1Лек ВМ англ Гаусс.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Theme: Gauss Method and Gauss. Jordan Method Literature: 1 , v. І, p. 107 -117, 2 , part І, p. 141 -152, 3 , p. 46 -62
Theme: Gauss Method and Gauss. Jordan Method Literature: 1 , v. І, p. 107 -117, 2 , part І, p. 141 -152, 3 , p. 46 -62
 1. The main definitions. 2. Gauss Method. 3. Implementation of the Gauss method in different cases. 4. Gauss-Jordan Method.
1. The main definitions. 2. Gauss Method. 3. Implementation of the Gauss method in different cases. 4. Gauss-Jordan Method.
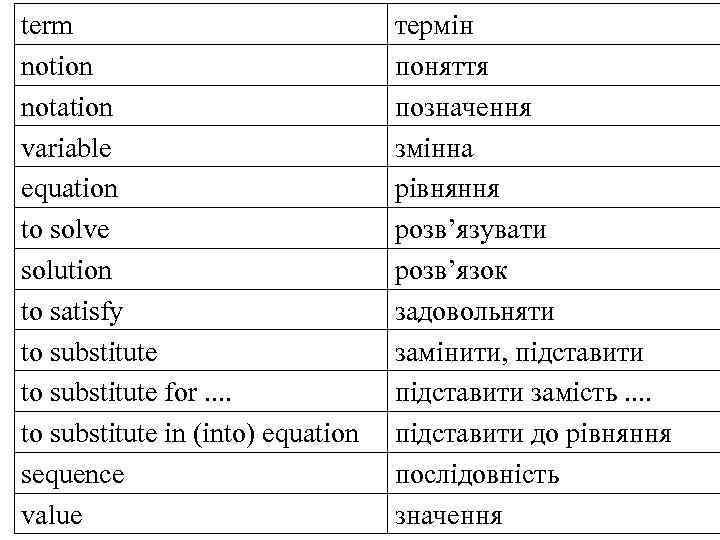 term notion notation variable equation to solve solution to satisfy to substitute for. . to substitute in (into) equation sequence value термін поняття позначення змінна рівняння розв’язувати розв’язок задовольняти замінити, підставити замість. . підставити до рівняння послідовність значення
term notion notation variable equation to solve solution to satisfy to substitute for. . to substitute in (into) equation sequence value термін поняття позначення змінна рівняння розв’язувати розв’язок задовольняти замінити, підставити замість. . підставити до рівняння послідовність значення
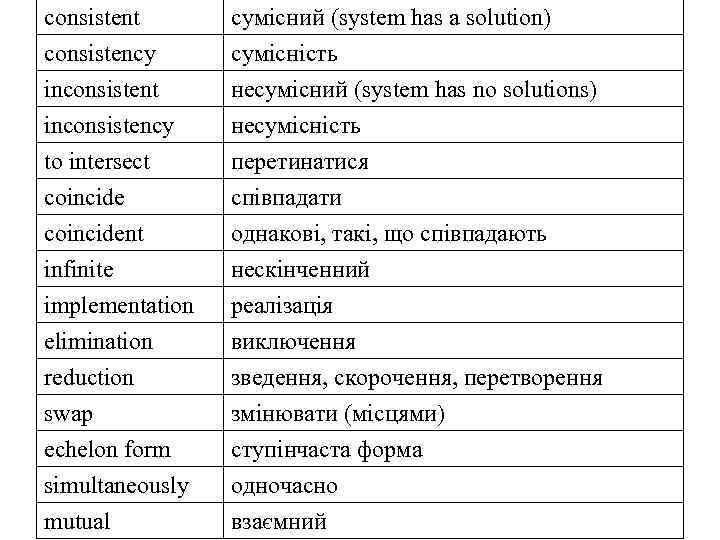 consistent consistency сумісний (system has a solution) сумісність inconsistent inconsistency несумісний (system has no solutions) несумісність to intersect coincident перетинатися співпадати однакові, такі, що співпадають infinite implementation elimination reduction swap echelon form simultaneously нескінченний реалізація виключення зведення, скорочення, перетворення змінювати (місцями) ступінчаста форма одночасно mutual взаємний
consistent consistency сумісний (system has a solution) сумісність inconsistent inconsistency несумісний (system has no solutions) несумісність to intersect coincident перетинатися співпадати однакові, такі, що співпадають infinite implementation elimination reduction swap echelon form simultaneously нескінченний реалізація виключення зведення, скорочення, перетворення змінювати (місцями) ступінчаста форма одночасно mutual взаємний
