Theoretical_grammardek.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Theoretical grammar SEC
Theoretical grammar SEC
 Type of Language According to Its Structure Analytical (English) n Synthetical (Ukrainian) n
Type of Language According to Its Structure Analytical (English) n Synthetical (Ukrainian) n
 Analytical (English) n n few grammatical inflections sparing use of sound alternations to denote grammatical forms wide use of prepositions to denote relations between objects and to connect words in the sentence prominent use of word order to denote grammatical relations
Analytical (English) n n few grammatical inflections sparing use of sound alternations to denote grammatical forms wide use of prepositions to denote relations between objects and to connect words in the sentence prominent use of word order to denote grammatical relations
 English Synthetical Forms n n Some morphemes used to derive forms of words: to form plural with 3 variants of pronunciation: -(e)s, -en, -ren; to denote genitive case of nouns with 3 variants of pronunciation: -‘s: to form degrees of comparison for adj. : -er, -est; to form tenses: -(e)s for 3 rd person singular Pres. Ind. with 3 variants of pronunciation, - (e)d Past Tense of certain verbs with 3 variants of pronunciation, -(e)n Participle II of certain verbs, -ing Participle I, Gerund
English Synthetical Forms n n Some morphemes used to derive forms of words: to form plural with 3 variants of pronunciation: -(e)s, -en, -ren; to denote genitive case of nouns with 3 variants of pronunciation: -‘s: to form degrees of comparison for adj. : -er, -est; to form tenses: -(e)s for 3 rd person singular Pres. Ind. with 3 variants of pronunciation, - (e)d Past Tense of certain verbs with 3 variants of pronunciation, -(e)n Participle II of certain verbs, -ing Participle I, Gerund
 English Analytical Forms use of a word to express some grammatical category of another word has invited, more vivid (has, more have only grammatical meaning) n grammatical repetition He knocked and knocked without reply n
English Analytical Forms use of a word to express some grammatical category of another word has invited, more vivid (has, more have only grammatical meaning) n grammatical repetition He knocked and knocked without reply n
 Relations in Language – system of signs (meaningful units) which are closely interconnected and interdependent
Relations in Language – system of signs (meaningful units) which are closely interconnected and interdependent
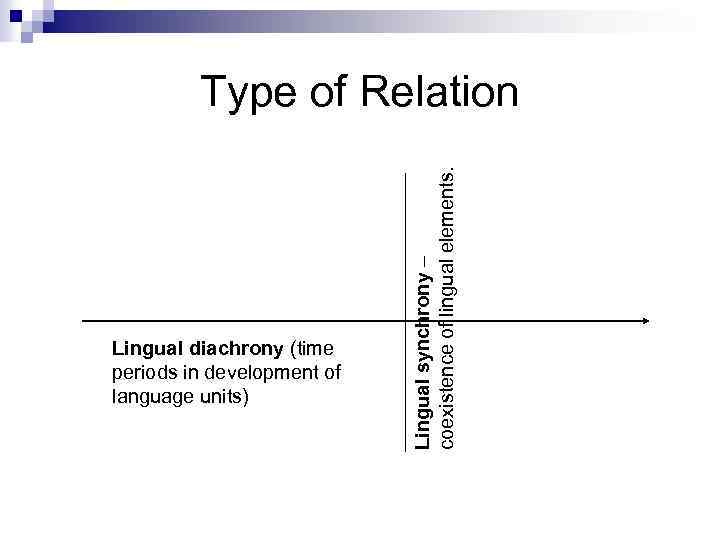 Lingual diachrony (time periods in development of language units) Lingual synchrony – coexistence of lingual elements. Type of Relation
