006c80a798f6b14cfc94e37f8cae80c7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 THERE IS NO SECURITY ON THIS EARTH, THERE IS ONLY OPPORTUNITY General Douglas Macarthur Somi
THERE IS NO SECURITY ON THIS EARTH, THERE IS ONLY OPPORTUNITY General Douglas Macarthur Somi
 BUDAPESTI GAZDASÁGI FŐISKOLA INTERNATIONAL MARKETING LECTURE- 3 In English 2 nd March 2012 – FRIDAY 0940 hr – 1110 hr (E. F. 13 -15) Miklós (Nicholas) SOÓS 0630 265 9638 miklosoos@hotmail. com somi
BUDAPESTI GAZDASÁGI FŐISKOLA INTERNATIONAL MARKETING LECTURE- 3 In English 2 nd March 2012 – FRIDAY 0940 hr – 1110 hr (E. F. 13 -15) Miklós (Nicholas) SOÓS 0630 265 9638 miklosoos@hotmail. com somi
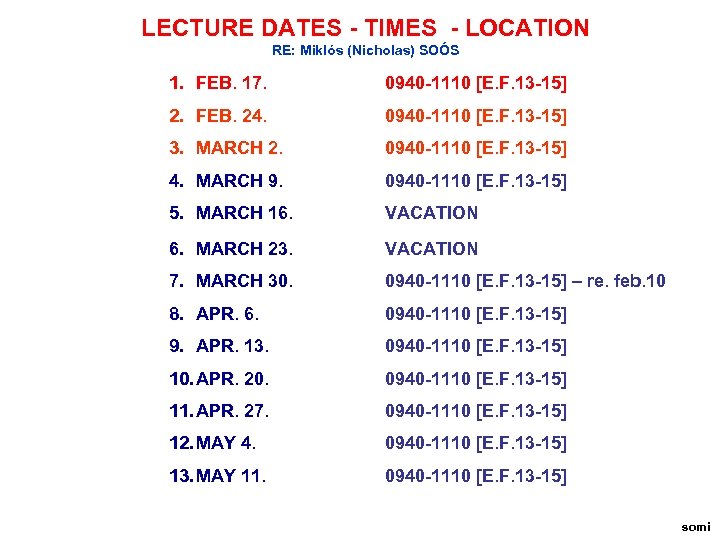 LECTURE DATES - TIMES - LOCATION RE: Miklós (Nicholas) SOÓS 1. FEB. 17. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 2. FEB. 24. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 3. MARCH 2. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 4. MARCH 9. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 5. MARCH 16. VACATION 6. MARCH 23. VACATION 7. MARCH 30. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] – re. feb. 10 8. APR. 6. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 9. APR. 13. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 10. APR. 20. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 11. APR. 27. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 12. MAY 4. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 13. MAY 11. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] somi
LECTURE DATES - TIMES - LOCATION RE: Miklós (Nicholas) SOÓS 1. FEB. 17. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 2. FEB. 24. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 3. MARCH 2. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 4. MARCH 9. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 5. MARCH 16. VACATION 6. MARCH 23. VACATION 7. MARCH 30. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] – re. feb. 10 8. APR. 6. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 9. APR. 13. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 10. APR. 20. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 11. APR. 27. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 12. MAY 4. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] 13. MAY 11. 0940 -1110 [E. F. 13 -15] somi
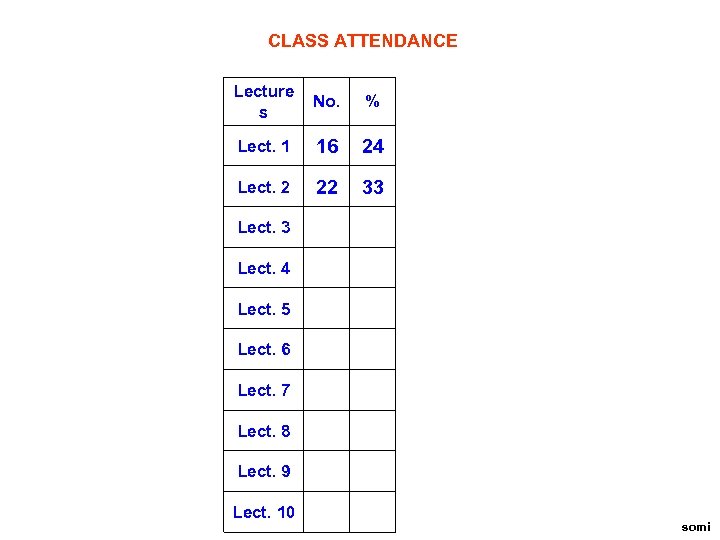 CLASS ATTENDANCE Lecture s No. % Lect. 1 16 24 Lect. 2 22 33 Lect. 3 Lect. 4 Lect. 5 Lect. 6 Lect. 7 Lect. 8 Lect. 9 Lect. 10 somi
