e5f89ad020bc3e7cc4db894453d0453d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 77
 THESIS PROPOSAL Simultaneous Point Matching and Recovery of Rigid and Nonrigid Shapes Eduard Serradell Domingo Thesis director Francesc Moreno Noguer Tutor Alberto Sanfeliu Cortés July 28 th, 2011
THESIS PROPOSAL Simultaneous Point Matching and Recovery of Rigid and Nonrigid Shapes Eduard Serradell Domingo Thesis director Francesc Moreno Noguer Tutor Alberto Sanfeliu Cortés July 28 th, 2011
 Objective Simultaneously solve the correspondence problem and recover rigid and nonrigid shapes. Given two point clouds extracted from different views of the same object, the objective is to simultaneously solve for point correspondence and recover the mapping between the two rigid or nonrigid model representations.
Objective Simultaneously solve the correspondence problem and recover rigid and nonrigid shapes. Given two point clouds extracted from different views of the same object, the objective is to simultaneously solve for point correspondence and recover the mapping between the two rigid or nonrigid model representations.
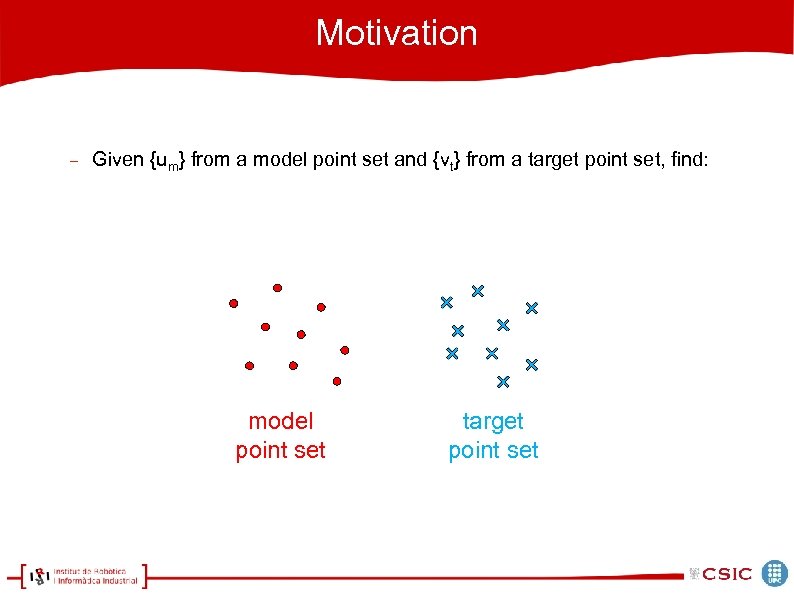 Motivation Given {um} from a model point set and {vt} from a target point set, find: model point set target point set
Motivation Given {um} from a model point set and {vt} from a target point set, find: model point set target point set
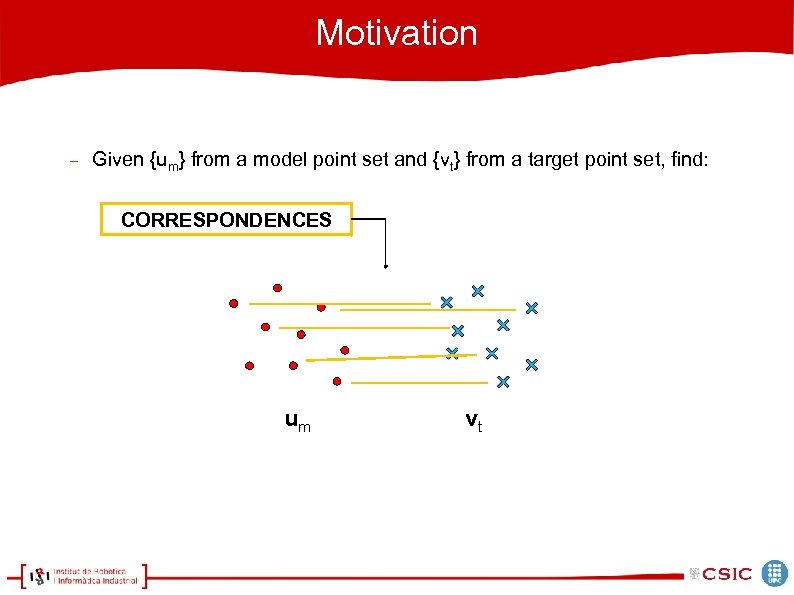 Motivation Given {um} from a model point set and {vt} from a target point set, find: CORRESPONDENCES um vt
Motivation Given {um} from a model point set and {vt} from a target point set, find: CORRESPONDENCES um vt
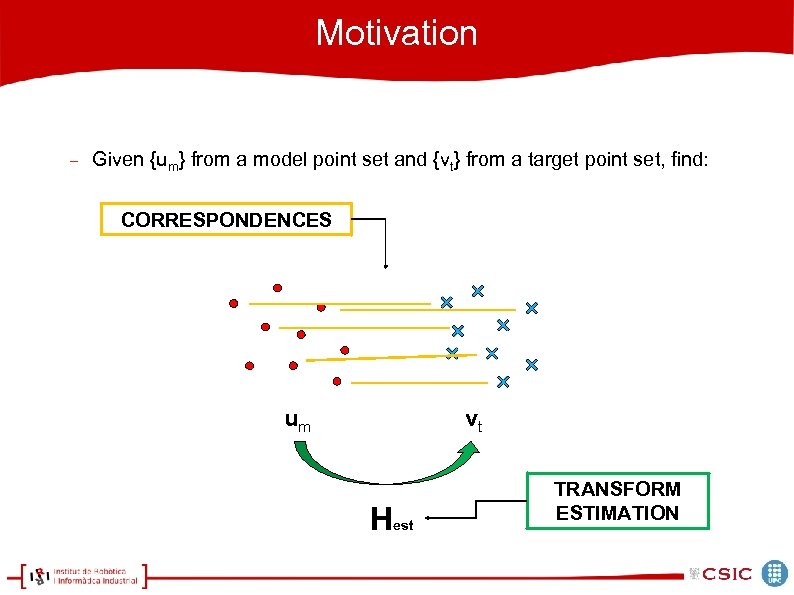 Motivation Given {um} from a model point set and {vt} from a target point set, find: CORRESPONDENCES um vt Hest TRANSFORM ESTIMATION
Motivation Given {um} from a model point set and {vt} from a target point set, find: CORRESPONDENCES um vt Hest TRANSFORM ESTIMATION
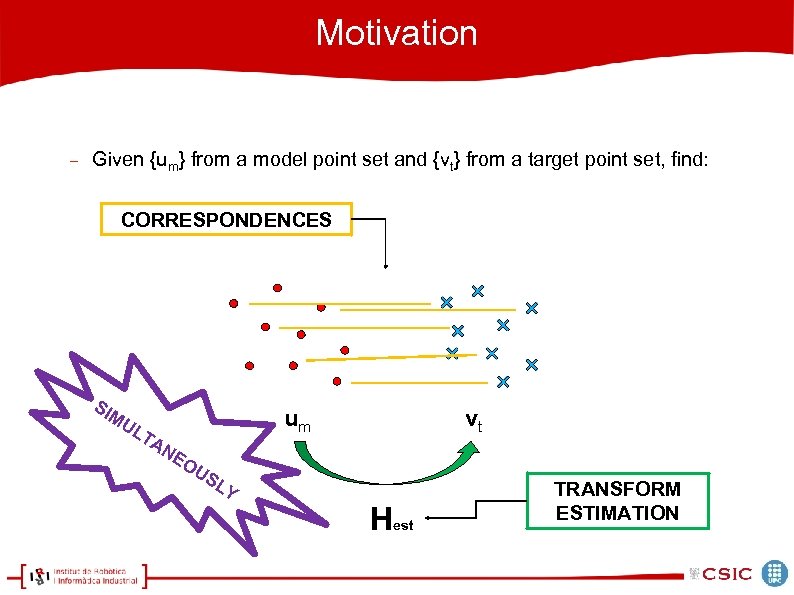 Motivation Given {um} from a model point set and {vt} from a target point set, find: CORRESPONDENCES SI MU LT AN um EO U SL vt Y Hest TRANSFORM ESTIMATION
Motivation Given {um} from a model point set and {vt} from a target point set, find: CORRESPONDENCES SI MU LT AN um EO U SL vt Y Hest TRANSFORM ESTIMATION
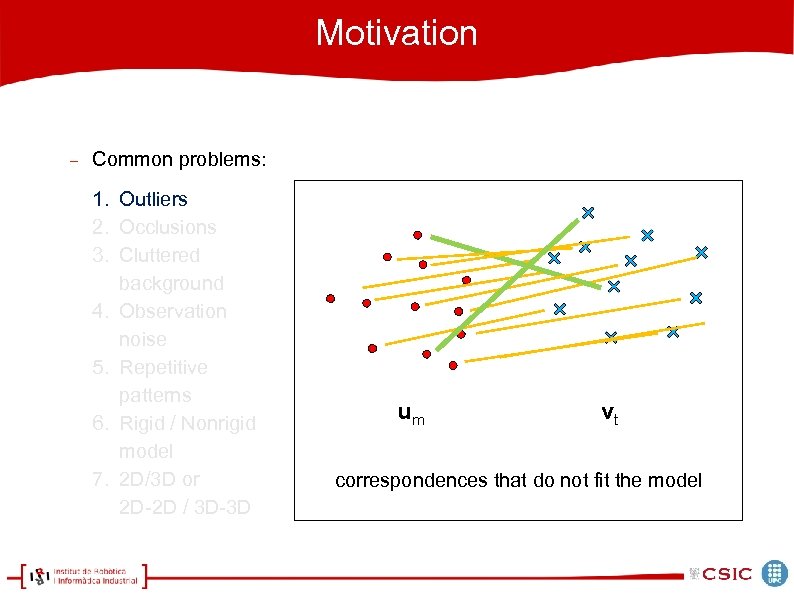 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt correspondences that do not fit the model
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt correspondences that do not fit the model
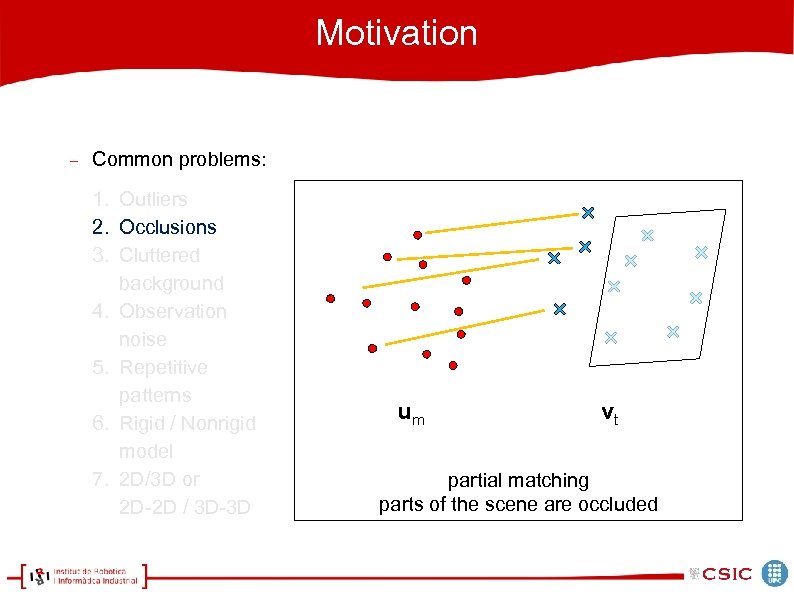 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt partial matching parts of the scene are occluded
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt partial matching parts of the scene are occluded
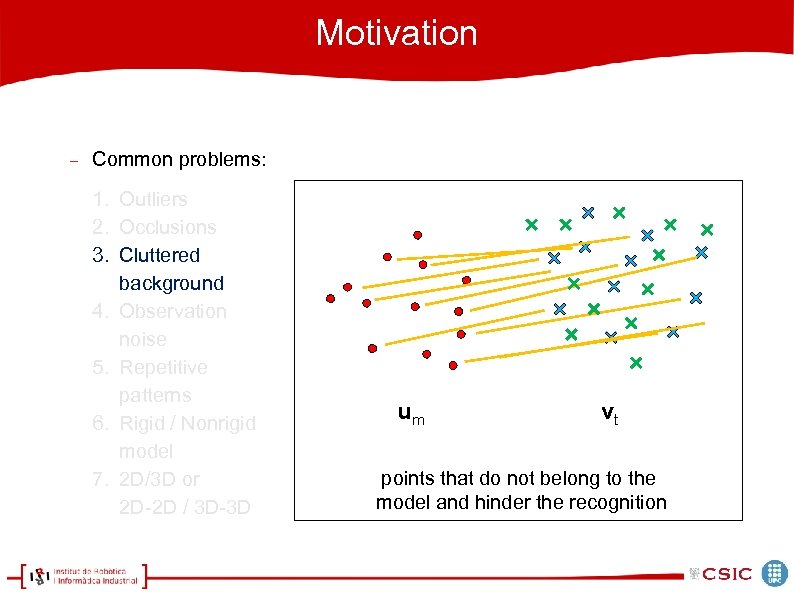 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt points that do not belong to the model and hinder the recognition
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt points that do not belong to the model and hinder the recognition
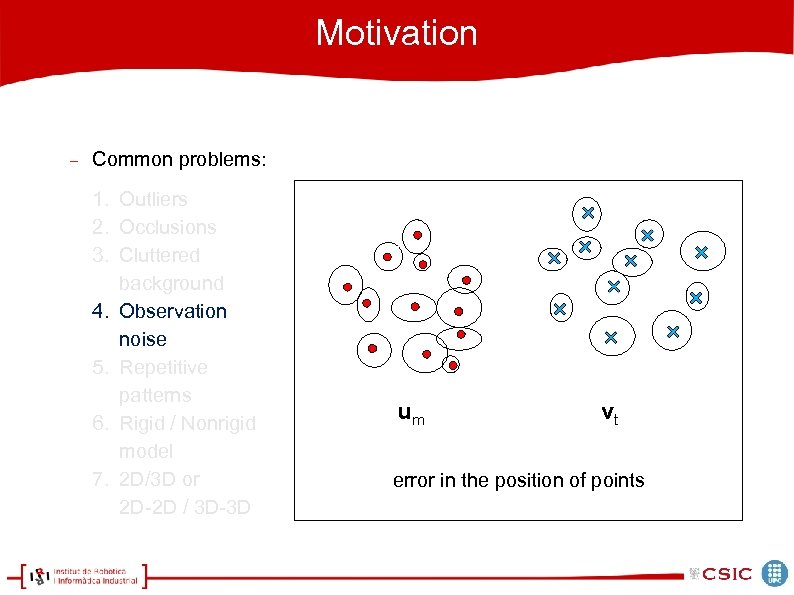 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt error in the position of points
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt error in the position of points
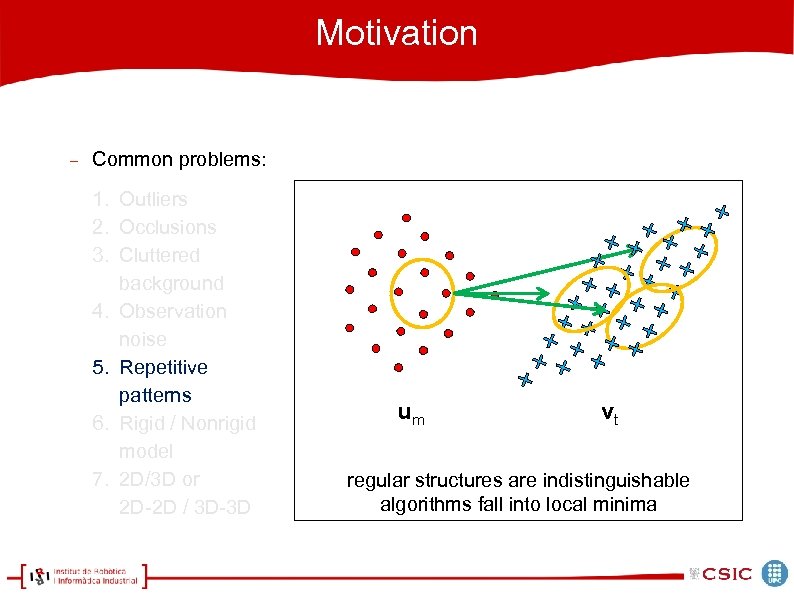 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt regular structures are indistinguishable algorithms fall into local minima
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt regular structures are indistinguishable algorithms fall into local minima
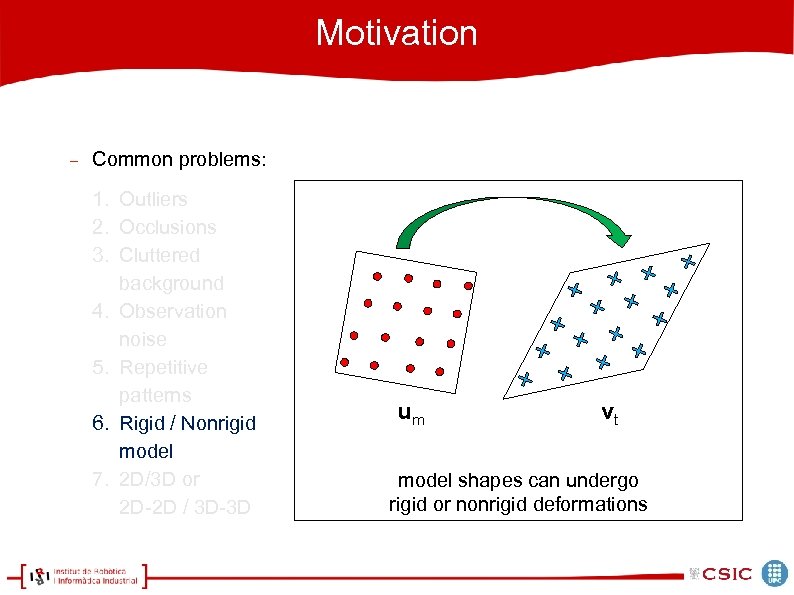 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt model shapes can undergo rigid or nonrigid deformations
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt model shapes can undergo rigid or nonrigid deformations
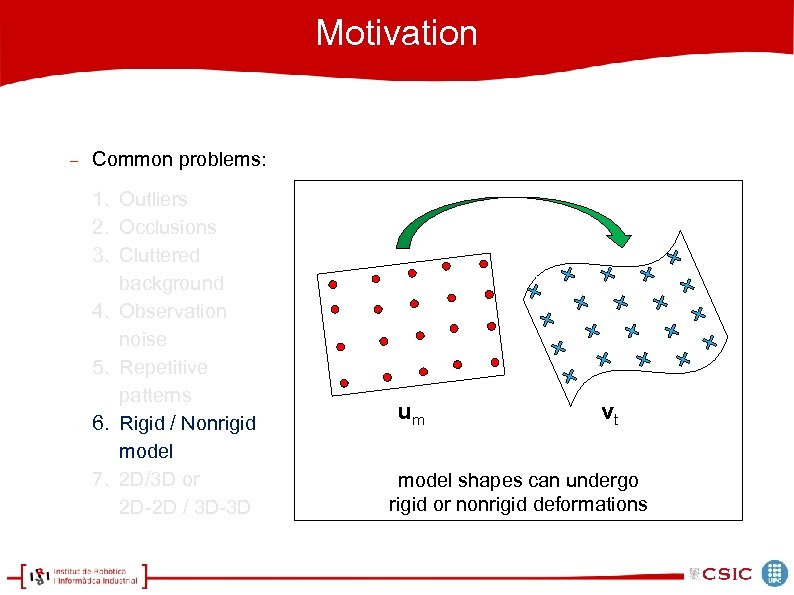 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt model shapes can undergo rigid or nonrigid deformations
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um vt model shapes can undergo rigid or nonrigid deformations
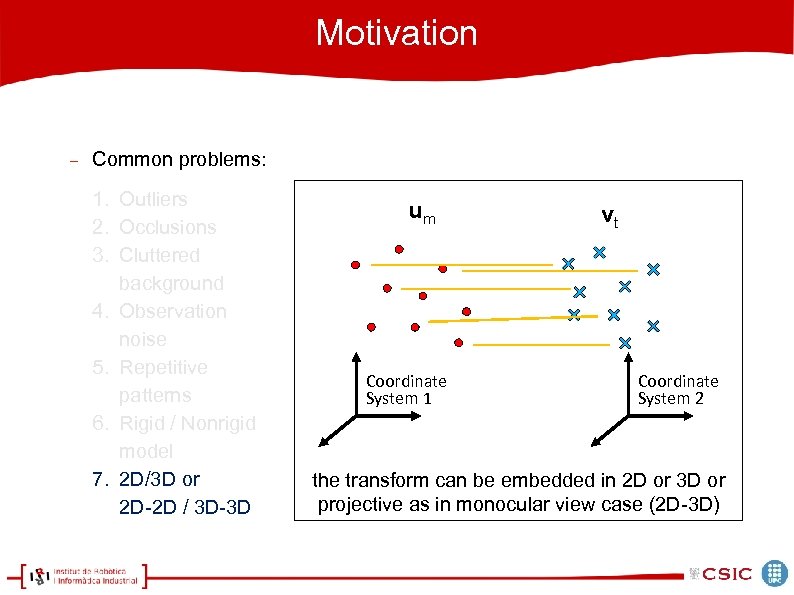 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um Coordinate System 1 vt Coordinate System 2 the transform can be embedded in 2 D or 3 D or projective as in monocular view case (2 D-3 D)
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um Coordinate System 1 vt Coordinate System 2 the transform can be embedded in 2 D or 3 D or projective as in monocular view case (2 D-3 D)
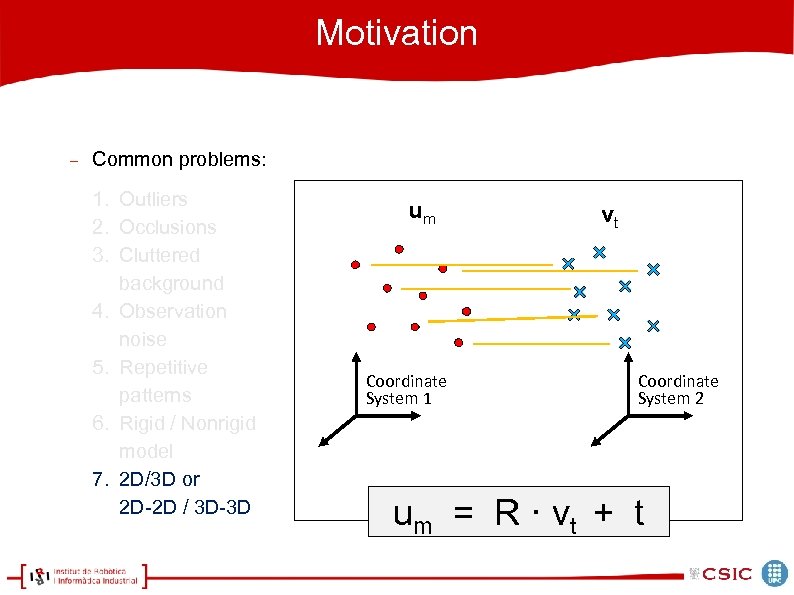 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um Coordinate System 1 vt Coordinate System 2 um = R · v t + t
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D um Coordinate System 1 vt Coordinate System 2 um = R · v t + t
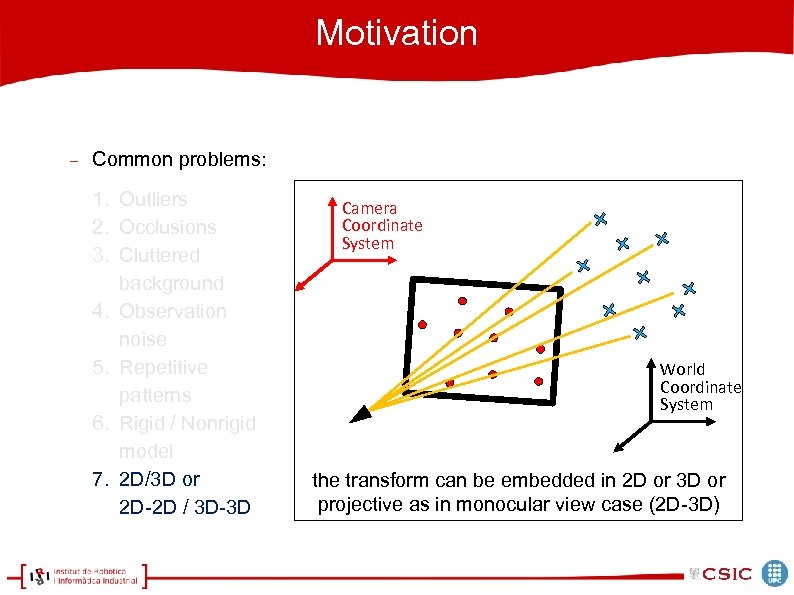 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Camera Coordinate System World Coordinate System the transform can be embedded in 2 D or 3 D or projective as in monocular view case (2 D-3 D)
