87c03de1e272901a91cc7185a11e3908.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Thermodynamics of relativistic fluids P. Ván Department of Theoretical Physics Research Institute of Particle and Nuclear Physics, Budapest, Hungary – Introduction Internal energy: –Thermodynamics and stability – Non-relativistic fluids – Stability paradox of dissipative relativistic fluids – About the temperature of moving bodies – Conclusions common work with T. S. Bíró and E. Molnár
Thermodynamics of relativistic fluids P. Ván Department of Theoretical Physics Research Institute of Particle and Nuclear Physics, Budapest, Hungary – Introduction Internal energy: –Thermodynamics and stability – Non-relativistic fluids – Stability paradox of dissipative relativistic fluids – About the temperature of moving bodies – Conclusions common work with T. S. Bíró and E. Molnár
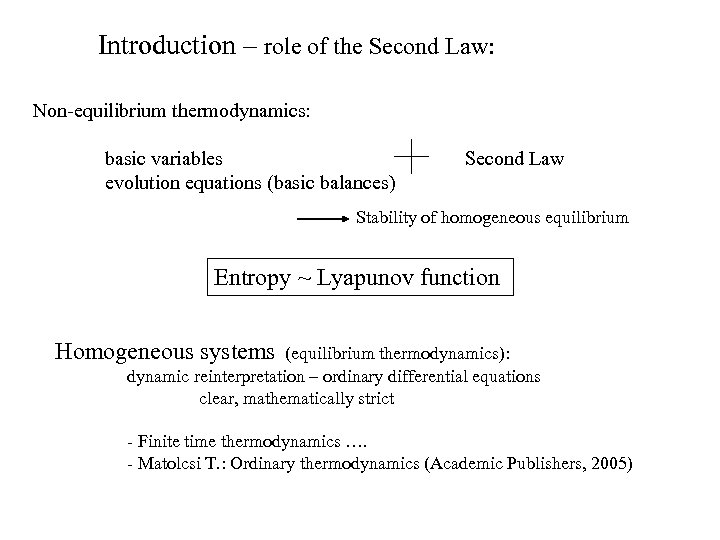 Introduction – role of the Second Law: Non-equilibrium thermodynamics: basic variables evolution equations (basic balances) Second Law Stability of homogeneous equilibrium Entropy ~ Lyapunov function Homogeneous systems (equilibrium thermodynamics): dynamic reinterpretation – ordinary differential equations clear, mathematically strict - Finite time thermodynamics …. - Matolcsi T. : Ordinary thermodynamics (Academic Publishers, 2005)