CLASS ATTENDANCE Lecture s No. % Lect. 1 16 24 Lect. 2 22 33 Lect. 3 Lect. 4 Lect. 5 Lect. 6 Lect. 7 Lect. 8 Lect. 9 Lect. 10 somi
 Please ensure that you personally sign the attendance sheet every time you attend a lecture. somi
Please ensure that you personally sign the attendance sheet every time you attend a lecture. somi
 The visual contents of lectures will be available internally on the following site: K: HallgatokANGOLSoós tanár úr somi
The visual contents of lectures will be available internally on the following site: K: HallgatokANGOLSoós tanár úr somi
 SOURCES, REFERENCES – SUGGESTED READINGS The course is NOT based on any specific textbook. The following are recommended. International Marketing, Cateora, P. & Graham, J. (2005) 12 th edition, Mc. Graw-Hill Global Marketing, Hollensen, S. (2004) 3 rd edition, Prentice Hall International Marketing Strategy, Doole, I. & Lowe, R (2004) 4 th edition Thomson International Marketing and Export Management, Albaum G, Prentice Hall London Principles of Marketing, Kotler P et. Al, 2 nd European edition, Prentice Hall E. 2003 Principles of Marketing, Jobber D, Mc. Graw-Hill Principles of Marketing, Brassington F, Financial Times Prentice Hall, 2000 Marketing on the Internet: Principles of online marketing, Strauss J & Raymond F, Prentice Hall, 1999 Internet sites: www. pmcinc. org/ www. tradeport. org www. FAS. USDA. gov somi
SOURCES, REFERENCES – SUGGESTED READINGS The course is NOT based on any specific textbook. The following are recommended. International Marketing, Cateora, P. & Graham, J. (2005) 12 th edition, Mc. Graw-Hill Global Marketing, Hollensen, S. (2004) 3 rd edition, Prentice Hall International Marketing Strategy, Doole, I. & Lowe, R (2004) 4 th edition Thomson International Marketing and Export Management, Albaum G, Prentice Hall London Principles of Marketing, Kotler P et. Al, 2 nd European edition, Prentice Hall E. 2003 Principles of Marketing, Jobber D, Mc. Graw-Hill Principles of Marketing, Brassington F, Financial Times Prentice Hall, 2000 Marketing on the Internet: Principles of online marketing, Strauss J & Raymond F, Prentice Hall, 1999 Internet sites: www. pmcinc. org/ www. tradeport. org www. FAS. USDA. gov somi
 ASSESSMENT METHOD End of year written examination 60% Two (2) ‘mini’ exams of 20 min. duration during unannounced lectures 40%
ASSESSMENT METHOD End of year written examination 60% Two (2) ‘mini’ exams of 20 min. duration during unannounced lectures 40%
 Where we finished last week.
Where we finished last week.