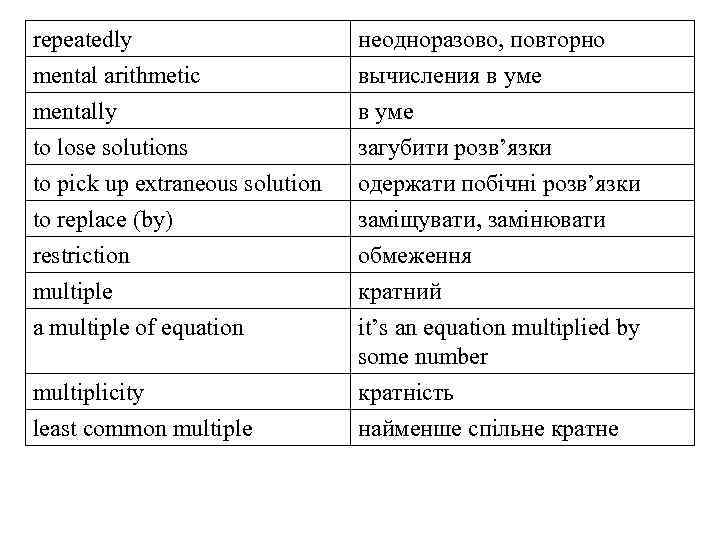 repeatedly mental arithmetic mentally to lose solutions неодноразово, повторно вычисления в уме загубити розв’язки to pick up extraneous solution to replace (by) restriction multiple a multiple of equation одержати побічні розв’язки заміщувати, замінювати обмеження кратний it’s an equation multiplied by some number multiplicity least common multiple кратність найменше спільне кратне
repeatedly mental arithmetic mentally to lose solutions неодноразово, повторно вычисления в уме загубити розв’язки to pick up extraneous solution to replace (by) restriction multiple a multiple of equation одержати побічні розв’язки заміщувати, замінювати обмеження кратний it’s an equation multiplied by some number multiplicity least common multiple кратність найменше спільне кратне
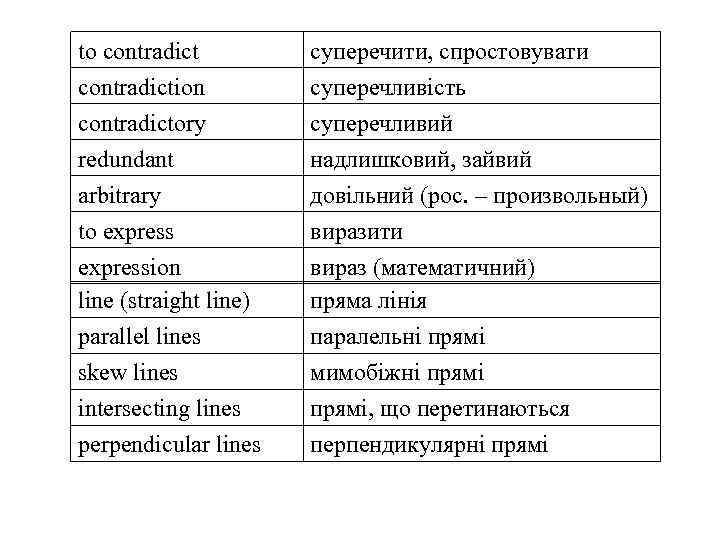 to contradiction contradictory redundant arbitrary to expression line (straight line) parallel lines skew lines intersecting lines суперечити, спростовувати суперечливість суперечливий надлишковий, зайвий довільний (рос. – произвольный) виразити вираз (математичний) пряма лінія паралельні прямі мимобіжні прямі, що перетинаються perpendicular lines перпендикулярні прямі
to contradiction contradictory redundant arbitrary to expression line (straight line) parallel lines skew lines intersecting lines суперечити, спростовувати суперечливість суперечливий надлишковий, зайвий довільний (рос. – произвольный) виразити вираз (математичний) пряма лінія паралельні прямі мимобіжні прямі, що перетинаються perpendicular lines перпендикулярні прямі
 An example of the linear equation in variables x, y, z? The main features of the linear equation?
