IBS 1.2 M&R week1(1).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56

Theme 1. 1 Research IBS 2012

Theme 1. 2 Research Jo Spaubeck Br. 1. 11 jo. spaubeck@hszuyd. nl

Week 1 Programme of the day: Overview theme 1. 1 M&R Courses Workload Research, the start-up Research process Research proposal Questionnaire

Overview theme 1. 1 (1) Theme components: 1. M&R 2. Statistics 3. Marketing plan (practice & skills) Lectures M&R during 7 weeks (week 1 -4 focus on research, week 5 -7 focus on marketing) Lectures 2 * 45 min. a week Input for the marketing plan and exam!

Overview theme 1. 1 (2) Practice & Skills Group work: writing the actual marketing plan (>111 hours!) 15 minute obligatory meeting in week 2, 4 and 6 Not attending a meeting will imply that you have lost your right to any feedback Before the meeting you hand in the written parts of the marketing plan 2 workdays before the meeting-> if nothing is handed in or if the email is too late, the meeting is cancelled.

Workload 7 actual work weeks During these 7 weeks you will do the market research AND write the marketing plan Week 1 -> pick a company and product, research proposal Week 2 -> finetuning of research proposal, the survey must be finished Conclusion -> a slow start-up is impossible (if you want to receive the credits)

Topic of your research (1) • Keep it simple • Who is the target group? e. g. students • b 2 c better than b 2 b for this research • Be creative. What are your interests? • The research must be international

Topic of your research (2) • • • You do the research in 2 markets For the students who have German or French as a 2 nd language: • You translate your English survey into German or French • The 2 nd market is therefore in Germany (e. g. Aachen) or Belgium (e. g. Liege) The other students (2 nd language = Spanish/Dutch) • You also have 2 markets, but both will be interviewed in English So when forming groups: Students who have German as a 2 nd language form groups amongs themselves Students who have French as a 2 nd language form groups amongs themselves The other students (2 nd language = Spanish/Dutch) form groups amongs themselves No mingling!

Deadlines Deadline marketingplan 16 th January 17. 00 hours (daytime)-> pigeon hole and digital. .

Structure marketing plan Table of contents Chapter 1. 1 Chapter 1. 2 Chapter 1. 3 Chapter 1. 4 Chapter 1. 5 Chapter 1. 6 Research proposal Introduction to chapter (should be in every chapter) Company description Problem statement/relevance Objective (assignment provider and researcher) Central question and research questions Methodology (Desk research, Field research) Type of research (has to be quantitative), describe population, sample size, nonresponse, validity, reliability, representativeness, research methodology, data collection method (has to be questionnaire).

Chapter 2 External analysis Macro-> Demografic, Economic, Social-Cultural, Technological, Ecological en Political-legal Meso -> customers (the results of your field research have to be put in this paragraph), competitors, suppliers, intermediaries, distributers en public groups. Analyze external environment to formulate opportunities and threats Use theory from theme 1 Chapter 3 Internal analysis Marketing mix Business functions and resources Analyze own company to formulate relative strengths and weaknesses Chapter 4 SWOT analysis en confrontation matrix Chapter 5 Conclusions en recommendations (concrete answers to the central question and research questions, e. g. how to use the marketing mix to make use of opportunities or defend against threats) Bibliography (Use APA style of referencing, plagiarism is fraud -> documents on Blackboard) Annexes (a. o. SPSS output)

Any questions about the course outline?

Week 1 Research, the start-up Topics: Research process Research proposal Questionnaire Theory: Baarda Ch 1, 3. 1 and 3. 2 This week market research: Decide on a company and product Research proposal Start making the questionnaire (must be finished in week 2!)