Lingual diachrony (time periods in development of language units) Lingual synchrony – coexistence of lingual elements. Type of Relation
 Relation Between Lingual Units Syntagmatic (immediate linear relations) Space / ship, launch / ed Syntagma: predicative (subj. + pred. ) objective (v + obj. ) attributive (n + attr. ) adverbial (v. , adj. , adv. + modifier) Paradigmatic Phonology: consonantism, voiceness, devoicedness, nasalization, length Vocabulary: synonymy, antonomy Grammar: number, case, person, tense
Relation Between Lingual Units Syntagmatic (immediate linear relations) Space / ship, launch / ed Syntagma: predicative (subj. + pred. ) objective (v + obj. ) attributive (n + attr. ) adverbial (v. , adj. , adv. + modifier) Paradigmatic Phonology: consonantism, voiceness, devoicedness, nasalization, length Vocabulary: synonymy, antonomy Grammar: number, case, person, tense
 Planes of Language Plane of content meaning Plane of expression form Polysemy, homonymy 2 or more units of the plane of content correspond to one unit of the plane of expression (Present Indefinite = habitual action, action at the present moment, general truth) Synonymy 2 or more units of the plane of expression correspond to one unit of the plane of content (Future Indefinite, Present Continuous = to denote future action)
Planes of Language Plane of content meaning Plane of expression form Polysemy, homonymy 2 or more units of the plane of content correspond to one unit of the plane of expression (Present Indefinite = habitual action, action at the present moment, general truth) Synonymy 2 or more units of the plane of expression correspond to one unit of the plane of content (Future Indefinite, Present Continuous = to denote future action)
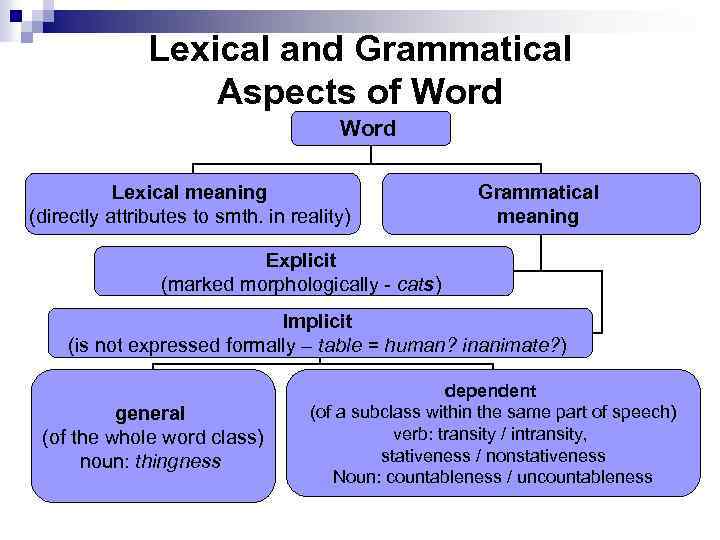 Lexical and Grammatical Aspects of Word Lexical meaning (directly attributes to smth. in reality) Grammatical meaning Explicit (marked morphologically - cats) Implicit (is not expressed formally – table = human? inanimate? ) general (of the whole word class) noun: thingness dependent (of a subclass within the same part of speech) verb: transity / intransity, stativeness / nonstativeness Noun: countableness / uncountableness
Lexical and Grammatical Aspects of Word Lexical meaning (directly attributes to smth. in reality) Grammatical meaning Explicit (marked morphologically - cats) Implicit (is not expressed formally – table = human? inanimate? ) general (of the whole word class) noun: thingness dependent (of a subclass within the same part of speech) verb: transity / intransity, stativeness / nonstativeness Noun: countableness / uncountableness
 Grammatical Category is the system of expressing a generalized grammatical meaning by means of paradigmatic correlation of grammatical forms in a category are exposed by the grammatical oppositions
