 Theme 2. Fundamentals of social production
Theme 2. Fundamentals of social production
 1. The bases of social production
1. The bases of social production
 Tangible benefit - that is all that can meet daily living material needs, to benefit. Some material goods (air, water, sunlight) are available for people everywhere and at all times. It's free and gratuitous benefit.
Tangible benefit - that is all that can meet daily living material needs, to benefit. Some material goods (air, water, sunlight) are available for people everywhere and at all times. It's free and gratuitous benefit.
 Production - is a process of human interaction with nature, in which they, converting material nature, adapting it to meet their needs. Needs - is the need of anything necessary to sustain an individual, social group or society as a whole.
Production - is a process of human interaction with nature, in which they, converting material nature, adapting it to meet their needs. Needs - is the need of anything necessary to sustain an individual, social group or society as a whole.
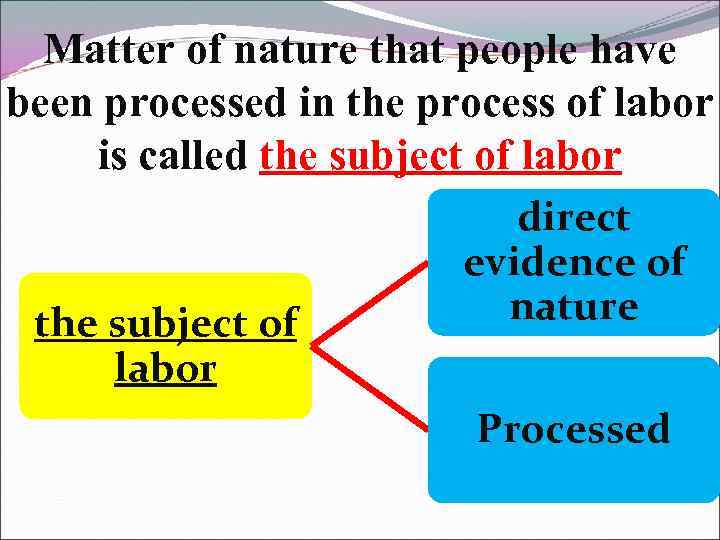 Matter of nature that people have been processed in the process of labor is called the subject of labor direct evidence of nature Processed
Matter of nature that people have been processed in the process of labor is called the subject of labor direct evidence of nature Processed
 Instruments of labor - this is what a person with a view to affecting labor. The subject of labor and means of labor, together constitute the means of production, or production resources. Resources - a combination of various elements of production, which can be used in the creation of goods and services.
Instruments of labor - this is what a person with a view to affecting labor. The subject of labor and means of labor, together constitute the means of production, or production resources. Resources - a combination of various elements of production, which can be used in the creation of goods and services.
 Natural resources - they are a natural base of production of material goods. They include: the land, its minerals, air, water, forests, etc. Physical resources - a collection of objects in which production takes place, they created a large mass of people, that is itself the result of production. Human resources - it is the population of working age, that is labor. Financial resources - are cash, which the company is committing to the production process. Information resources - is the data necessary for the operation of automated production and management with the help of computer technology.
Natural resources - they are a natural base of production of material goods. They include: the land, its minerals, air, water, forests, etc. Physical resources - a collection of objects in which production takes place, they created a large mass of people, that is itself the result of production. Human resources - it is the population of working age, that is labor. Financial resources - are cash, which the company is committing to the production process. Information resources - is the data necessary for the operation of automated production and management with the help of computer technology.
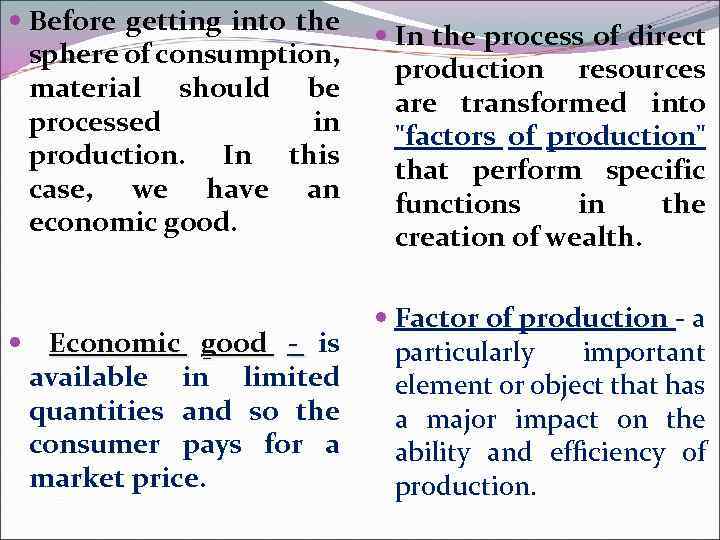 Before getting into the sphere of consumption, material should be processed in production. In this case, we have an economic good. Economic good - is available in limited quantities and so the consumer pays for a market price. In the process of direct production resources are transformed into "factors of production" that perform specific functions in the creation of wealth. Factor of production - a particularly important element or object that has a major impact on the ability and efficiency of production.