Introduction – role of the Second Law: Non-equilibrium thermodynamics: basic variables evolution equations (basic balances) Second Law Stability of homogeneous equilibrium Entropy ~ Lyapunov function Homogeneous systems (equilibrium thermodynamics): dynamic reinterpretation – ordinary differential equations clear, mathematically strict - Finite time thermodynamics …. - Matolcsi T. : Ordinary thermodynamics (Academic Publishers, 2005)
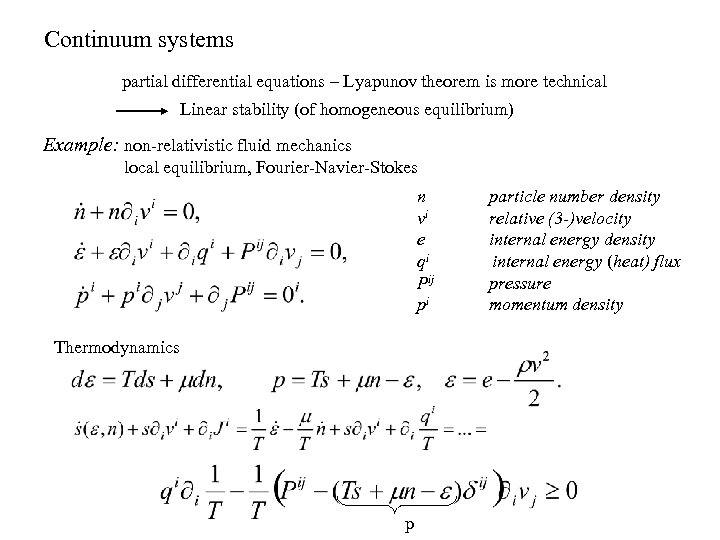 Continuum systems partial differential equations – Lyapunov theorem is more technical Linear stability (of homogeneous equilibrium) Example: non-relativistic fluid mechanics local equilibrium, Fourier-Navier-Stokes n vi e qi Pij pi Thermodynamics p particle number density relative (3 -)velocity internal energy density internal energy (heat) flux pressure momentum density
Continuum systems partial differential equations – Lyapunov theorem is more technical Linear stability (of homogeneous equilibrium) Example: non-relativistic fluid mechanics local equilibrium, Fourier-Navier-Stokes n vi e qi Pij pi Thermodynamics p particle number density relative (3 -)velocity internal energy density internal energy (heat) flux pressure momentum density
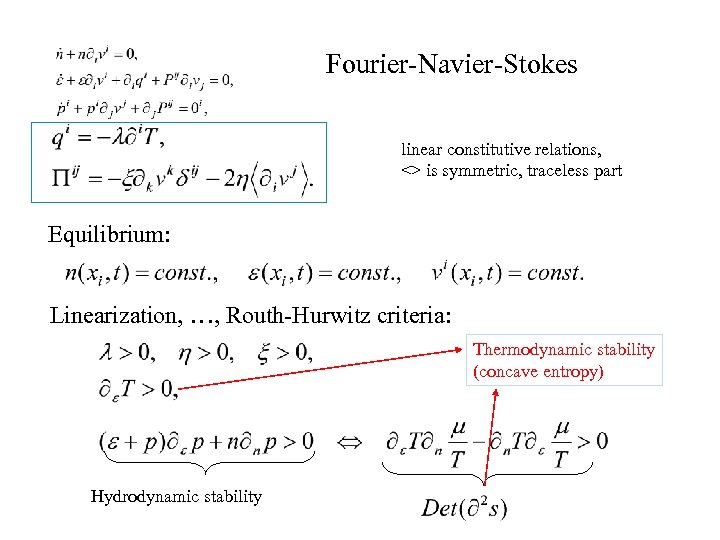 Fourier-Navier-Stokes linear constitutive relations, <> is symmetric, traceless part Equilibrium: Linearization, …, Routh-Hurwitz criteria: Thermodynamic stability (concave entropy) Hydrodynamic stability
