2Презентац_Контроллинг_тема2(англ).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Theme 2. Controlling objects and their classification K. Yakovenko

Controlling Objects: Costs Responsibility Centers

Classification of costs according to three types of management tasks For costing, pricing and revenue costs are divided into: • Manufacturing Costs and Non-Manufacturing Costs • Prime Costs and Overheads • Direct Cost and Indirect Cost • Expired Costs and Unexpired Costs

Classification of costs according to three types of management tasks For decision-making in Controlling are the following costs: • Fixed Costs and Variable Costs • Relevant Costs and Irrelevant Costs • Outlay Costs and Opportunity Costs • Differential Costs and Marginal Costs

Classification of costs according to three types of management tasks For operational management of the process control and regulation costs are classified by such characteristics: • Possibly referring to a specific cost object • The nature depending on the amount of industrial activity • The degree of adjustability • Controllable Costs and Non-Controllable Costs

Cost analysis for decision (the concept of relevant costs) example: To build a new manufacturing building spent 1300 thous. UAH. For its commissioning will need to spend another 1, 200 thous. UAH. Revenue from product sales, which will be made in this industrial building for the next five years will amount to 2300 thous. UAH. You must decide whether to continue construction.
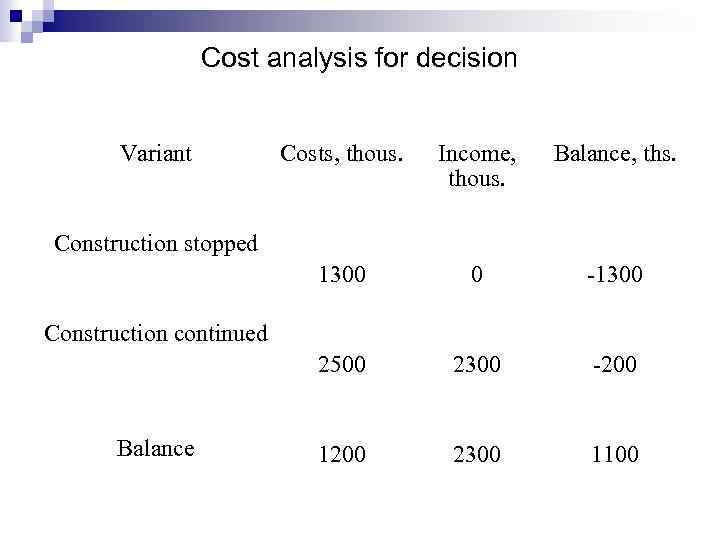
Cost analysis for decision Variant Costs, thous. Income, thous. Balance, ths. 1300 0 -1300 2500 2300 -200 1200 2300 1100 Construction stopped Construction continued Balance

The concept of opportunity cost example: The plant has the ability to execute the order of some company. The costs of the implementation of the order will amount to UAH 100 thousand UAH. The plant operates at full capacity, so to run this company will be able to order only at the expense of another order, the profits from which would have amounted to 35 thousand UAH. You must decide on the value price of the order.

Classification of costs relative to objectives Issues facing the managers Classification of costs How will the income when assessing changes in prices and production costs? What consequences will have a change in product mix? What is the optimal product mix? What should be the output? According to the dynamics of costs relative to the volume of production: fixed; variable; semi variable What are the costs of production as a whole? What is the cost of producing this type of product or products? What is the cost of this department? Possibly referring to a specific cost object: direct; Indirect How large are the deviations from the plan and the fact of what they called? Who is responsible for the deviation? What are the specific reserve saving? According to the degree of adjustability: fully adjustable; partially controlled poorly regulated (set)