 SUBSETS OF INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS International business Source: Omar (2009) International trade International management International marketing International finance Global marketing somi
SUBSETS OF INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS International business Source: Omar (2009) International trade International management International marketing International finance Global marketing somi
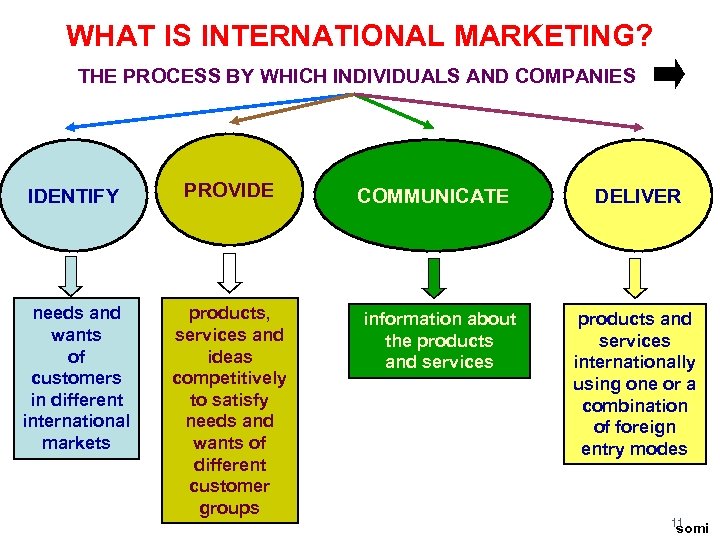 WHAT IS INTERNATIONAL MARKETING? THE PROCESS BY WHICH INDIVIDUALS AND COMPANIES IDENTIFY needs and wants of customers in different international markets PROVIDE products, services and ideas competitively to satisfy needs and wants of different customer groups COMMUNICATE information about the products and services DELIVER products and services internationally using one or a combination of foreign entry modes 11 somi
WHAT IS INTERNATIONAL MARKETING? THE PROCESS BY WHICH INDIVIDUALS AND COMPANIES IDENTIFY needs and wants of customers in different international markets PROVIDE products, services and ideas competitively to satisfy needs and wants of different customer groups COMMUNICATE information about the products and services DELIVER products and services internationally using one or a combination of foreign entry modes 11 somi
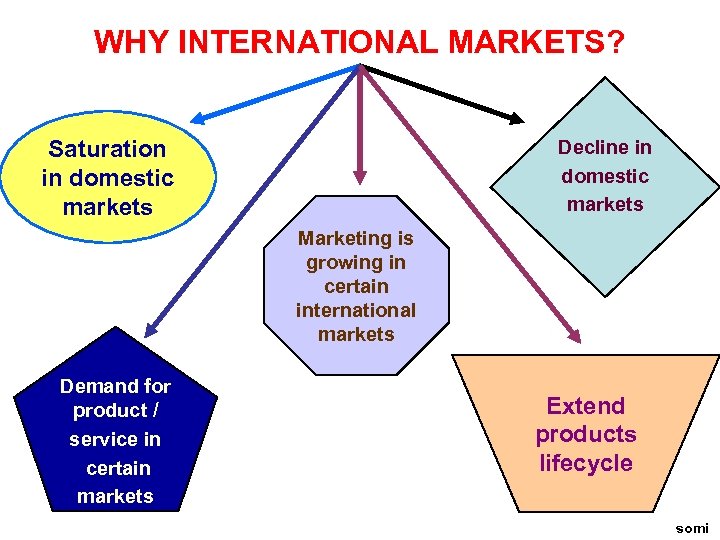 WHY INTERNATIONAL MARKETS? Saturation in domestic markets Decline in domestic markets Marketing is growing in certain international markets Demand for product / service in certain markets Extend products lifecycle somi
WHY INTERNATIONAL MARKETS? Saturation in domestic markets Decline in domestic markets Marketing is growing in certain international markets Demand for product / service in certain markets Extend products lifecycle somi
 KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL MARKETING • International Marketing is more complex – higher risk • Usually involves a greater number of stakeholders • International - Greater competition • International Marketing involves the STANDARDISATION V ADAPTATION dilemma somi
KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL MARKETING • International Marketing is more complex – higher risk • Usually involves a greater number of stakeholders • International - Greater competition • International Marketing involves the STANDARDISATION V ADAPTATION dilemma somi