An example of the linear equation in variables x, y, z? The main features of the linear equation?
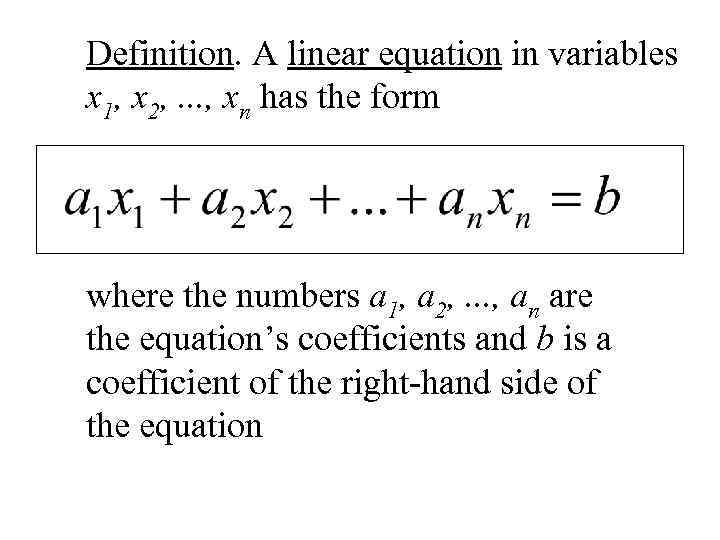 Definition. A linear equation in variables x 1, x 2, . . . , xn has the form where the numbers a 1, a 2, . . . , an are the equation’s coefficients and b is a coefficient of the right-hand side of the equation
Definition. A linear equation in variables x 1, x 2, . . . , xn has the form where the numbers a 1, a 2, . . . , an are the equation’s coefficients and b is a coefficient of the right-hand side of the equation
 Definition. The ordered sequence of n numbers (s 1, s 2, . . . , sn) is the solution of the equation (1), if it satisfies this equation. (The ordered sequence of n numbers is often called n-tuple)
Definition. The ordered sequence of n numbers (s 1, s 2, . . . , sn) is the solution of the equation (1), if it satisfies this equation. (The ordered sequence of n numbers is often called n-tuple)
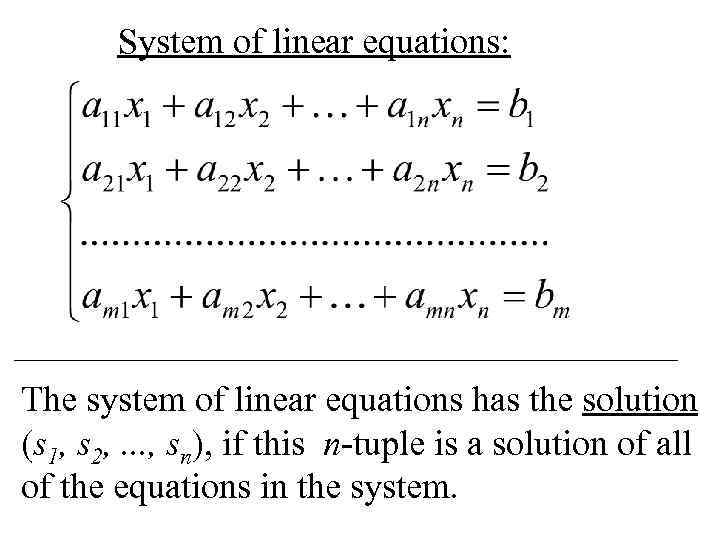 System of linear equations: The system of linear equations has the solution (s 1, s 2, . . . , sn), if this n-tuple is a solution of all of the equations in the system.
