presentation. course.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 14
 THEME: DEVELOPING WRITING COMPETENCE ACCORDING TO THE NATIONAL STANDARDS OF UZBEKISTAN
THEME: DEVELOPING WRITING COMPETENCE ACCORDING TO THE NATIONAL STANDARDS OF UZBEKISTAN
 PLAN: 1. Introduction 2. National standards of foreign language teaching of Uzbekistan. Model of teaching ad learning foreign language 3. Developing writing competence according to FLT of Uzbekistan 4. Writing as a goal and means of EL teaching and learning. 5. Conclusion
PLAN: 1. Introduction 2. National standards of foreign language teaching of Uzbekistan. Model of teaching ad learning foreign language 3. Developing writing competence according to FLT of Uzbekistan 4. Writing as a goal and means of EL teaching and learning. 5. Conclusion
 1. INTRODUCTION The Resolution of President Islam Karimov «On measures for further improvement the system of foreign languages learning» (December 10, 2012)64 is a key factor for modernization of teaching foreign languages at all stages, in which the importance of teaching and learning a foreign language across the country were pointed out. So, a foreign language becomes one of the important educational subjects, at all educational institutions. In the ELT the writing is the goal and means of teaching and learning. The goal of teaching writing is to teach production of written texts which students can write in the mother tongue. To produce the written text students should master mechanics of writing
1. INTRODUCTION The Resolution of President Islam Karimov «On measures for further improvement the system of foreign languages learning» (December 10, 2012)64 is a key factor for modernization of teaching foreign languages at all stages, in which the importance of teaching and learning a foreign language across the country were pointed out. So, a foreign language becomes one of the important educational subjects, at all educational institutions. In the ELT the writing is the goal and means of teaching and learning. The goal of teaching writing is to teach production of written texts which students can write in the mother tongue. To produce the written text students should master mechanics of writing
 2. NATIONAL STANDARDS OF FOREIGN LANGUAGE TEACHING OF UZBEKISTAN. MODEL OF TEACHING AD LEARNING FOREIGN LANGUAGE On December 10, 2012 President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Islam Karimov signed a decree “On measures to further improve foreign language learning system”. Since that time a comprehensive foreign languages’ teaching system has been created. Uzbekistan changed the model of foreign language teaching and made great strides in the development. Our country advanced in creating harmoniously developed, highly educated, modern-thinking young generation, further integration of the country to the world community
2. NATIONAL STANDARDS OF FOREIGN LANGUAGE TEACHING OF UZBEKISTAN. MODEL OF TEACHING AD LEARNING FOREIGN LANGUAGE On December 10, 2012 President of the Republic of Uzbekistan Islam Karimov signed a decree “On measures to further improve foreign language learning system”. Since that time a comprehensive foreign languages’ teaching system has been created. Uzbekistan changed the model of foreign language teaching and made great strides in the development. Our country advanced in creating harmoniously developed, highly educated, modern-thinking young generation, further integration of the country to the world community
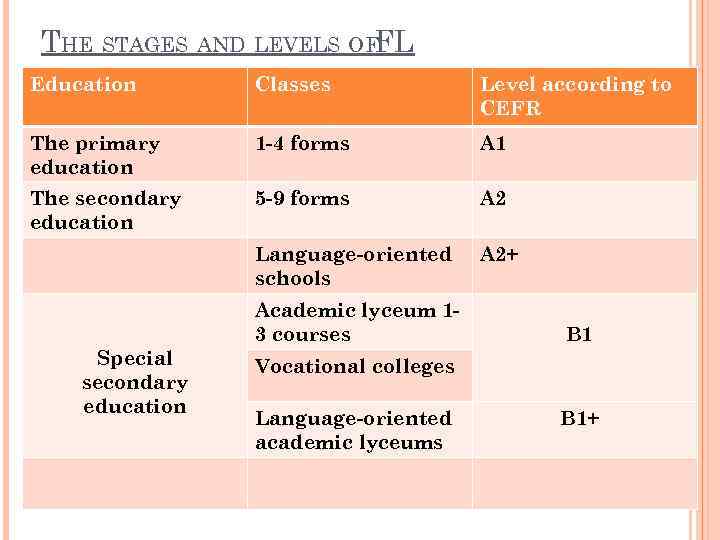 THE STAGES AND LEVELS OFFL Education Classes Level according to CEFR The primary education 1 -4 forms A 1 The secondary education 5 -9 forms A 2 Language-oriented schools A 2+ Academic lyceum 13 courses Special secondary education B 1 Vocational colleges Language-oriented academic lyceums B 1+
THE STAGES AND LEVELS OFFL Education Classes Level according to CEFR The primary education 1 -4 forms A 1 The secondary education 5 -9 forms A 2 Language-oriented schools A 2+ Academic lyceum 13 courses Special secondary education B 1 Vocational colleges Language-oriented academic lyceums B 1+