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Camera Coordinate System World Coordinate System the transform can be embedded in 2 D or 3 D or projective as in monocular view case (2 D-3 D)
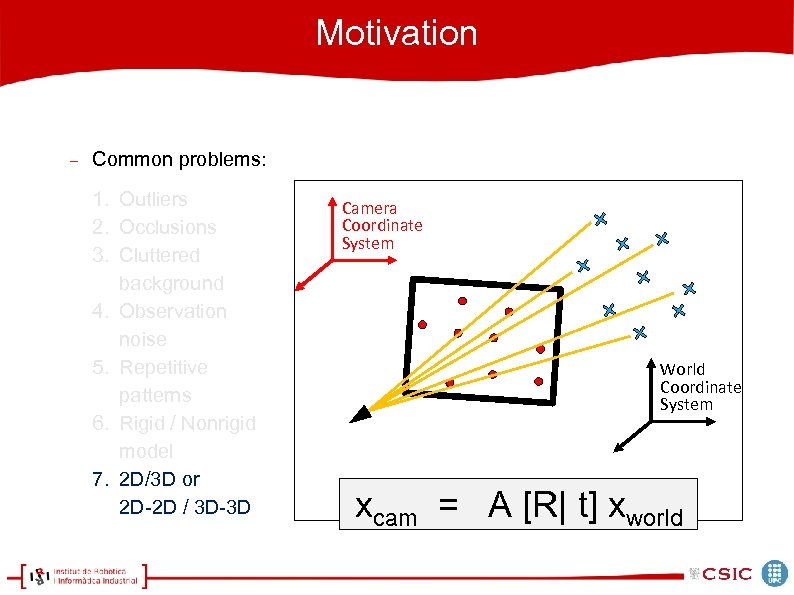 Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Camera Coordinate System World Coordinate System xcam = A [R| t] xworld
Motivation Common problems: 1. Outliers 2. Occlusions 3. Cluttered background 4. Observation noise 5. Repetitive patterns 6. Rigid / Nonrigid model 7. 2 D/3 D or 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Camera Coordinate System World Coordinate System xcam = A [R| t] xworld
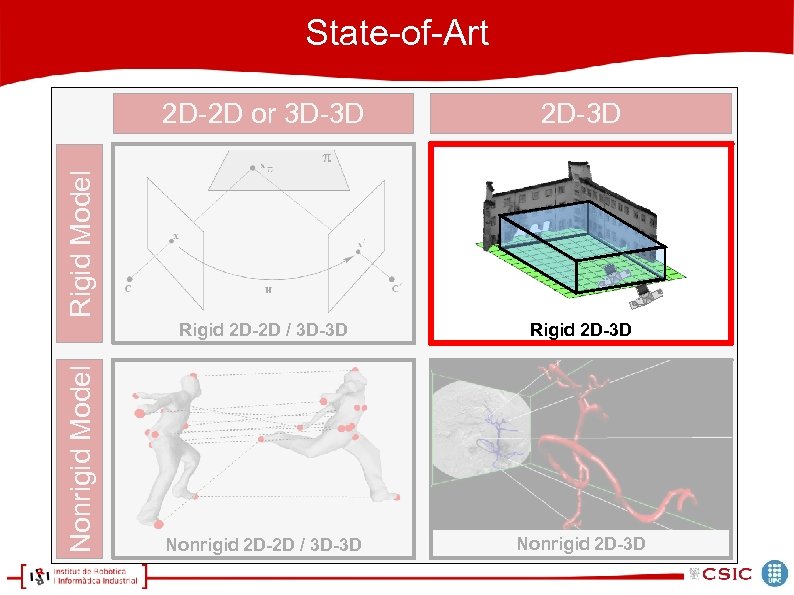
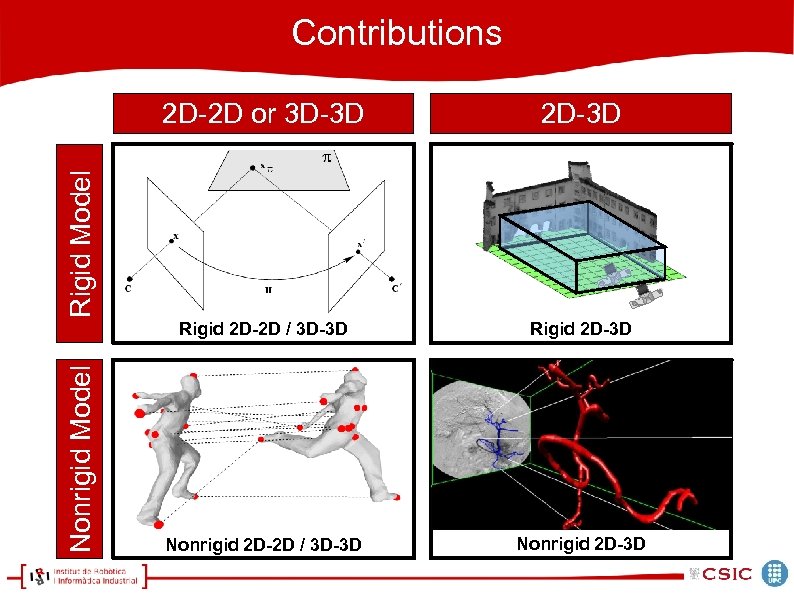
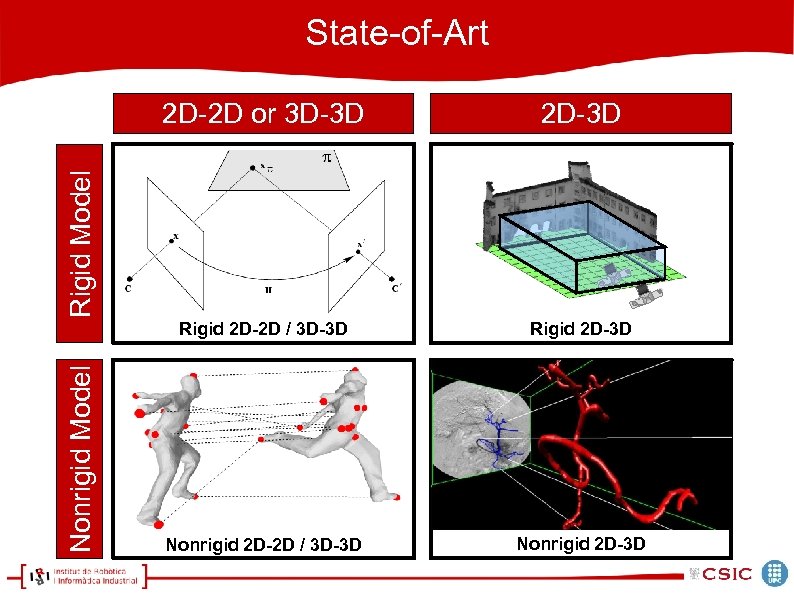 State-of-Art 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
State-of-Art 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
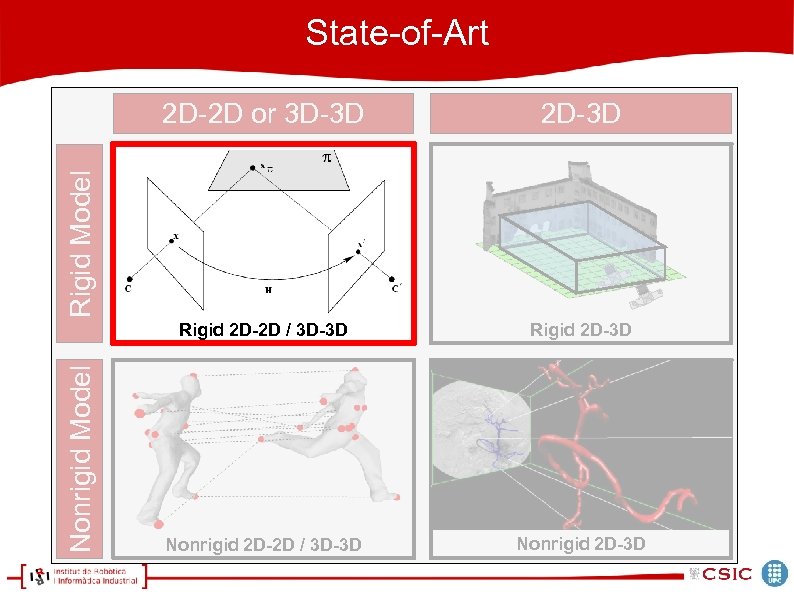 State-of-Art 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
State-of-Art 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
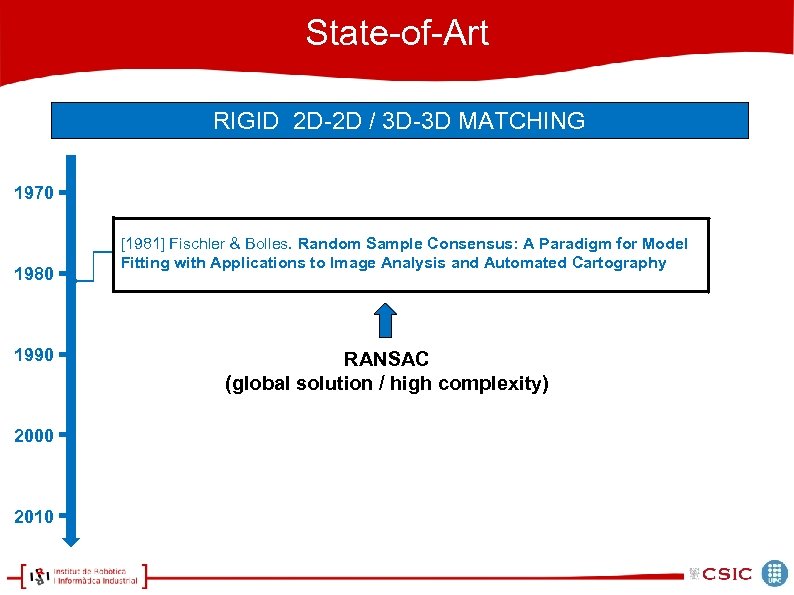 State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography RANSAC (global solution / high complexity)
State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography RANSAC (global solution / high complexity)
![State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 [1981] State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 [1981]](https://present5.com/presentation/e5f89ad020bc3e7cc4db894453d0453d/image-21.jpg) State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography [1992] Besl & Mc. Kay, A Method for Registration of 3 D Shapes ICP : Iterative Closest Point (requires good initialization) 2000 2010
State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography [1992] Besl & Mc. Kay, A Method for Registration of 3 D Shapes ICP : Iterative Closest Point (requires good initialization) 2000 2010
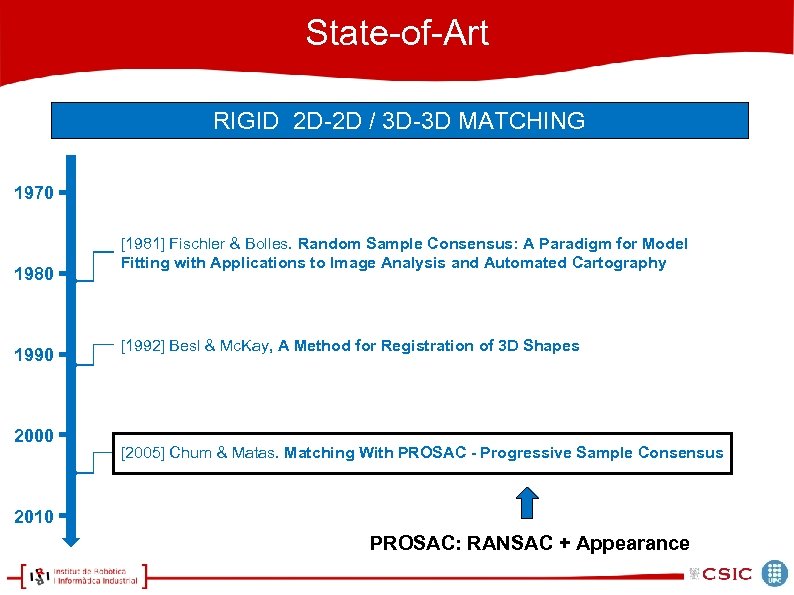 State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography [1992] Besl & Mc. Kay, A Method for Registration of 3 D Shapes [2005] Chum & Matas. Matching With PROSAC - Progressive Sample Consensus 2010 PROSAC: RANSAC + Appearance
State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography [1992] Besl & Mc. Kay, A Method for Registration of 3 D Shapes [2005] Chum & Matas. Matching With PROSAC - Progressive Sample Consensus 2010 PROSAC: RANSAC + Appearance
![State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 Unsolved when: [1981] State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 Unsolved when: [1981]](https://present5.com/presentation/e5f89ad020bc3e7cc4db894453d0453d/image-23.jpg) State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 Unsolved when: [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model 1980 1990 2000 2010 Fitting With Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography • Weak detection, - outliers, - occlusions, [1992] Besl & Mc. Kay, A Method for Registration of 3 D Shapes - image noise, - repetitive patterns, - highly textured scenes, - oblique angles [2005] Chum & Matas. Matching With PROSAC - Progressive Sample Consensus - … • PROSAC complexity similar to RANSAC (too high)
State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 Unsolved when: [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model 1980 1990 2000 2010 Fitting With Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography • Weak detection, - outliers, - occlusions, [1992] Besl & Mc. Kay, A Method for Registration of 3 D Shapes - image noise, - repetitive patterns, - highly textured scenes, - oblique angles [2005] Chum & Matas. Matching With PROSAC - Progressive Sample Consensus - … • PROSAC complexity similar to RANSAC (too high)
 State-of-Art 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
State-of-Art 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
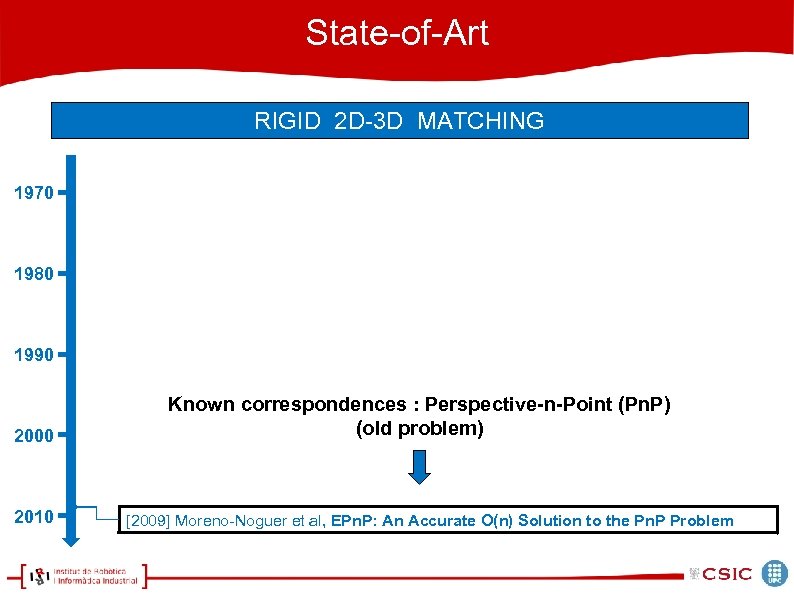 State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Known correspondences : Perspective-n-Point (Pn. P) (old problem) [2009] Moreno-Noguer et al, EPn. P: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the Pn. P Problem
State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Known correspondences : Perspective-n-Point (Pn. P) (old problem) [2009] Moreno-Noguer et al, EPn. P: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the Pn. P Problem
![State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random](https://present5.com/presentation/e5f89ad020bc3e7cc4db894453d0453d/image-26.jpg) State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting With Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography RANSAC: Random Sampled Consensus & DLT: Direct Linear Transform (high complexity) 2000 2010 [2009] Moreno-Noguer et al, EPn. P: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the Pn. P Problem
