f7cce90edfd02af55db48d67bc329da8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65

Therapy

AP EXAM Treatment of Abnormal Behavior (5– 7%) This section of the course provides students with an understanding of empirically based treatments of psychological disorders. The topic emphasizes descriptions of treatment modalities based on various orientations in psychology. AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: Describe the central characteristics of psychotherapeutic intervention Describe major treatment orientations used in therapy (e. g. , behavioral, cognitive, humanistic) and how those orientations influence therapeutic planning. Compare and contrast different treatment formats (e. g. , individual, group). Summarize effectiveness of specific treatments used to address specific problems. Discuss how cultural and ethnic context influence choice and success of treatment (e. g. , factors that lead to premature termination of treatment). Describe prevention strategies that build resilience and promote competence. Identify major figures in psychological treatment (e. g. , Aaron Beck, Albert Ellis, Sigmund Freud, Mary Cover Jones, Carl Rogers, B. F. Skinner, Joseph Wolpe).

What are Therapists Professionals who know the art of establishing a helping relationship Know how to apply the knowledge of psychology to an individual struggling with problems and choices.

Therapy We often hear that someone was in therapy, but what is therapy? There are many stereotypes about therapy like the picture of a bearded therapist taking notes while a patient lies on a couch and spills his or her guts. This is a very Freudian image.

Therapy is a term used for any treatment process; in psychology and psychiatry, therapy refers to a variety of techniques used to deal with mental disorders or cope with problems of living. There are endless reasons why people go to see a therapist or counselor: ◦ ◦ making difficult decisions dealing with academic problems coping with the loss of a loved one dealing with an unhappy relationship.

History of Therapy Much like the history of psychology itself and psychological disorders, therapy has had its fair share of misguided theories. In medieval Europe, people often thought mental disorders were the work of the devil and other demons. The job therapists was to perform exorcisms.

Bedlam and its Origins One of the most well known asylums was that of Bethlehem Hospital in London. On the weekend, a person could pay a few pence to go sightseeing and watch the inmates who often put on a noisy and wild show. As a result, “Bedlam, ” the shortened term Londoners used for Bethlehem, became a word used to describe any noisy, chaotic place (Zimbardo et al. ) Video: http: //topdocumentaryfilms. com/bedlam-the -history-of-bethlem-hospital/

Medieval Asylums In the medieval asylums ◦ patients, at most only custodial care ◦ they were neglected ◦ put in cruel restraints such as cages and straightjackets. Some received other forms of torture like beatings and cold showers.

