Theme: Psychology as a Scientific and Human Endeavor



























l_1_introduction_to_psy.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Theme: Psychology as a Scientific and Human Endeavor Senior lecturer: Zh. S. Bekbayeva Master of Education
Theme: Psychology as a Scientific and Human Endeavor Senior lecturer: Zh. S. Bekbayeva Master of Education
 contents 1- What is Psychology 2- Approaches to Psychology 3-Influence of Research on Psychology 4-Fields of Psychology
contents 1- What is Psychology 2- Approaches to Psychology 3-Influence of Research on Psychology 4-Fields of Psychology
 Dictionary Approach (es) – подход (ы); Behavior – поведение; Observation – наблюдение; Intention -намерение; Consciousness-сознание.
Dictionary Approach (es) – подход (ы); Behavior – поведение; Observation – наблюдение; Intention -намерение; Consciousness-сознание.
 What is Psychology Definition of psychology – the science of the human soul; specifically, the systematic or scientific knowledge of the powers & functions of the human soul, so far as they are known by consciousness; a treatise on the human soul. Definition of Psychology –the systematic, scientific study of behaviors & mental processes. Psychology is the scientific study of human mind and behaviour: how we think, feel, act and interact individually and in groups.
What is Psychology Definition of psychology – the science of the human soul; specifically, the systematic or scientific knowledge of the powers & functions of the human soul, so far as they are known by consciousness; a treatise on the human soul. Definition of Psychology –the systematic, scientific study of behaviors & mental processes. Psychology is the scientific study of human mind and behaviour: how we think, feel, act and interact individually and in groups.
 The study of psychology has five basic goals: 1. Describe – The first goal is to observe behavior and describe, often in minute detail, what was observed as objectively as possible 2. Explain – While descriptions come from observable data, psychologists must go beyond what is obvious and explain their observations. In other words, why did the subject do what he or she did? 3. Predict – Once we know what happens, and why it happens, we can begin to speculate what will happen in the future. There’s an old saying, which very often holds true: "the best predictor of future behavior is past behavior."
The study of psychology has five basic goals: 1. Describe – The first goal is to observe behavior and describe, often in minute detail, what was observed as objectively as possible 2. Explain – While descriptions come from observable data, psychologists must go beyond what is obvious and explain their observations. In other words, why did the subject do what he or she did? 3. Predict – Once we know what happens, and why it happens, we can begin to speculate what will happen in the future. There’s an old saying, which very often holds true: "the best predictor of future behavior is past behavior."
 The study of psychology has five basic goals: 4. Control – Once we know what happens, why it happens and what is likely to happen in the future, we can excerpt control over it. In other words, if we know you choose abusive partners because your father was abusive, we can assume you will choose another abusive partner, and can therefore intervene to change this negative behavior. 5. Improve – Not only do psychologists attempt to control behavior, they want to do so in a positive manner, they want to improve a person’s life, not make it worse. This is not always the case, but it should always be the intention.
The study of psychology has five basic goals: 4. Control – Once we know what happens, why it happens and what is likely to happen in the future, we can excerpt control over it. In other words, if we know you choose abusive partners because your father was abusive, we can assume you will choose another abusive partner, and can therefore intervene to change this negative behavior. 5. Improve – Not only do psychologists attempt to control behavior, they want to do so in a positive manner, they want to improve a person’s life, not make it worse. This is not always the case, but it should always be the intention.
 Structure of the psyche The Psyche is a subject of studying of psychology science. The psyche - this is particular property of highly organized matter, subjectively reflect objective reality, it's necessary to man (and animals) for guidance and active interaction with the environment, and on the human level is the necessary to control their behavior.
Structure of the psyche The Psyche is a subject of studying of psychology science. The psyche - this is particular property of highly organized matter, subjectively reflect objective reality, it's necessary to man (and animals) for guidance and active interaction with the environment, and on the human level is the necessary to control their behavior.