System of linear equations: The system of linear equations has the solution (s 1, s 2, . . . , sn), if this n-tuple is a solution of all of the equations in the system.
 The system is called a consistent one if it has some solutions It is called an inconsistent one if it has no solutions
The system is called a consistent one if it has some solutions It is called an inconsistent one if it has no solutions
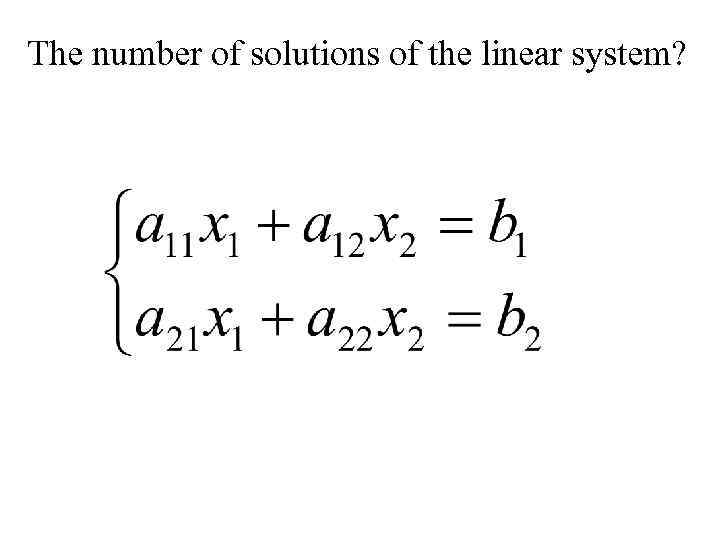 The number of solutions of the linear system?
The number of solutions of the linear system?
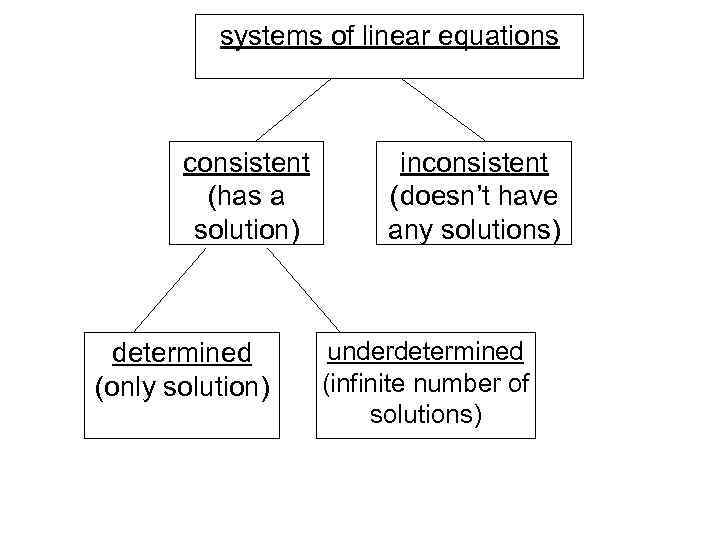 systems of linear equations consistent (has a solution) determined (only solution) inconsistent (doesn’t have any solutions) underdetermined (infinite number of solutions)
