6608c1f1f626eb5b0ec111905ff0877c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 The World is Flat One: While I Was Sleeping How the World Became Flat Prepared by F. Sibel Salman Indr 481 Information Systems course, Koc University 1
The World is Flat One: While I Was Sleeping How the World Became Flat Prepared by F. Sibel Salman Indr 481 Information Systems course, Koc University 1
 The Beginning o Thomas Friedman traveled to Bangalore in February 2004 n to understand why India had become such an important pool for the outsourcing of service and information technology work from U. S. and other industrialized countries o He returned back with the conclusion that “The World is Flat” o How did he come to this conclusion? o What does he actually mean? 2
The Beginning o Thomas Friedman traveled to Bangalore in February 2004 n to understand why India had become such an important pool for the outsourcing of service and information technology work from U. S. and other industrialized countries o He returned back with the conclusion that “The World is Flat” o How did he come to this conclusion? o What does he actually mean? 2
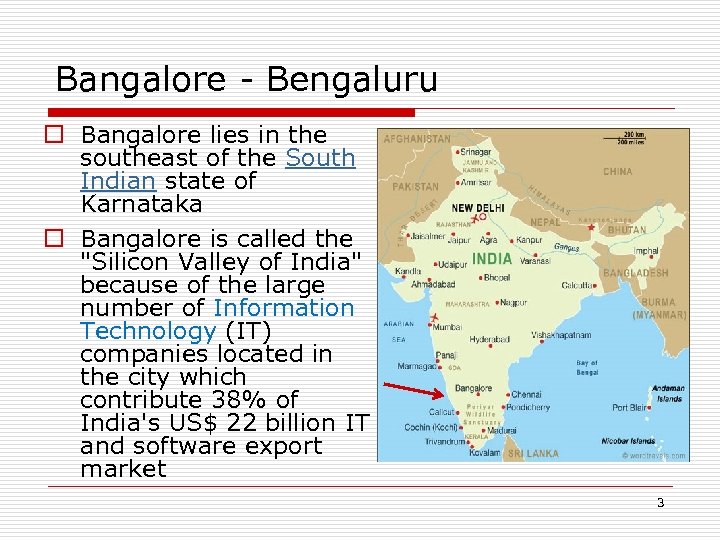 Bangalore - Bengaluru o Bangalore lies in the southeast of the South Indian state of Karnataka o Bangalore is called the "Silicon Valley of India" because of the large number of Information Technology (IT) companies located in the city which contribute 38% of India's US$ 22 billion IT and software export market 3
Bangalore - Bengaluru o Bangalore lies in the southeast of the South Indian state of Karnataka o Bangalore is called the "Silicon Valley of India" because of the large number of Information Technology (IT) companies located in the city which contribute 38% of India's US$ 22 billion IT and software export market 3
 Bangalore - Bengaluru o Bangalore's IT industry is divided into three main "clusters“ n n Software Technology Parks of India, Bangalore (STPI) International Technology Park Bangalore (ITPB), Electronics City Infosys and Wipro, India's second and third largest software companies, have their largest campus in Electronics City. o As headquarters to many of the global SEICMM Level 5 Companies, Bangalore's place in the global IT map is prominent. (SEI-Software Engineering Institute, CMM-Capability Maturity Model) 4
Bangalore - Bengaluru o Bangalore's IT industry is divided into three main "clusters“ n n Software Technology Parks of India, Bangalore (STPI) International Technology Park Bangalore (ITPB), Electronics City Infosys and Wipro, India's second and third largest software companies, have their largest campus in Electronics City. o As headquarters to many of the global SEICMM Level 5 Companies, Bangalore's place in the global IT map is prominent. (SEI-Software Engineering Institute, CMM-Capability Maturity Model) 4
 CMM-Capability Maturity Model o A maturity model can be viewed as a set of structured levels that describe how well the behaviors, practices and processes of an organization can reliably and sustainably produce required outcomes. o A maturity model can be used as a benchmark for comparison and as an aid to understanding - for example, for comparative assessment of different organizations where there is something in common that can be used as a basis for comparison. o In the case of the CMM, for example, the basis for comparison would be the organizations' software development processes 5
CMM-Capability Maturity Model o A maturity model can be viewed as a set of structured levels that describe how well the behaviors, practices and processes of an organization can reliably and sustainably produce required outcomes. o A maturity model can be used as a benchmark for comparison and as an aid to understanding - for example, for comparative assessment of different organizations where there is something in common that can be used as a basis for comparison. o In the case of the CMM, for example, the basis for comparison would be the organizations' software development processes 5
 CMM-Levels (cont. ’d) There are five levels defined along the continuum of the model and, according to the SEI: "Predictability, effectiveness, and control of an organization's software processes are believed to improve as the organization moves up these five levels. o Initial (chaotic, ad hoc, individual heroics) - the starting point for use of a new or undocumented repeat process. o Repeatable - the process is at least documented sufficiently such that repeating the same steps may be attempted. o Defined - the process is defined/confirmed as a standard business process, and decomposed to levels 0, 1 and 2 (the last being Work Instructions). o Managed - the process is quantitatively managed in accordance with agreed-upon metrics. o Optimizing - process management includes deliberate process optimization/improvement. 6
