Theory of Linguistic Communication Якуба Валентина Володимирівна –


Theory of Linguistic Communication Якуба Валентина Володимирівна – кафедра англійської філології, [email protected] ауд. 309

The course’s structure: Basic notions of the Theory of Communication Structure of Communication, Participants of Communication Discourse analysis and Communication Speech Acts and Communicative Strategies, Maxims of communication Deictics and ambiguity Linguo-pragmatics and Semiotics Context of Communication, non-verbal communication

Textbook and sources Селіванова О.О. Основи теорії мовної комунікації. − Черкаси: Чабаненко Ю.А., 2011. − 350 с. Семенюк О. А. , Паращук В. Ю. Основи теорії мовної комунікації. – K., 2010. - 240 с. Яшенкова О. В. Основи теорії мовної комунікації. – K., Академія, 2011.

Speech and Communication W. von Humboldt : language in action, individual/social components of speech F. de Saussure: language (as a system) Speech (as implementation of it in practice) Rhetorics – the art of influencing through the instruments of speech 3 approaches to speech: Process (using a language), Result (texts, recordings), Art (oratory skills)

Speech, Language, Communication System of signs (paradigmatic relations) – usage of signs (syntagmatic relations) – selection and purpose; Potential ability to use language – situational usage – appropriateness; Stable rules – changeable usage – quality of the changes; General language rules – individual deviations – social convention National language – individual styles (jargons, etc) – choice of social context

Definitions of Communications 7 basic approaches to the term: Establishing norms and exercising forms of control in society; Creating a community of people; A form of human interaction; A kind of influence on people; A way of understanding and perception of the reality; An exchange of meanings (ideas); Transmission of information.

Basics of Communication Communication is contextually determined interaction of communicants consisting of intellectually determined and linguistically implemented acts which are descrete in time and space. Components of communication: Participants (addresser - addressee); Context (physical, social, linguistic); Message (idea, information); Contact (means and ways).

Types of Communication Differentiation according to: Historical aspect: 3 periods – Pre-industrial, printing, mass-media Means and process: Oral-written, Live-virtual, Face-to-face - distance Participants: Intra-communication, dialogue, polylogue, corporate, public, mass

Models of Communication R. Yakobson’s model (encoding-decoding)
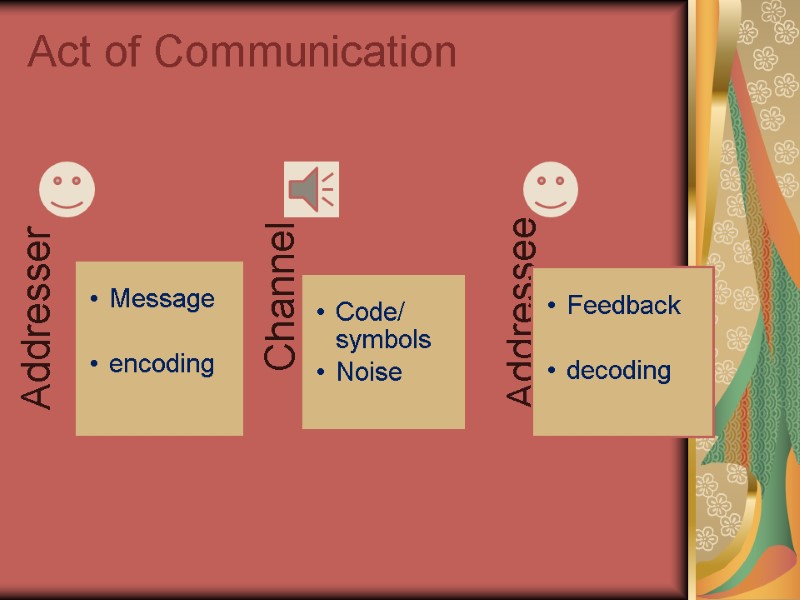
Act of Communication

See you next week! Any questions?
14004-toc-zv.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