Modern Therapy There a variety of techniques and methods therapists and counselors use but all center on developing a strong, supportive relationship with the patient. Another similarity amongst all therapy techniques is their end goal of changing a person’s functioning in some way. Psychologists may use an eclectic approach which is like a buffet table; they select various techniques to help individuals
Components of Therapy In addition to developing a strong relationship between client/patient and counselor, therapeutic process generally involves some or all of the following processes: 1. Identifying the problem 2. Identifying the cause of the problem or the current conditions that maintain the problem 3. Deciding on and carrying out some form of treatment
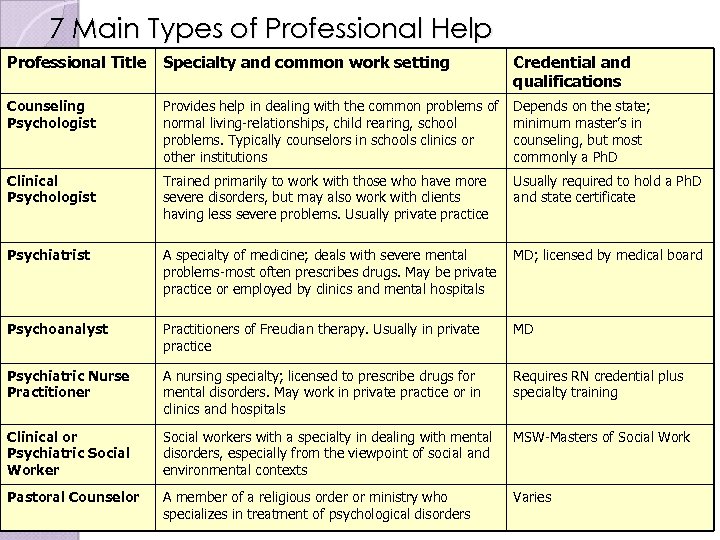
7 Main Types of Professional Help Professional Title Specialty and common work setting Credential and qualifications Counseling Psychologist Provides help in dealing with the common problems of normal living-relationships, child rearing, school problems. Typically counselors in schools clinics or other institutions Depends on the state; minimum master’s in counseling, but most commonly a Ph. D Clinical Psychologist Trained primarily to work with those who have more severe disorders, but may also work with clients having less severe problems. Usually private practice Usually required to hold a Ph. D and state certificate Psychiatrist A specialty of medicine; deals with severe mental problems-most often prescribes drugs. May be private practice or employed by clinics and mental hospitals MD; licensed by medical board Psychoanalyst Practitioners of Freudian therapy. Usually in private practice MD Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner A nursing specialty; licensed to prescribe drugs for mental disorders. May work in private practice or in clinics and hospitals Requires RN credential plus specialty training Clinical or Psychiatric Social Worker Social workers with a specialty in dealing with mental disorders, especially from the viewpoint of social and environmental contexts MSW-Masters of Social Work Pastoral Counselor A member of a religious order or ministry who specializes in treatment of psychological disorders Varies
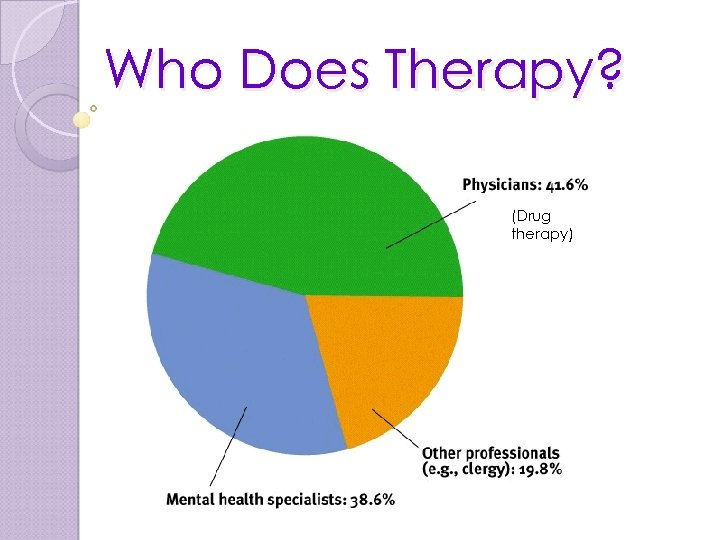
Who Does Therapy? (Drug therapy)

Therapy Gentler treatment brought about by: Philipe Pinel (FRANCE) Dorothea Dis (US, CANADA, SCOTLAND) Creation of mental hospitals Mid 1950 s creation of psychotropic drugs empty hospitals Psychotherapy an emotionally charged, confiding interaction between a trained therapist and someone who suffers from psychological difficulties. E. g. psychoanalysis, CBT, insight therapy etc. Biomedical Approach Medication or medical procedures to act on nervous system Eclectic Approach an approach to psychotherapy that, depending on the client’s problems, uses techniques from various forms of therapy
Freudian Psychoanalysis Freudian view; psychological problems arise from: ◦ Tension in the unconscious mind by forbidden impulses and threatening memories. Psychoanalysis ◦ Probes the unconscious attempt to bring these issues into the “light of day” or into consciousness. ◦ The major goal of psychoanalysis reveal and interpret the contents of the unconscious mind.

Therapy - Psychoanalysis – involving psychological techniques Interactions b/w trained therapist & patient First therapy available Aims Disorders fueled by childhood residue or repressed impulses/conflicts Patients work through buried feelings & take responsibility for growth