Fourier-Navier-Stokes linear constitutive relations, <> is symmetric, traceless part Equilibrium: Linearization, …, Routh-Hurwitz criteria: Thermodynamic stability (concave entropy) Hydrodynamic stability
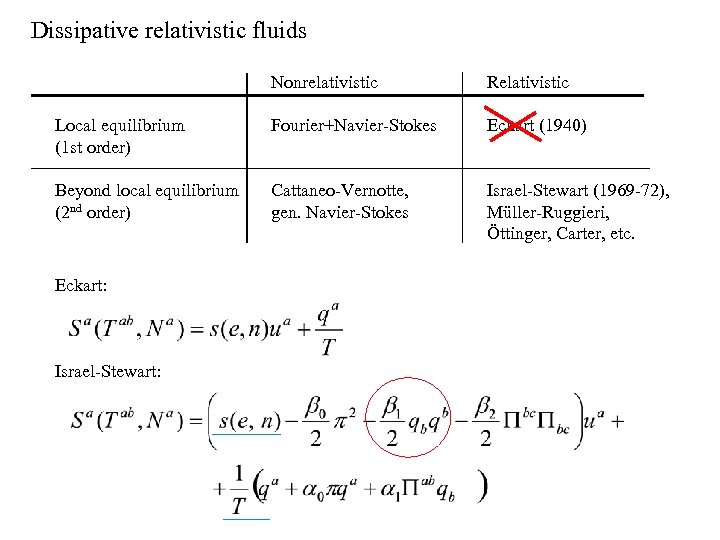 Dissipative relativistic fluids Nonrelativistic Relativistic Local equilibrium (1 st order) Fourier+Navier-Stokes Eckart (1940) Beyond local equilibrium (2 nd order) Cattaneo-Vernotte, gen. Navier-Stokes Israel-Stewart (1969 -72), Müller-Ruggieri, Öttinger, Carter, etc. Eckart: Israel-Stewart:
Dissipative relativistic fluids Nonrelativistic Relativistic Local equilibrium (1 st order) Fourier+Navier-Stokes Eckart (1940) Beyond local equilibrium (2 nd order) Cattaneo-Vernotte, gen. Navier-Stokes Israel-Stewart (1969 -72), Müller-Ruggieri, Öttinger, Carter, etc. Eckart: Israel-Stewart:
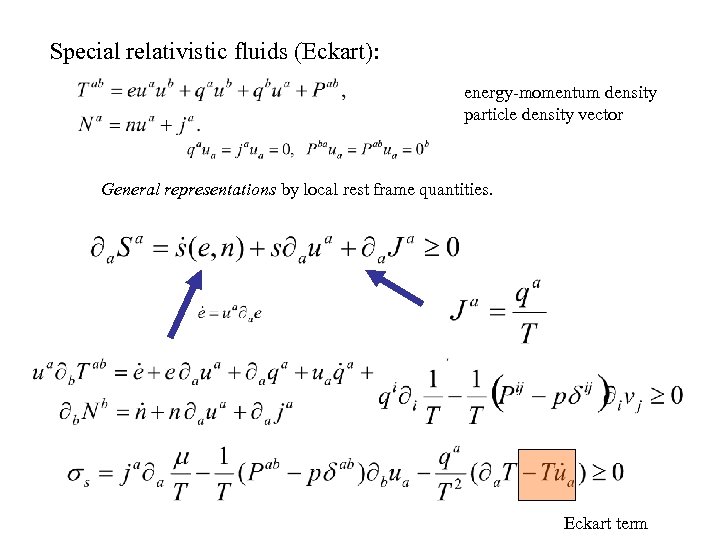 Special relativistic fluids (Eckart): energy-momentum density particle density vector General representations by local rest frame quantities. Eckart term
Special relativistic fluids (Eckart): energy-momentum density particle density vector General representations by local rest frame quantities. Eckart term
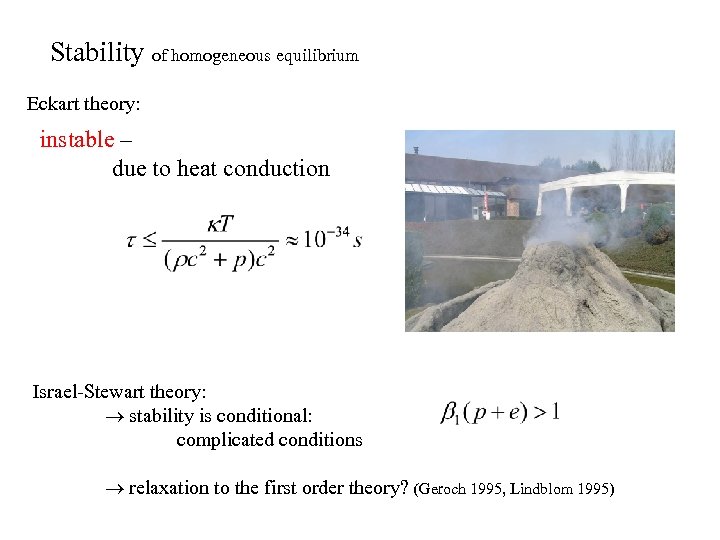 Stability of homogeneous equilibrium Eckart theory: instable – due to heat conduction water Israel-Stewart theory: stability is conditional: complicated conditions relaxation to the first order theory? (Geroch 1995, Lindblom 1995)