CMM-Levels (cont. ’d) There are five levels defined along the continuum of the model and, according to the SEI: "Predictability, effectiveness, and control of an organization's software processes are believed to improve as the organization moves up these five levels. o Initial (chaotic, ad hoc, individual heroics) - the starting point for use of a new or undocumented repeat process. o Repeatable - the process is at least documented sufficiently such that repeating the same steps may be attempted. o Defined - the process is defined/confirmed as a standard business process, and decomposed to levels 0, 1 and 2 (the last being Work Instructions). o Managed - the process is quantitatively managed in accordance with agreed-upon metrics. o Optimizing - process management includes deliberate process optimization/improvement. 6
 Development of Software Industry in India o In the 1990 s, an increasing number of traditional Fortune 500 companies as well as newer multi-national technology corporations turned to India for software programming and development, call centers and back office operations. o India’s revenue from exports of these industries is expected to grow by 25% a year to $60 billion by 2010 (Nasscom-Mc. Kinsey Report 2005). 7
Development of Software Industry in India o In the 1990 s, an increasing number of traditional Fortune 500 companies as well as newer multi-national technology corporations turned to India for software programming and development, call centers and back office operations. o India’s revenue from exports of these industries is expected to grow by 25% a year to $60 billion by 2010 (Nasscom-Mc. Kinsey Report 2005). 7
 Development of Software Industry in India o Industry giants like General Electric, Microsoft Corp. and Dell Inc. rapidly increased their workforce in India; many multi-ational corporations like Motorola, Larsen and Toubro and Siemens actively recruited Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) to work in their India-based operations. o Simultaneously, Indian IT leaders like Infosys Technologies, Wipro and Tata Consultancy Services increased recruitment and extended their domain to other parts of the world, setting up offices in the United States and Canada, Europe, East Asia, Australia, and the Middle East. o Infosys Technologies recruited 25 Asian Indian graduates from premier American universities for its competitive 100 -seat summer internship. 8
Development of Software Industry in India o Industry giants like General Electric, Microsoft Corp. and Dell Inc. rapidly increased their workforce in India; many multi-ational corporations like Motorola, Larsen and Toubro and Siemens actively recruited Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) to work in their India-based operations. o Simultaneously, Indian IT leaders like Infosys Technologies, Wipro and Tata Consultancy Services increased recruitment and extended their domain to other parts of the world, setting up offices in the United States and Canada, Europe, East Asia, Australia, and the Middle East. o Infosys Technologies recruited 25 Asian Indian graduates from premier American universities for its competitive 100 -seat summer internship. 8
 Infosys o Infosys Technologies Ltd. provides consulting and IT services to clients globally n Application development and maintenance n Systems integration n concept-to-market R&D and engineering services o over 130, 000 employees worldwide o one of the pioneers in o strategic offshore o outsourcing of software services o Chairman of the Board and Chief Mentor: Narayana N. R. Murthy Co-Chairman of the Board of Directors: Nandan M. Nilekani Chief Executive Officer and Managing Director : S. Gopalakrishnan 9
Infosys o Infosys Technologies Ltd. provides consulting and IT services to clients globally n Application development and maintenance n Systems integration n concept-to-market R&D and engineering services o over 130, 000 employees worldwide o one of the pioneers in o strategic offshore o outsourcing of software services o Chairman of the Board and Chief Mentor: Narayana N. R. Murthy Co-Chairman of the Board of Directors: Nandan M. Nilekani Chief Executive Officer and Managing Director : S. Gopalakrishnan 9
 Infosys o Key milestones n n n Year of Incorporation : 1981 Became a public limited company in India : 1992 ISO 9001/Tick. IT Certification : 1993 Attained SEI-CMM Level 4 : 1997 Listed on NASDAQ : 1999 Crossed $100 million in annual revenues : 1999 Attained SEI-CMM Level 5 : 1999 Crossed $ half a billion in revenues : 2002 Crossed $ billion in revenues : 2004 Crossed $ 2 billion in revenues : 2006 Added to the NASDAQ-100 Index : 2006 Crossed $ 3 billion in revenues : 2007 10