Therapy - Psychoanalysis Methods Historical reconstruction Uses past to unmask present Free Association Resistance Blocking from consciousness of anxiety-laden material Interpretation The analyst’s noting supposed dream meanings, resistances, and other significant behaviors in order to promote insight
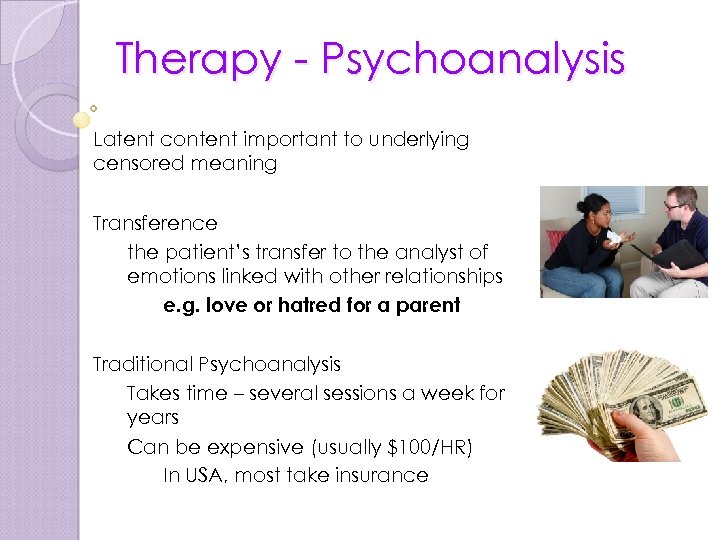
Therapy - Psychoanalysis Latent content important to underlying censored meaning Transference the patient’s transfer to the analyst of emotions linked with other relationships e. g. love or hatred for a parent Traditional Psychoanalysis Takes time – several sessions a week for years Can be expensive (usually $100/HR) In USA, most take insurance

Psychoanalysis According to this theory, people will recover when they are finally released from the repressive mental restraints established in the relationship with their parents during early childhood.
Neo-Freudian Psychodynamic Therapies These therapies were developed by psychologists why embraced some of Freud’s ideas, but disagreed with others. While they follow many of the same techniques, their emphasis is on the conscious, rather than the unconscious, mind. Basically they spend less time probing for hidden conflicts and repressed memories.

Therapy – Psychodynamic • Understand current symptoms by focusing on themes across important relationships • Help explore & gain perspective on defended-against thoughts/feelings • Face-to-face once a week for only a few months Interpersonal Therapy – • • Brief variation of psychodynamic Help gain insight into roots of difficulties Goal – become symptom free in the present not in overall personality change Focusing on current relationships/relationship skills

Insight Therapies Attempts to change people on the inside-changing the way they think and feel. ◦ think therapies ◦ distressed persons need to develop an understanding of the disordered thoughts, emotions and motives that underline their mental difficulties.

Humanistic Therapies Generally motivated by healthy needs for growth and psychological well being. Problems only occur when conditions interfere with normal development and produce low self esteem. Help clients confront their problems by recognizing their own freedom, enhancing their self-esteem and realizing their fullest potential.

Humanistic Therapy Aims to boost self-fulfillment by growing selfawareness & self-acceptance Referred to as Insight Therapies Aim to improve psychological functioning awareness of underlying motives & defenses Different than psychoanalytic • Present & future focus • Consciousness • Immediate responsibility for own feelings • Promoting growth instead of cure • Clients rather than patients

Humanistic Therapy Client-Centered Therapy • Developed by Carl Rogers • Uses techniques such as active listening within a genuine, accepting, empathic environment to facilitate clients’ growth Nondirective therapy • Therapist listens • No judgment • Refrain from directing towards insights Carl Rogers with his client Gloria

Humanistic Therapy Active Listening • Empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies Unconditional positive regard • Accept worst traits & feel valued & whole Psychological problems decrease as selfawareness grows

Behavior Therapies Based on the assumption that undesirable behaviors have been learned, and therefore, can be unlearned. Behavior therapist focus on the problem behaviors rather than inner thoughts, motives or emotions. Their goal is to determine how these behaviors were learned and see if they can eliminate them.

Behavior Therapy • Therapy that applies learning principles to the elimination of unwanted behaviors • Derived from Pavlov’s ideas • Learned behaviors/emotions cause psychological issues Counterconditioning • Procedure that conditions new responses to stimuli that trigger unwanted behaviors • Based on classical conditioning • Includes systematic desensitization and aversive conditioning

