Lecture 1.1 Theory.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 THEORY OF PHONETICS
THEORY OF PHONETICS
 Lecture 1. Phonetics as a branch of Linguistics
Lecture 1. Phonetics as a branch of Linguistics
 Plan: 1. 2. 3. 4. The role of sound in communication. A definition of Phonetics & its subject matter. Types of Phonetics and methods of investigation. The place of Phonetics among other branches of Linguistics. 5. Practical and theoretical significance of Phonetics.
Plan: 1. 2. 3. 4. The role of sound in communication. A definition of Phonetics & its subject matter. Types of Phonetics and methods of investigation. The place of Phonetics among other branches of Linguistics. 5. Practical and theoretical significance of Phonetics.
 1. The role of sound in communication.
1. The role of sound in communication.
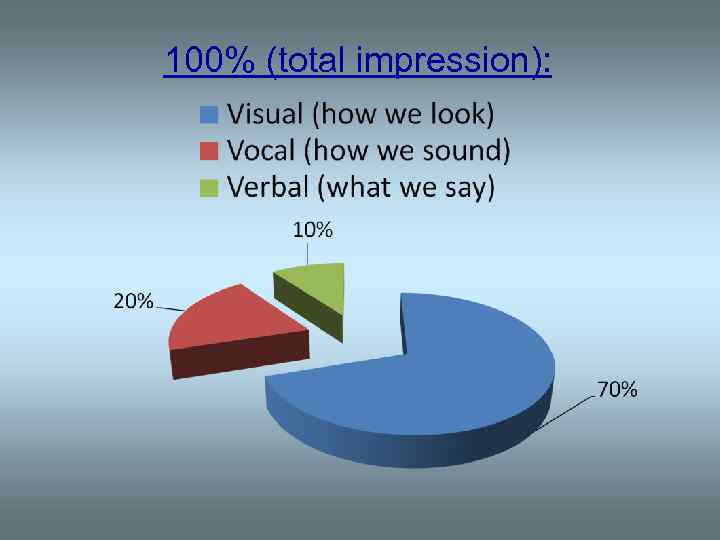 100% (total impression):
100% (total impression):
 How do sounds contribute to the process of communication? • Human communication is based on exchanging messages. • To convey a message a person can use a variety of visual or audible means.
How do sounds contribute to the process of communication? • Human communication is based on exchanging messages. • To convey a message a person can use a variety of visual or audible means.
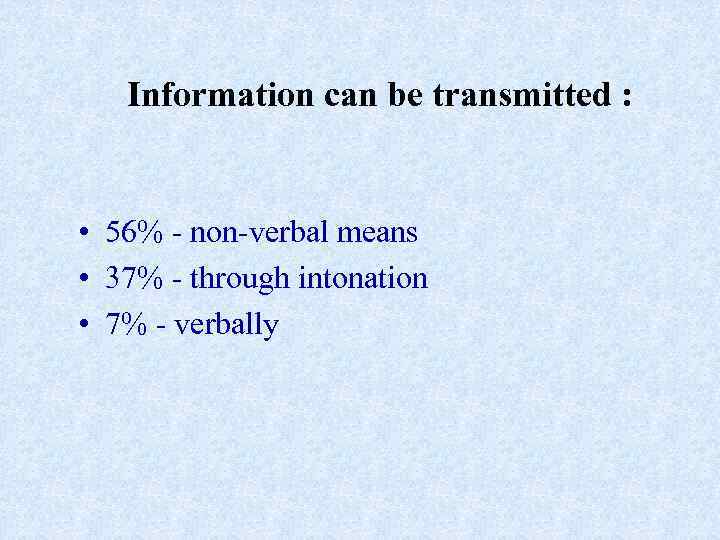 Information can be transmitted : • 56% - non-verbal means • 37% - through intonation • 7% - verbally
Information can be transmitted : • 56% - non-verbal means • 37% - through intonation • 7% - verbally
 Whilst the medium may vary, the message does not.
Whilst the medium may vary, the message does not.
 Phonetics studies the human noises by which “the message” is actualized or given audible shape: • the nature of those noises, • their combinations, • their function in relation to the message.
Phonetics studies the human noises by which “the message” is actualized or given audible shape: • the nature of those noises, • their combinations, • their function in relation to the message.