Infosys o Key milestones n n n Year of Incorporation : 1981 Became a public limited company in India : 1992 ISO 9001/Tick. IT Certification : 1993 Attained SEI-CMM Level 4 : 1997 Listed on NASDAQ : 1999 Crossed $100 million in annual revenues : 1999 Attained SEI-CMM Level 5 : 1999 Crossed $ half a billion in revenues : 2002 Crossed $ billion in revenues : 2004 Crossed $ 2 billion in revenues : 2006 Added to the NASDAQ-100 Index : 2006 Crossed $ 3 billion in revenues : 2007 10
 Leveling of the business world o Nandan Nilekani of Infosys explains n Massive investment in technology, broadband connectivity around the world n Cheaper computing power n Explosion of software: e-mail, search engines, proprietary software that can distribute work n Platform where intellectual work could be delivered from anywhere o Disaggregate, deliver, distribute, produce and put back together again n The playing field is being leveled 11
Leveling of the business world o Nandan Nilekani of Infosys explains n Massive investment in technology, broadband connectivity around the world n Cheaper computing power n Explosion of software: e-mail, search engines, proprietary software that can distribute work n Platform where intellectual work could be delivered from anywhere o Disaggregate, deliver, distribute, produce and put back together again n The playing field is being leveled 11
 Flat World o It is now possible for more people than ever to collaborate and compete in real time n n in different corners of the world in different kinds of work on a more equal basis using computers, e-mail, workforce software, teleconferencing, fiber-optic networks o Connects all the knowledge centers in the world into a single global network 12
Flat World o It is now possible for more people than ever to collaborate and compete in real time n n in different corners of the world in different kinds of work on a more equal basis using computers, e-mail, workforce software, teleconferencing, fiber-optic networks o Connects all the knowledge centers in the world into a single global network 12
 Three Eras of Globalization o Globalization 1. 0: 1492 (Columbus) – 1800 n Trade between the Old World and the New World started n Countries and muscles o Dynamic force is powerful countries o Countries drove global integration o Global competition among countries n It shrank the world from large size to medium size 13
Three Eras of Globalization o Globalization 1. 0: 1492 (Columbus) – 1800 n Trade between the Old World and the New World started n Countries and muscles o Dynamic force is powerful countries o Countries drove global integration o Global competition among countries n It shrank the world from large size to medium size 13
 Three Eras of Globalization o Globalization 2. 0: 1800 – 2000 (interrupted by the Great Depression, World Wars I & II) n Started with industrial revolution n Dynamic force driving global integration was multinational companies and breakthroughs in hardware n In the first half powered by o falling transportation costs due to steam engine, railroads n In the second half powered by o falling telecommunication costs due to telegraph, telephones, the PC, satellites, fiber-optic cable, early version of the www 14
Three Eras of Globalization o Globalization 2. 0: 1800 – 2000 (interrupted by the Great Depression, World Wars I & II) n Started with industrial revolution n Dynamic force driving global integration was multinational companies and breakthroughs in hardware n In the first half powered by o falling transportation costs due to steam engine, railroads n In the second half powered by o falling telecommunication costs due to telegraph, telephones, the PC, satellites, fiber-optic cable, early version of the www 14
 Three Eras of Globalization o Globalization 2. 0: 1800 – 2000 n Movement of goods and information among continents n Global competition among companies n It shrank the world from medium size to small size 15
Three Eras of Globalization o Globalization 2. 0: 1800 – 2000 n Movement of goods and information among continents n Global competition among companies n It shrank the world from medium size to small size 15
 Three Eras of Globalization o Globalization 3. 0: 2000 – n Dynamic force driving global integration is individuals n Powered by the flat-world platform o PC+ telecomm+ work flow software n Global collaboration and competition among individuals n It shrank the world from small size to tiny size 16
Three Eras of Globalization o Globalization 3. 0: 2000 – n Dynamic force driving global integration is individuals n Powered by the flat-world platform o PC+ telecomm+ work flow software n Global collaboration and competition among individuals n It shrank the world from small size to tiny size 16
 Facilitators of Outsourcing o Investment in broadband connectivity o Cheaper PC and IT hardware o Availability of search engines and software Altogether these created a platform where intellectual work, intellectual capital, could be delivered from anywhere leading to easier remote development, i. e. , It could be disaggregated, delivered, distributed, produced, and put back together again 17