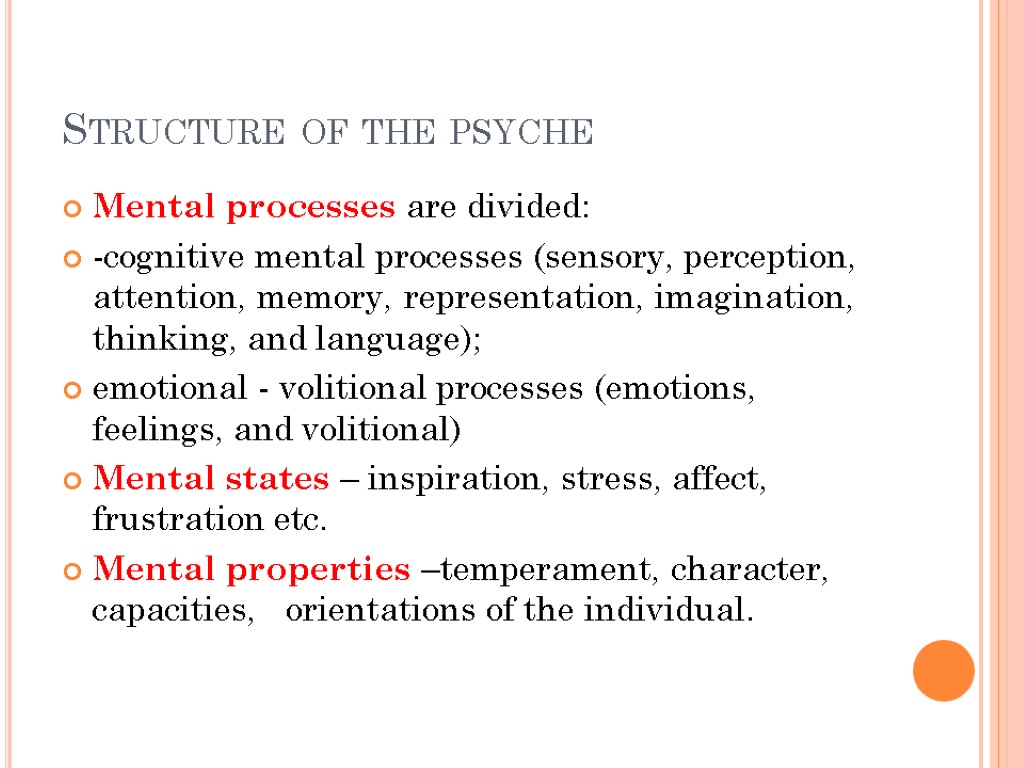
 Structure of the psyche Mental processes are divided: -cognitive mental processes (sensory, perception, attention, memory, representation, imagination, thinking, and language); emotional - volitional processes (emotions, feelings, and volitional) Mental states – inspiration, stress, affect, frustration etc. Mental properties –temperament, character, capacities, orientations of the individual.
Structure of the psyche Mental processes are divided: -cognitive mental processes (sensory, perception, attention, memory, representation, imagination, thinking, and language); emotional - volitional processes (emotions, feelings, and volitional) Mental states – inspiration, stress, affect, frustration etc. Mental properties –temperament, character, capacities, orientations of the individual.
 2- Approaches to Psychology The behaviorist approach which looks at the way that our environment affects our behavior. Behaviorists are interested in learning and habits, and they often believe that psychologists should study only behavior, not thoughts and experiences, as behavior is the only thing that other people can really see.
2- Approaches to Psychology The behaviorist approach which looks at the way that our environment affects our behavior. Behaviorists are interested in learning and habits, and they often believe that psychologists should study only behavior, not thoughts and experiences, as behavior is the only thing that other people can really see.
 Approaches to Psychology The cognitive approach which is all about the study of our mental processes. Cognitive psychologists believe that if we want to understand how they think, remember and reason. The are interested in how we interpret and make sense of the world around us.