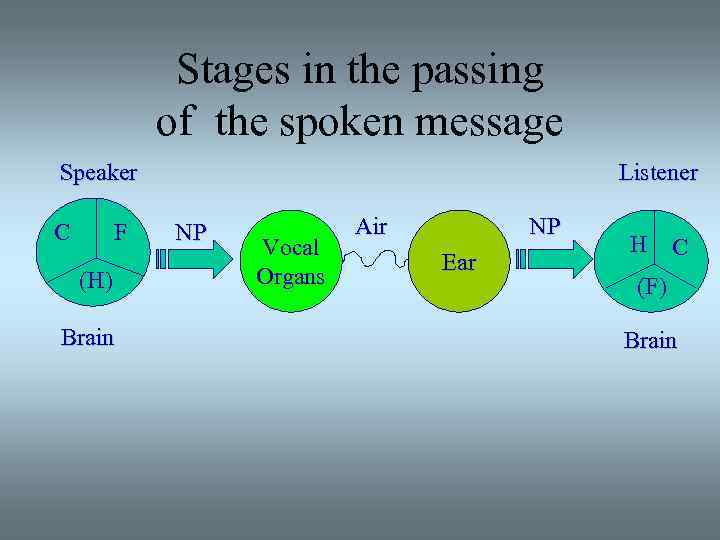 Stages in the passing of the spoken message Speaker C F (H) Brain Listener NP Vocal Organs Air NP Ear H C (F) Brain
Stages in the passing of the spoken message Speaker C F (H) Brain Listener NP Vocal Organs Air NP Ear H C (F) Brain
 Stages in the passing of a spoken message & the brain functions • Creative function • Forwarding function • Hearing & creative function
Stages in the passing of a spoken message & the brain functions • Creative function • Forwarding function • Hearing & creative function
 Creative function This is the central function and it is through it that the message is conceived and formed. Stored in the brain is a profound knowledge of the way in which the language operates. Every individual's store is to a greater or lesser extent different from everyone else's. But if we are to communicate efficiently there must be a sufficient stock of common information at our disposal.
Creative function This is the central function and it is through it that the message is conceived and formed. Stored in the brain is a profound knowledge of the way in which the language operates. Every individual's store is to a greater or lesser extent different from everyone else's. But if we are to communicate efficiently there must be a sufficient stock of common information at our disposal.
 Forwarding function The part of the brain which is concerned with controlling muscular movements now sends out patterned instructions in the form of nervous impulses along the nervous pathways connecting the brain to the muscles of the organs responsible for speech sounds, the lungs, larynx, tongue, etc. These instructions call upon the muscles concerned to perform various delicate combinations and sequences of movement which will result in the 'right' sounds being emitted in the 'right' order.
Forwarding function The part of the brain which is concerned with controlling muscular movements now sends out patterned instructions in the form of nervous impulses along the nervous pathways connecting the brain to the muscles of the organs responsible for speech sounds, the lungs, larynx, tongue, etc. These instructions call upon the muscles concerned to perform various delicate combinations and sequences of movement which will result in the 'right' sounds being emitted in the 'right' order.
 Hearing Function The impulses coming from the ear are accepted as sound sequences of constantly changing quality and characteristic length, pitch, loudness. The listener hears the message but does not yet understand it. To understand the message the listener must interpret the sounds he hears in accordance with the stored knowledge in his brain.
Hearing Function The impulses coming from the ear are accepted as sound sequences of constantly changing quality and characteristic length, pitch, loudness. The listener hears the message but does not yet understand it. To understand the message the listener must interpret the sounds he hears in accordance with the stored knowledge in his brain.
 2. A definition of Phonetics & its subject matter. Phonetics is that branch of linguistics which studies the sounds of language.
2. A definition of Phonetics & its subject matter. Phonetics is that branch of linguistics which studies the sounds of language.
 Phonetics is an independent branch of linguistics which studies and gives a systematic description of the sound structure of languages.
Phonetics is an independent branch of linguistics which studies and gives a systematic description of the sound structure of languages.