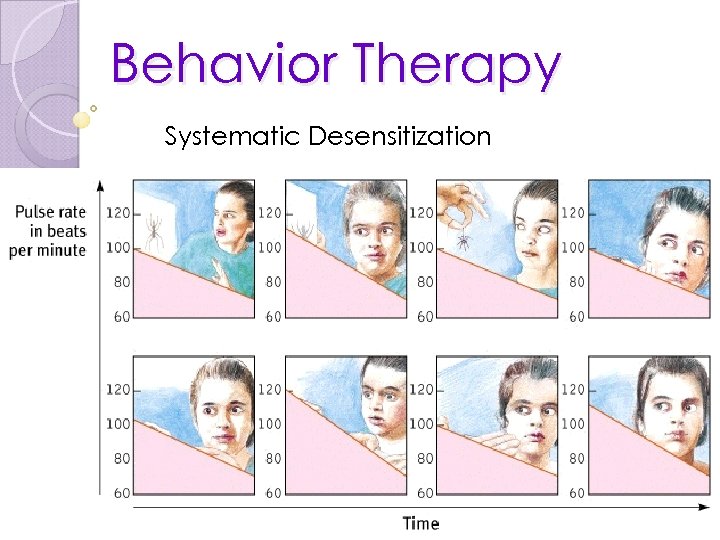
Behavior – Exposure Therapies • Exposure to stimuli that is normally avoided Progressive Relaxation • Relax 1 muscle group after another until one reaches complete relaxation Systematic Desensitization • Type of counterconditioning • Associates a pleasant, relaxed state with gradually increasing anxietytriggering stimuli • Commonly used to treat phobias

Steps of Systematic Desensitization For a fear of public speaking: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Seeing a picture of a person giving a speech Watching another person give a speech Preparing a speech to give Having to introduce oneself to a large group Waiting to be called upon to speak at a meeting. 6. Being introduced as a speaker to a group 7. Walking to the podium to make a speech 8. Making a speech to a large group
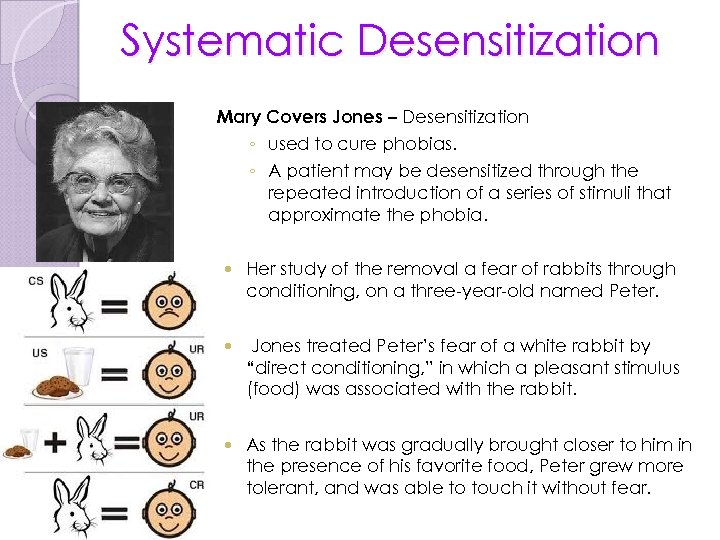
Systematic Desensitization Mary Covers Jones – Desensitization ◦ used to cure phobias. ◦ A patient may be desensitized through the repeated introduction of a series of stimuli that approximate the phobia. Her study of the removal a fear of rabbits through conditioning, on a three-year-old named Peter. Jones treated Peter’s fear of a white rabbit by “direct conditioning, ” in which a pleasant stimulus (food) was associated with the rabbit. As the rabbit was gradually brought closer to him in the presence of his favorite food, Peter grew more tolerant, and was able to touch it without fear.

Systematic Desensitization John Wolpe – Hierarchical of Anxiety • Cannot be both relaxed anxious at the same time. • Client and therapist create a hierarchy of anxieties • (i. e. list of all the things that produce anxiety in all its different forms) starting with what produces the lowest level of anxiety to what produces the most anxiety. • Client needs to be fully relaxed while imaging the anxiety producing stimulus. • Depending on what their reaction is, whether they feel no anxiety or a great amount of anxiety, the stimulus will then be changed to a stronger or weaker one. NOTE: Systematic desensitization, though successful, has flaws as well. • The patient may give misleading hierarchies, have trouble relaxing, or not be able to adequately imagine the scenarios. Despite this possible flaw, it seems to be most successful
Behavior Therapy Systematic Desensitization

Exposure Therapies Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy Progressive exposure to simulations of fears Aversive Conditioning type of counterconditioning associates an unpleasant state with an unwanted behavior nausea ---> alcohol