Influence factors on the cost Factors Room space Value of property Number of employees Number of Orders Number of changeovers Types of costs Rent Insurance The cost of maintaining the dining room The cost of processing orders The cost of retooling equipment
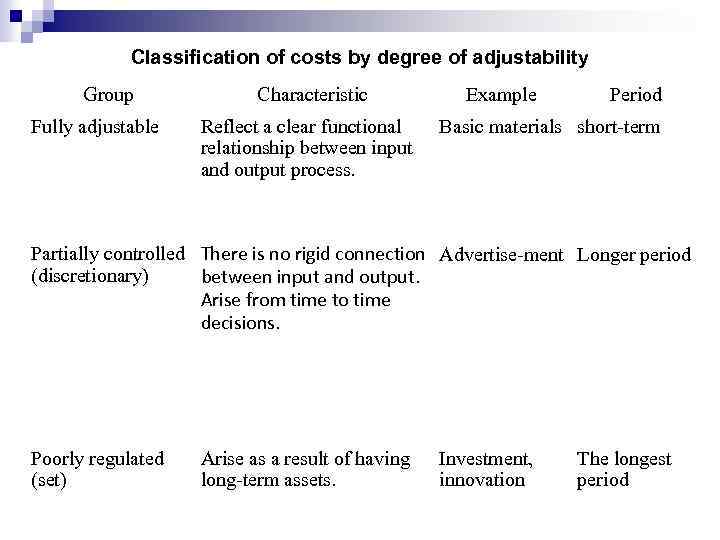
Classification of costs by degree of adjustability Group Fully adjustable Characteristic Reflect a clear functional relationship between input and output process. Example Period Basic materials short-term Partially controlled There is no rigid connection Advertise-ment Longer period (discretionary) between input and output. Arise from time to time decisions. Poorly regulated (set) Arise as a result of having long-term assets. Investment, innovation The longest period
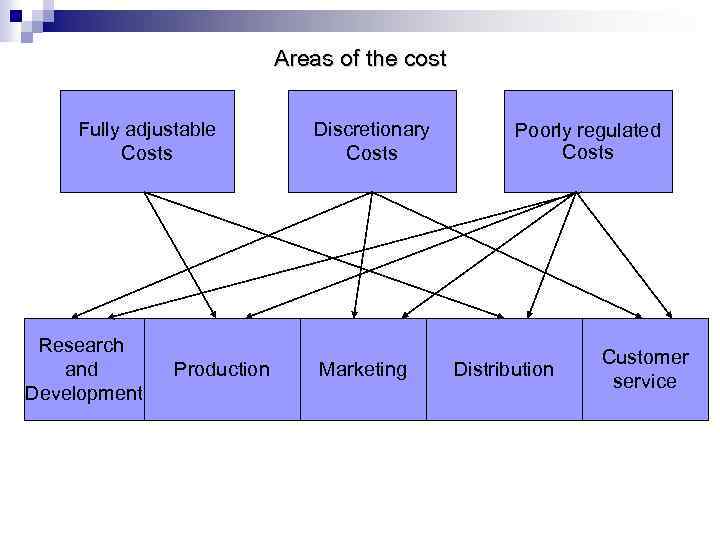
Areas of the cost Fully adjustable Costs Research and Development Production Discretionary Costs Marketing Poorly regulated Costs Distribution Customer service