systems of linear equations consistent (has a solution) determined (only solution) inconsistent (doesn’t have any solutions) underdetermined (infinite number of solutions)
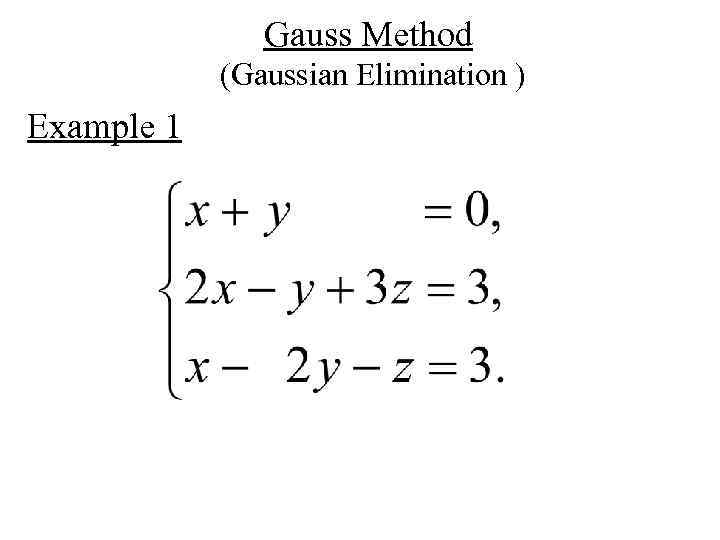 Gauss Method (Gaussian Elimination ) Example 1
Gauss Method (Gaussian Elimination ) Example 1
 Advantages of Gauss method: - fast and easy, - can be used for any linear system, -safe (never loses solutions or picks up extraneous solutions)
Advantages of Gauss method: - fast and easy, - can be used for any linear system, -safe (never loses solutions or picks up extraneous solutions)
