Theme 12.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Theme 12. Cyclical economic development and economic growth
Theme 12. Cyclical economic development and economic growth
 1. Cyclical development of a market economy.
1. Cyclical development of a market economy.
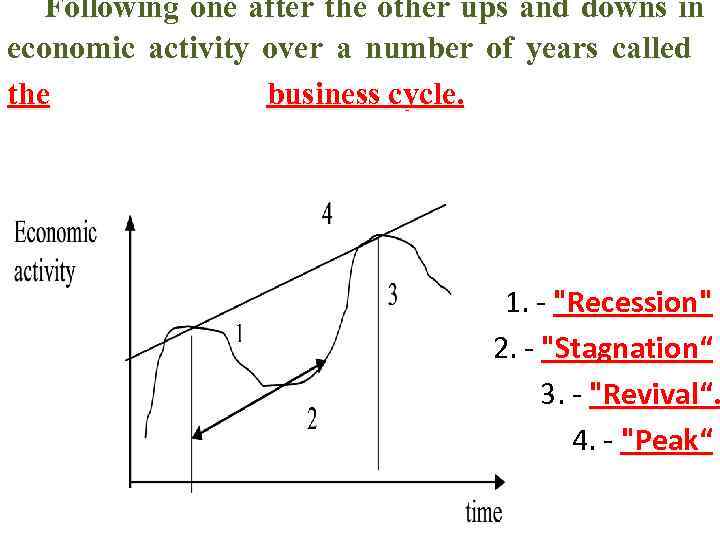 Following one after the other ups and downs in economic activity over a number of years called the business cycle. 1. - "Recession" 2. - "Stagnation“ 3. - "Revival“. 4. - "Peak“
Following one after the other ups and downs in economic activity over a number of years called the business cycle. 1. - "Recession" 2. - "Stagnation“ 3. - "Revival“. 4. - "Peak“
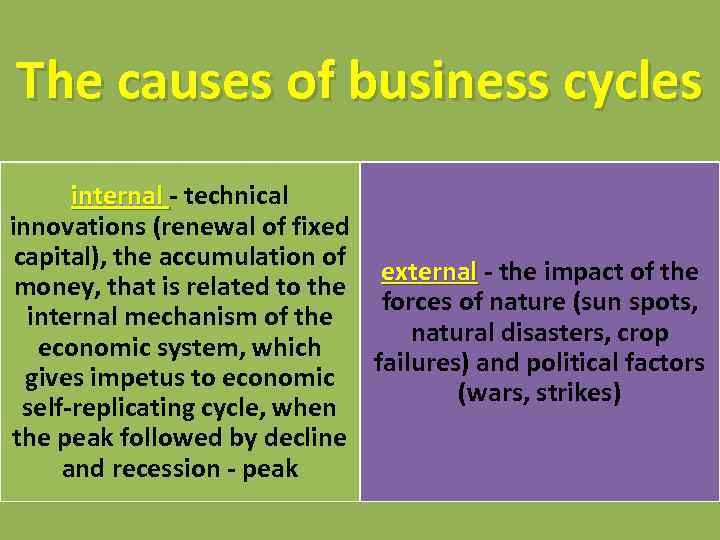 The causes of business cycles internal - technical innovations (renewal of fixed capital), the accumulation of external - the impact of the money, that is related to the forces of nature (sun spots, internal mechanism of the natural disasters, crop economic system, which failures) and political factors gives impetus to economic (wars, strikes) self-replicating cycle, when the peak followed by decline and recession - peak
The causes of business cycles internal - technical innovations (renewal of fixed capital), the accumulation of external - the impact of the money, that is related to the forces of nature (sun spots, internal mechanism of the natural disasters, crop economic system, which failures) and political factors gives impetus to economic (wars, strikes) self-replicating cycle, when the peak followed by decline and recession - peak
 The economic crisis of overproduction has two sides devastating. It is improving. It is devastating associated with the inevitable, because removal of the existing during the Depression abnormal proportions falling prices makes in the economy, when production the production of goods unprofitable: it does is much higher than not give the usual, the consumer demand. average profit.
The economic crisis of overproduction has two sides devastating. It is improving. It is devastating associated with the inevitable, because removal of the existing during the Depression abnormal proportions falling prices makes in the economy, when production the production of goods unprofitable: it does is much higher than not give the usual, the consumer demand. average profit.