Stability of homogeneous equilibrium Eckart theory: instable – due to heat conduction water Israel-Stewart theory: stability is conditional: complicated conditions relaxation to the first order theory? (Geroch 1995, Lindblom 1995)
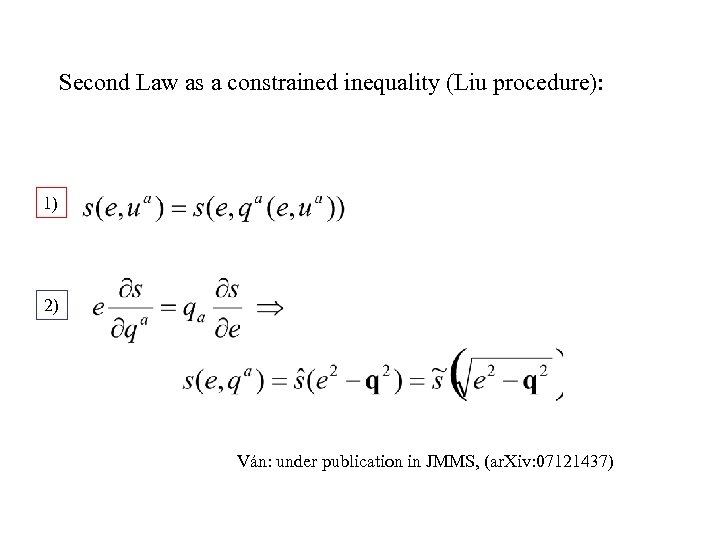 Second Law as a constrained inequality (Liu procedure): 1) 2) Ván: under publication in JMMS, (ar. Xiv: 07121437)
Second Law as a constrained inequality (Liu procedure): 1) 2) Ván: under publication in JMMS, (ar. Xiv: 07121437)
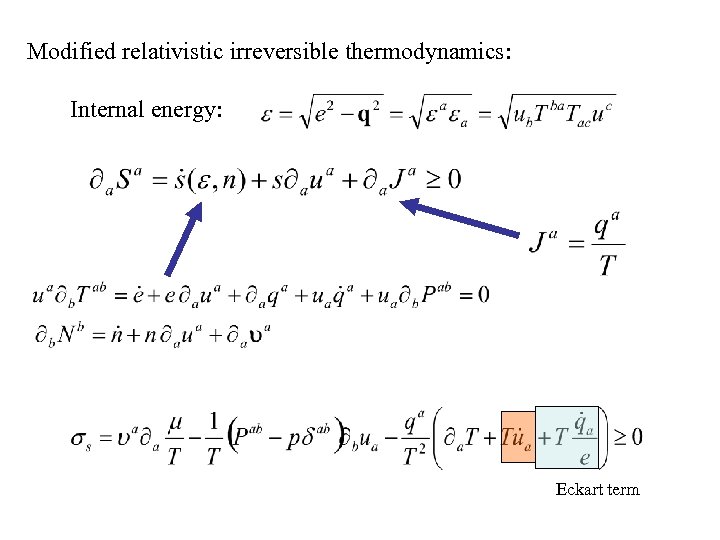 Modified relativistic irreversible thermodynamics: Internal energy: Eckart term
Modified relativistic irreversible thermodynamics: Internal energy: Eckart term
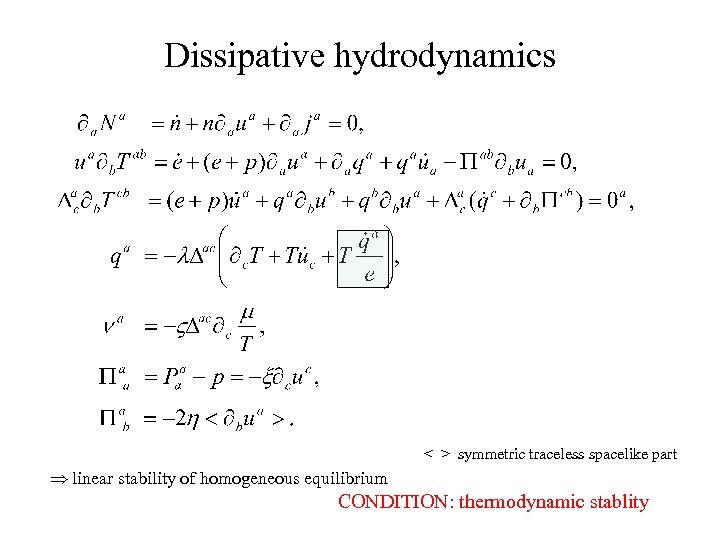 Dissipative hydrodynamics < > symmetric traceless spacelike part Þ linear stability of homogeneous equilibrium CONDITION: thermodynamic stablity
Dissipative hydrodynamics < > symmetric traceless spacelike part Þ linear stability of homogeneous equilibrium CONDITION: thermodynamic stablity
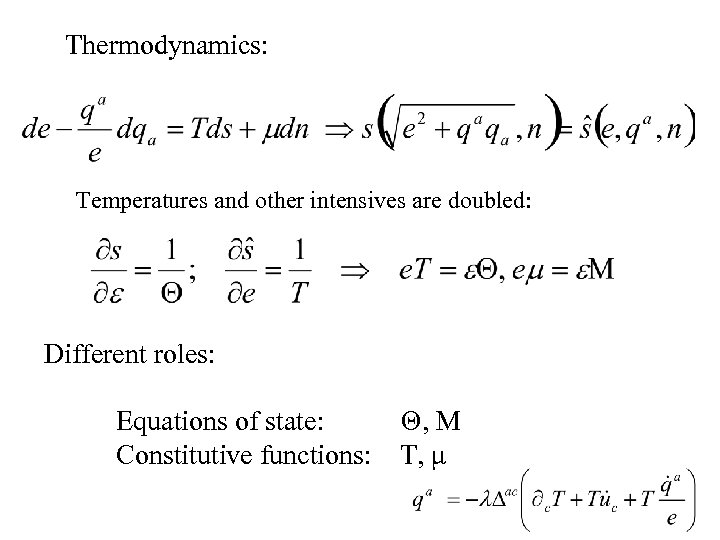 Thermodynamics: Temperatures and other intensives are doubled: Different roles: Equations of state: Constitutive functions: Θ, M T, μ
Thermodynamics: Temperatures and other intensives are doubled: Different roles: Equations of state: Constitutive functions: Θ, M T, μ
 About the temperature of moving bodies: moving body CRETE inertial observer
About the temperature of moving bodies: moving body CRETE inertial observer