Approaches to Psychology The cognitive approach which is all about the study of our mental processes. Cognitive psychologists believe that if we want to understand how they think, remember and reason. The are interested in how we interpret and make sense of the world around us.
 Approaches to Psychology The biological approach which is all about how our internal physiological processes and our genetic make up influence our behavior. However, human beings are not biological robots: our biology is designed to enable us to act more effectively in the real world. So biological psychologists are interested in the interactions between our environment and our internal physiology, and how those interactions influence our experience.
Approaches to Psychology The biological approach which is all about how our internal physiological processes and our genetic make up influence our behavior. However, human beings are not biological robots: our biology is designed to enable us to act more effectively in the real world. So biological psychologists are interested in the interactions between our environment and our internal physiology, and how those interactions influence our experience.
 Approaches to Psychology The social approach which is to do with how we interact with other people. Some social psychologists emphasize the individual factors that are involved in social behavior; some are interested in social beliefs and attitudes; others are interested in groups and shared sicial experience.
Approaches to Psychology The social approach which is to do with how we interact with other people. Some social psychologists emphasize the individual factors that are involved in social behavior; some are interested in social beliefs and attitudes; others are interested in groups and shared sicial experience.
 Approaches to Psychology The development approach which is to do with how human beings (and sometimes animals) change over time. Developmental psychologists tend to be particularly interested in three areas of human development: emotional development, social development, and cognitive development. However, as the person who is developing is a young human being, it isn’t always easy to separate the three areas: each can influence the others.
Approaches to Psychology The development approach which is to do with how human beings (and sometimes animals) change over time. Developmental psychologists tend to be particularly interested in three areas of human development: emotional development, social development, and cognitive development. However, as the person who is developing is a young human being, it isn’t always easy to separate the three areas: each can influence the others.
 Approaches to Psychology The humanistic approach which focuses on individual experience, rather than on people in general. Humanistic psychologists are particularly concerned with personal growth and with what people’s subjective experience is like. They regard every individual as unique and are interested in helping people to uncover and use their own special potential.
Approaches to Psychology The humanistic approach which focuses on individual experience, rather than on people in general. Humanistic psychologists are particularly concerned with personal growth and with what people’s subjective experience is like. They regard every individual as unique and are interested in helping people to uncover and use their own special potential.
 3-Influence of Research on Psychology Research helps us understand what makes people think, feel, and act in certain ways; allows us to categorize psychological disorders in order to understand the symptoms and impact on the individual and society; helps us to understand how intimate relationships, development, schools, family, peers, and religion affect us as individuals and as a society; and helps us to develop effective treatments to improve the quality of life of individuals and groups.
3-Influence of Research on Psychology Research helps us understand what makes people think, feel, and act in certain ways; allows us to categorize psychological disorders in order to understand the symptoms and impact on the individual and society; helps us to understand how intimate relationships, development, schools, family, peers, and religion affect us as individuals and as a society; and helps us to develop effective treatments to improve the quality of life of individuals and groups.