 Elementary operations: - swapping, - rescaling (multiplying by a scalar), -pivoting (replacing by the sum of some equation and multiple of another).
Elementary operations: - swapping, - rescaling (multiplying by a scalar), -pivoting (replacing by the sum of some equation and multiple of another).
 The systems are called the equivalent ones if they have the coincident solutions.
The systems are called the equivalent ones if they have the coincident solutions.
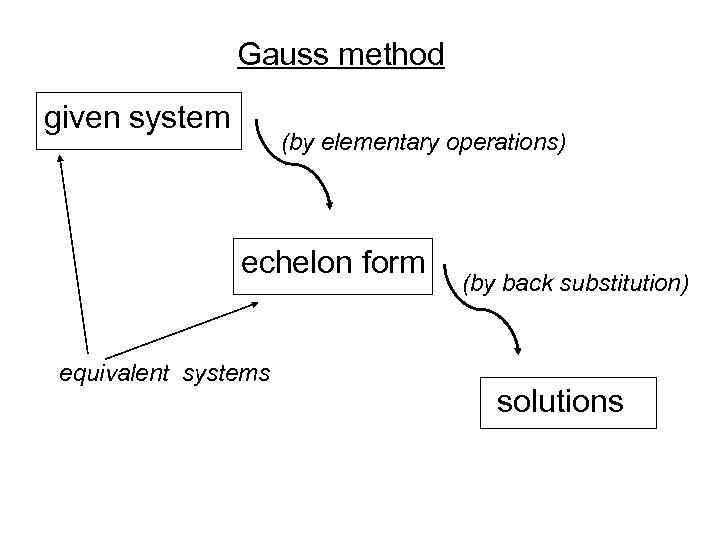 Gauss method given system (by elementary operations) echelon form equivalent systems (by back substitution) solutions
Gauss method given system (by elementary operations) echelon form equivalent systems (by back substitution) solutions