State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting With Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography RANSAC: Random Sampled Consensus & DLT: Direct Linear Transform (high complexity) 2000 2010 [2009] Moreno-Noguer et al, EPn. P: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the Pn. P Problem
![State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 [1981] Fischler & State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 [1981] Fischler &](https://present5.com/presentation/e5f89ad020bc3e7cc4db894453d0453d/image-27.jpg) State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting With Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography Soft. POSIT: Unknown correspondences [2002] David et al, Soft. POSIT: Simultaneous Pose and Correspondence Determination [2009] Moreno-Noguer et al, EPn. P: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the Pn. P Problem
State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting With Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography Soft. POSIT: Unknown correspondences [2002] David et al, Soft. POSIT: Simultaneous Pose and Correspondence Determination [2009] Moreno-Noguer et al, EPn. P: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the Pn. P Problem
![State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 [1981] Fischler & Bolles.](https://present5.com/presentation/e5f89ad020bc3e7cc4db894453d0453d/image-28.jpg) State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting With Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography Blind Pn. P: Unknown correspondences Pose Priors (geometrical consistency) Kalman Filter to propagate pose uncertainty [2002] David et al, Soft. POSIT: Simultaneous Pose and Correspondence Determination [2008] Moreno-Noguer et al, Pose Priors for Simultaneously Solving Alignment and Correspondence. 2010 [2009] Moreno-Noguer et al, EPn. P: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the Pn. P Problem
State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 [1981] Fischler & Bolles. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting With Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography Blind Pn. P: Unknown correspondences Pose Priors (geometrical consistency) Kalman Filter to propagate pose uncertainty [2002] David et al, Soft. POSIT: Simultaneous Pose and Correspondence Determination [2008] Moreno-Noguer et al, Pose Priors for Simultaneously Solving Alignment and Correspondence. 2010 [2009] Moreno-Noguer et al, EPn. P: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the Pn. P Problem
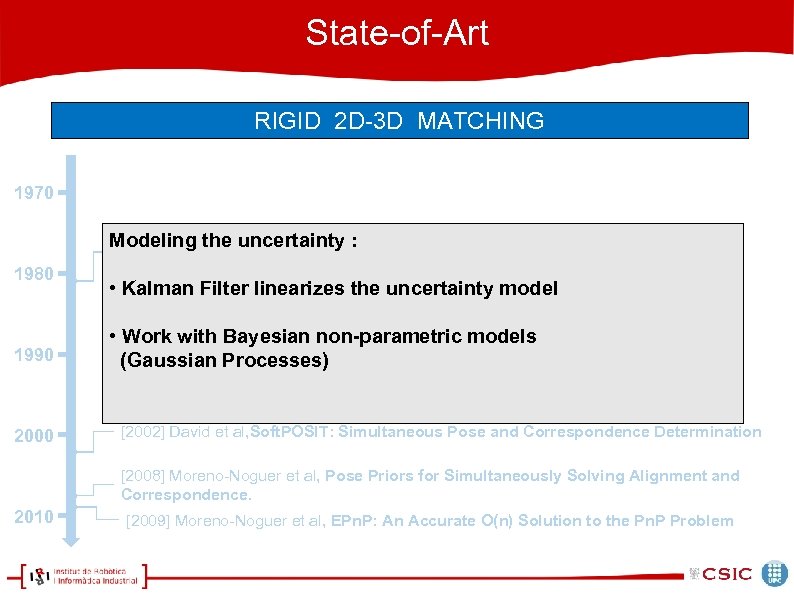 State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 Modeling the&uncertainty : Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model [1981] Fischler Bolles. Random 1980 1990 2000 Fitting With Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography • Kalman Filter linearizes the uncertainty model • Work with Bayesian non-parametric models (Gaussian Processes) [2002] David et al, Soft. POSIT: Simultaneous Pose and Correspondence Determination [2008] Moreno-Noguer et al, Pose Priors for Simultaneously Solving Alignment and Correspondence. 2010 [2009] Moreno-Noguer et al, EPn. P: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the Pn. P Problem
State-of-Art RIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 Modeling the&uncertainty : Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model [1981] Fischler Bolles. Random 1980 1990 2000 Fitting With Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography • Kalman Filter linearizes the uncertainty model • Work with Bayesian non-parametric models (Gaussian Processes) [2002] David et al, Soft. POSIT: Simultaneous Pose and Correspondence Determination [2008] Moreno-Noguer et al, Pose Priors for Simultaneously Solving Alignment and Correspondence. 2010 [2009] Moreno-Noguer et al, EPn. P: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the Pn. P Problem
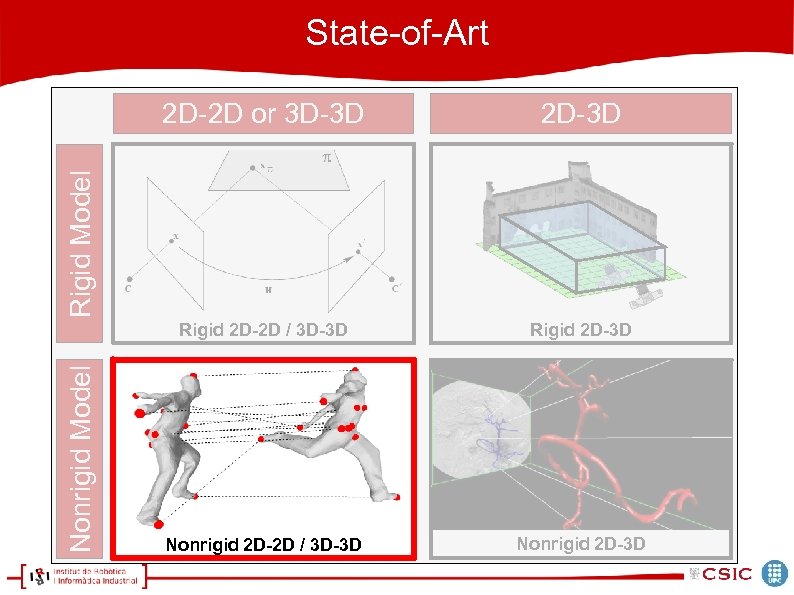 State-of-Art 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
State-of-Art 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
 State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 Soft-assign (requires good initialization) [1998] Gold et al. . New Algorithms for 2 D and 3 D Point Matching: Point Estimation and Correspondence 1990 2000 2010 [2003] Chui & Rangarajan. A New Point Matching Algorithm for Non-Rigid Registration Soft-assign + Thin-plate splines (requires good initialization) (smooth deformations)
State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 Soft-assign (requires good initialization) [1998] Gold et al. . New Algorithms for 2 D and 3 D Point Matching: Point Estimation and Correspondence 1990 2000 2010 [2003] Chui & Rangarajan. A New Point Matching Algorithm for Non-Rigid Registration Soft-assign + Thin-plate splines (requires good initialization) (smooth deformations)