Virtual Technology Exposure Therapy

Aversion Therapy Aversion therapy takes on the psychological problems with a conditioning procedure designed to make tempting stimulus less provocative by pairing them with an unpleasant (aversive) stimuli. In time, the negative reaction (UCR) associated with the averse stimuli come to be associated with the conditioned stimuli. This is usually a last resort type of therapy, though it has been shown to be successful. Clockwork Orange ◦ https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Jv 1 Bmne 20 l 4
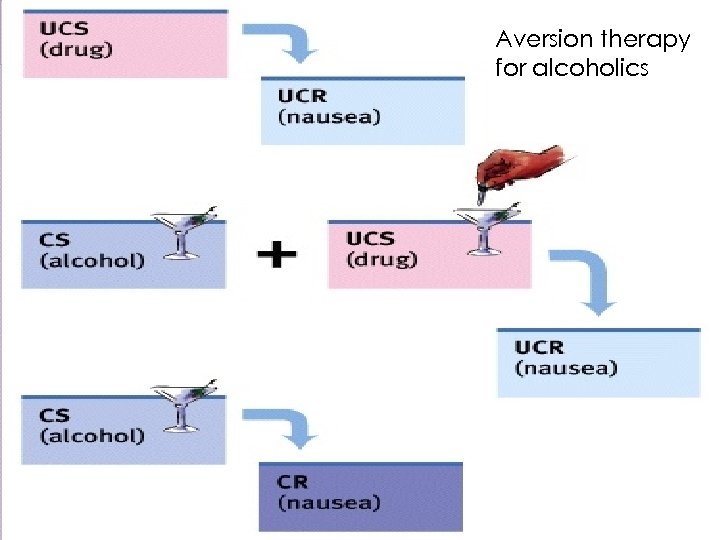
Aversion therapy for alcoholics

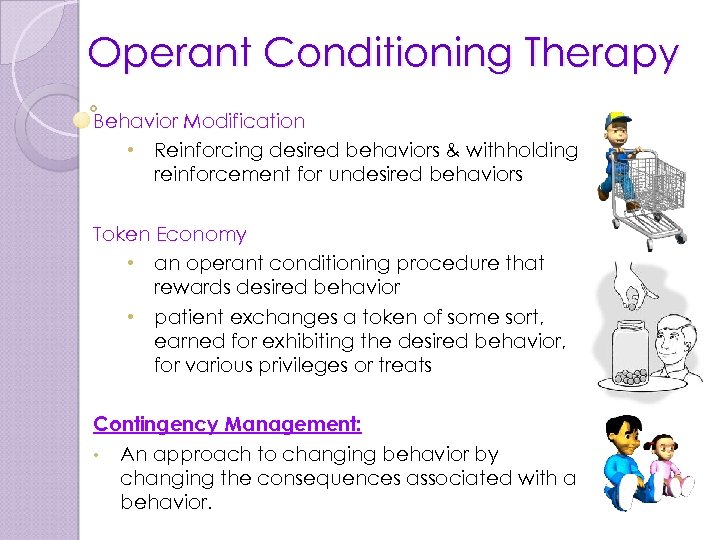
Operant Conditioning Therapy Behavior Modification • Reinforcing desired behaviors & withholding reinforcement for undesired behaviors Token Economy • an operant conditioning procedure that rewards desired behavior • patient exchanges a token of some sort, earned for exhibiting the desired behavior, for various privileges or treats Contingency Management: • An approach to changing behavior by changing the consequences associated with a behavior.

