97c41ab518ae3bd9aebf270410170f90.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 The World in Spatial Terms “Where are we? ” n Absolute Location: • Latitude and longitude (global location) • Sugar Land is located at 29°N, 96°W • Street address (local location)
The World in Spatial Terms “Where are we? ” n Absolute Location: • Latitude and longitude (global location) • Sugar Land is located at 29°N, 96°W • Street address (local location)
 The World in Spatial Terms n Relative Location: • Described by landmarks, time, distance from one place to another, etc. Sugar Land is southwest of Houston n College Station is 1 hr 45 min away n Israel is next to Lebanon & Jordan n
The World in Spatial Terms n Relative Location: • Described by landmarks, time, distance from one place to another, etc. Sugar Land is southwest of Houston n College Station is 1 hr 45 min away n Israel is next to Lebanon & Jordan n

 GEOGRAPHY SKILLS PACKET
GEOGRAPHY SKILLS PACKET
 Lines of Latitude n n A. K. A. —”parallels” Measure distance north or south of the Equator n n n North Pole: 90°N; South Pole: 90°S Arctic Circle: 66½°N; Antarctic Circle: 66½°S Tropic of Cancer: 23½°N; Tropic of Capricorn: 23½°S
Lines of Latitude n n A. K. A. —”parallels” Measure distance north or south of the Equator n n n North Pole: 90°N; South Pole: 90°S Arctic Circle: 66½°N; Antarctic Circle: 66½°S Tropic of Cancer: 23½°N; Tropic of Capricorn: 23½°S
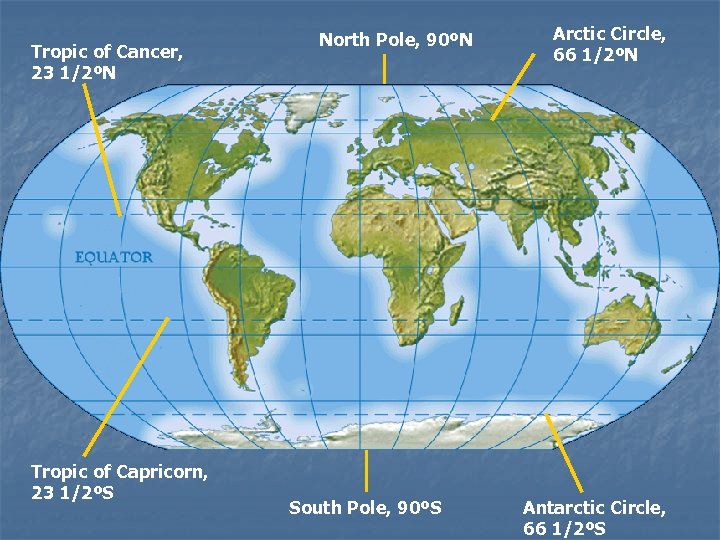 Tropic of Cancer, 23 1/2ºN Tropic of Capricorn, 23 1/2ºS North Pole, 90ºN South Pole, 90ºS Arctic Circle, 66 1/2ºN Antarctic Circle, 66 1/2ºS
Tropic of Cancer, 23 1/2ºN Tropic of Capricorn, 23 1/2ºS North Pole, 90ºN South Pole, 90ºS Arctic Circle, 66 1/2ºN Antarctic Circle, 66 1/2ºS
 Lines of Longitude n n A. K. A. —Meridians Measures distance EAST or WEST of the Prime Meridian Eastern Hemisphere (east longitude) lies at places east of the Prime Meridian Western Hemisphere (west longitude) lies at places west of the Prime Meridian
Lines of Longitude n n A. K. A. —Meridians Measures distance EAST or WEST of the Prime Meridian Eastern Hemisphere (east longitude) lies at places east of the Prime Meridian Western Hemisphere (west longitude) lies at places west of the Prime Meridian
 n The EQUATOR creates the Northern & Southern Hemisphere n n 0° latitude = Equator The PRIME MERIDIAN creates the Eastern & Western Hemisphere n 0° longitude = Prime Meridian
n The EQUATOR creates the Northern & Southern Hemisphere n n 0° latitude = Equator The PRIME MERIDIAN creates the Eastern & Western Hemisphere n 0° longitude = Prime Meridian
 Practice n What major city has the following coordinates? 41ºN, 73ºW (USA) New York City n 33ºN, 13ºE (Africa) Tripoli, Libya n 33ºS, 71ºW (South America) Santiago, Chile n n Name the global address of: Hanoi, Vietnam 21°N, 105°E 21 n Athens, Greece 37°N, 23°E 37 n Tehran, Iran 35°N, 51°E 35 51 n
Practice n What major city has the following coordinates? 41ºN, 73ºW (USA) New York City n 33ºN, 13ºE (Africa) Tripoli, Libya n 33ºS, 71ºW (South America) Santiago, Chile n n Name the global address of: Hanoi, Vietnam 21°N, 105°E 21 n Athens, Greece 37°N, 23°E 37 n Tehran, Iran 35°N, 51°E 35 51 n
 Get out skills packet and begin working on the Projections section. Please read and follow the instructions.