 Bachelor degree nonlinguistic institutes and universities Higher education Master degree nonlinguistic institutes and universities B 2 The second language in Bachelor and Master degree institutions and universities Bachelor degree linguistic institutes and universities Master degree linguistic institutes and universities C 1
Bachelor degree nonlinguistic institutes and universities Higher education Master degree nonlinguistic institutes and universities B 2 The second language in Bachelor and Master degree institutions and universities Bachelor degree linguistic institutes and universities Master degree linguistic institutes and universities C 1
 School education falls apart into two stages: 1) the primary education (1 -4 forms) and 2) the secondary education (5 -9 forms). Education at academic lyceums is considered as upper secondary education. At vocational colleges ELT concerns 1) General English and 2) English for Specific Purposes (ESP) or English for Occupational Purposes (EOP). ESP is traditionally associated with Study at college and non-linguistic institute and university. The higher education provides training of qualified specialists at the Bachelor and Masters’ degree departments (Pre-service FL training). The Table above does not present post-graduate education (institution of senior scientific personnel and researches) and upgrading courses of In-service teachers training and retraining to change a qualification.
School education falls apart into two stages: 1) the primary education (1 -4 forms) and 2) the secondary education (5 -9 forms). Education at academic lyceums is considered as upper secondary education. At vocational colleges ELT concerns 1) General English and 2) English for Specific Purposes (ESP) or English for Occupational Purposes (EOP). ESP is traditionally associated with Study at college and non-linguistic institute and university. The higher education provides training of qualified specialists at the Bachelor and Masters’ degree departments (Pre-service FL training). The Table above does not present post-graduate education (institution of senior scientific personnel and researches) and upgrading courses of In-service teachers training and retraining to change a qualification.
 3. Developing writing competence according to FLT of Uzbekistan. At the beginning level (2 -4 classes) we teach graphics in EL (handwriting), i. e. teaching to write letters (alphabet) which interrelates with teaching reading as graphic-phonemic correspondence. Pupils must acquire print hand letters. At the same time we form elementary writing skills for conducting communicative-cognitive objectives in the written form. The second stage (5 -9 classes) at school must provide more intensive development of writing skills in different situations of communication. Topics and capacity of writing messages is broaden; the quality of produced text in the written form is improved At an academic lyceum and vocational college the level of the language proficiency in writing must provide more effective using it as a means of teaching, self-learning and academic study.
3. Developing writing competence according to FLT of Uzbekistan. At the beginning level (2 -4 classes) we teach graphics in EL (handwriting), i. e. teaching to write letters (alphabet) which interrelates with teaching reading as graphic-phonemic correspondence. Pupils must acquire print hand letters. At the same time we form elementary writing skills for conducting communicative-cognitive objectives in the written form. The second stage (5 -9 classes) at school must provide more intensive development of writing skills in different situations of communication. Topics and capacity of writing messages is broaden; the quality of produced text in the written form is improved At an academic lyceum and vocational college the level of the language proficiency in writing must provide more effective using it as a means of teaching, self-learning and academic study.