Grammatical Category is the system of expressing a generalized grammatical meaning by means of paradigmatic correlation of grammatical forms in a category are exposed by the grammatical oppositions
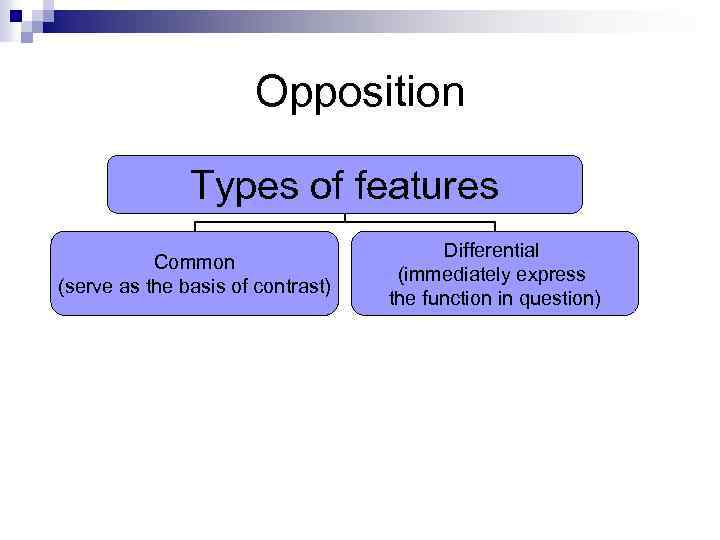 Opposition Types of features Common (serve as the basis of contrast) Differential (immediately express the function in question)
Opposition Types of features Common (serve as the basis of contrast) Differential (immediately express the function in question)
 Qualitative Types of Oppositions By the number of members binary ternary quaterary
Qualitative Types of Oppositions By the number of members binary ternary quaterary
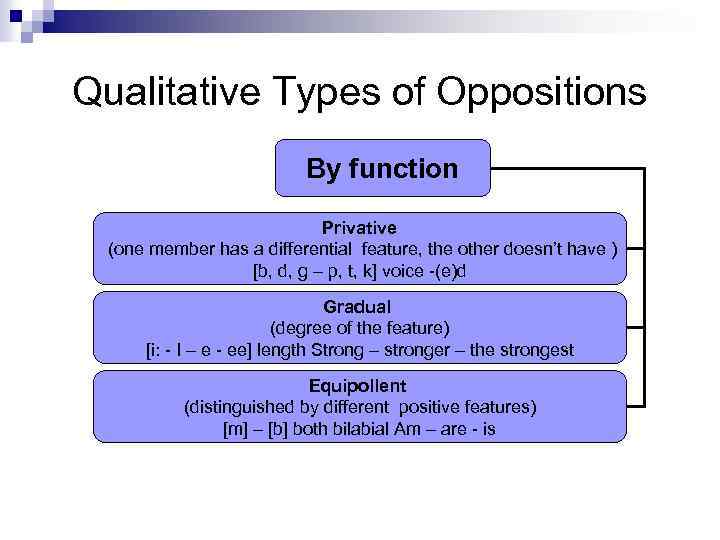 Qualitative Types of Oppositions By function Privative (one member has a differential feature, the other doesn’t have ) [b, d, g – p, t, k] voice -(e)d Gradual (degree of the feature) [i: - I – e - ee] length Strong – stronger – the strongest Equipollent (distinguished by different positive features) [m] – [b] both bilabial Am – are - is
Qualitative Types of Oppositions By function Privative (one member has a differential feature, the other doesn’t have ) [b, d, g – p, t, k] voice -(e)d Gradual (degree of the feature) [i: - I – e - ee] length Strong – stronger – the strongest Equipollent (distinguished by different positive features) [m] – [b] both bilabial Am – are - is
 Noun n n Meaning: substance, thingness Function: subject, object, attributive, adverbial, predicative Form: Gender, Number, Case, Article determination Subclasses: proper – common, animate – inanimate, human – nonhuman, countable – uncountable, concrete - abstract
Noun n n Meaning: substance, thingness Function: subject, object, attributive, adverbial, predicative Form: Gender, Number, Case, Article determination Subclasses: proper – common, animate – inanimate, human – nonhuman, countable – uncountable, concrete - abstract
 Verb n n Meaning: verbality (the ability to denote a process developing in time) Function: predicate, adverbial modifier Form: tense, aspect, voice, mood, person, number, finitude, phase Subclasses: morphological, lexicalmorphological, syntactical, functional classifications
Verb n n Meaning: verbality (the ability to denote a process developing in time) Function: predicate, adverbial modifier Form: tense, aspect, voice, mood, person, number, finitude, phase Subclasses: morphological, lexicalmorphological, syntactical, functional classifications
 Classification of English Verb Morphological classification According to stem-type Simple (to go) According to the way of forming part tenses regular irregular Expanded (with the help of affixes - justify) Sound-replacive (food – to feed) Composite (correspond to composite nouns – to blackmail) Stress-replacive (import – to import) Phrasal (to have a smoke)