Get out skills packet and begin working on the Projections section. Please read and follow the instructions.
 Winkel Tripel Projection
Winkel Tripel Projection
 Winkel Tripel Projection n Pros: n n n Good balance of size & shape of land areas as shown on the maps No distortion Cons: n n None! This is the most widely used projection for world maps!!!
Winkel Tripel Projection n Pros: n n n Good balance of size & shape of land areas as shown on the maps No distortion Cons: n n None! This is the most widely used projection for world maps!!!
 Robinson Projection
Robinson Projection
 Robinson Projection n Pros n n Sizes & shapes near the edges of the map are accurate Cons n Shapes of the polar areas are distorted (misshaped)
Robinson Projection n Pros n n Sizes & shapes near the edges of the map are accurate Cons n Shapes of the polar areas are distorted (misshaped)
 Goode’s Interrupted Equal-Area Projection
Goode’s Interrupted Equal-Area Projection
 Goode’s Interrupted Equal. Area Projection n Pros n n The size & shape of the countries are true to size Cons n Distances between countries are not true to size & not accurate
Goode’s Interrupted Equal. Area Projection n Pros n n The size & shape of the countries are true to size Cons n Distances between countries are not true to size & not accurate
 Mercator Projection
Mercator Projection
 Mercator Projection n Pros: n n n Directions are true to the map The shapes of the landmasses are accurate Cons: n n The size & distance becomes more inaccurate as you move away from the equator This is a commonly used projection (good for seafaring!)
Mercator Projection n Pros: n n n Directions are true to the map The shapes of the landmasses are accurate Cons: n n The size & distance becomes more inaccurate as you move away from the equator This is a commonly used projection (good for seafaring!)