 State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 [1998] Gold et al. . New Algorithms for 2 D and 3 D Point Matching: Point Estimation and Correspondence [2003] Hannel et al. . An Extension of the ICP Algorithm for Modeling Nonrigid Objects with Mobile Robots [2003] Chui & Rangarajan. A New Point Matching Algorithm for Non-Rigid Registration [2008] Li et al, Global Correspondence Optimization for Non-Rigid Registration of Depth Scans Nonrigid ICP Variants (Require a good initialization)
State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 [1998] Gold et al. . New Algorithms for 2 D and 3 D Point Matching: Point Estimation and Correspondence [2003] Hannel et al. . An Extension of the ICP Algorithm for Modeling Nonrigid Objects with Mobile Robots [2003] Chui & Rangarajan. A New Point Matching Algorithm for Non-Rigid Registration [2008] Li et al, Global Correspondence Optimization for Non-Rigid Registration of Depth Scans Nonrigid ICP Variants (Require a good initialization)
 State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 Graph Matching + Thin-plate splines (Smooth deformations) Shape appearance + Thin-plate splines (Smooth deformations) 1980 1990 2000 2010 [1998] Gold et al. . New Algorithms for 2 D and 3 D Point Matching: Point Estimation and Correspondence [2002] Belongui, Shape matching and Object Recognition Using Shape Contexts [2003] Hannel et al. . An Extension of the ICP Algorithm for Modeling Nonrigid Objects with Mobile Robots [2003] Chui & Rangarajan. A New Point Matching Algorithm for Non-Rigid Registration [2008] Li et al, Global Correspondence Optimization for Non-Rigid Registration of Depth Scans [2010] Deng et al, Retinal Fundus Image Registration via Vascular Structure Graph Matching
State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 Graph Matching + Thin-plate splines (Smooth deformations) Shape appearance + Thin-plate splines (Smooth deformations) 1980 1990 2000 2010 [1998] Gold et al. . New Algorithms for 2 D and 3 D Point Matching: Point Estimation and Correspondence [2002] Belongui, Shape matching and Object Recognition Using Shape Contexts [2003] Hannel et al. . An Extension of the ICP Algorithm for Modeling Nonrigid Objects with Mobile Robots [2003] Chui & Rangarajan. A New Point Matching Algorithm for Non-Rigid Registration [2008] Li et al, Global Correspondence Optimization for Non-Rigid Registration of Depth Scans [2010] Deng et al, Retinal Fundus Image Registration via Vascular Structure Graph Matching
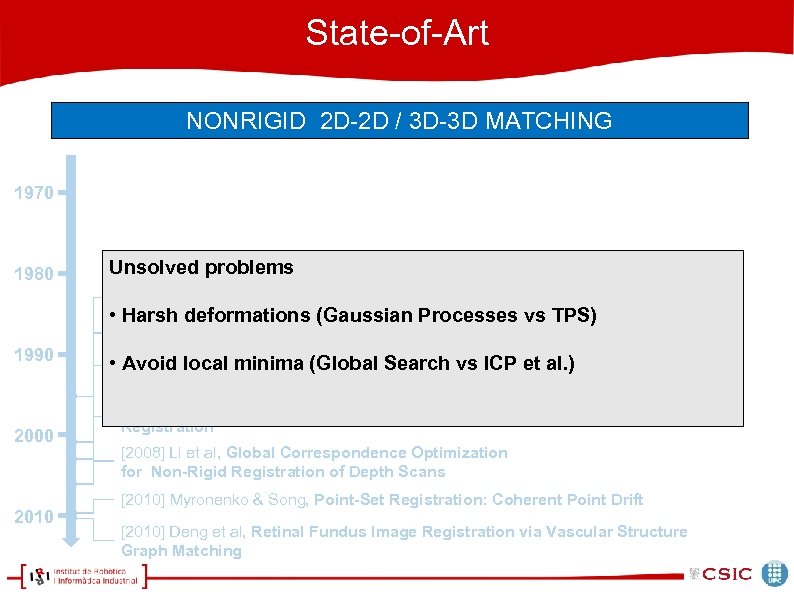 State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 Unsolved problems [1998] Gold et al. . New Algorithms for 2 D and 3 D Point Matching: Point Estimation and Correspondence • Harsh deformations (Gaussian Processes vs TPS) 1990 2000 2010 [2002] Belongui, Shape matching and Object Recognition Using Shape Contexts • [2003] Hannel etminima (Globalof the ICP Algorithm al. ) Avoid local al. . An Extension Search vs ICP et for Modeling Nonrigid Objects with Mobile Robots [2003] Chui & Rangarajan. A New Point Matching Algorithm for Non-Rigid Registration [2008] Li et al, Global Correspondence Optimization for Non-Rigid Registration of Depth Scans [2010] Myronenko & Song, Point-Set Registration: Coherent Point Drift [2010] Deng et al, Retinal Fundus Image Registration via Vascular Structure Graph Matching
State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D MATCHING 1970 1980 Unsolved problems [1998] Gold et al. . New Algorithms for 2 D and 3 D Point Matching: Point Estimation and Correspondence • Harsh deformations (Gaussian Processes vs TPS) 1990 2000 2010 [2002] Belongui, Shape matching and Object Recognition Using Shape Contexts • [2003] Hannel etminima (Globalof the ICP Algorithm al. ) Avoid local al. . An Extension Search vs ICP et for Modeling Nonrigid Objects with Mobile Robots [2003] Chui & Rangarajan. A New Point Matching Algorithm for Non-Rigid Registration [2008] Li et al, Global Correspondence Optimization for Non-Rigid Registration of Depth Scans [2010] Myronenko & Song, Point-Set Registration: Coherent Point Drift [2010] Deng et al, Retinal Fundus Image Registration via Vascular Structure Graph Matching
 State-of-Art 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
State-of-Art 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
 State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces Articulated structures 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces Articulated structures 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