 2. The economic cycle and its variants
2. The economic cycle and its variants
 The Economic cycle and its variants Kitchin cycles (cycles of reserves) -short waves (2 -4 years) on the basis of a study of the accounts and sales prices moving inventory. The medium-term crisis Zhuglara (business cycle, industrial cycle) - 712 years. They coincided with the cycles of investment, which in turn brought about a change of GNP, investment, and employment. Kuznets cycles (16 - 25 years). In construction, they have the largest years). relative amplitude. Kondratieff cycles (40 -60 years).
The Economic cycle and its variants Kitchin cycles (cycles of reserves) -short waves (2 -4 years) on the basis of a study of the accounts and sales prices moving inventory. The medium-term crisis Zhuglara (business cycle, industrial cycle) - 712 years. They coincided with the cycles of investment, which in turn brought about a change of GNP, investment, and employment. Kuznets cycles (16 - 25 years). In construction, they have the largest years). relative amplitude. Kondratieff cycles (40 -60 years).
 Crises of the late twentieth century are different from those that occurred earlier. Fourth, in the postwar period Secondly - the First of all, - the has increased shorter was the Third, blurs the phase of the duration of depression boundaries crisis was recovery phase, and in between the accompanied and the post-war phase of by increased amplitude of crisis it is recovery and general level of fluctuations in difficult to recovery phase. prices. business detect. activity decreased.
Crises of the late twentieth century are different from those that occurred earlier. Fourth, in the postwar period Secondly - the First of all, - the has increased shorter was the Third, blurs the phase of the duration of depression boundaries crisis was recovery phase, and in between the accompanied and the post-war phase of by increased amplitude of crisis it is recovery and general level of fluctuations in difficult to recovery phase. prices. business detect. activity decreased.
 3. The concept of economic growth and its measurement
3. The concept of economic growth and its measurement
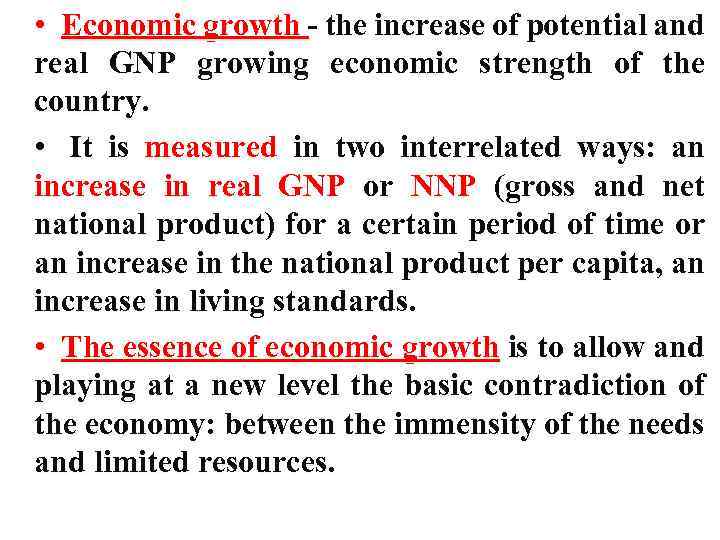 • Economic growth - the increase of potential and real GNP growing economic strength of the country. • It is measured in two interrelated ways: an increase in real GNP or NNP (gross and net national product) for a certain period of time or an increase in the national product per capita, an increase in living standards. • The essence of economic growth is to allow and playing at a new level the basic contradiction of the economy: between the immensity of the needs and limited resources.
• Economic growth - the increase of potential and real GNP growing economic strength of the country. • It is measured in two interrelated ways: an increase in real GNP or NNP (gross and net national product) for a certain period of time or an increase in the national product per capita, an increase in living standards. • The essence of economic growth is to allow and playing at a new level the basic contradiction of the economy: between the immensity of the needs and limited resources.
 Goals are to economic growth Maintenance Raising living of national standards security
Goals are to economic growth Maintenance Raising living of national standards security
 Economic growth is measured by the following indicators: • increase in quality of life (social protection of unemployed, the disabled) • increased investment in human capital • NI growth per capita • improving the quality and increasing diversity of manufactured goods and services • . improve the distribution of NI in the population, ie growth in real income per capita • increase in free time • reducing inflation • employment growth
Economic growth is measured by the following indicators: • increase in quality of life (social protection of unemployed, the disabled) • increased investment in human capital • NI growth per capita • improving the quality and increasing diversity of manufactured goods and services • . improve the distribution of NI in the population, ie growth in real income per capita • increase in free time • reducing inflation • employment growth
 Average. year. % = GNP growth this year, GNP growth last year GNP growth last year
Average. year. % = GNP growth this year, GNP growth last year GNP growth last year