Cognitive Therapy • Teaches people new, more adaptive ways of thinking and acting • Based on the assumption that thoughts intervene between events and our emotional reactions
Cognitive Therapy The Cognitive Revolution
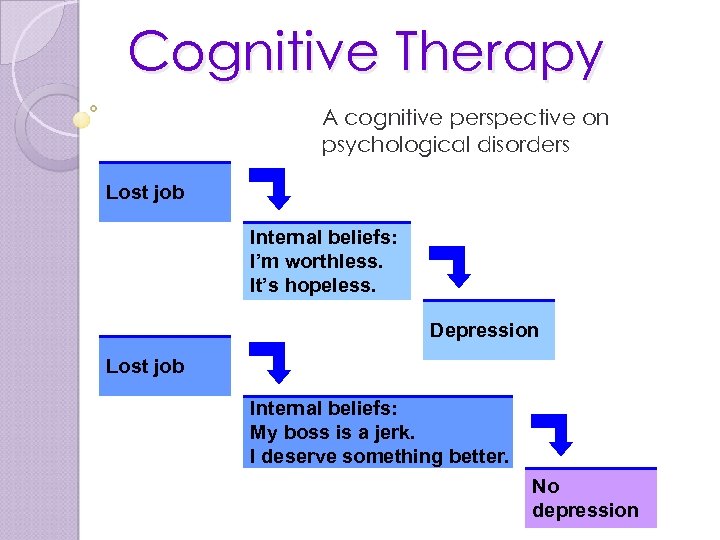
Cognitive Therapy A cognitive perspective on psychological disorders Lost job Internal beliefs: I’m worthless. It’s hopeless. Depression Lost job Internal beliefs: My boss is a jerk. I deserve something better. No depression
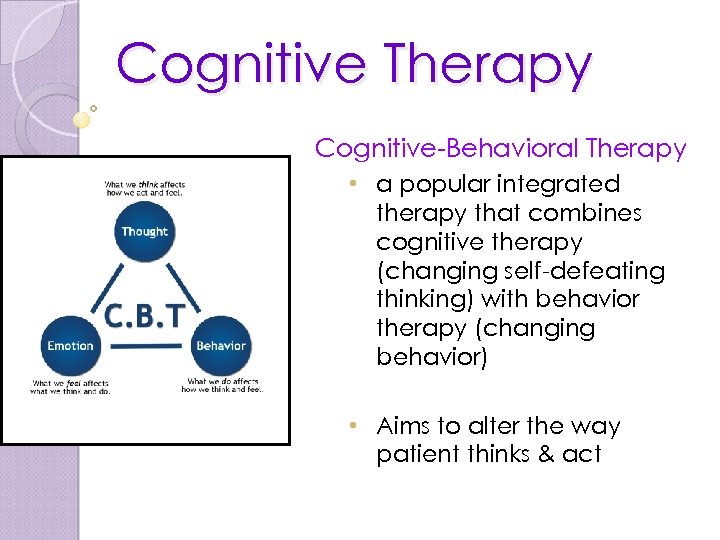
Cognitive Therapy Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy • a popular integrated therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior) • Aims to alter the way patient thinks & act

Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy This approach assumes that an irrational self -statement often underlies maladaptive behavior.

Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy In this form of treatment, therapist and client work together to: modify irrational self-talk, set attainable behavioral goals develop realistic strategies for attaining them. In this way, people change the way they approach problems and gradually develop new skills and a sense of self-efficacy.
Group/Family Therapies Group Therapy • Benefit = social context allows people to discover others have similar problems & give feedback to each other Family Therapy • treats the family as a system • views an individual’s unwanted behaviors as influenced by or directed at other family members • attempts to guide family members toward positive relationships and improved communication

Group/Family Therapies Most focus on hard-to-discuss or stigmatized illness AIDS patients high amongst group therapy The worse the illness, the more people actually attend groups
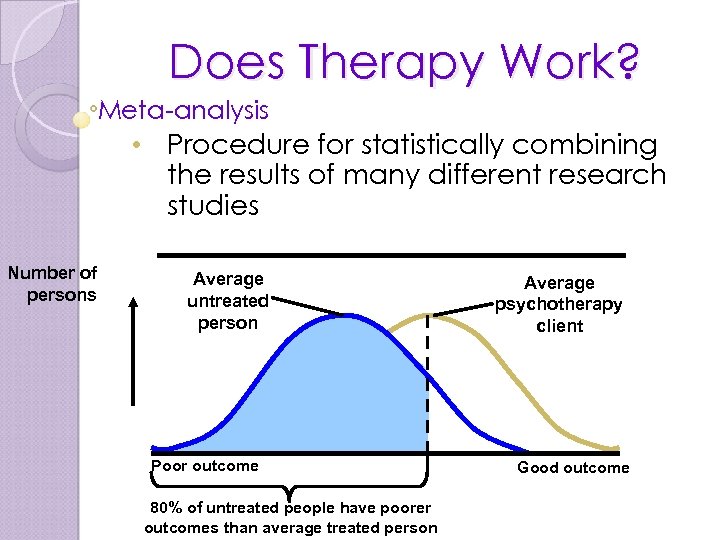
Does Therapy Work? Meta-analysis • Procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies Number of persons Average untreated person Poor outcome 80% of untreated people have poorer outcomes than average treated person Average psychotherapy client Good outcome

Does Therapy Actually Work? In 1952, Hans Eysenck shook the psychology world by releasing a study that suggested 2/3 of all people with non- psychotic problems recovered within two years if the onset of the problem, whether they received therapy or not. Essentially he was arguing that therapy was worthless, and is no better than having any treatment at all.