![State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 1990 Articulated structures [2003] State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 1990 Articulated structures [2003]](https://present5.com/presentation/e5f89ad020bc3e7cc4db894453d0453d/image-37.jpg) State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 1990 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich et al. , Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing [2006] Sigal & Black, Humaneva: Synchronized Video and Motion Capture Dataset for Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion Discriminative methods: Database learning & Nearest Neigbour Selection 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 1990 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich et al. , Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing [2006] Sigal & Black, Humaneva: Synchronized Video and Motion Capture Dataset for Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion Discriminative methods: Database learning & Nearest Neigbour Selection 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
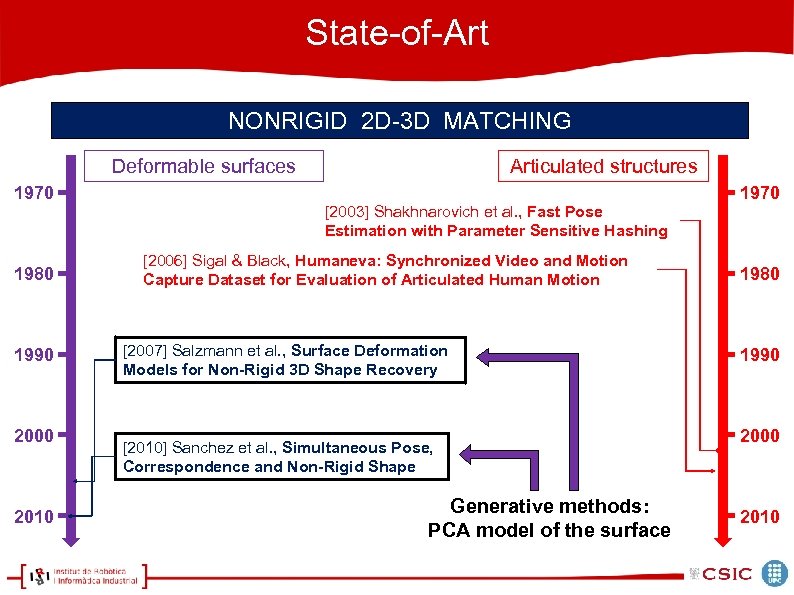 State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich et al. , Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing [2006] Sigal & Black, Humaneva: Synchronized Video and Motion Capture Dataset for Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion [2007] Salzmann et al. , Surface Deformation Models for Non-Rigid 3 D Shape Recovery [2010] Sanchez et al. , Simultaneous Pose, Correspondence and Non-Rigid Shape Generative methods: PCA model of the surface 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich et al. , Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing [2006] Sigal & Black, Humaneva: Synchronized Video and Motion Capture Dataset for Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion [2007] Salzmann et al. , Surface Deformation Models for Non-Rigid 3 D Shape Recovery [2010] Sanchez et al. , Simultaneous Pose, Correspondence and Non-Rigid Shape Generative methods: PCA model of the surface 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
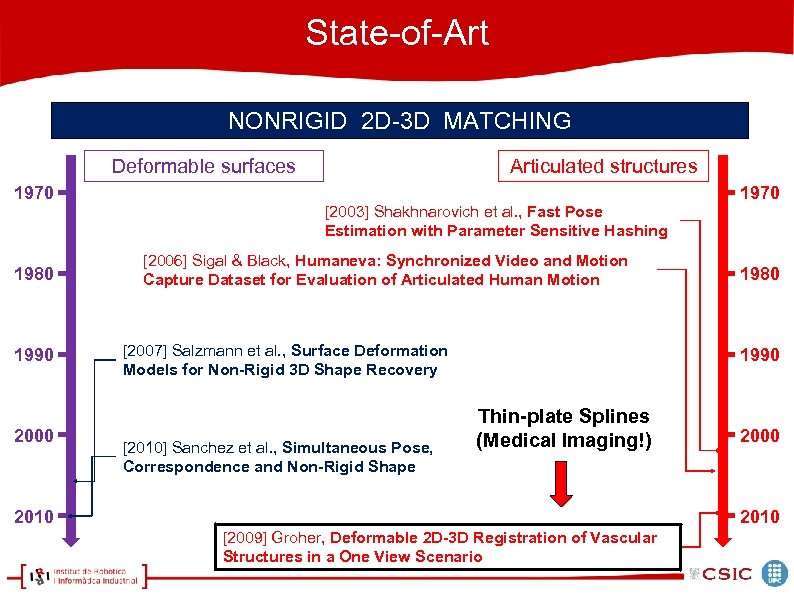 State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 1990 2000 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich et al. , Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing [2006] Sigal & Black, Humaneva: Synchronized Video and Motion Capture Dataset for Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion [2007] Salzmann et al. , Surface Deformation Models for Non-Rigid 3 D Shape Recovery [2010] Sanchez et al. , Simultaneous Pose, Correspondence and Non-Rigid Shape 1970 1980 1990 Thin-plate Splines (Medical Imaging!) 2010 2000 2010 [2009] Groher, Deformable 2 D-3 D Registration of Vascular Structures in a One View Scenario
State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 1990 2000 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich et al. , Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing [2006] Sigal & Black, Humaneva: Synchronized Video and Motion Capture Dataset for Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion [2007] Salzmann et al. , Surface Deformation Models for Non-Rigid 3 D Shape Recovery [2010] Sanchez et al. , Simultaneous Pose, Correspondence and Non-Rigid Shape 1970 1980 1990 Thin-plate Splines (Medical Imaging!) 2010 2000 2010 [2009] Groher, Deformable 2 D-3 D Registration of Vascular Structures in a One View Scenario
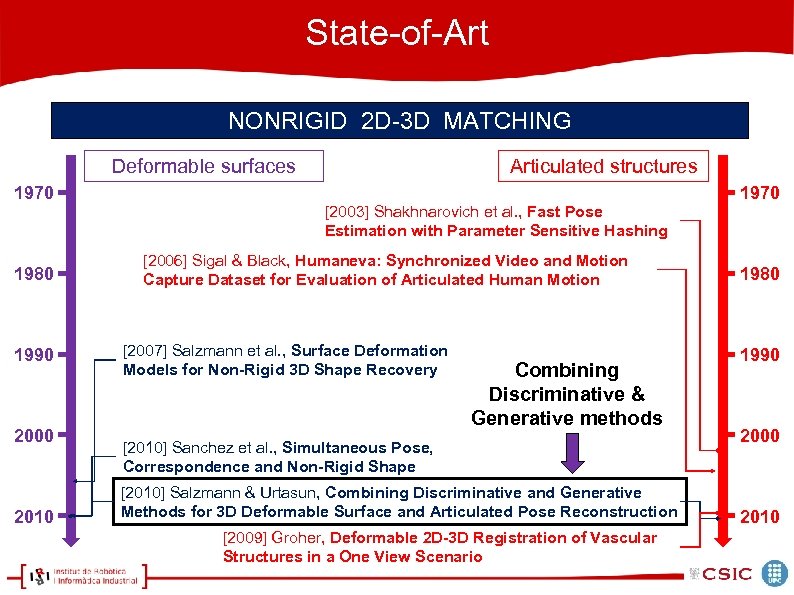 State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich et al. , Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing [2006] Sigal & Black, Humaneva: Synchronized Video and Motion Capture Dataset for Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion [2007] Salzmann et al. , Surface Deformation Models for Non-Rigid 3 D Shape Recovery Combining Discriminative & Generative methods [2010] Sanchez et al. , Simultaneous Pose, Correspondence and Non-Rigid Shape [2010] Salzmann & Urtasun, Combining Discriminative and Generative Methods for 3 D Deformable Surface and Articulated Pose Reconstruction [2009] Groher, Deformable 2 D-3 D Registration of Vascular Structures in a One View Scenario 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich et al. , Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing [2006] Sigal & Black, Humaneva: Synchronized Video and Motion Capture Dataset for Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion [2007] Salzmann et al. , Surface Deformation Models for Non-Rigid 3 D Shape Recovery Combining Discriminative & Generative methods [2010] Sanchez et al. , Simultaneous Pose, Correspondence and Non-Rigid Shape [2010] Salzmann & Urtasun, Combining Discriminative and Generative Methods for 3 D Deformable Surface and Articulated Pose Reconstruction [2009] Groher, Deformable 2 D-3 D Registration of Vascular Structures in a One View Scenario 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
![State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich](https://present5.com/presentation/e5f89ad020bc3e7cc4db894453d0453d/image-41.jpg) State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich et al. , Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing [2006] Potential. Sigal & Black, Humaneva: Synchronized Video and Motion improvements Capture Dataset for Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion 1970 1980 • Better parameterization for articulated structures 1990 2000 2010 [2007] Salzmann et al. , Surface Deformation • Harsh for Non-Rigid 3 D Shape Recovery Models deformations (Gaussian Processes vs TPS) [2010] Sanchez et al. , Simultaneous Pose, Correspondence and Non-Rigid Shape [2010] Salzmann & Urtasun, Combining Discriminative and Generative Methods for 3 D Deformable Surface and Articulated Pose Reconstruction [2009] Groher, Deformable 2 D-3 D Registration of Vascular Structures in a One View Scenario 1990 2000 2010