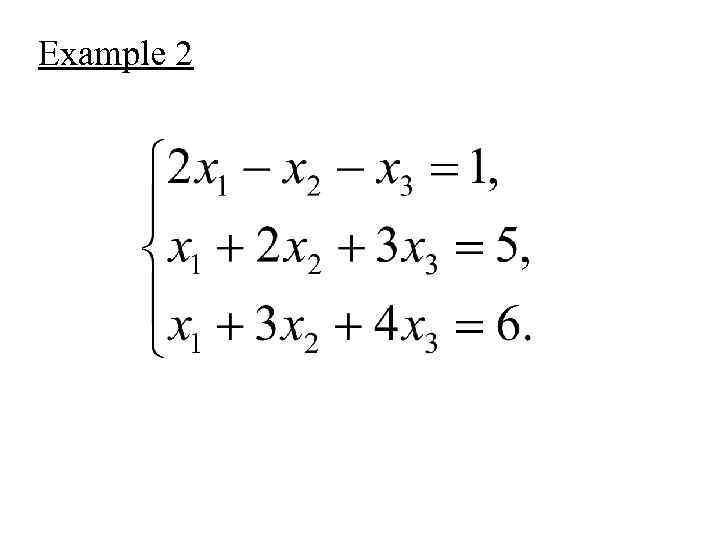 Example 2
Example 2
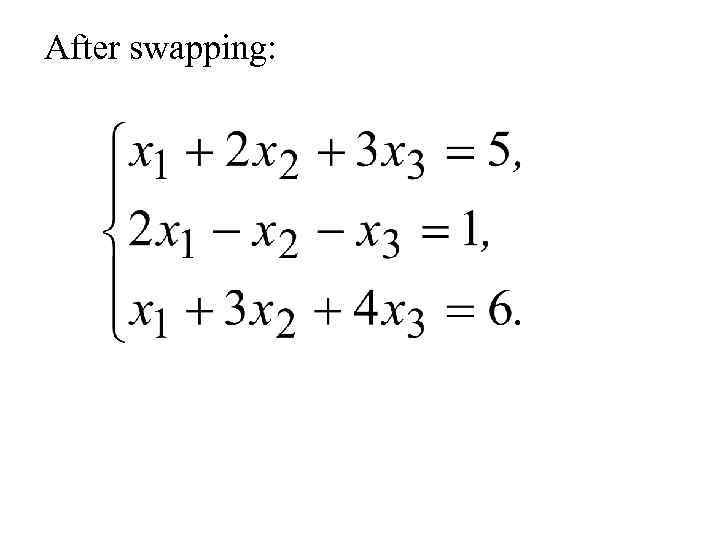 After swapping:
After swapping:
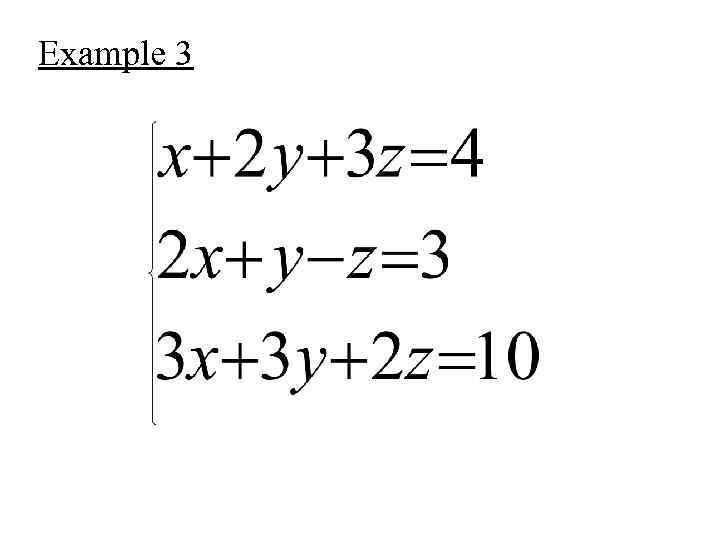 Example 3
Example 3
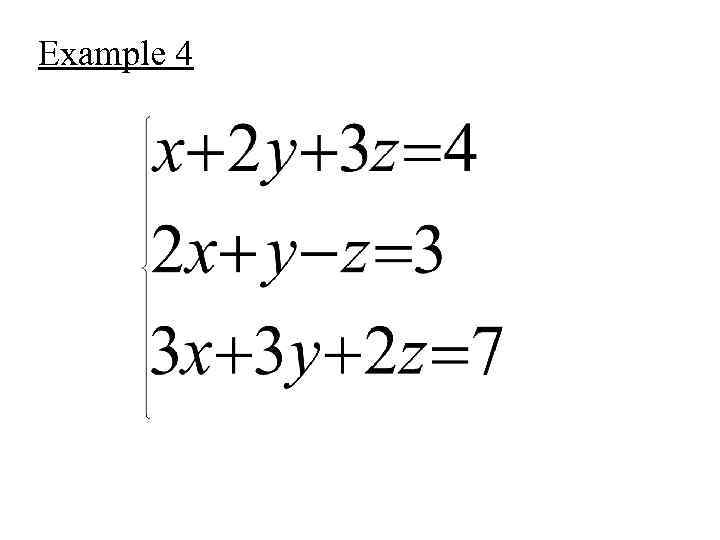 Example 4
Example 4
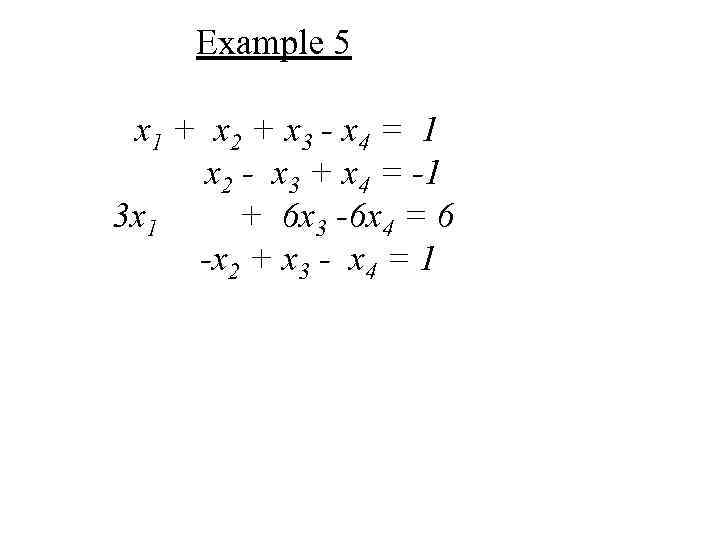 Example 5 х1 + х 2 + х3 - х4 = 1 х2 - х3 + х4 = -1 3 х1 + 6 х3 -6 х4 = 6 -х2 + х3 - х4 = 1
Example 5 х1 + х 2 + х3 - х4 = 1 х2 - х3 + х4 = -1 3 х1 + 6 х3 -6 х4 = 6 -х2 + х3 - х4 = 1
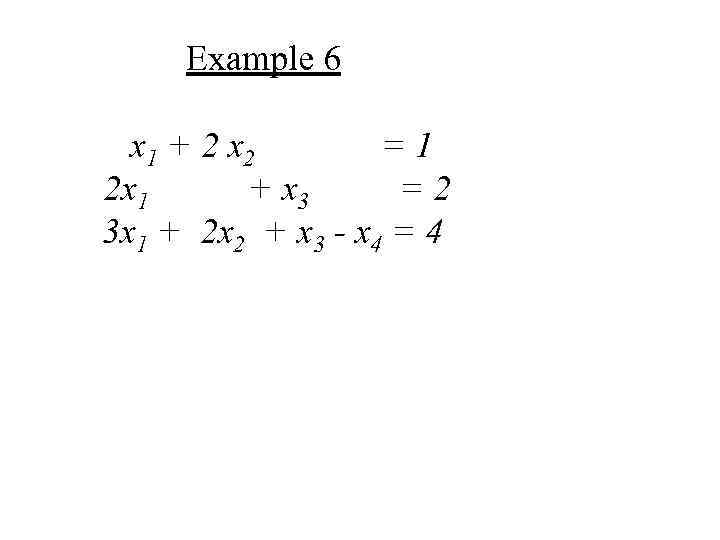 Example 6 х1 + 2 х2 =1 2 х1 + х3 =2 3 х1 + 2 х2 + х3 - х4 = 4
Example 6 х1 + 2 х2 =1 2 х1 + х3 =2 3 х1 + 2 х2 + х3 - х4 = 4


