(4∙ 5. 67∙ 10 -8 W/m 2 K 4) The earth temperature according to this model is • • -100 C; -18 C; 30 C; 100 C.
Q 1 T 4 Earth = (1 -A) S /4 σ = (1 - 0. 3) 1367 W/m 2/(4∙ 5. 67∙ 10 -8 W/m 2 K 4) The earth temperature according to this model is • • -100 C; -18 C; 30 C; 100 C.
 • So we actually obtained a temperature of the Earth as seen from far away – the temperature of the atmosphere, not the surface temperature!! • What are the effects of atmosphere ? ?
• So we actually obtained a temperature of the Earth as seen from far away – the temperature of the atmosphere, not the surface temperature!! • What are the effects of atmosphere ? ?
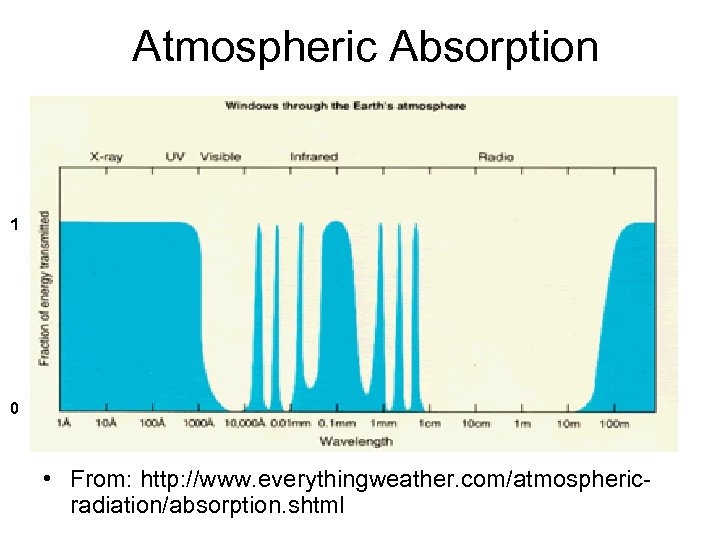 Atmospheric Absorption 1 0 • From: http: //www. everythingweather. com/atmosphericradiation/absorption. shtml
Atmospheric Absorption 1 0 • From: http: //www. everythingweather. com/atmosphericradiation/absorption. shtml
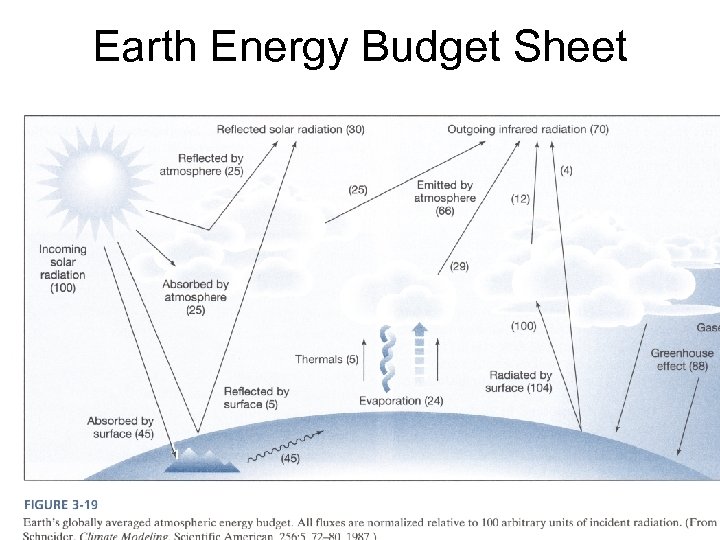 Earth Energy Budget Sheet
Earth Energy Budget Sheet