ToC-zv.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

Theory of Linguistic Communication Якуба Валентина Володимирівна – кафедра англійської філології, yakubaval@i. ua ауд. 309

The course’s structure: Basic notions of the Theory of Communication Structure of Communication, Participants of Communication Discourse analysis and Communication Speech Acts and Communicative Strategies, Maxims of communication Deictics and ambiguity Linguo-pragmatics and Semiotics Context of Communication, non-verbal communication

Textbook and sources Селіванова О. О. Основи теорії мовної комунікації. − Черкаси: Чабаненко Ю. А. , 2011. − 350 с. Семенюк О. А. , Паращук В. Ю. Основи теорії мовної комунікації. – K. , 2010. - 240 с. Яшенкова О. В. Основи теорії мовної комунікації. – K. , Академія, 2011.

Speech and Communication W. von Humboldt : language in action, individual/social components of speech F. de Saussure: language (as a system) Speech (as implementation of it in practice) Rhetorics – the art of influencing through the instruments of speech 3 approaches to speech: Process (using a language), Result (texts, recordings), Art (oratory skills)

Speech, Language, Communication System of signs (paradigmatic relations) – usage of signs (syntagmatic relations) – selection and purpose; Potential ability to use language – situational usage – appropriateness; Stable rules – changeable usage – quality of the changes; General language rules – individual deviations – social convention National language – individual styles (jargons, etc) – choice of social context

Definitions of Communications 7 basic approaches to the term: Establishing norms and exercising forms of control in society; Creating a community of people; A form of human interaction; A kind of influence on people; A way of understanding and perception of the reality; An exchange of meanings (ideas); Transmission of information.

Basics of Communication is contextually determined interaction of communicants consisting of intellectually determined and linguistically implemented acts which are descrete in time and space. Components of communication: Participants (addresser - addressee); Context (physical, social, linguistic); Message (idea, information); Contact (means and ways).

Types of Communication Differentiation according to: Historical aspect: 3 periods – Pre-industrial, printing, mass-media Means and process: Oral-written, Live-virtual, Face-to-face - distance Participants: Intra-communication, dialogue, polylogue, corporate, public, mass
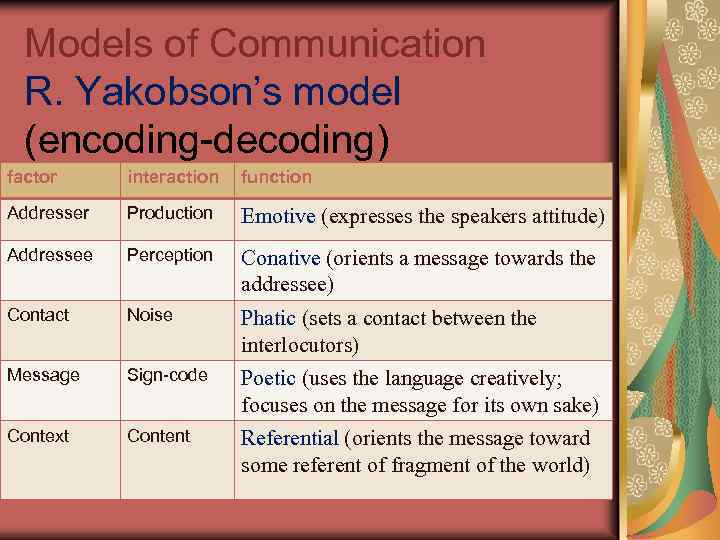
Models of Communication R. Yakobson’s model (encoding-decoding) factor interaction function Addresser Production Emotive (expresses the speakers attitude) Addressee Perception Conative (orients a message towards the addressee) Contact Noise Phatic (sets a contact between the interlocutors) Message Sign-code Poetic (uses the language creatively; focuses on the message for its own sake) Context Content Referential (orients the message toward some referent of fragment of the world)
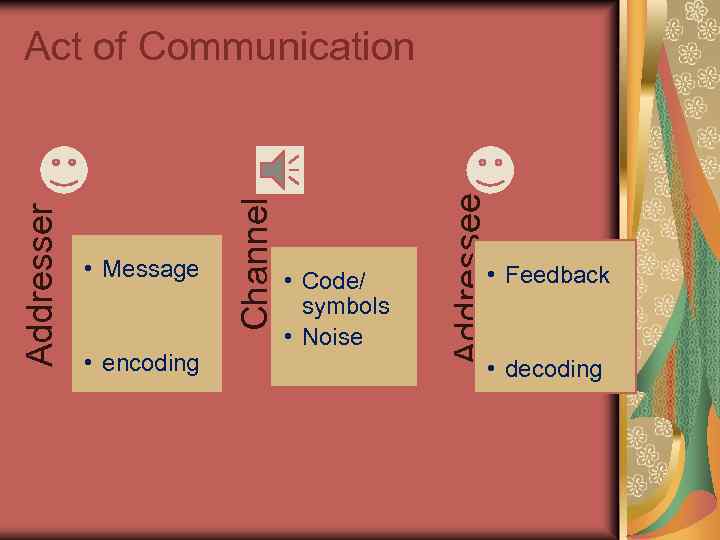
• encoding • Code/ symbols • Noise Addressee • Message Channel Addresser Act of Communication • Feedback • decoding

See you next week!
ToC-zv.ppt