 The sound structure of languages • Speech sounds (their production, perception and acoustic characteristics) • Rules governing the combination of speech sounds into syllables and larger phonological constructions • The phenomena of stress, rhythm and intonation • Correlation between spoken and written language
The sound structure of languages • Speech sounds (their production, perception and acoustic characteristics) • Rules governing the combination of speech sounds into syllables and larger phonological constructions • The phenomena of stress, rhythm and intonation • Correlation between spoken and written language
 3. Types of Phonetics and methods of investigation. 1. 2. 3. 4. Articulatory (physiological) Acoustic Auditory (perceptive) Phonological or functional (linguistic)
3. Types of Phonetics and methods of investigation. 1. 2. 3. 4. Articulatory (physiological) Acoustic Auditory (perceptive) Phonological or functional (linguistic)
 Other types of phonetics: • General Phonetics (studies speech sounds of the languages of the world) • Special Phonetics (deals with the sound system of a given language)
Other types of phonetics: • General Phonetics (studies speech sounds of the languages of the world) • Special Phonetics (deals with the sound system of a given language)
 Special Phonetics • Descriptive • Historical/diachronic • Comparative • Dialectology • Normative/orthoepic • Clinical/speech • Voice training • Telephonic • Speech recognition
Special Phonetics • Descriptive • Historical/diachronic • Comparative • Dialectology • Normative/orthoepic • Clinical/speech • Voice training • Telephonic • Speech recognition
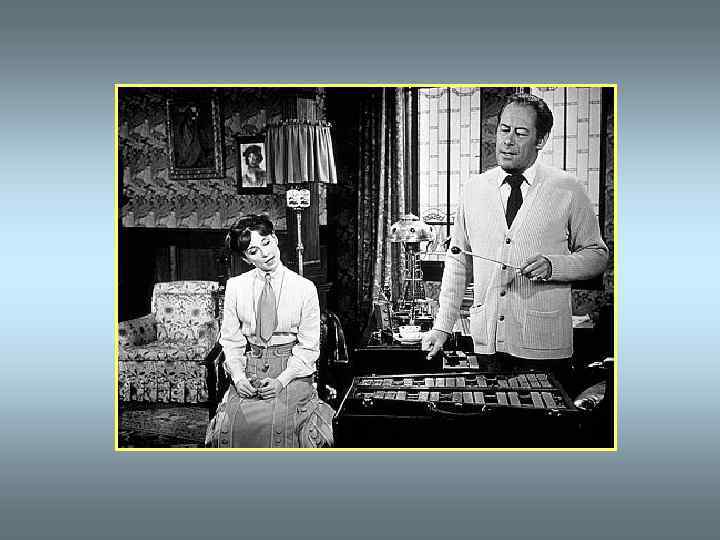
 Which type of Phonetics did Professor Higgins practise?
Which type of Phonetics did Professor Higgins practise?
 “My Fair Lady” Audrey Hepburn and Rex Harrison Film Date, 1964 Warner Bros.
“My Fair Lady” Audrey Hepburn and Rex Harrison Film Date, 1964 Warner Bros.

 Some dates from the history of phonetic development 1829 laryngoscope was invented 1852 first observations of the vocal cords were made 1877 gramophone was invented 1866 International Phonetic Association (IPA) was founded. IPA started publications of a special phonetic magazine It stated phonetic symbols for sounds of many existing languages.
Some dates from the history of phonetic development 1829 laryngoscope was invented 1852 first observations of the vocal cords were made 1877 gramophone was invented 1866 International Phonetic Association (IPA) was founded. IPA started publications of a special phonetic magazine It stated phonetic symbols for sounds of many existing languages.
 Was there a real Professor Higgins?
Was there a real Professor Higgins?
 • Rex Harrison's character, Henry Higgins, was based on Daniel Jones, a leading British phonetician of the early 20 th century, author of the first Pronunciation Dictionary.
• Rex Harrison's character, Henry Higgins, was based on Daniel Jones, a leading British phonetician of the early 20 th century, author of the first Pronunciation Dictionary.
 Which linguist was invited as a phonetics consultant for the film “My Fair Lady”?
Which linguist was invited as a phonetics consultant for the film “My Fair Lady”?