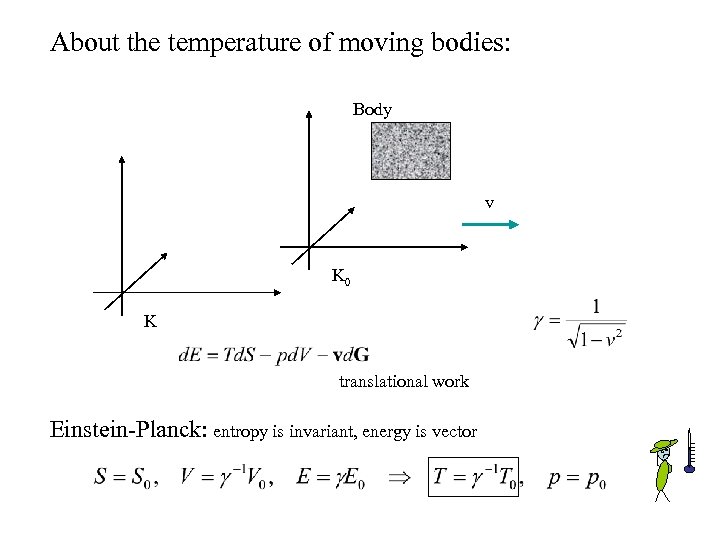 About the temperature of moving bodies: Body v K 0 K translational work Einstein-Planck: entropy is invariant, energy is vector
About the temperature of moving bodies: Body v K 0 K translational work Einstein-Planck: entropy is invariant, energy is vector
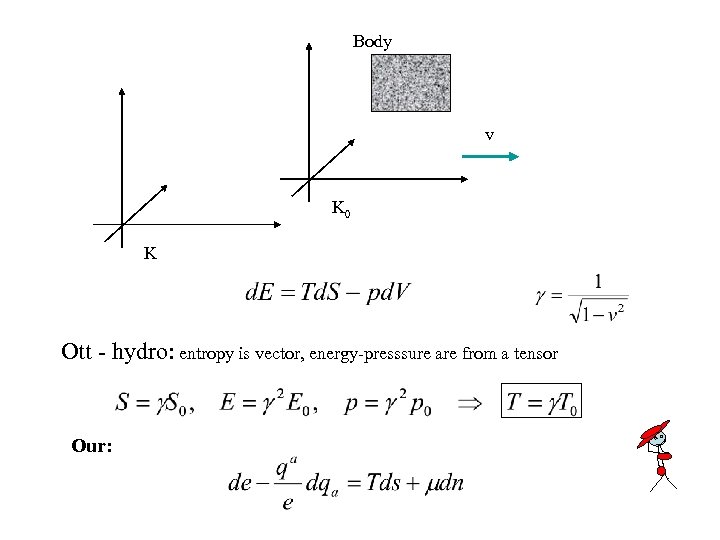 Body v K 0 K Ott - hydro: entropy is vector, energy-presssure are from a tensor Our:
Body v K 0 K Ott - hydro: entropy is vector, energy-presssure are from a tensor Our:
 Summary – energy ≠ internal energy → generic stability without extra conditions - relativistic thermodynamics: there is no local equilibrium - different temperatures in Fourier-law (equilibration) and in state functions out of local equilibrium. - causality /Ván and Bíró, EPJ, (2007), 155, p 201 -212, (ar. Xiv: 0704. 2039 v 2)/ - hyperbolic(-like) extensions, solutions /Bíró, Molnár and Ván: under publication in PRC, (ar. Xiv: 0805. 1061)/
Summary – energy ≠ internal energy → generic stability without extra conditions - relativistic thermodynamics: there is no local equilibrium - different temperatures in Fourier-law (equilibration) and in state functions out of local equilibrium. - causality /Ván and Bíró, EPJ, (2007), 155, p 201 -212, (ar. Xiv: 0704. 2039 v 2)/ - hyperbolic(-like) extensions, solutions /Bíró, Molnár and Ván: under publication in PRC, (ar. Xiv: 0805. 1061)/
 Thank you for your attention!
Thank you for your attention!