Before getting into the sphere of consumption, material should be processed in production. In this case, we have an economic good. Economic good - is available in limited quantities and so the consumer pays for a market price. In the process of direct production resources are transformed into "factors of production" that perform specific functions in the creation of wealth. Factor of production - a particularly important element or object that has a major impact on the ability and efficiency of production.
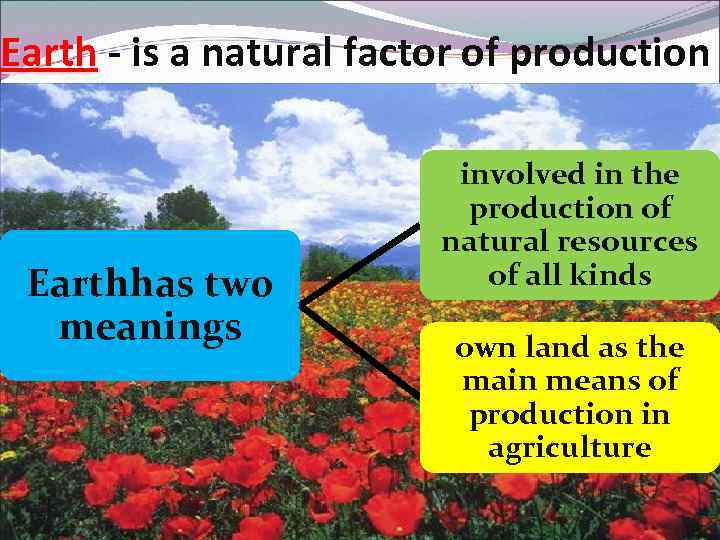 Earth - is a natural factor of production Earthhas two meanings involved in the production of natural resources of all kinds own land as the main means of production in agriculture
Earth - is a natural factor of production Earthhas two meanings involved in the production of natural resources of all kinds own land as the main means of production in agriculture
 Capital - a collection made of material goods, which are used for the production of future wealth. This - tools, equipment, facilities, communications, transportation, distributi on network, etc. Work - as a factor of production is the process of implementation of the ability of people to productive activities. Entrepreneurial activity (ability) this is a specific factor of production. It involves the use of initiative, ingenuity and risk in the organization of production.
Capital - a collection made of material goods, which are used for the production of future wealth. This - tools, equipment, facilities, communications, transportation, distributi on network, etc. Work - as a factor of production is the process of implementation of the ability of people to productive activities. Entrepreneurial activity (ability) this is a specific factor of production. It involves the use of initiative, ingenuity and risk in the organization of production.
 2. Structure of social production
2. Structure of social production
 production material nonmaterial production
production material nonmaterial production
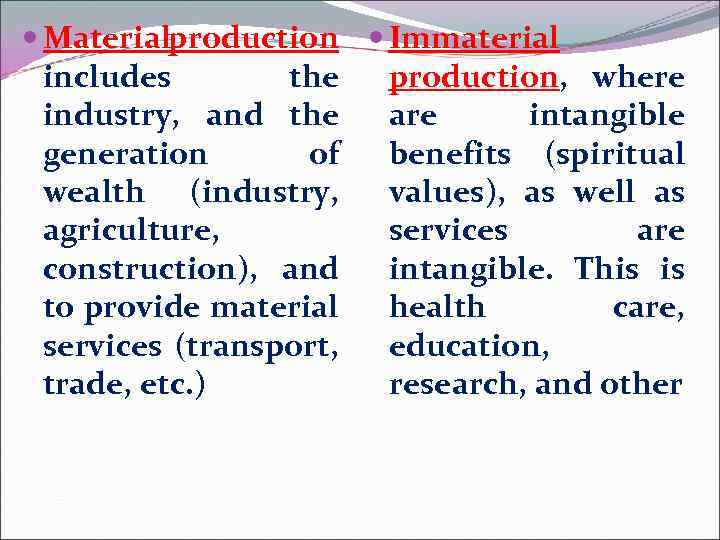 Materialproduction Immaterial includes the production, where industry, and the are intangible generation of benefits (spiritual wealth (industry, values), as well as agriculture, services are construction), and intangible. This is to provide material health care, services (transport, education, trade, etc. ) research, and other