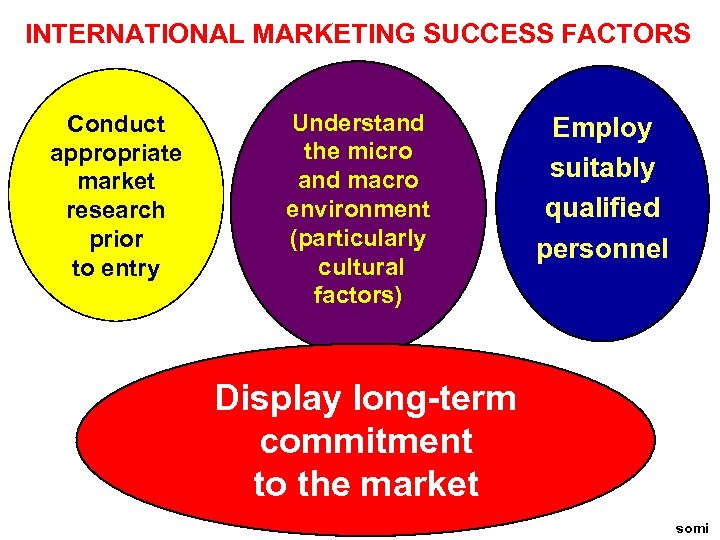 INTERNATIONAL MARKETING SUCCESS FACTORS Conduct appropriate market research prior to entry Understand the micro and macro environment (particularly cultural factors) Employ suitably qualified personnel Display long-term commitment to the market somi
INTERNATIONAL MARKETING SUCCESS FACTORS Conduct appropriate market research prior to entry Understand the micro and macro environment (particularly cultural factors) Employ suitably qualified personnel Display long-term commitment to the market somi
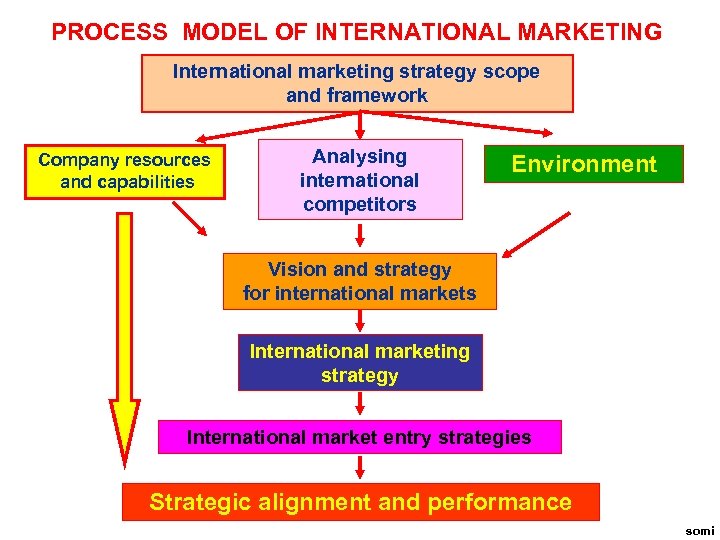 PROCESS MODEL OF INTERNATIONAL MARKETING International marketing strategy scope and framework Company resources and capabilities Analysing international competitors Environment Vision and strategy for international markets International marketing strategy International market entry strategies Strategic alignment and performance somi
PROCESS MODEL OF INTERNATIONAL MARKETING International marketing strategy scope and framework Company resources and capabilities Analysing international competitors Environment Vision and strategy for international markets International marketing strategy International market entry strategies Strategic alignment and performance somi
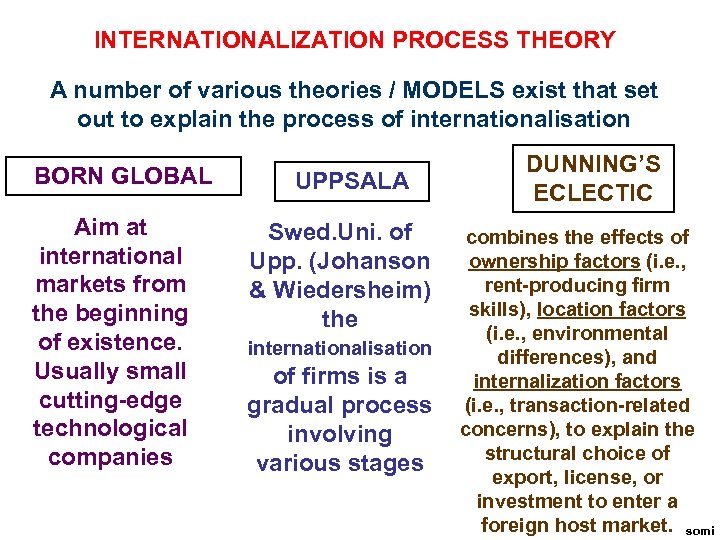 INTERNATIONALIZATION PROCESS THEORY A number of various theories / MODELS exist that set out to explain the process of internationalisation BORN GLOBAL Aim at international markets from the beginning of existence. Usually small cutting-edge technological companies UPPSALA DUNNING’S ECLECTIC Swed. Uni. of combines the effects of Upp. (Johanson ownership factors (i. e. , rent-producing firm & Wiedersheim) skills), location factors the (i. e. , environmental internationalisation differences), and of firms is a internalization factors gradual process (i. e. , transaction-related concerns), to explain the involving structural choice of various stages export, license, or investment to enter a foreign host market. somi
INTERNATIONALIZATION PROCESS THEORY A number of various theories / MODELS exist that set out to explain the process of internationalisation BORN GLOBAL Aim at international markets from the beginning of existence. Usually small cutting-edge technological companies UPPSALA DUNNING’S ECLECTIC Swed. Uni. of combines the effects of Upp. (Johanson ownership factors (i. e. , rent-producing firm & Wiedersheim) skills), location factors the (i. e. , environmental internationalisation differences), and of firms is a internalization factors gradual process (i. e. , transaction-related concerns), to explain the involving structural choice of various stages export, license, or investment to enter a foreign host market. somi