State-of-Art NONRIGID 2 D-3 D MATCHING Deformable surfaces 1970 1980 Articulated structures [2003] Shakhnarovich et al. , Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing [2006] Potential. Sigal & Black, Humaneva: Synchronized Video and Motion improvements Capture Dataset for Evaluation of Articulated Human Motion 1970 1980 • Better parameterization for articulated structures 1990 2000 2010 [2007] Salzmann et al. , Surface Deformation • Harsh for Non-Rigid 3 D Shape Recovery Models deformations (Gaussian Processes vs TPS) [2010] Sanchez et al. , Simultaneous Pose, Correspondence and Non-Rigid Shape [2010] Salzmann & Urtasun, Combining Discriminative and Generative Methods for 3 D Deformable Surface and Articulated Pose Reconstruction [2009] Groher, Deformable 2 D-3 D Registration of Vascular Structures in a One View Scenario 1990 2000 2010
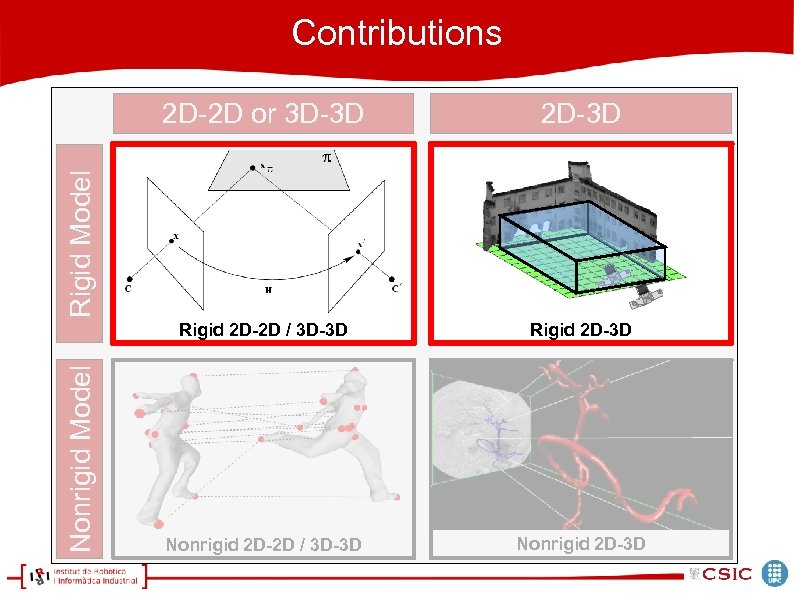 Contributions 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
Contributions 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
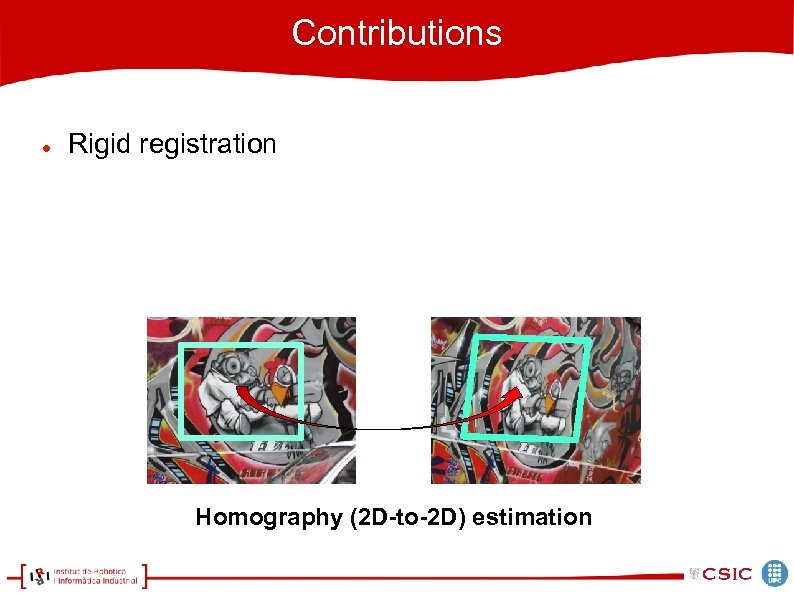 Contributions Rigid registration Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
Contributions Rigid registration Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
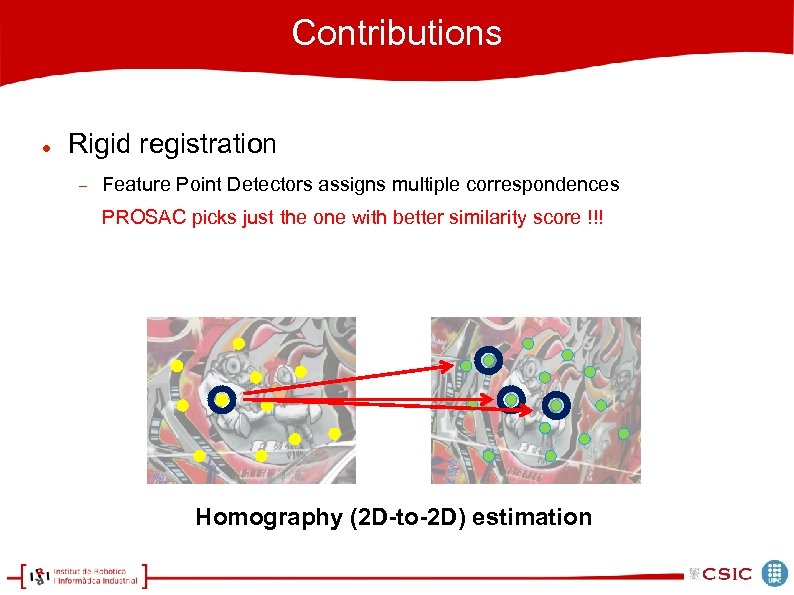 Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences PROSAC picks just the one with better similarity score !!! Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences PROSAC picks just the one with better similarity score !!! Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
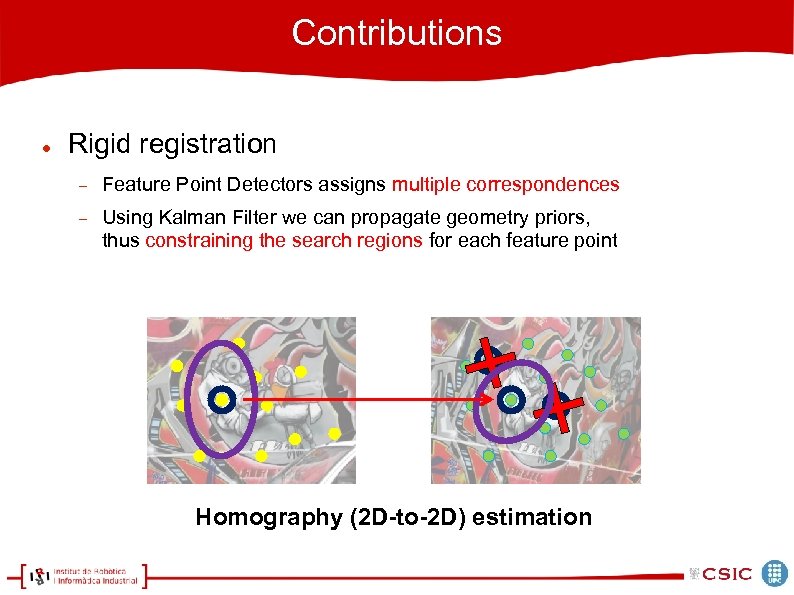 Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences Using Kalman Filter we can propagate geometry priors, thus constraining the search regions for each feature point Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences Using Kalman Filter we can propagate geometry priors, thus constraining the search regions for each feature point Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
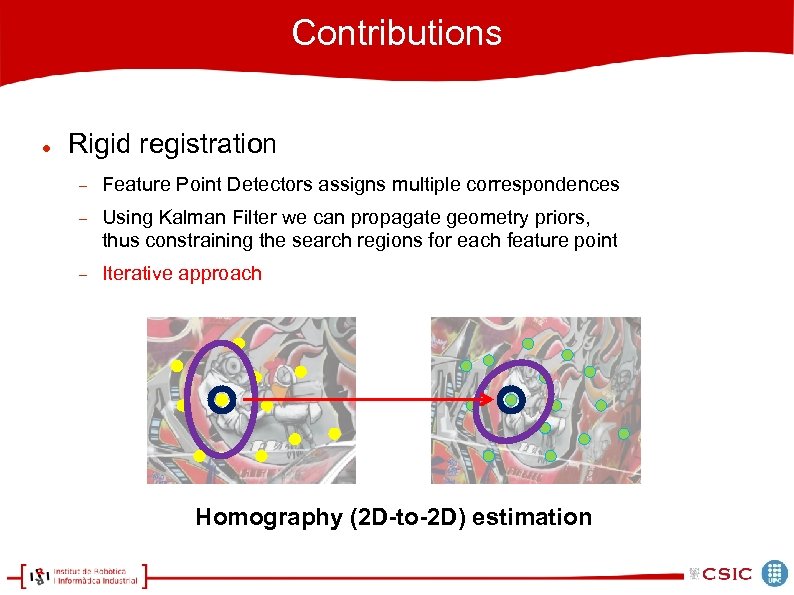 Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences Using Kalman Filter we can propagate geometry priors, thus constraining the search regions for each feature point Iterative approach Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences Using Kalman Filter we can propagate geometry priors, thus constraining the search regions for each feature point Iterative approach Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
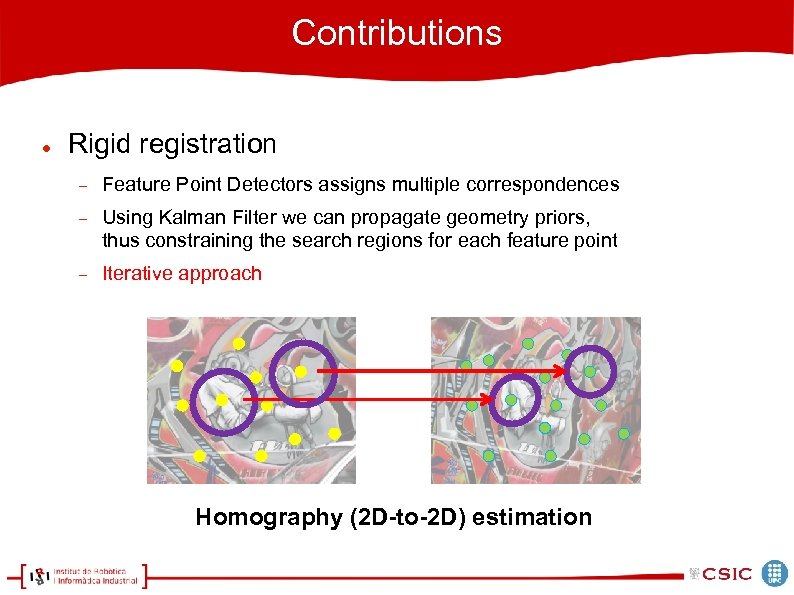 Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences Using Kalman Filter we can propagate geometry priors, thus constraining the search regions for each feature point Iterative approach Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences Using Kalman Filter we can propagate geometry priors, thus constraining the search regions for each feature point Iterative approach Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
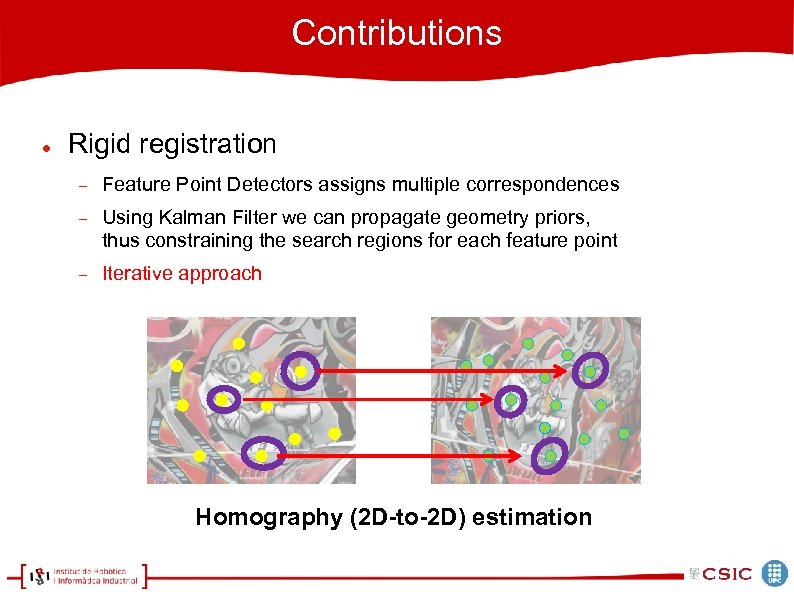 Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences Using Kalman Filter we can propagate geometry priors, thus constraining the search regions for each feature point Iterative approach Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences Using Kalman Filter we can propagate geometry priors, thus constraining the search regions for each feature point Iterative approach Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
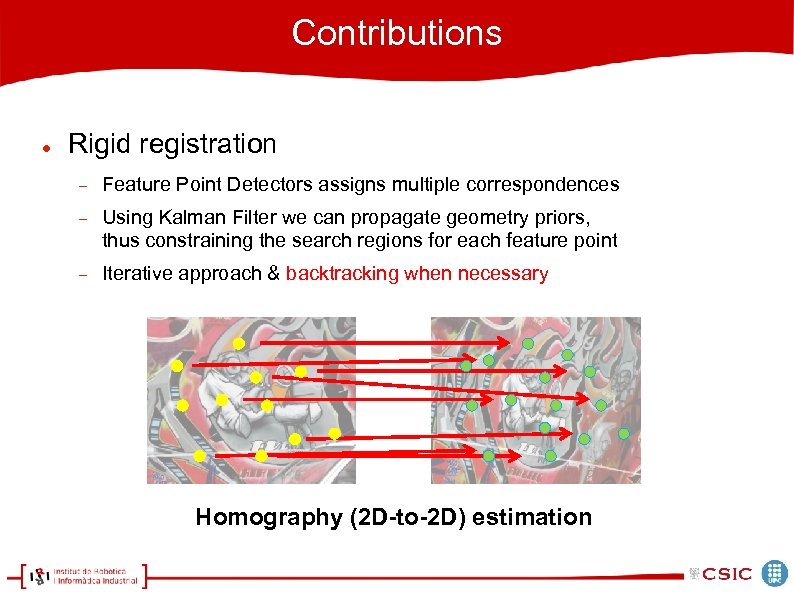 Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences Using Kalman Filter we can propagate geometry priors, thus constraining the search regions for each feature point Iterative approach & backtracking when necessary Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
Contributions Rigid registration Feature Point Detectors assigns multiple correspondences Using Kalman Filter we can propagate geometry priors, thus constraining the search regions for each feature point Iterative approach & backtracking when necessary Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
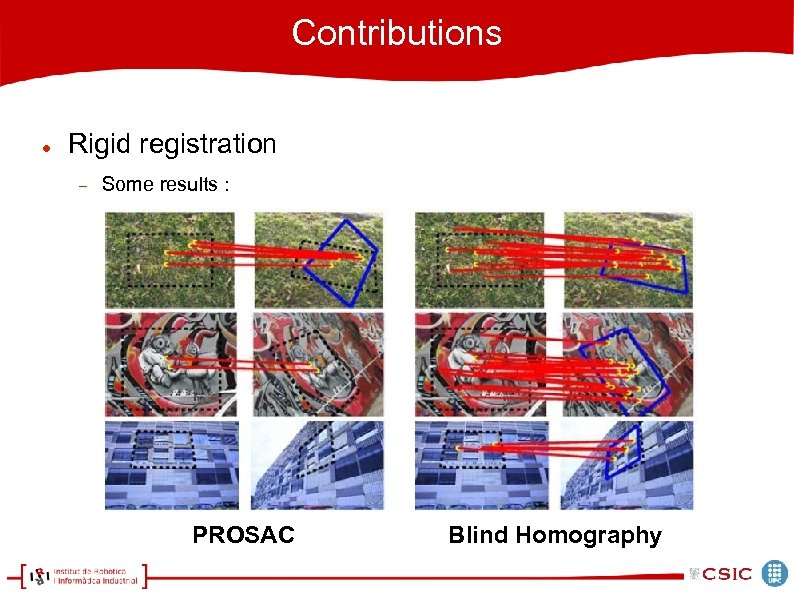 Contributions Rigid registration Some results : PROSAC Blind Homography
Contributions Rigid registration Some results : PROSAC Blind Homography
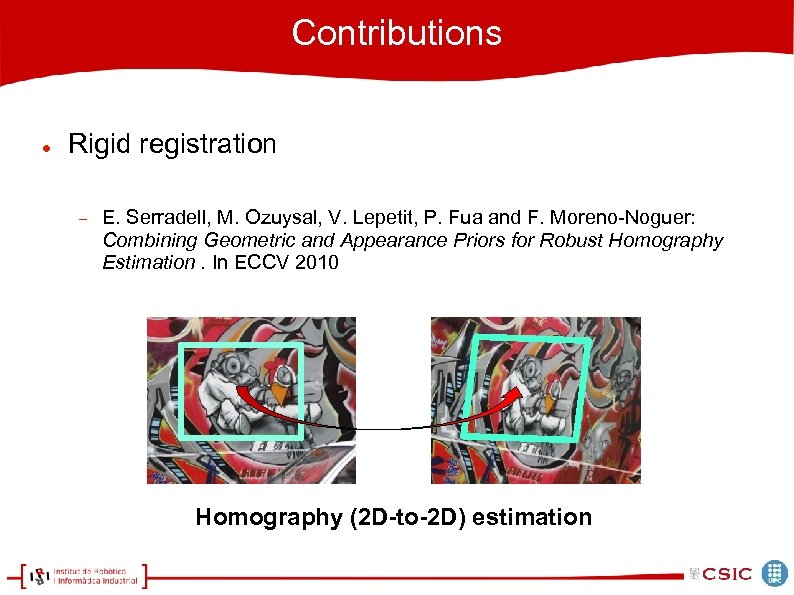 Contributions Rigid registration E. Serradell, M. Ozuysal, V. Lepetit, P. Fua and F. Moreno-Noguer: Combining Geometric and Appearance Priors for Robust Homography Estimation. In ECCV 2010 Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