 3-Influence of Research on Psychology In this sense, psychological research is typically used for the following: Study development and external factors and the role they play on individuals' mental health Study people with specific psychological disorders, symptoms, or characteristics Develop tests to measure specific psychological phenomenon Develop treatment approaches to improve individuals' mental health
3-Influence of Research on Psychology In this sense, psychological research is typically used for the following: Study development and external factors and the role they play on individuals' mental health Study people with specific psychological disorders, symptoms, or characteristics Develop tests to measure specific psychological phenomenon Develop treatment approaches to improve individuals' mental health
 Types of Research Naturalistic Observation. Observing behavior in their natural environment Often involves counting behaviors, such as number of aggressive acts, number of smiles, etc. Advantages: Behavior is naturally occurring and is not manipulated by a researcher and it can provide more qualitative data as opposed to merely quantitative information. Limitations: Even the presence of someone observing can cause those being observed to alter their behavior. Researcher’s beliefs can also alter their observations. And, it is very difficult to coordinate multiple observers since observed behaviors must be operationally defined (e.g. what constitutes an aggressive act)
Types of Research Naturalistic Observation. Observing behavior in their natural environment Often involves counting behaviors, such as number of aggressive acts, number of smiles, etc. Advantages: Behavior is naturally occurring and is not manipulated by a researcher and it can provide more qualitative data as opposed to merely quantitative information. Limitations: Even the presence of someone observing can cause those being observed to alter their behavior. Researcher’s beliefs can also alter their observations. And, it is very difficult to coordinate multiple observers since observed behaviors must be operationally defined (e.g. what constitutes an aggressive act)
 Types of Research Case Study Following a single case, typically over an extended period of time can involve naturalistic observations, and include psychological testing, interviews, interviews with others, and the application of a treatment or observation Advantages: Can gather extensive information, both qualitative and quantitative and it can be helpful in better understanding rare cases or very specific interventions Limitations: Only one case is involved, severely limiting the generalization to the rest of the population. Can be very time consuming and can involve other problems specific to the techniques used, including researcher bias.
Types of Research Case Study Following a single case, typically over an extended period of time can involve naturalistic observations, and include psychological testing, interviews, interviews with others, and the application of a treatment or observation Advantages: Can gather extensive information, both qualitative and quantitative and it can be helpful in better understanding rare cases or very specific interventions Limitations: Only one case is involved, severely limiting the generalization to the rest of the population. Can be very time consuming and can involve other problems specific to the techniques used, including researcher bias.
 Types of Research Survey Everyone has probably heard of this and many of you have been involved in research involving surveys. They are often used in the news, especially to gather viewer opinions such as during a race for president. Advantages: Can gather large amounts of information in a relatively short time, especially now with many surveys being conducted on the internet. Limitations: Survey data is based solely on subjects’ responses which can be inaccurate due to outright lying, misunderstanding of the question, placebo effect, and even the manner in which the question is asked.
Types of Research Survey Everyone has probably heard of this and many of you have been involved in research involving surveys. They are often used in the news, especially to gather viewer opinions such as during a race for president. Advantages: Can gather large amounts of information in a relatively short time, especially now with many surveys being conducted on the internet. Limitations: Survey data is based solely on subjects’ responses which can be inaccurate due to outright lying, misunderstanding of the question, placebo effect, and even the manner in which the question is asked.
 Types of Research Psychological Testing Utilizing testing to gather information about a group or an individual Advantages: Most tests are normed and standardized, which means they have very reliable and valid results. Popular with businesses looking for data on employees and with difficult or specific therapy cases Limitations: Tests which are not rigorously normed and standardized can easily result in inaccurate results.
Types of Research Psychological Testing Utilizing testing to gather information about a group or an individual Advantages: Most tests are normed and standardized, which means they have very reliable and valid results. Popular with businesses looking for data on employees and with difficult or specific therapy cases Limitations: Tests which are not rigorously normed and standardized can easily result in inaccurate results.
 Types of Research Correlational Studies Correlation means relationship, so the purpose of a correlational study is to determine if a relationship exists, what direction the relationship is, and how strong it is. Advantages: Can assess the strength of a relationship. Is popular with lay population because it is relatively easy to explain and understand. Limitations: Can not make any assumptions of cause and effect (explain how third a variable can be involved, or how the variables can influence each other).
Types of Research Correlational Studies Correlation means relationship, so the purpose of a correlational study is to determine if a relationship exists, what direction the relationship is, and how strong it is. Advantages: Can assess the strength of a relationship. Is popular with lay population because it is relatively easy to explain and understand. Limitations: Can not make any assumptions of cause and effect (explain how third a variable can be involved, or how the variables can influence each other).