Materialproduction Immaterial includes the production, where industry, and the are intangible generation of benefits (spiritual wealth (industry, values), as well as agriculture, services are construction), and intangible. This is to provide material health care, services (transport, education, trade, etc. ) research, and other
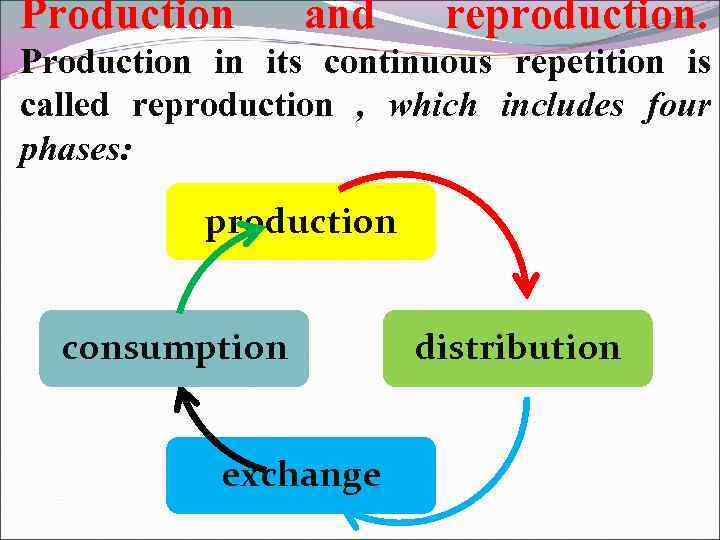 Production and reproduction. Production in its continuous repetition is called reproduction , which includes four phases: production consumption exchange distribution
Production and reproduction. Production in its continuous repetition is called reproduction , which includes four phases: production consumption exchange distribution
 Production is vital to the economy, as the standard of living of people in any country depends on how much wealth is created in it for everyone. Distribution reveals the share of each person to create wealth. It depends on the number of created wealth for distribution. Exchange determined by the nature and the development of production. They set the amount of exchange and its social form - or barter, or exchange of goods. Consumption is the final stage of the product flow. It sold its use-ability.
Production is vital to the economy, as the standard of living of people in any country depends on how much wealth is created in it for everyone. Distribution reveals the share of each person to create wealth. It depends on the number of created wealth for distribution. Exchange determined by the nature and the development of production. They set the amount of exchange and its social form - or barter, or exchange of goods. Consumption is the final stage of the product flow. It sold its use-ability.
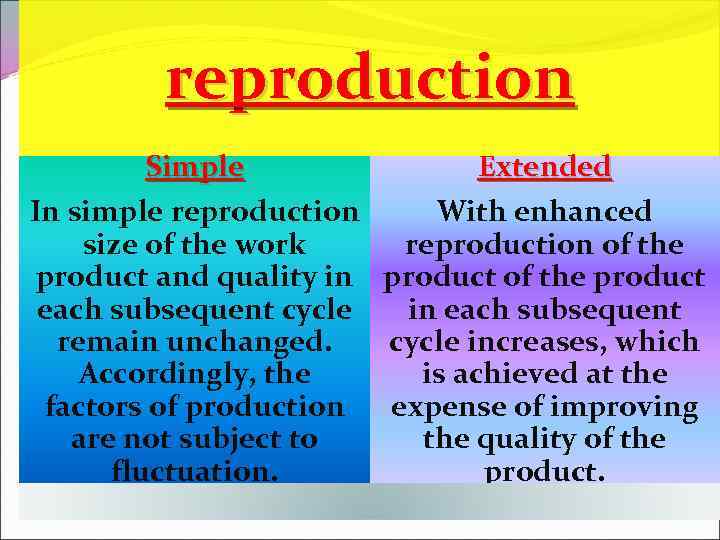 reproduction Simple Extended In simple reproduction With enhanced size of the work reproduction of the product and quality in product of the product each subsequent cycle in each subsequent remain unchanged. cycle increases, which Accordingly, the is achieved at the factors of production expense of improving are not subject to the quality of the fluctuation. product.
reproduction Simple Extended In simple reproduction With enhanced size of the work reproduction of the product and quality in product of the product each subsequent cycle in each subsequent remain unchanged. cycle increases, which Accordingly, the is achieved at the factors of production expense of improving are not subject to the quality of the fluctuation. product.