Contributions Rigid registration E. Serradell, M. Ozuysal, V. Lepetit, P. Fua and F. Moreno-Noguer: Combining Geometric and Appearance Priors for Robust Homography Estimation. In ECCV 2010 Homography (2 D-to-2 D) estimation
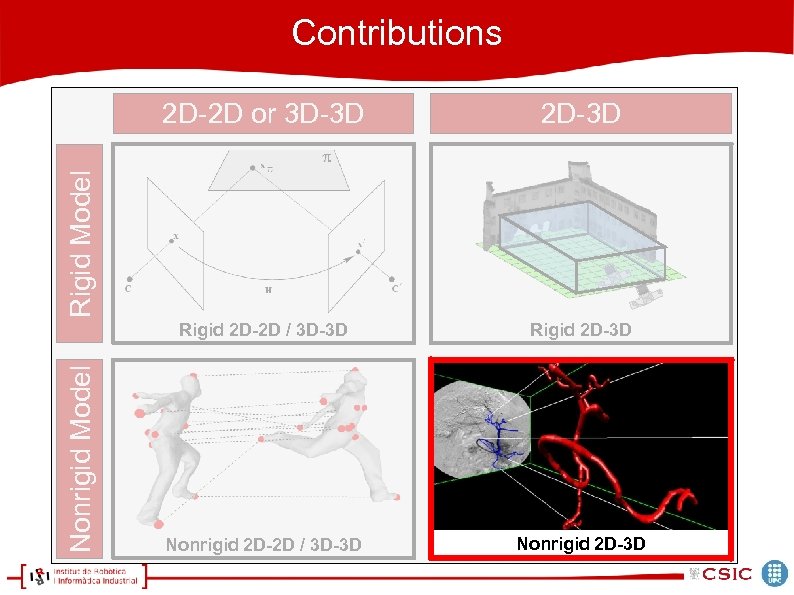 Contributions 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
Contributions 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
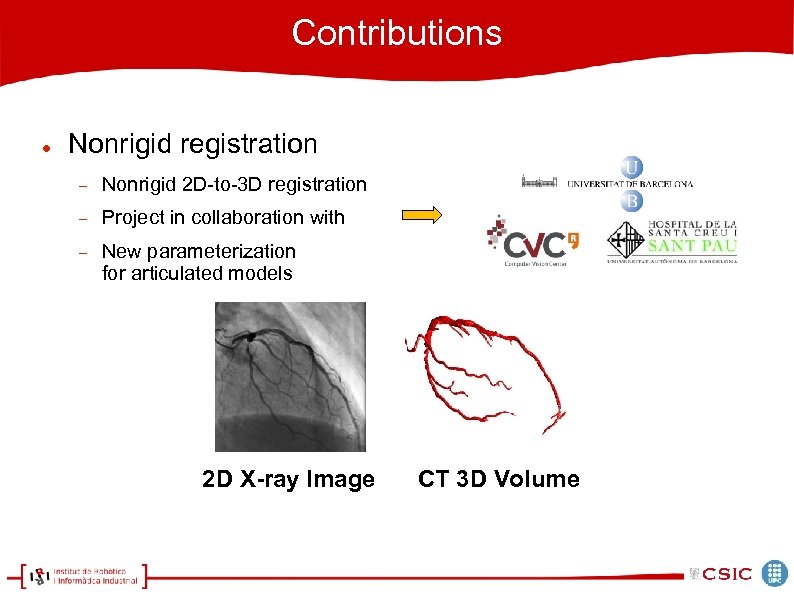 Contributions Nonrigid registration Nonrigid 2 D-to-3 D registration Project in collaboration with New parameterization for articulated models 2 D X-ray Image CT 3 D Volume
Contributions Nonrigid registration Nonrigid 2 D-to-3 D registration Project in collaboration with New parameterization for articulated models 2 D X-ray Image CT 3 D Volume
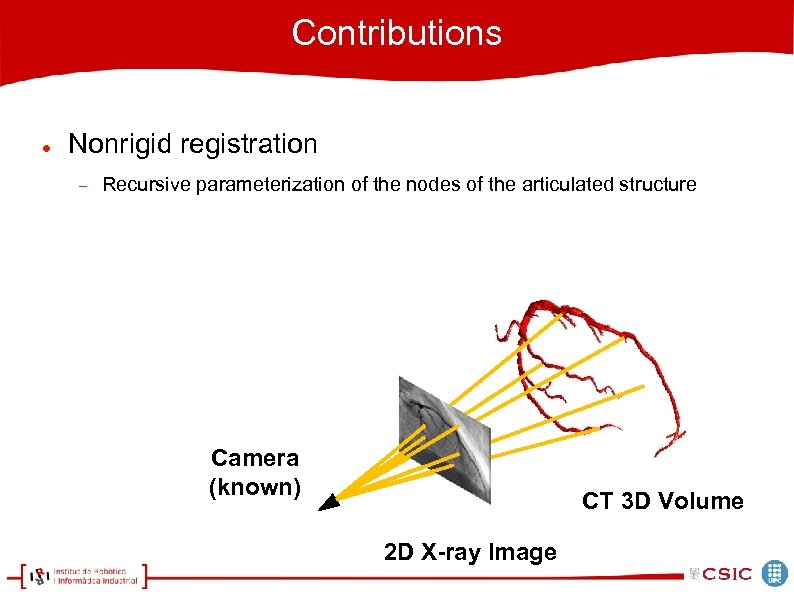 Contributions Nonrigid registration Recursive parameterization of the nodes of the articulated structure Camera (known) CT 3 D Volume 2 D X-ray Image
Contributions Nonrigid registration Recursive parameterization of the nodes of the articulated structure Camera (known) CT 3 D Volume 2 D X-ray Image
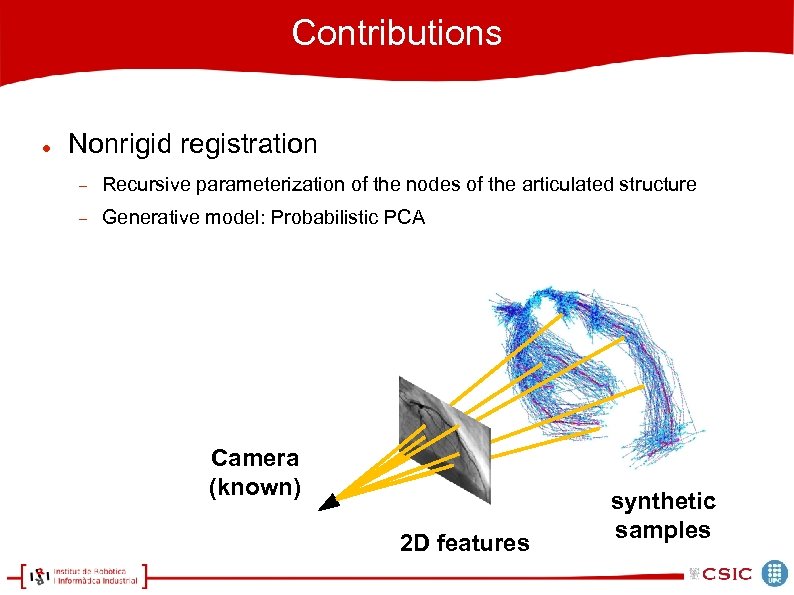 Contributions Nonrigid registration Recursive parameterization of the nodes of the articulated structure Generative model: Probabilistic PCA Camera (known) 2 D features synthetic samples
Contributions Nonrigid registration Recursive parameterization of the nodes of the articulated structure Generative model: Probabilistic PCA Camera (known) 2 D features synthetic samples
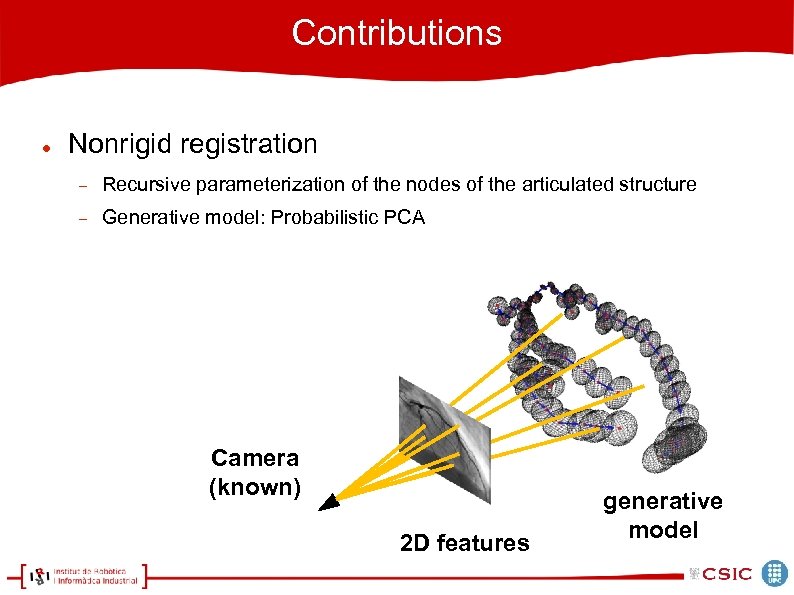 Contributions Nonrigid registration Recursive parameterization of the nodes of the articulated structure Generative model: Probabilistic PCA Camera (known) 2 D features generative model
Contributions Nonrigid registration Recursive parameterization of the nodes of the articulated structure Generative model: Probabilistic PCA Camera (known) 2 D features generative model
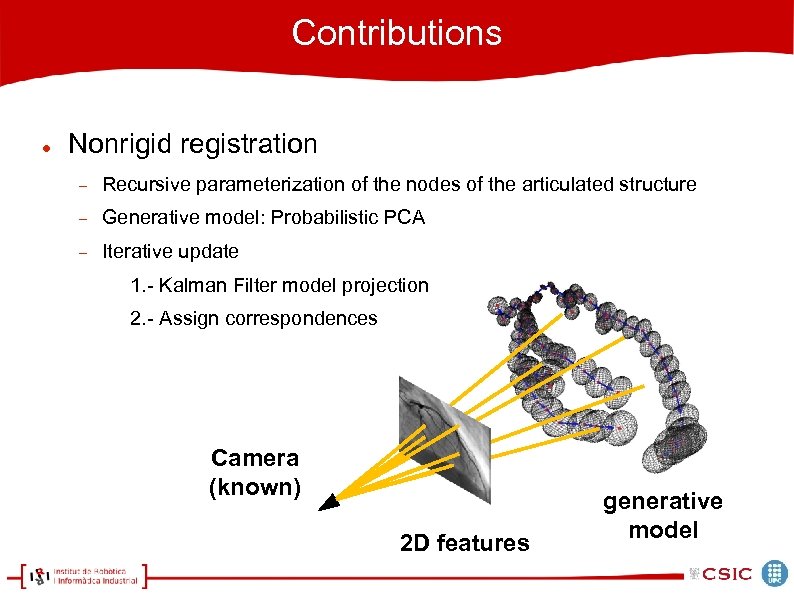 Contributions Nonrigid registration Recursive parameterization of the nodes of the articulated structure Generative model: Probabilistic PCA Iterative update 1. - Kalman Filter model projection 2. - Assign correspondences Camera (known) 2 D features generative model
Contributions Nonrigid registration Recursive parameterization of the nodes of the articulated structure Generative model: Probabilistic PCA Iterative update 1. - Kalman Filter model projection 2. - Assign correspondences Camera (known) 2 D features generative model
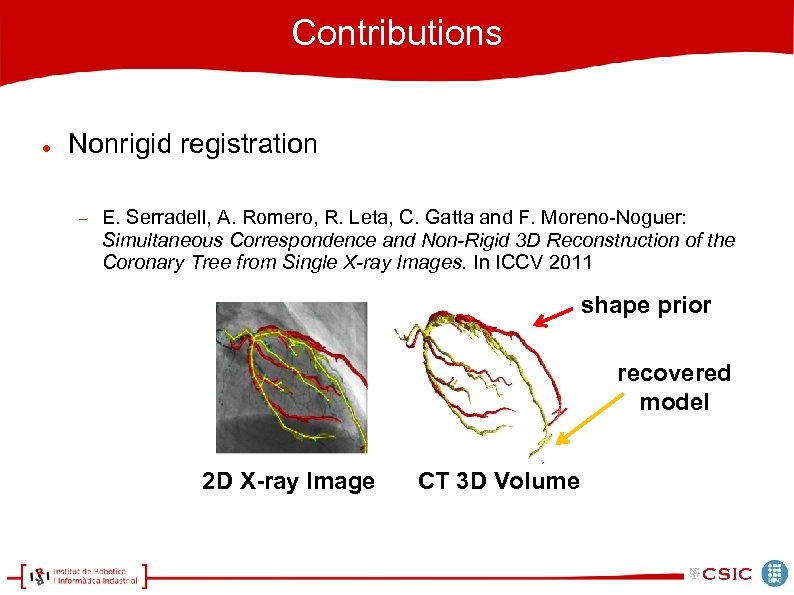 Contributions Nonrigid registration E. Serradell, A. Romero, R. Leta, C. Gatta and F. Moreno-Noguer: Simultaneous Correspondence and Non-Rigid 3 D Reconstruction of the Coronary Tree from Single X-ray Images. In ICCV 2011 shape prior recovered model 2 D X-ray Image CT 3 D Volume
Contributions Nonrigid registration E. Serradell, A. Romero, R. Leta, C. Gatta and F. Moreno-Noguer: Simultaneous Correspondence and Non-Rigid 3 D Reconstruction of the Coronary Tree from Single X-ray Images. In ICCV 2011 shape prior recovered model 2 D X-ray Image CT 3 D Volume
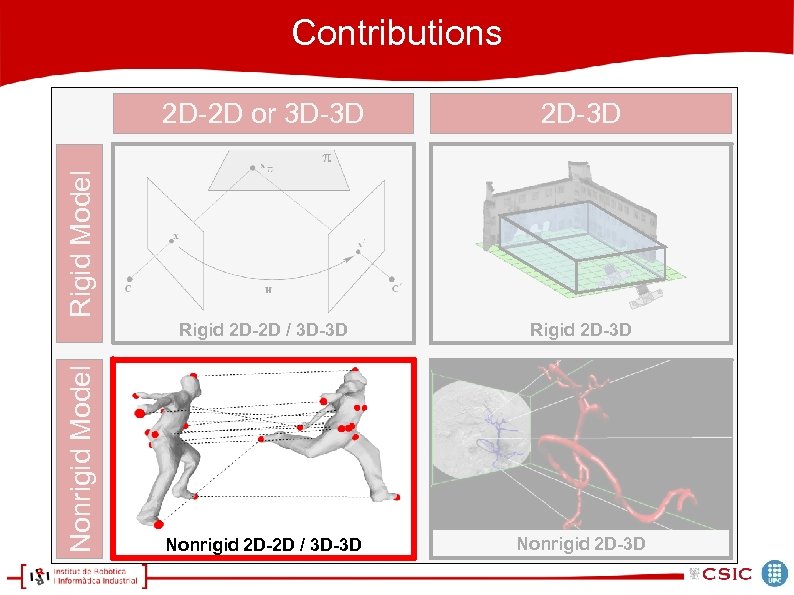 Contributions 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
Contributions 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
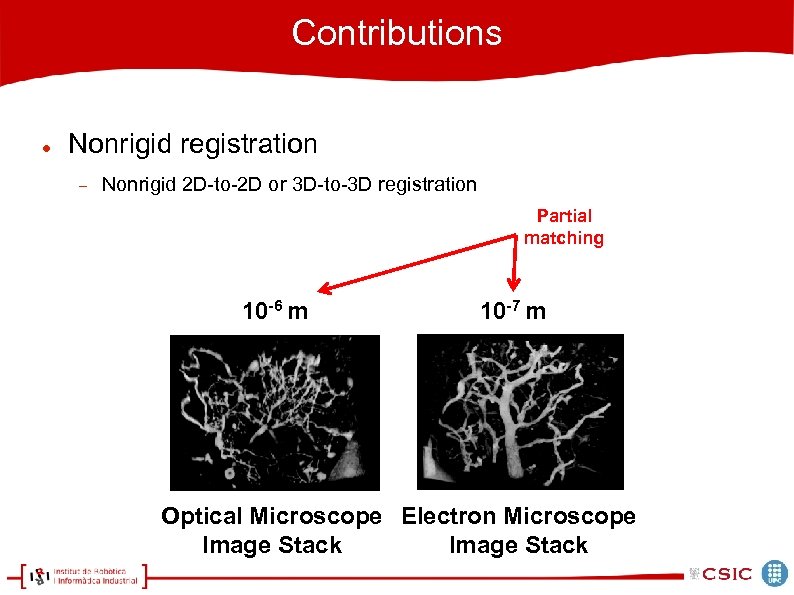 Contributions Nonrigid registration Nonrigid 2 D-to-2 D or 3 D-to-3 D registration Partial matching 10 -6 m 10 -7 m Optical Microscope Electron Microscope Image Stack
Contributions Nonrigid registration Nonrigid 2 D-to-2 D or 3 D-to-3 D registration Partial matching 10 -6 m 10 -7 m Optical Microscope Electron Microscope Image Stack
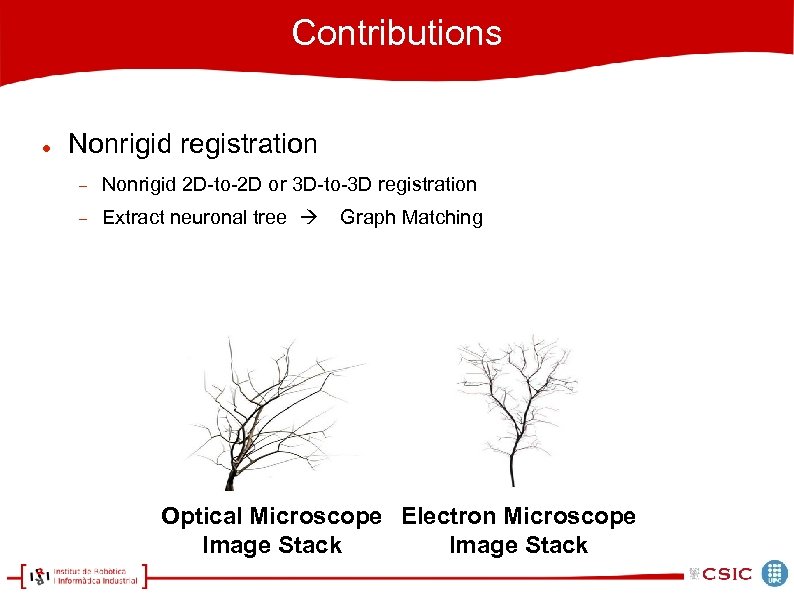 Contributions Nonrigid registration Nonrigid 2 D-to-2 D or 3 D-to-3 D registration Extract neuronal tree Graph Matching Optical Microscope Electron Microscope Image Stack
Contributions Nonrigid registration Nonrigid 2 D-to-2 D or 3 D-to-3 D registration Extract neuronal tree Graph Matching Optical Microscope Electron Microscope Image Stack
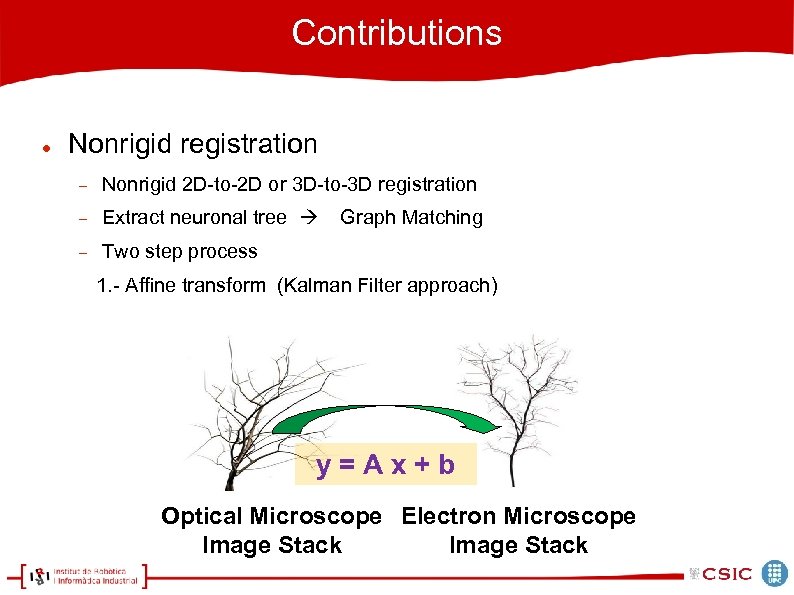 Contributions Nonrigid registration Nonrigid 2 D-to-2 D or 3 D-to-3 D registration Extract neuronal tree Two step process Graph Matching 1. - Affine transform (Kalman Filter approach) y=Ax+b Optical Microscope Electron Microscope Image Stack
Contributions Nonrigid registration Nonrigid 2 D-to-2 D or 3 D-to-3 D registration Extract neuronal tree Two step process Graph Matching 1. - Affine transform (Kalman Filter approach) y=Ax+b Optical Microscope Electron Microscope Image Stack
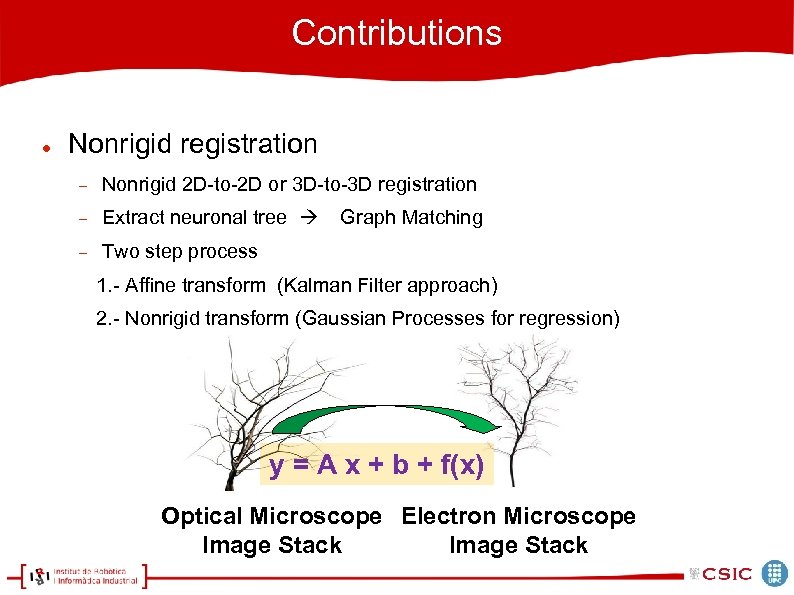 Contributions Nonrigid registration Nonrigid 2 D-to-2 D or 3 D-to-3 D registration Extract neuronal tree Two step process Graph Matching 1. - Affine transform (Kalman Filter approach) 2. - Nonrigid transform (Gaussian Processes for regression) y = A x + b + f(x) Optical Microscope Electron Microscope Image Stack