Costs by activity: Costs of procurement activity; Production costs; Costs of sales activity; Costs of organizational activity.
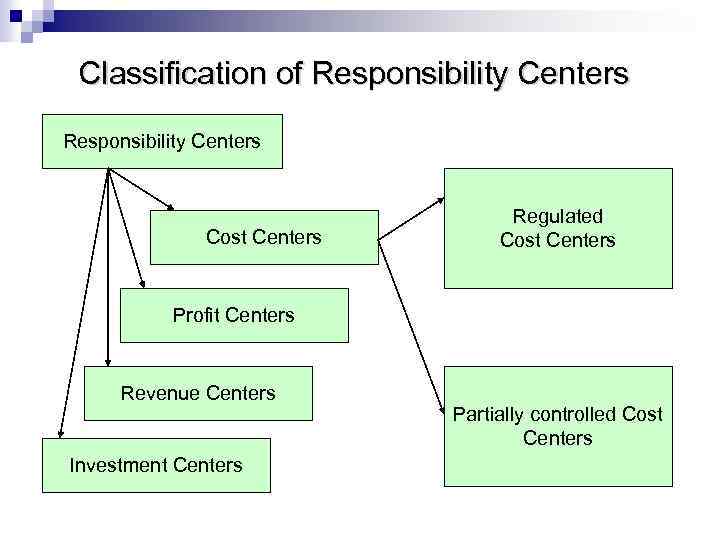
Classification of Responsibility Centers Cost Centers Regulated Cost Centers Profit Centers Revenue Centers Investment Centers Partially controlled Cost Centers
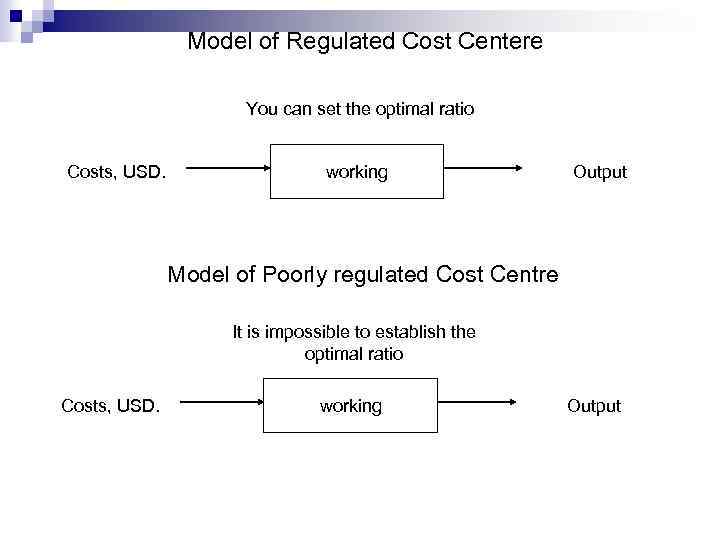
Model of Regulated Cost Centere You can set the optimal ratio Costs, USD. working Output Model of Poorly regulated Cost Centre It is impossible to establish the optimal ratio Costs, USD. working Output
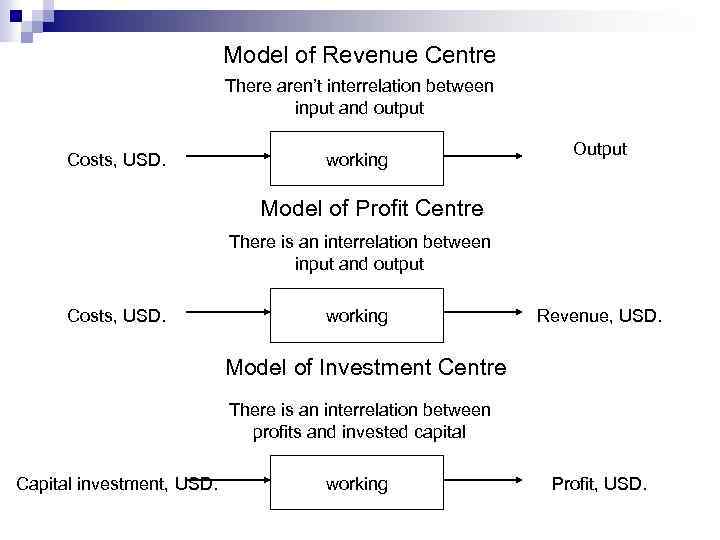
Model of Revenue Centre There aren’t interrelation between input and output Costs, USD. working Output Model of Profit Centre There is an interrelation between input and output Costs, USD. working Revenue, USD. Model of Investment Centre There is an interrelation between profits and invested capital Capital investment, USD. working Profit, USD.
2Презентац_Контроллинг_тема2(англ).ppt