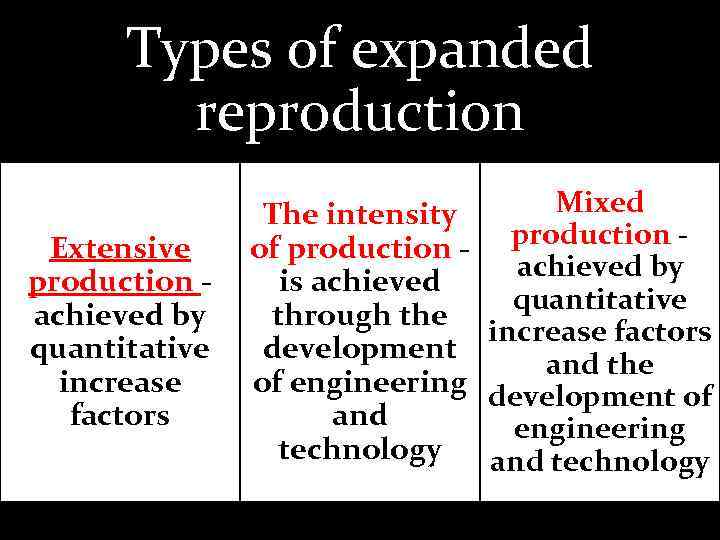 Types of expanded reproduction Extensive production achieved by quantitative increase factors Mixed The intensity production of production achieved by is achieved quantitative through the increase factors development and the of engineering development of and engineering technology and technology
Types of expanded reproduction Extensive production achieved by quantitative increase factors Mixed The intensity production of production achieved by is achieved quantitative through the increase factors development and the of engineering development of and engineering technology and technology
 3. Types of economic systems
3. Types of economic systems
 System - a set of components and parts in relation to each other, forming the integrity, unity Systems forms Technology biological social
System - a set of components and parts in relation to each other, forming the integrity, unity Systems forms Technology biological social
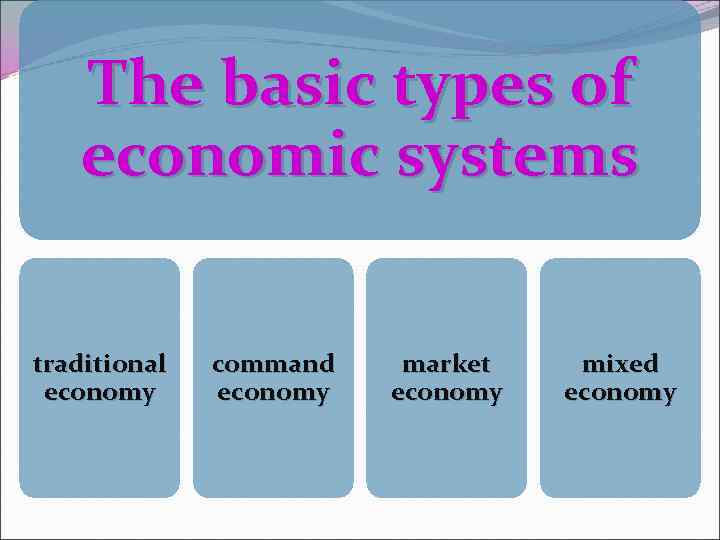 The basic types of economic systems traditional economy command economy market economy mixed economy
The basic types of economic systems traditional economy command economy market economy mixed economy
 The characteristic features of a traditional economy production, distribution and exchange is based on the customs, traditions, religious rites • predominant primary sector (agriculture) low reproductive rates and socio-economic stagnation • limitations of technical progress • Sustainable excess population growth over the pace of growth in industrial production • significant external financial debt • the high role of the state and law enforcement agencies
The characteristic features of a traditional economy production, distribution and exchange is based on the customs, traditions, religious rites • predominant primary sector (agriculture) low reproductive rates and socio-economic stagnation • limitations of technical progress • Sustainable excess population growth over the pace of growth in industrial production • significant external financial debt • the high role of the state and law enforcement agencies
 Command Systems economy is specific and differs from other systems. In economics, there is only the state ownership of the means of production Its economic base is a directive (central) planning. Centralized economic plan is required on all business entities. Mixed economy - a set of different historical determined forms of ownership and their residual effects that exist in a particular nation-state economic system.
Command Systems economy is specific and differs from other systems. In economics, there is only the state ownership of the means of production Its economic base is a directive (central) planning. Centralized economic plan is required on all business entities. Mixed economy - a set of different historical determined forms of ownership and their residual effects that exist in a particular nation-state economic system.
 The market economy • private property • freedom of choice • a personal interest • Competition • free pricing • State intervention is limited
The market economy • private property • freedom of choice • a personal interest • Competition • free pricing • State intervention is limited
 Homework You need to prepare the following topics as the report : The main aspects of the traditional economy The main aspects of the command economy The main aspects of the market economy The main aspects of the mixed economy Types of expanded reproduction Production and reproduction
Homework You need to prepare the following topics as the report : The main aspects of the traditional economy The main aspects of the command economy The main aspects of the market economy The main aspects of the mixed economy Types of expanded reproduction Production and reproduction