Response to Eysenck As you can imagine, this set off a fire storm of studies on this subject. Overall (375 studies) research supports two major conclusions: 1. Therapy is more effective than non-therapy. 2. Eysenck overestimated the improvement rate in no-therapy control groups.
Biomedical Approach Changing the brain’s chemistry with drugs, its circuitry with surgery or its patterns of activity with pulses of electricity or magnetic fields.
Biomedical Therapies Psychopharmacology • Study of the effects of drugs on mind and behavior Lithium • Chemical that provides an effective drug therapy for the mood swings of bipolar (manicdepressive) disorders

Drug Therapy/Psychopharmacology The first psychological drugs were administered in 1953 with the antipsychotic drugs. In 1955, over ½ a million Americans were living in mental institutions, each staying an average of a few years. Then, with the introduction of tranquilizers, the number declined. By 1965, the number of patients was down to ¼ million, with most patients staying for only a few months.

Antipsychotic Drugs Antipsychotic drugs are used to treat the symptoms of psychosis: delusions, hallucinations, social withdrawal and agitation. Most work by reducing the activity of the neurotransmitter dopamine. These drugs (Thorazine) often have powerful side effects

+/- of Antipsychotic Drugs While these drugs reduce the overall brain activity, they do not simple put the patient in a trance. Instead they simply reduce the “positive” symptoms of psychosis. Unfortunately, long-term use can cause problems like tardive dyskinesia, which produces an uncontrollable disturbance of motor control, especially in the facial muscles.
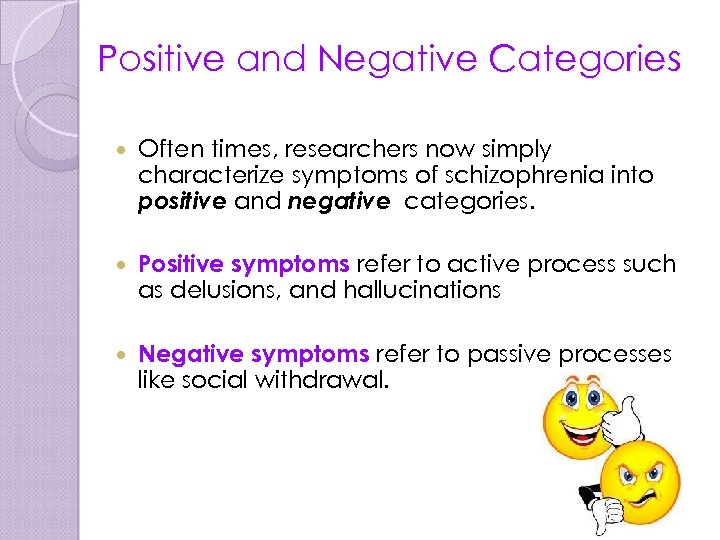
Positive and Negative Categories Often times, researchers now simply characterize symptoms of schizophrenia into positive and negative categories. Positive symptoms refer to active process such as delusions, and hallucinations Negative symptoms refer to passive processes like social withdrawal.

Antidepressant Drugs There are three major classes of antidepressant drugs, and all three work by “turning up the volume” on messages transmitted over certain brain pathways, especially those using norepinephrine and serotonin. The major downside of these drugs is that it often takes a few weeks for them to have an effect.

Antianxiety Drugs Antianxiety drugs most commonly fall into two categories: barbiturates and benzodiazepines. Barbiturates act as a central nervous system depressant, so they have a relaxing effect. Benzodiazepines work by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters.

Stimulants is a broad category that includes everything from caffeine to nicotine to amphetamines to cocaine-they are any drugs that produce excitement or hyperactivity. These drugs are prescribed for a variety of disorders including narcolepsy and ADHD.