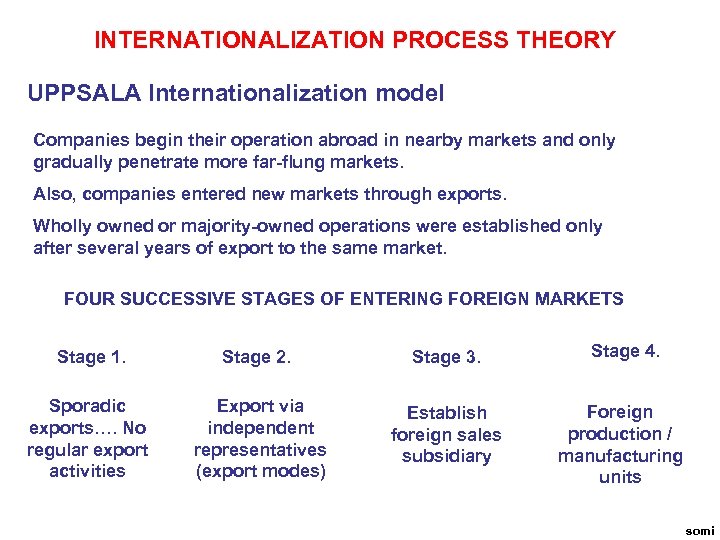 INTERNATIONALIZATION PROCESS THEORY UPPSALA Internationalization model Companies begin their operation abroad in nearby markets and only gradually penetrate more far-flung markets. Also, companies entered new markets through exports. Wholly owned or majority-owned operations were established only after several years of export to the same market. FOUR SUCCESSIVE STAGES OF ENTERING FOREIGN MARKETS Stage 1. Sporadic exports…. No regular export activities Stage 2. Export via independent representatives (export modes) Stage 3. Stage 4. Establish foreign sales subsidiary Foreign production / manufacturing units somi
INTERNATIONALIZATION PROCESS THEORY UPPSALA Internationalization model Companies begin their operation abroad in nearby markets and only gradually penetrate more far-flung markets. Also, companies entered new markets through exports. Wholly owned or majority-owned operations were established only after several years of export to the same market. FOUR SUCCESSIVE STAGES OF ENTERING FOREIGN MARKETS Stage 1. Sporadic exports…. No regular export activities Stage 2. Export via independent representatives (export modes) Stage 3. Stage 4. Establish foreign sales subsidiary Foreign production / manufacturing units somi
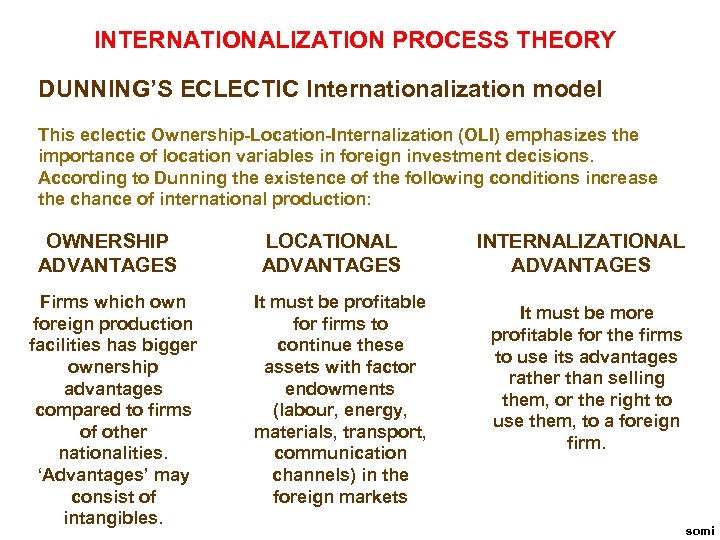 INTERNATIONALIZATION PROCESS THEORY DUNNING’S ECLECTIC Internationalization model This eclectic Ownership-Location-Internalization (OLI) emphasizes the importance of location variables in foreign investment decisions. According to Dunning the existence of the following conditions increase the chance of international production: OWNERSHIP ADVANTAGES Firms which own foreign production facilities has bigger ownership advantages compared to firms of other nationalities. ‘Advantages’ may consist of intangibles. LOCATIONAL ADVANTAGES It must be profitable for firms to continue these assets with factor endowments (labour, energy, materials, transport, communication channels) in the foreign markets INTERNALIZATIONAL ADVANTAGES It must be more profitable for the firms to use its advantages rather than selling them, or the right to use them, to a foreign firm. somi