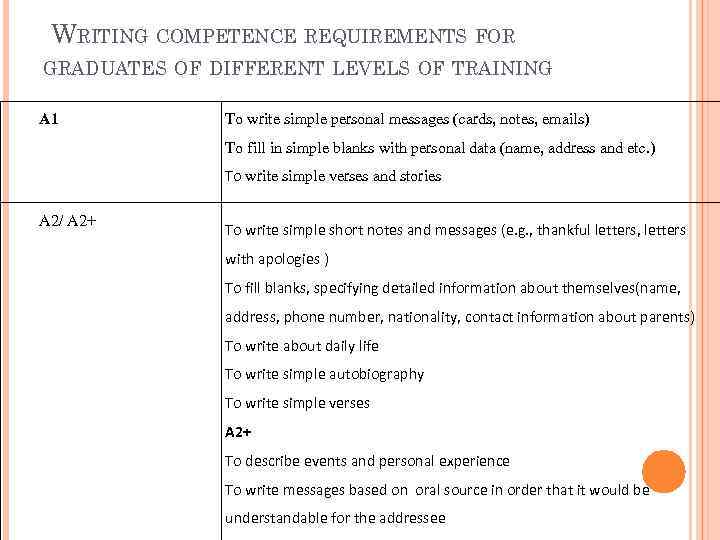 WRITING COMPETENCE REQUIREMENTS FOR GRADUATES OF DIFFERENT LEVELS OF TRAINING A 1 To write simple personal messages (cards, notes, emails) To fill in simple blanks with personal data (name, address and etc. ) To write simple verses and stories A 2/ A 2+ To write simple short notes and messages (e. g. , thankful letters, letters with apologies ) To fill blanks, specifying detailed information about themselves(name, address, phone number, nationality, contact information about parents) To write about daily life To write simple autobiography To write simple verses A 2+ To describe events and personal experience To write messages based on oral source in order that it would be understandable for the addressee
WRITING COMPETENCE REQUIREMENTS FOR GRADUATES OF DIFFERENT LEVELS OF TRAINING A 1 To write simple personal messages (cards, notes, emails) To fill in simple blanks with personal data (name, address and etc. ) To write simple verses and stories A 2/ A 2+ To write simple short notes and messages (e. g. , thankful letters, letters with apologies ) To fill blanks, specifying detailed information about themselves(name, address, phone number, nationality, contact information about parents) To write about daily life To write simple autobiography To write simple verses A 2+ To describe events and personal experience To write messages based on oral source in order that it would be understandable for the addressee
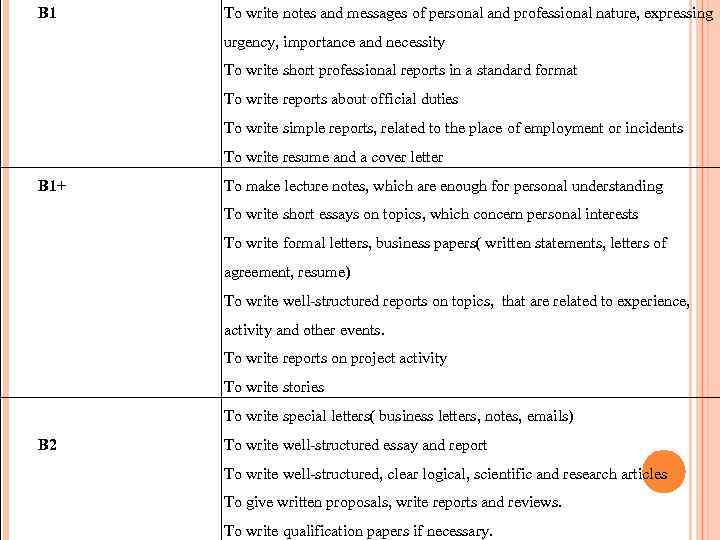 B 1 To write notes and messages of personal and professional nature, expressing urgency, importance and necessity To write short professional reports in a standard format To write reports about official duties To write simple reports, related to the place of employment or incidents To write resume and a cover letter B 1+ To make lecture notes, which are enough for personal understanding To write short essays on topics, which concern personal interests To write formal letters, business papers( written statements, letters of agreement, resume) To write well-structured reports on topics, that are related to experience, activity and other events. To write reports on project activity To write stories To write special letters( business letters, notes, emails) B 2 To write well-structured essay and report To write well-structured, clear logical, scientific and research articles To give written proposals, write reports and reviews. To write qualification papers if necessary.
B 1 To write notes and messages of personal and professional nature, expressing urgency, importance and necessity To write short professional reports in a standard format To write reports about official duties To write simple reports, related to the place of employment or incidents To write resume and a cover letter B 1+ To make lecture notes, which are enough for personal understanding To write short essays on topics, which concern personal interests To write formal letters, business papers( written statements, letters of agreement, resume) To write well-structured reports on topics, that are related to experience, activity and other events. To write reports on project activity To write stories To write special letters( business letters, notes, emails) B 2 To write well-structured essay and report To write well-structured, clear logical, scientific and research articles To give written proposals, write reports and reviews. To write qualification papers if necessary.