Truth About Drugs Cannot cure any mental illness Can alter the brain to suppress some symptoms Can have negative long term effects Can be habit forming Often over prescribed
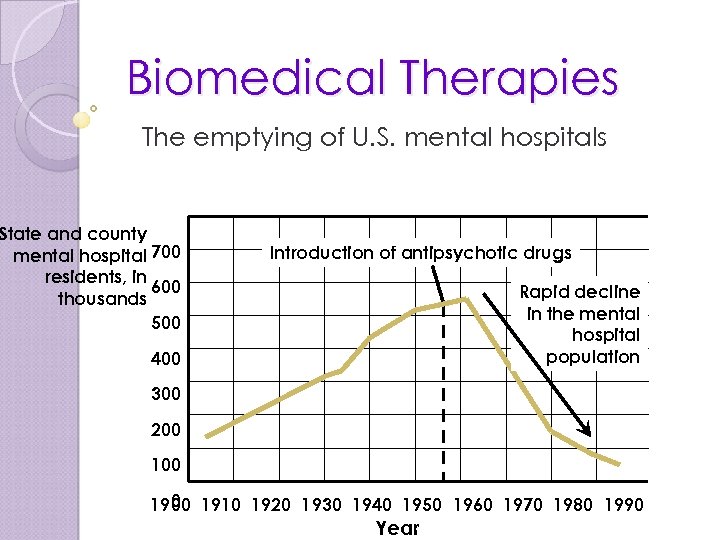
Biomedical Therapies The emptying of U. S. mental hospitals State and county mental hospital 700 residents, in 600 thousands 500 Introduction of antipsychotic drugs Rapid decline in the mental hospital population 400 300 200 100 0 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 Year
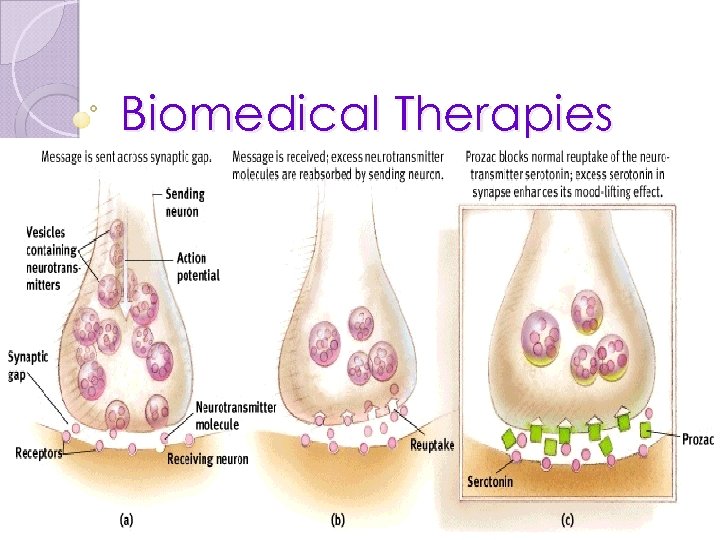
Biomedical Therapies
Biomedical Therapies Psychosurgery • Surgery that removes or destroys brain tissue in an effort to change behavior lobotomy • Egas Moniz developed the lobotomy in the 1930 s. • Now-rare psychosurgical procedure once used to calm uncontrollably emotional or violent patients Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) • Therapy for severely depressed patients in which a brief electric current is sent through the brain of an anesthetized patient
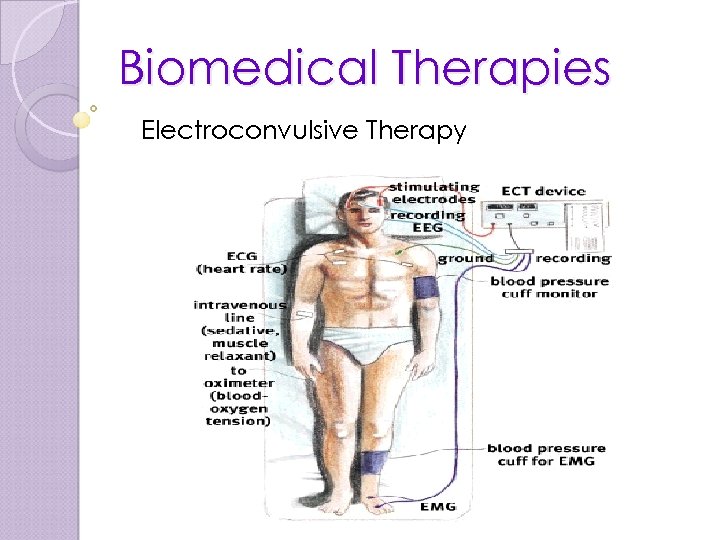
Biomedical Therapies Electroconvulsive Therapy

Disorders and Therapies in Cultural Settings The way a disorder is treated relies on the way it is viewed. The way it is viewed is heavily dependent on the culture is being treated in. Individualistic: • Western views generally regard psychological disorders to be a result of: • disease process • abnormal genetics • disordered thinking • unhealthy environments or stressors. Collectivist : • Cultures often think of mental disorders as a disconnect between the person and the group. • In such cultures, treating mentally disturbed people by removing them from society is unthinkable.
f7cce90edfd02af55db48d67bc329da8.ppt