The nature of research Research = ‘Something that people undertake in order to find things out in a systematic way, thereby increasing their knowledge’ Saunders et al. (2009) Characteristics: Data are collected systematically Data are interpreted systematically There is a clear purpose to find things out

2 types of research Basic and applied research
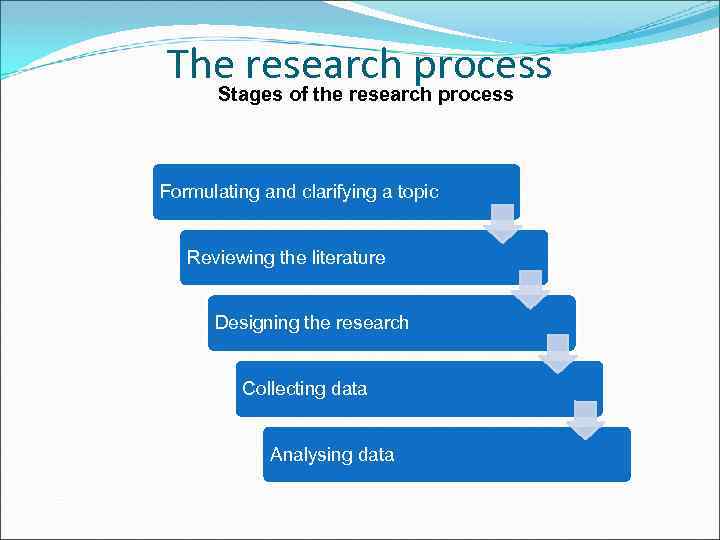
The research process Stages of the research process Formulating and clarifying a topic Reviewing the literature Designing the research Collecting data Analysing data

Turning ideas into research projects Examples of research ideas and their derived focus questions

Turning ideas into research projects Include SMART Personal objectives S pecific M easurable A chievable R ealistic T imely I nspiring C ompetence

The importance of theory Asking for opinions and gathering facts – 'what' questions (descriptive research) Using questions that go beyond description and require analysis – 'why' questions In order to: Explain phenomena Analyse relationships Predict outcomes Compare and generalise

Writing your research proposal Purposes of the research proposal To organise your ideas To convince your audience To contract with your client (your tutor) To meet ethical requirements

The research proposal includes… You plan to conduct a decent market research A. Problem statement. Describe the current (unwanted) situation = the reason you are doing the research B. The objective. Objective of the researcher and the objective of the company (SMARTIC) C. Central question = objective of the researcher (purpose of the research) D. Research questions = several questions that enable you to answer the central question E. Types of research-> field research (primary), desk (secondary) research F. Methodology = research methods e. g. experimental, survey, . . 21

An example. . Many traffic accidents occur because drivers ignore red traffic lights. A preliminary study has shown that less accidents occur at crossroads where camera’s have been placed to control these drivers. Problem statement; ignoring red traffic lights causes traffic accidents… Objective; decrease the number of traffic accidents Central question; Which tools could be used to decrease the number of traffic accidents caused by ignoring red 22 traffic lights?

The first phases of the market research Ad. A) Problem statement= relevance : what is going on? -> background of the problem, thourough! theoretical -> contribute to scientific knowledge practical -> research helps to solve the problem e. g. start up a business, make money Ad. B) Objective Most important: objective of the company that has ordered/hired the researcher/consultant to conduct the research Ad. C) Central question Objective of the researcher that is doing the research 23
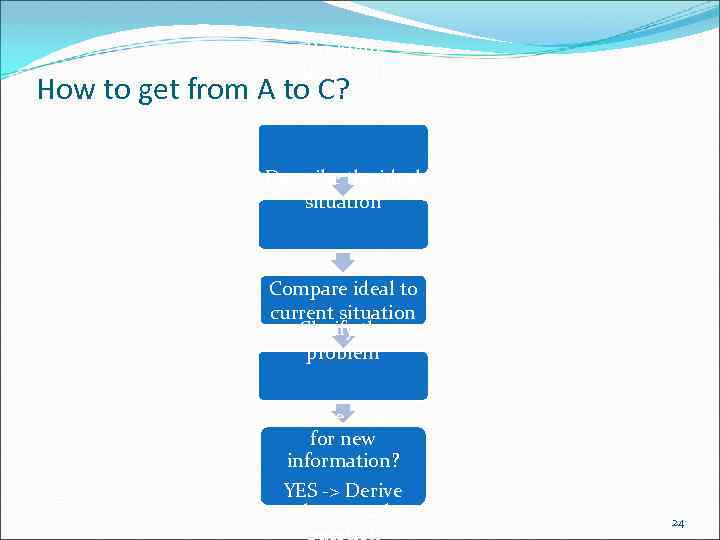
Problem statement How to get from A to C? Describe the ideal situation Compare ideal to current situation Clarify the problem Is there a need for new information? YES -> Derive the central question 24