 4- Fields of Psychology Educational psychology is concerned with children and young people in educational and early years settings. Social Psychology: Social psychology looks at a wide range of social topics, including group behavior, social perception, leadership, nonverbal behavior, conformity, aggression and prejudice. Industrial-Organizational Psychology: Industrial organizational psychology is a field of psychology that applies psychological theories and principles to organizations Personality Psychology: Personality psychology looks at the patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behavior that make a person unique.
4- Fields of Psychology Educational psychology is concerned with children and young people in educational and early years settings. Social Psychology: Social psychology looks at a wide range of social topics, including group behavior, social perception, leadership, nonverbal behavior, conformity, aggression and prejudice. Industrial-Organizational Psychology: Industrial organizational psychology is a field of psychology that applies psychological theories and principles to organizations Personality Psychology: Personality psychology looks at the patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behavior that make a person unique.
 Fields of Psychology Experimental Psychology: Experimental psychology is an area of psychology that utilizes scientific methods to research the mind and behavior.. Forensic Psychology: Forensic psychology is defined as the intersection of psychology and the law, but forensic psychologists can perform many roles so this definition can vary.
Fields of Psychology Experimental Psychology: Experimental psychology is an area of psychology that utilizes scientific methods to research the mind and behavior.. Forensic Psychology: Forensic psychology is defined as the intersection of psychology and the law, but forensic psychologists can perform many roles so this definition can vary.
 Fields of Psychology Cognitive Psychology: Cognitive psychology is the branch of psychology that studies mental processes including how people think, perceive, remember and learn. Comparative Psychology: Comparative psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the study of animal behavior. Developmental Psychology: This field of psychology looks at development throughout the lifespan, from childhood to adulthood. The scientific study of human development seeks to understand and explain how and why people change throughout life. This includes all aspects of human growth, including physical, emotional, intellectual, social, perceptual and personality development.
Fields of Psychology Cognitive Psychology: Cognitive psychology is the branch of psychology that studies mental processes including how people think, perceive, remember and learn. Comparative Psychology: Comparative psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the study of animal behavior. Developmental Psychology: This field of psychology looks at development throughout the lifespan, from childhood to adulthood. The scientific study of human development seeks to understand and explain how and why people change throughout life. This includes all aspects of human growth, including physical, emotional, intellectual, social, perceptual and personality development.
 Fields of Psychology Abnormal Psychology: Abnormal psychology is a field of psychology that deals with psychopathology and abnormal behavior. Biopsychology: Biopsychology is a field of psychology that analyzes how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors, thoughts and feelings. This field can be thought of as a combination of basic psychology and neuroscience. Clinical Psychology: Clinical psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the assessment and treatment of mental illness, abnormal behavior and psychiatric problems.
Fields of Psychology Abnormal Psychology: Abnormal psychology is a field of psychology that deals with psychopathology and abnormal behavior. Biopsychology: Biopsychology is a field of psychology that analyzes how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors, thoughts and feelings. This field can be thought of as a combination of basic psychology and neuroscience. Clinical Psychology: Clinical psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the assessment and treatment of mental illness, abnormal behavior and psychiatric problems.
 Questions: 1. What are some of the strengths of modern psychology? What are some of the weakness? 2. Does common sense provide us with a view of human behavior? Does psychology differ from common sense? 3. What is psychology? What kind of approaches in psychology do you know? 4. What are the main methods of investigation available to psychologist? What are the main disadvantages of these methods? What are the advantages of these methods? 5. What is the experimental method? Why has it been used so often in psychological research? 6. What are the main features of ethical research? Why is it important for experiments to be ethical?
Questions: 1. What are some of the strengths of modern psychology? What are some of the weakness? 2. Does common sense provide us with a view of human behavior? Does psychology differ from common sense? 3. What is psychology? What kind of approaches in psychology do you know? 4. What are the main methods of investigation available to psychologist? What are the main disadvantages of these methods? What are the advantages of these methods? 5. What is the experimental method? Why has it been used so often in psychological research? 6. What are the main features of ethical research? Why is it important for experiments to be ethical?
 THANK YOU!
THANK YOU!