INTERNATIONALIZATION PROCESS THEORY DUNNING’S ECLECTIC Internationalization model This eclectic Ownership-Location-Internalization (OLI) emphasizes the importance of location variables in foreign investment decisions. According to Dunning the existence of the following conditions increase the chance of international production: OWNERSHIP ADVANTAGES Firms which own foreign production facilities has bigger ownership advantages compared to firms of other nationalities. ‘Advantages’ may consist of intangibles. LOCATIONAL ADVANTAGES It must be profitable for firms to continue these assets with factor endowments (labour, energy, materials, transport, communication channels) in the foreign markets INTERNALIZATIONAL ADVANTAGES It must be more profitable for the firms to use its advantages rather than selling them, or the right to use them, to a foreign firm. somi
 INTERNATIONAL MARKETING CONCEPT? So what are the differences between domestic and international marketing? The concepts, the methods are the same the culture the enviroment are the differences. 19/29 somi
INTERNATIONAL MARKETING CONCEPT? So what are the differences between domestic and international marketing? The concepts, the methods are the same the culture the enviroment are the differences. 19/29 somi
 INTERNATIONAL MARKETING Why are we concerned with culture? The marketing significance of culture is that it affects buyer behaviour So…. What is culture ? ? “Ways of living, built up by a group of human beings” 20/29 A set of standards and beliefs shared by a group of people, which helps an individual decide what is ‘right’, what can be ok, how to feel, what to do and how to go about it…. . “The way we do things around here” The sum of conscious and unconscious values, ideas, attitudes and symbols that shape human behaviour and that are transmitted from one generation to the next…. “The collective programming of the mind that somi
INTERNATIONAL MARKETING Why are we concerned with culture? The marketing significance of culture is that it affects buyer behaviour So…. What is culture ? ? “Ways of living, built up by a group of human beings” 20/29 A set of standards and beliefs shared by a group of people, which helps an individual decide what is ‘right’, what can be ok, how to feel, what to do and how to go about it…. . “The way we do things around here” The sum of conscious and unconscious values, ideas, attitudes and symbols that shape human behaviour and that are transmitted from one generation to the next…. “The collective programming of the mind that somi
 DIFFICULTIES ARE STEPPING STONES TO SUCCESS. Somi
DIFFICULTIES ARE STEPPING STONES TO SUCCESS. Somi