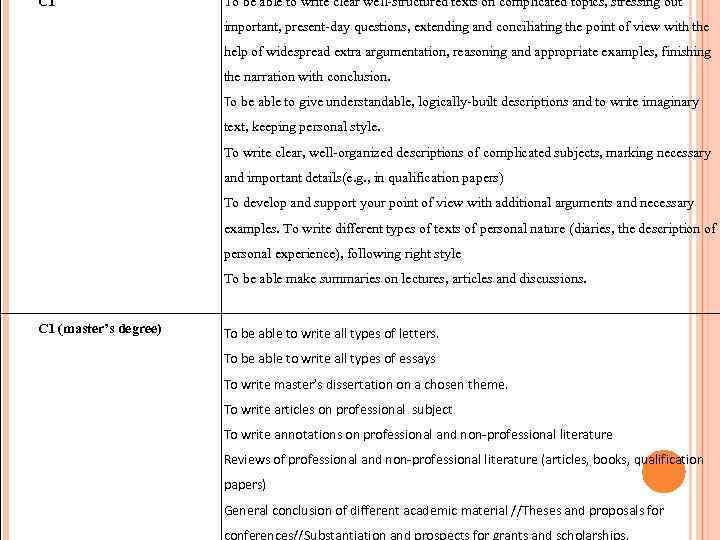 C 1 To be able to write clear well-structured texts on complicated topics, stressing out important, present-day questions, extending and conciliating the point of view with the help of widespread extra argumentation, reasoning and appropriate examples, finishing the narration with conclusion. To be able to give understandable, logically-built descriptions and to write imaginary text, keeping personal style. To write clear, well-organized descriptions of complicated subjects, marking necessary and important details(e. g. , in qualification papers) To develop and support your point of view with additional arguments and necessary examples. To write different types of texts of personal nature (diaries, the description of personal experience), following right style To be able make summaries on lectures, articles and discussions. C 1 (master’s degree) To be able to write all types of letters. To be able to write all types of essays To write master’s dissertation on a chosen theme. To write articles on professional subject To write annotations on professional and non-professional literature Reviews of professional and non-professional literature (articles, books, qualification papers) General conclusion of different academic material //Theses and proposals for conferences//Substantiation and prospects for grants and scholarships.
C 1 To be able to write clear well-structured texts on complicated topics, stressing out important, present-day questions, extending and conciliating the point of view with the help of widespread extra argumentation, reasoning and appropriate examples, finishing the narration with conclusion. To be able to give understandable, logically-built descriptions and to write imaginary text, keeping personal style. To write clear, well-organized descriptions of complicated subjects, marking necessary and important details(e. g. , in qualification papers) To develop and support your point of view with additional arguments and necessary examples. To write different types of texts of personal nature (diaries, the description of personal experience), following right style To be able make summaries on lectures, articles and discussions. C 1 (master’s degree) To be able to write all types of letters. To be able to write all types of essays To write master’s dissertation on a chosen theme. To write articles on professional subject To write annotations on professional and non-professional literature Reviews of professional and non-professional literature (articles, books, qualification papers) General conclusion of different academic material //Theses and proposals for conferences//Substantiation and prospects for grants and scholarships.
 4. WRITING AS A GOAL AND MEANS OFEL TEACHING AND LEARNING. Writing is a complex communicative activity. It helps to communicate in the written form with the help of graphical symbols. Writing is a type of speech activity as «a communicative skill to encode, store and send messages with the help of written symbols» . The product of this type of speech activity is a text for reading. In the ELT the writing is the goal and means of teaching and learning. The goal of teaching writing is to teach production of written texts which students can write in the mother tongue. To produce the written text students should master mechanics of writing. That’s why, in domestic methodology the two types of writing are distinguished: 1) mechanics of writing (handwriting, spelling, punctuation); 2) process of expressing ideas in a graphical form.
4. WRITING AS A GOAL AND MEANS OFEL TEACHING AND LEARNING. Writing is a complex communicative activity. It helps to communicate in the written form with the help of graphical symbols. Writing is a type of speech activity as «a communicative skill to encode, store and send messages with the help of written symbols» . The product of this type of speech activity is a text for reading. In the ELT the writing is the goal and means of teaching and learning. The goal of teaching writing is to teach production of written texts which students can write in the mother tongue. To produce the written text students should master mechanics of writing. That’s why, in domestic methodology the two types of writing are distinguished: 1) mechanics of writing (handwriting, spelling, punctuation); 2) process of expressing ideas in a graphical form.
 Teaching writing proposes mastering the text format as a typical layout of the text as a congratulation and condolences, telegrams, notes, signs, labels, captions, notices, menus, advertisements, personal or business letters, invitations, application for a job. CV (Curriculum Vitae), references, recipes, diaries, . log-books, dictation, note-taking, reproductions, abstracts, summaries, reviews, reports, precis, synopsis, case-studies, projects, essay, stories, poems.
Teaching writing proposes mastering the text format as a typical layout of the text as a congratulation and condolences, telegrams, notes, signs, labels, captions, notices, menus, advertisements, personal or business letters, invitations, application for a job. CV (Curriculum Vitae), references, recipes, diaries, . log-books, dictation, note-taking, reproductions, abstracts, summaries, reviews, reports, precis, synopsis, case-studies, projects, essay, stories, poems.