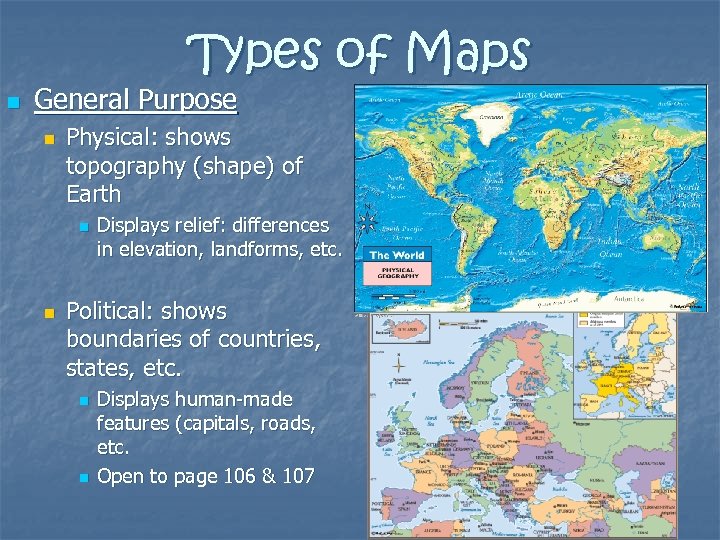 Types of Maps n General Purpose n Physical: shows topography (shape) of Earth n n Displays relief: differences in elevation, landforms, etc. Political: shows boundaries of countries, states, etc. n n Displays human-made features (capitals, roads, etc. Open to page 106 & 107
Types of Maps n General Purpose n Physical: shows topography (shape) of Earth n n Displays relief: differences in elevation, landforms, etc. Political: shows boundaries of countries, states, etc. n n Displays human-made features (capitals, roads, etc. Open to page 106 & 107
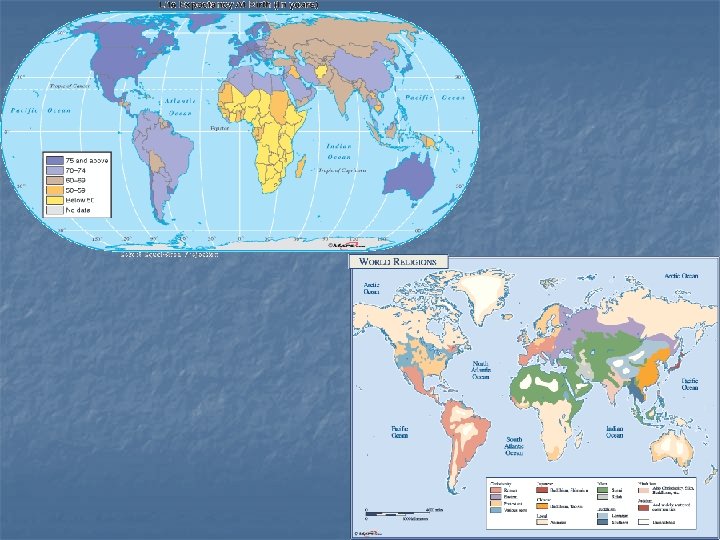
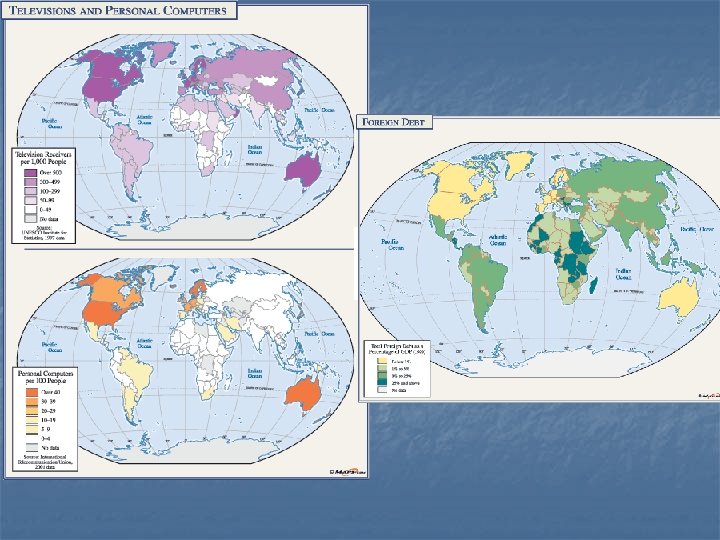
 Types of Maps n Special Purpose n Emphasize n Climate a particular kind of information (pg 122) n Vegetation (pg 123) n Population density (pg 108) n Economic activity (pg 109) n Cartogram (RA 38) n Other Thematic Maps (AIDS, Child Labor, Oil Production, etc)
Types of Maps n Special Purpose n Emphasize n Climate a particular kind of information (pg 122) n Vegetation (pg 123) n Population density (pg 108) n Economic activity (pg 109) n Cartogram (RA 38) n Other Thematic Maps (AIDS, Child Labor, Oil Production, etc)