Ad. C. Central question Always a question Translation of the research proposal No general questions that are too vague So no: “How come? ” and “Why? ” “How…? No normative questions -> “What is good/bad/ugly to…? ” Can be different for everyone 25

Ad. D) Research questions The central questions splits up into to several research questions. Making research questions specific takes time and effort Research questions will help you find solutions for the central question Back to the example: Central question: Which tools could be used to decrease the number of traffic accidents caused by ignoring red traffic lights? 1 possible underlying research question: Will placing camera’s on the crossroads lead to a decrease in car drivers ignoring red traffic lights? 26

Ad. D) Research questions Types of research questions are generally: Frequency questions (how many, how often) Questions that explain differences -> (red traffic light -> difference camera’s yes/no) Questions that explain relations (is there a connection between. . ? ) Causal vs. Correlation Do ice-creams cause drowning? Keep in mind!! Research questions are not survey questions 27

Questionnaires

Use of questionnaires (1) Definition of Questionnaires Techniques of data collection in which each person is asked to respond to the same set of questions in a predetermined order Adapted from de. Vaus (2002)

Use of questionnaires (2) When to use questionnaires For explanatory or descriptive research Linked with other methods in a multiple-methods research design To collect responses from a large sample prior to quantitative analysis
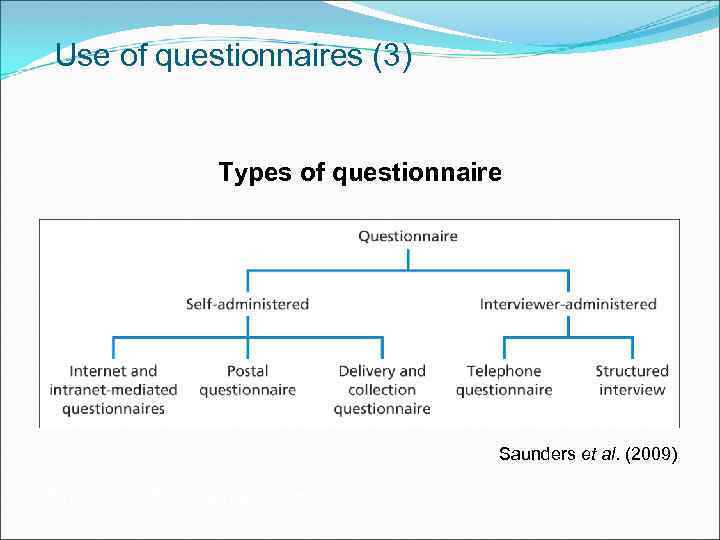
Use of questionnaires (3) Types of questionnaire Saunders et al. (2009) Figure 11. 1 Types of questionnaire
Personal vs. Telephone vs. Mail interviews 1) Face to face: Small sample Many questions Complicated questions Takes time and money 32

Personal vs. Telephone vs. Mail interviews 2) Telephone: Large sample Easy questions Open-ended questions Respondent can’t look anything up Fast 33

Personal vs. Telephone vs. Mail interviews 3) Mail: Hard to reach large sample -> low response Closed questions Interesting questions Personal questions Less time and money 34
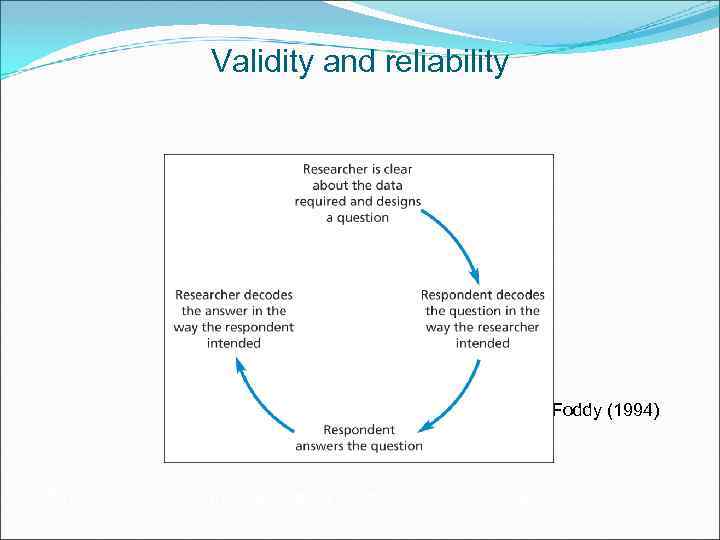
Validity and reliability Source: developed from Foddy (1994) Figure 11. 2 Stages that must occur if a question is to be valid and reliable