Classification of English Verb Morphological classification According to stem-type Simple (to go) According to the way of forming part tenses regular irregular Expanded (with the help of affixes - justify) Sound-replacive (food – to feed) Composite (correspond to composite nouns – to blackmail) Stress-replacive (import – to import) Phrasal (to have a smoke)
 Classification of English Verb Lexical-morphological classification (based on the implicit grammatical meaning) Transitive Intransitive Stative Dynamic Terminative Durative
Classification of English Verb Lexical-morphological classification (based on the implicit grammatical meaning) Transitive Intransitive Stative Dynamic Terminative Durative
 Classification of English Verb Syntactic classification According to the nature of predication finite non-finite According to syntagmatic properties obligatory optional
Classification of English Verb Syntactic classification According to the nature of predication finite non-finite According to syntagmatic properties obligatory optional
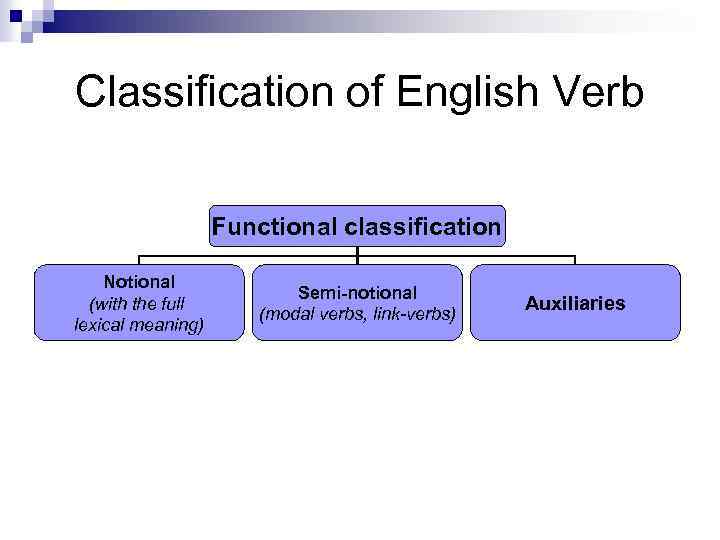 Classification of English Verb Functional classification Notional (with the full lexical meaning) Semi-notional (modal verbs, link-verbs) Auxiliaries
Classification of English Verb Functional classification Notional (with the full lexical meaning) Semi-notional (modal verbs, link-verbs) Auxiliaries
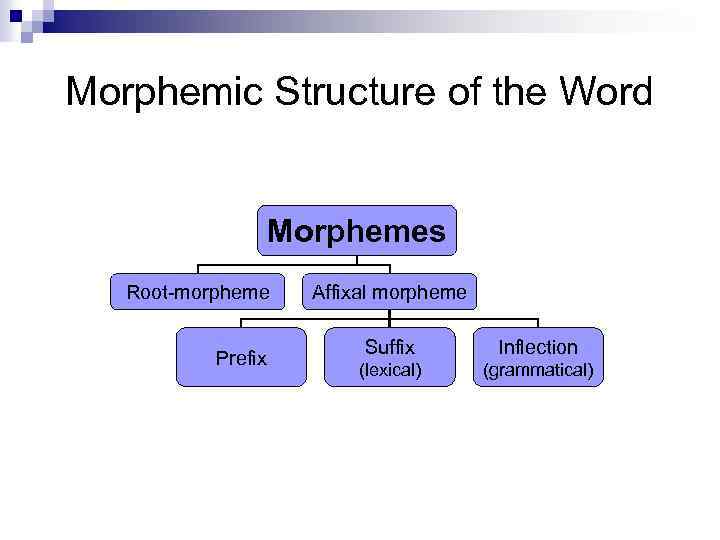 Morphemic Structure of the Word Morphemes Root-morpheme Prefix Affixal morpheme Suffix Inflection (lexical) (grammatical)
Morphemic Structure of the Word Morphemes Root-morpheme Prefix Affixal morpheme Suffix Inflection (lexical) (grammatical)
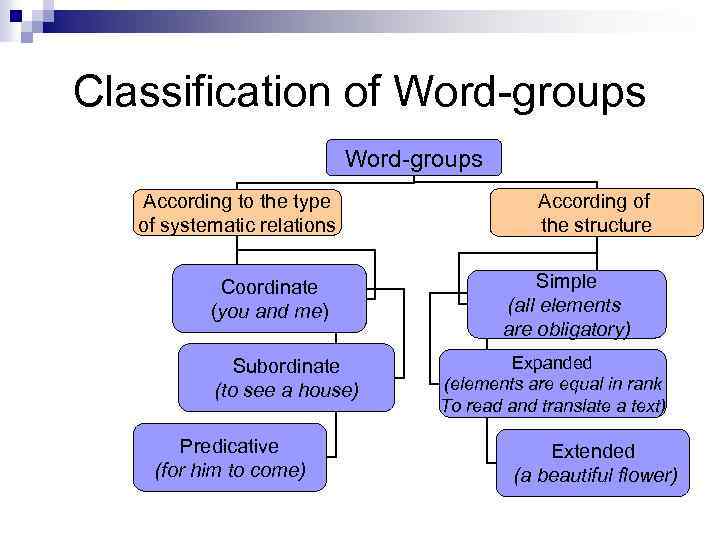 Classification of Word-groups According to the type of systematic relations Coordinate (you and me) Subordinate (to see a house) Predicative (for him to come) According of the structure Simple (all elements are obligatory) Expanded (elements are equal in rank To read and translate a text) Extended (a beautiful flower)
Classification of Word-groups According to the type of systematic relations Coordinate (you and me) Subordinate (to see a house) Predicative (for him to come) According of the structure Simple (all elements are obligatory) Expanded (elements are equal in rank To read and translate a text) Extended (a beautiful flower)
 Types of Sentences According to the types of communication: Declarative Imperative Interrogative According to the structure: Simple Composite
Types of Sentences According to the types of communication: Declarative Imperative Interrogative According to the structure: Simple Composite