Contributions Nonrigid registration Nonrigid 2 D-to-2 D or 3 D-to-3 D registration Extract neuronal tree Two step process Graph Matching 1. - Affine transform (Kalman Filter approach) 2. - Nonrigid transform (Gaussian Processes for regression) y = A x + b + f(x) Optical Microscope Electron Microscope Image Stack
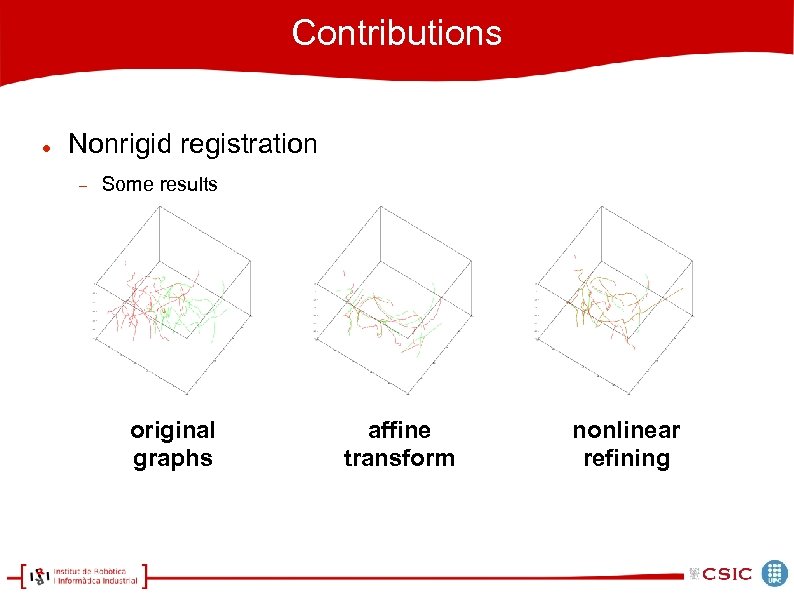 Contributions Nonrigid registration Some results original graphs affine transform nonlinear refining
Contributions Nonrigid registration Some results original graphs affine transform nonlinear refining
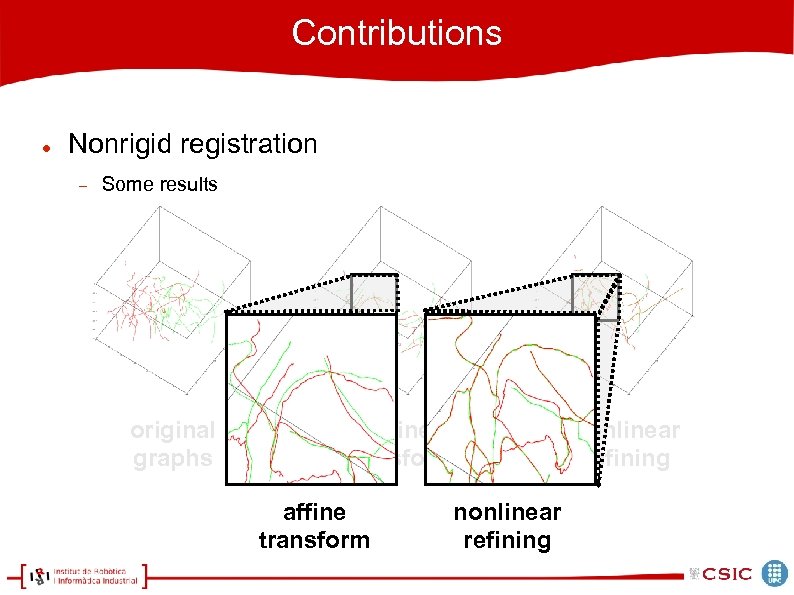 Contributions Nonrigid registration Some results original graphs affine transform nonlinear refining
Contributions Nonrigid registration Some results original graphs affine transform nonlinear refining
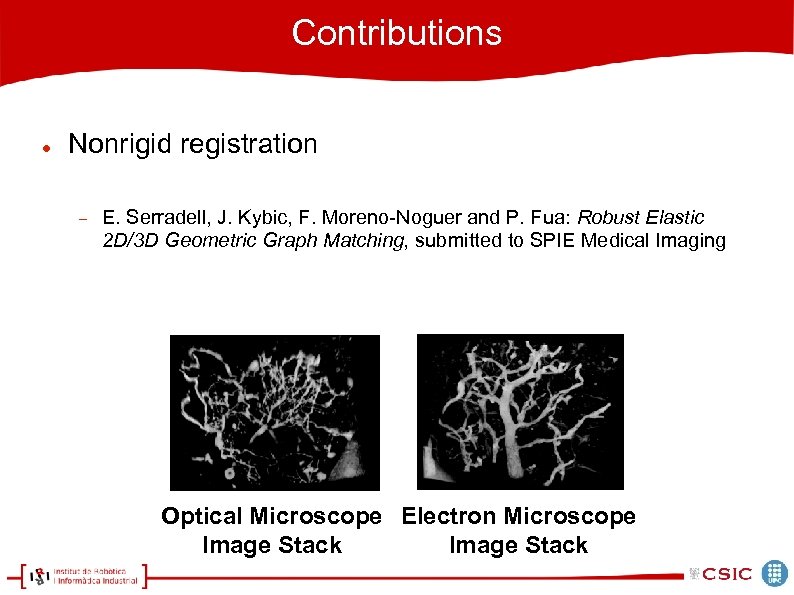 Contributions Nonrigid registration E. Serradell, J. Kybic, F. Moreno-Noguer and P. Fua: Robust Elastic 2 D/3 D Geometric Graph Matching, submitted to SPIE Medical Imaging Optical Microscope Electron Microscope Image Stack
Contributions Nonrigid registration E. Serradell, J. Kybic, F. Moreno-Noguer and P. Fua: Robust Elastic 2 D/3 D Geometric Graph Matching, submitted to SPIE Medical Imaging Optical Microscope Electron Microscope Image Stack
 Contributions 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
Contributions 2 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Rigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-2 D / 3 D-3 D Nonrigid 2 D-3 D Nonrigid Model Rigid Model 2 D-2 D or 3 D-3 D
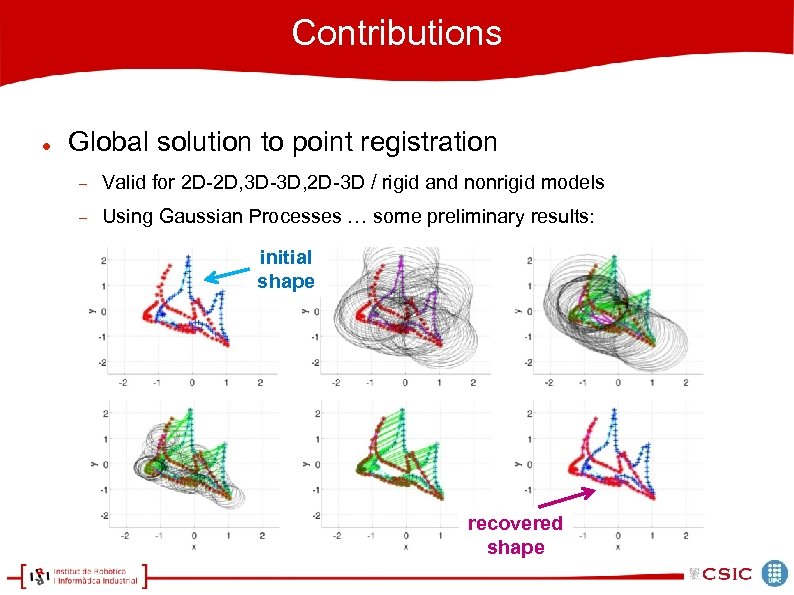 Contributions Global solution to point registration Valid for 2 D-2 D, 3 D-3 D, 2 D-3 D / rigid and nonrigid models Using Gaussian Processes … some preliminary results: initial shape recovered shape
Contributions Global solution to point registration Valid for 2 D-2 D, 3 D-3 D, 2 D-3 D / rigid and nonrigid models Using Gaussian Processes … some preliminary results: initial shape recovered shape
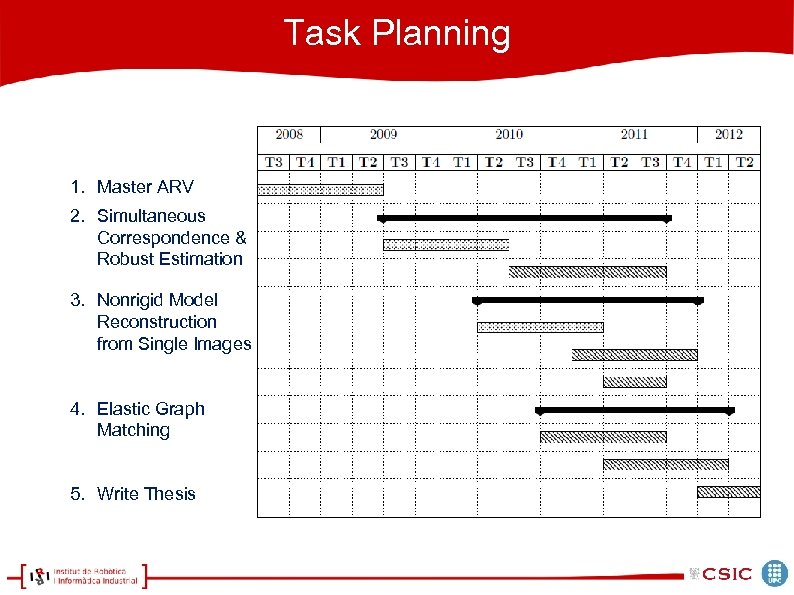 Task Planning 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis
Task Planning 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis
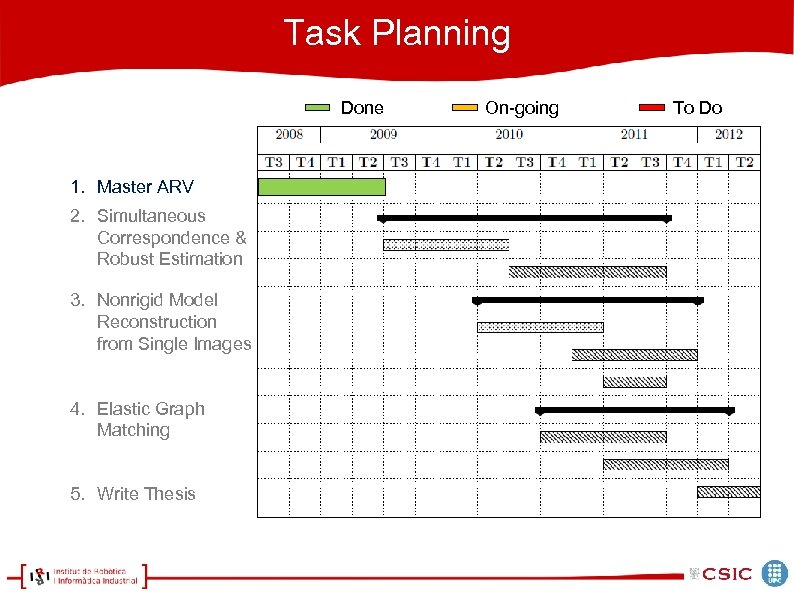 Task Planning Done 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis On-going To Do
Task Planning Done 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis On-going To Do
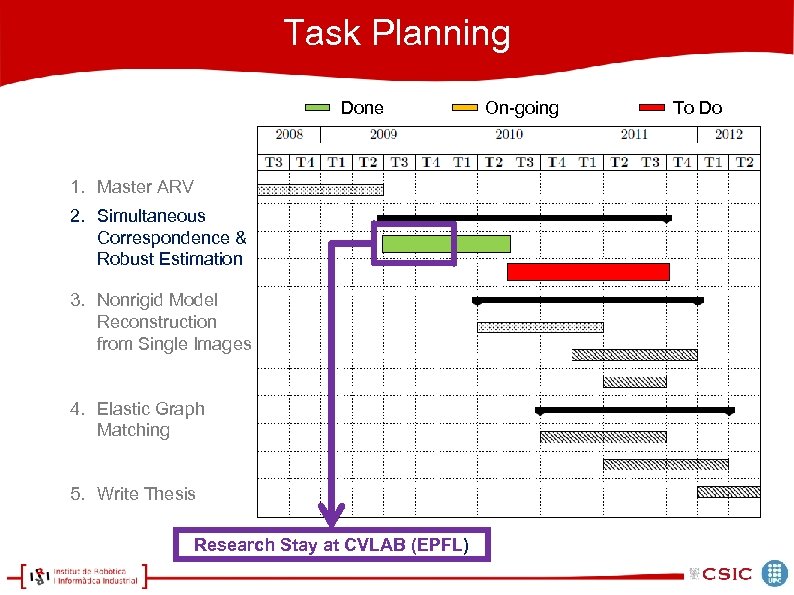 Task Planning Done 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis Research Stay at CVLAB (EPFL) On-going To Do
Task Planning Done 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis Research Stay at CVLAB (EPFL) On-going To Do
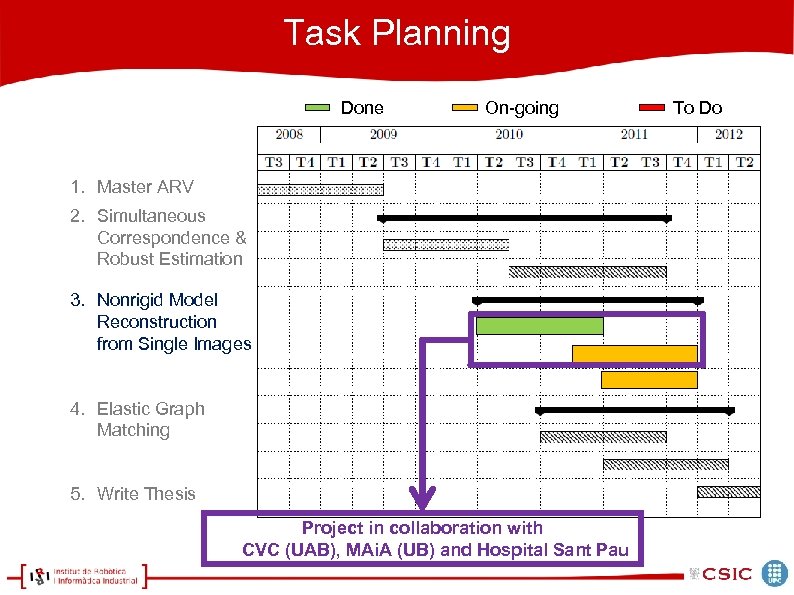 Task Planning Done On-going 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis Project in collaboration with CVC (UAB), MAi. A (UB) and Hospital Sant Pau To Do
Task Planning Done On-going 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis Project in collaboration with CVC (UAB), MAi. A (UB) and Hospital Sant Pau To Do
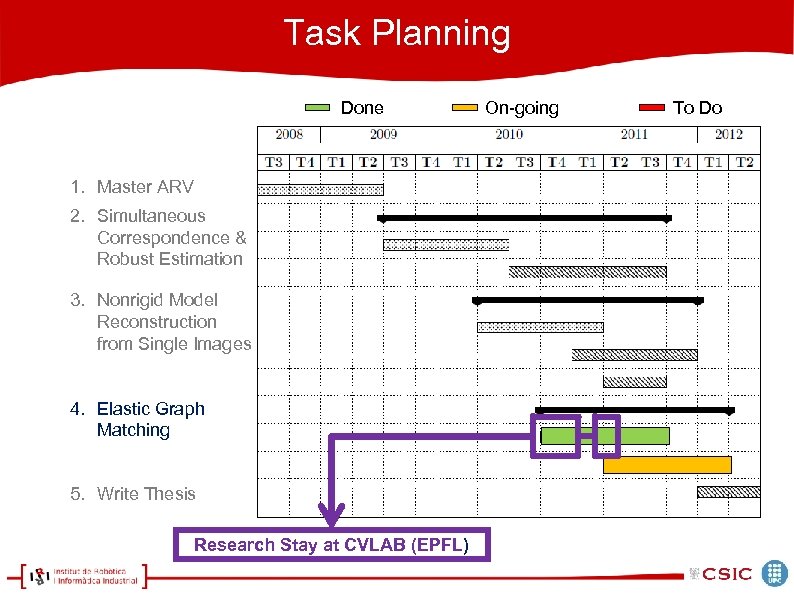 Task Planning Done 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis Research Stay at CVLAB (EPFL) On-going To Do
Task Planning Done 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis Research Stay at CVLAB (EPFL) On-going To Do
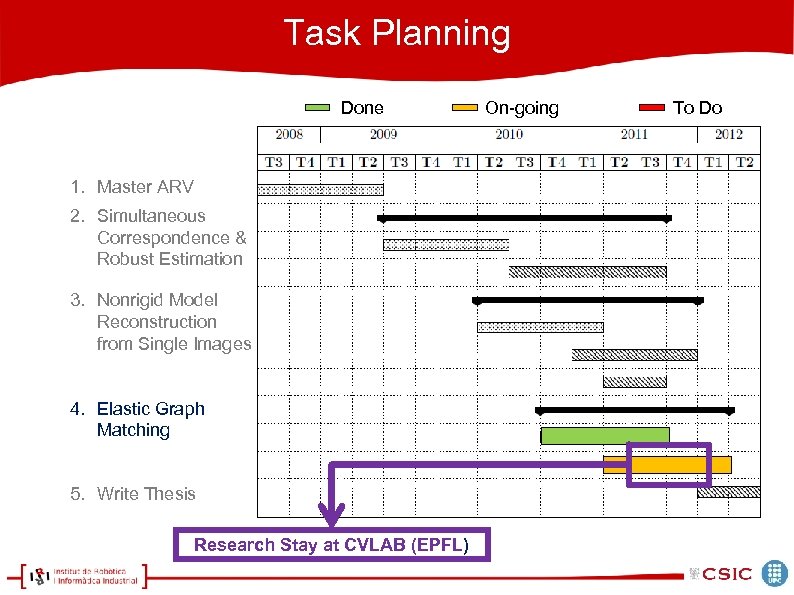 Task Planning Done 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis Research Stay at CVLAB (EPFL) On-going To Do
Task Planning Done 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis Research Stay at CVLAB (EPFL) On-going To Do
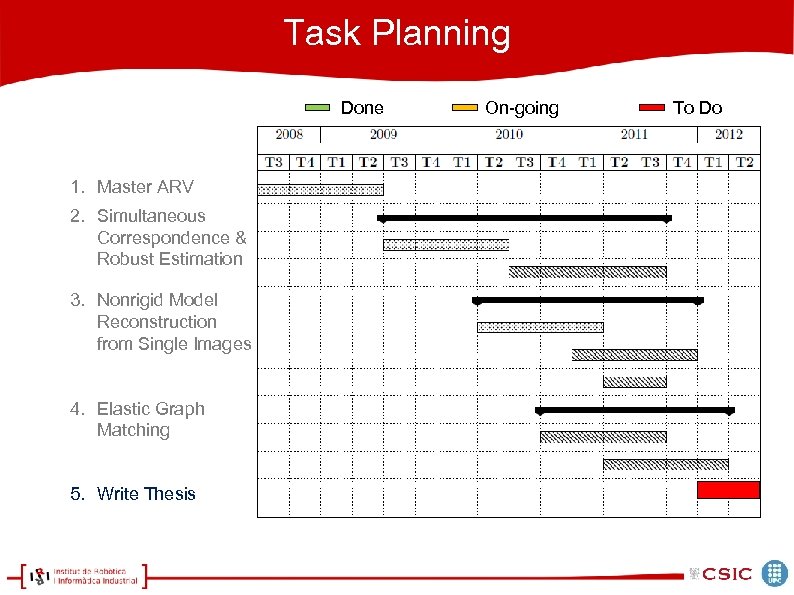 Task Planning Done 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis On-going To Do
Task Planning Done 1. Master ARV 2. Simultaneous Correspondence & Robust Estimation 3. Nonrigid Model Reconstruction from Single Images 4. Elastic Graph Matching 5. Write Thesis On-going To Do
 Summary of achievements Published papers E. Serradell, M. Ozuysal, V. Lepetit, P. Fua and F. Moreno-Noguer: Combining Geometric and Appearance Priors for Robust Homography Estimation. In ECCV 2010* E. Serradell, A. Romero, R. Leta, C. Gatta and F. Moreno-Noguer: Simultaneous Correspondence and Non-Rigid 3 D Reconstruction of the Coronary Tree from Single X-ray Images. In ICCV 2011* * ICCV, ECCV acceptance rate < 30% Submitted papers E. Serradell, J. Kybic, F. Moreno-Noguer and P. Fua: Robust Elastic 2 D/3 D Geometric Graph Matching, submitted to SPIE Medical Imaging
Summary of achievements Published papers E. Serradell, M. Ozuysal, V. Lepetit, P. Fua and F. Moreno-Noguer: Combining Geometric and Appearance Priors for Robust Homography Estimation. In ECCV 2010* E. Serradell, A. Romero, R. Leta, C. Gatta and F. Moreno-Noguer: Simultaneous Correspondence and Non-Rigid 3 D Reconstruction of the Coronary Tree from Single X-ray Images. In ICCV 2011* * ICCV, ECCV acceptance rate < 30% Submitted papers E. Serradell, J. Kybic, F. Moreno-Noguer and P. Fua: Robust Elastic 2 D/3 D Geometric Graph Matching, submitted to SPIE Medical Imaging
 THANKS!
THANKS!