Assessing validity Internal -> am I measuring what I wanted to measure? Content -> do the questions in the questionnaire cover my research questions? Criterion – related (predictive) -> can I predict how the respondent will behave based on his answers? Construct -> do the questions actually measure the constructs I intended to measure?

Testing for reliability- the 3 stage process Test re-test -> administrating the same questionnaire to a respondent twice Internal consistency ->correlating the response of a question to another question Alternative form -> using control questions to ask the same thing twice Mitchell (1996)

Examples of question types Open-ended questions List questions -> respondent selects from a list Category questions -> respondent selects from set of categories Ranking questions -> respondent is asked to place something in order Rating questions -> use of a rating device/list Quantity questions -> respondent gives an amount to answer the questions Matrix questions -> use of a grid to answer 2 or more questions A small test. .

What type of question is it? Open-ended questions List questions Category questions Ranking questions Rating questions Quantity questions Matrix questions ? 7 What is your religion? Please tick the appropriate box Buddhist Christian Hindu Jewish Muslim Sikh None Other Saunders et al. (2009)

What type of question is it? List questions 7 What is your religion? Please tick the appropriate box Buddhist Christian Hindu Jewish Muslim Sikh None Other Saunders et al. (2009)

What type of question is it? Open-ended questions List questions Category questions Ranking questions Rating questions Quantity questions Matrix questions ? 6 Please list up to three things you like about your job 1…………………… 2…………………… 3…………………… Saunders et al. (2009)

What type of question is it? Open questions 6 Please list up to three things you like about your job 1…………………… 2…………………… 3…………………… Saunders et al. (2009)
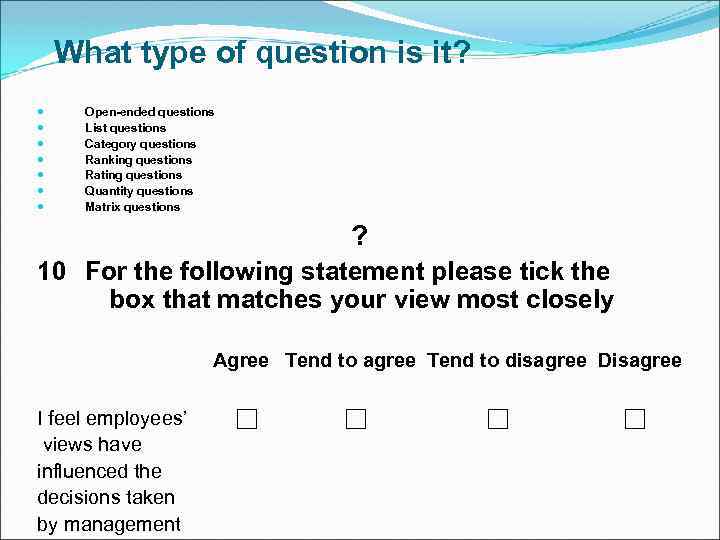
What type of question is it? Open-ended questions List questions Category questions Ranking questions Rating questions Quantity questions Matrix questions ? 10 For the following statement please tick the box that matches your view most closely Agree Tend to agree Tend to disagree Disagree I feel employees’ views have influenced the decisions taken by management

What type of question is it? Rating questions 10 For the following statement please tick the box that matches your view most closely Agree Tend to agree Tend to disagree Disagree I feel employees’ views have influenced the decisions taken by management Saunders et al. (2009)

What type of question is it? Open-ended questions List questions Category questions Ranking questions Rating questions Quantity questions Matrix questions ? 8 How often do you visit the shopping centre? Interviewer: listen to the respondent’s answer and tick as appropriate First visit Once a week Less than fortnightly to once a month 2 or more times a week Less than once a week to fortnightly Less often Saunders et al. (2009)