Facilitators of Outsourcing o Investment in broadband connectivity o Cheaper PC and IT hardware o Availability of search engines and software Altogether these created a platform where intellectual work, intellectual capital, could be delivered from anywhere leading to easier remote development, i. e. , It could be disaggregated, delivered, distributed, produced, and put back together again 17
 Outsourcing Examples o Accounting work – US tax returns prepared in India n n In 2003: 25, 000; 2004: 100, 000; 2005: 400, 000 Software product called VTR, Virtual Tax Room Medium size firms get a chance to outsource Data protection and security is high 18
Outsourcing Examples o Accounting work – US tax returns prepared in India n n In 2003: 25, 000; 2004: 100, 000; 2005: 400, 000 Software product called VTR, Virtual Tax Room Medium size firms get a chance to outsource Data protection and security is high 18
 Outsourcing Examples o Medical – Radiologists outsourcing reading of CAT scans to doctors in India and Australia n Teleradiology – ship images to radiologists abroad n CAT and MRI images are already in digital format and available on a network with a standardized protocol n After-hours readings by “Nighthawks” 19
Outsourcing Examples o Medical – Radiologists outsourcing reading of CAT scans to doctors in India and Australia n Teleradiology – ship images to radiologists abroad n CAT and MRI images are already in digital format and available on a network with a standardized protocol n After-hours readings by “Nighthawks” 19
 Outsourcing Examples o Journalism – News about company earnings and related business news n Reuters – 2300 journalists worldwide in 197 bureaus serving investment bankers, derivatives traders, stockbrokers, newspapers, radio, TV, Internet outlets n Create the news flashes n Then, value added work: analysis n Cost and speed efficiency o Analysts are paid $15, 000 in Bangalore, as opposed to $80, 000 in New York or London o Financially literate and highly motivated employees in India 20
Outsourcing Examples o Journalism – News about company earnings and related business news n Reuters – 2300 journalists worldwide in 197 bureaus serving investment bankers, derivatives traders, stockbrokers, newspapers, radio, TV, Internet outlets n Create the news flashes n Then, value added work: analysis n Cost and speed efficiency o Analysts are paid $15, 000 in Bangalore, as opposed to $80, 000 in New York or London o Financially literate and highly motivated employees in India 20
 Outsourcing Examples o Call Centers 24/7 operations, inbound and outbound calls o As of 2005, 245, 000 Indian operators answering calls from all over the world o Low-wage, low-prestige jobs in the US, but high-wage, high-prestige in India n You can work at night and go to school during part of the day, cost of an operator is $500/month n Japan outsourcing to China, Dalian 21
Outsourcing Examples o Call Centers 24/7 operations, inbound and outbound calls o As of 2005, 245, 000 Indian operators answering calls from all over the world o Low-wage, low-prestige jobs in the US, but high-wage, high-prestige in India n You can work at night and go to school during part of the day, cost of an operator is $500/month n Japan outsourcing to China, Dalian 21
 Outsourcing Examples o Globalization of innovation o Research and development tasks outsourced to India, Russia and China o Indian offices of Cisco, Intel, IBM, Texas Instruments, GE filing patents in U. S. Patent Office o GE transferred Indian engineers who worked in US back to India 22
Outsourcing Examples o Globalization of innovation o Research and development tasks outsourced to India, Russia and China o Indian offices of Cisco, Intel, IBM, Texas Instruments, GE filing patents in U. S. Patent Office o GE transferred Indian engineers who worked in US back to India 22
 Outsourcing Examples o Personal remote executive assistant n $1500 -2000/month o Jet. Blue Airways homesourcing, reservation agents working from home o Mc. Donald’s drive-through ordering o E-tutoring 23
Outsourcing Examples o Personal remote executive assistant n $1500 -2000/month o Jet. Blue Airways homesourcing, reservation agents working from home o Mc. Donald’s drive-through ordering o E-tutoring 23
 Flat world The flattening of the world means is that o we are now connecting all the knowledge centers on the planet together into a single global network. o Pro: can usher in an amazing era of prosperity and innovation o Con: Higher competition o Risks: Politics, terrorism, . . . 24
Flat world The flattening of the world means is that o we are now connecting all the knowledge centers on the planet together into a single global network. o Pro: can usher in an amazing era of prosperity and innovation o Con: Higher competition o Risks: Politics, terrorism, . . . 24