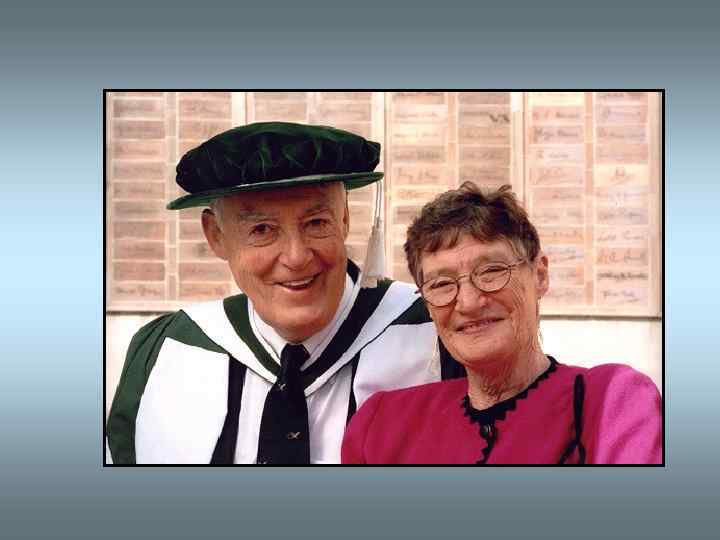
 Peter Ladefoged Professor of Linguistics, 1925 – 2006 • advised on equipping Henry Higgins's phonetics lab • made all the phonetic transcriptions seen onscreen • it is his voice heard producing the vowel sounds
Peter Ladefoged Professor of Linguistics, 1925 – 2006 • advised on equipping Henry Higgins's phonetics lab • made all the phonetic transcriptions seen onscreen • it is his voice heard producing the vowel sounds

 Major publications • A Course in Phonetics, Peter Ladefoged • Vowels and Consonants, Peter Ladefoged
Major publications • A Course in Phonetics, Peter Ladefoged • Vowels and Consonants, Peter Ladefoged
 4. The place of Phonetics among other branches of Linguistics. • Non- linguistic • Linguistic Acoustics Physiology Psychology Logic Grammar Lexicology Stylistics
4. The place of Phonetics among other branches of Linguistics. • Non- linguistic • Linguistic Acoustics Physiology Psychology Logic Grammar Lexicology Stylistics
 Links of Phonetics with Grammar System of rules of reading Sound interchange Intonation component
Links of Phonetics with Grammar System of rules of reading Sound interchange Intonation component
 Links of Phonetics with Lexicology • Stress • Homographs • Homonymous words and word groups
Links of Phonetics with Lexicology • Stress • Homographs • Homonymous words and word groups
 Links of Phonetics with Stylistics • Through intonation • Graphical expressive means • Repetition of words, phrases and sounds • Alliteration • Onomatopoeia
Links of Phonetics with Stylistics • Through intonation • Graphical expressive means • Repetition of words, phrases and sounds • Alliteration • Onomatopoeia
 5. Practical and theoretical significance of phonetics.
5. Practical and theoretical significance of phonetics.
 Vocal component • • Stress Pace Intonation Volume Pauses Voice Techniques Rhetorical devices
Vocal component • • Stress Pace Intonation Volume Pauses Voice Techniques Rhetorical devices
 The longest recorded pause - England would have her neck wrung like a chicken… - Some chicken. . . Some neck. [Pause. ] Winston Churchill’s address to the Canadian Parliament in 1941
The longest recorded pause - England would have her neck wrung like a chicken… - Some chicken. . . Some neck. [Pause. ] Winston Churchill’s address to the Canadian Parliament in 1941
 Plan: 1. 2. 3. 4. The role of sound in communication. A definition of Phonetics & its subject matter. Types of Phonetics and methods of investigation. The place of Phonetics among other branches of Linguistics. 5. Practical and theoretical significance of Phonetics.
Plan: 1. 2. 3. 4. The role of sound in communication. A definition of Phonetics & its subject matter. Types of Phonetics and methods of investigation. The place of Phonetics among other branches of Linguistics. 5. Practical and theoretical significance of Phonetics.
 Seminar 1 Question List 1. What role does sound play in communication? 2. How does a single act of communication happen? 3. What is the subject-matter of phonetics? 4. How is Phonetics connected with other sciences? 5. What are the branches of Phonetics? 6. What is the practical and theoretical significance of Phonetics?
Seminar 1 Question List 1. What role does sound play in communication? 2. How does a single act of communication happen? 3. What is the subject-matter of phonetics? 4. How is Phonetics connected with other sciences? 5. What are the branches of Phonetics? 6. What is the practical and theoretical significance of Phonetics?
 Recommended Literature • A Theoretical Course of English Phonetics by S. F. Leontyeva • Encyclopaedia of the English Language by D. Crystal
Recommended Literature • A Theoretical Course of English Phonetics by S. F. Leontyeva • Encyclopaedia of the English Language by D. Crystal