What type of question is it? Category questions 8 How often do you visit the shopping centre? Interviewer: listen to the respondent’s answer and tick as appropriate First visit Once a week Less than fortnightly to once a month 2 or more times a week Less than once a week to fortnightly Less often Saunders et al. (2009)

What type of question is it? ? 9 Please number each of the factors listed below in order of importance to you in choosing a new car. Number the most important 1, the next 2 and so on. If a factor has no importance at all, please leave blank. Factor Carbon dioxide emissions Boot size Depreciation Price Importance [ ] [ ] Adapted from Saunders et al. (2009)

What type of question is it? Ranking questions 9 Please number each of the factors listed below in order of importance to you in choosing a new car. Number the most important 1, the next 2 and so on. If a factor has no importance at all, please leave blank. Factor Carbon dioxide emissions Boot size Depreciation Price Importance [ ] [ ] Adapted from Saunders et al. (2009)

What type of question is it? Open-ended questions List questions Category questions Ranking questions Rating questions Quantity questions Matrix questions ? 14 What is your year of birth? (For example, for 1988 write: ) 1 9 8 8
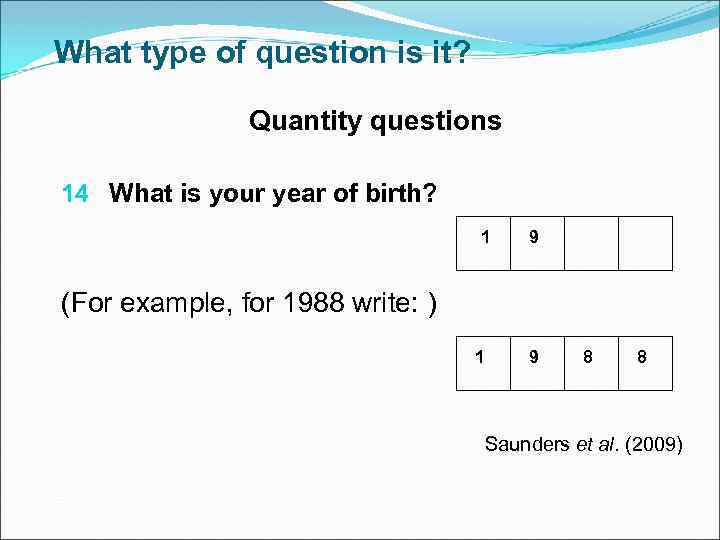
What type of question is it? Quantity questions 14 What is your year of birth? 1 9 (For example, for 1988 write: ) 1 9 8 8 Saunders et al. (2009)
Open ended vs. Close-ended questions Open (no answer set provided) vs closed (answer set provided). Open questions provide you with more information but are more difficult to interpret/code Closed questions are sometimes limited but are easier to code -> for marketingplan: only closed questions 51

Setting up the questionnaire One subject at the time Clear No difficult use of language No jargon -> “what do you think of the marketing mix of coca cola? ” Short sentences Questions have to be relevant Neutral statements: no suggestive or leading questions Do you hate the president of the United States? Don’t presume facts to be general knowledge “It is said that Barrack Obama is a communist, do you agree? ” 52

Setting up the questionnaire Ordening of questions is important -> there has to be a certain structure Cluster questions about the same subject Start with general questions Questions that measure knowledge at the start of the questionnaire First question must be neutral, clear, interesting and appealing to every respondent SED variables (socio-economic, demographic) first or before last question “What’s your income? ” Last question is for comments of the respondent Lay out 53

To do’s (1) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Decide on your topic (company and product) 1. Hand in via email asap. Deadline Friday 16 Nov. – jo. spaubeck@zuyd. nl 2. Must be approved, keep it simple 3. Keep in mind who the respondents are (students vs. CEO’s) If you have not found a team you will be assigned to one Discuss in your group which company you will start up. This includes a short description, mission and vision. For next week you will finish the: Research proposal, table of contents and questionnaire. You start doing the desk research Sign in for meetings in week 2, 4, and 6

To do’s (2) Study for next week Baarda If you have any questions-> jo. spaubeck@zuyd. nl

See you next week!
IBS 1.2 M&R week1(1).ppt