6593712a3b38e4b88c2932474a7b10a9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

THE WORLD BANK: INCLUSIVE DEVELOPMENT and DISABILITY European Conference on Disability & Development Cooperation The UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities: Impact and Opportunities for Persons with Disabilities in Developing Countries Session Title: How to implement inclusive development approaches Day Two - 21 November 2006 10: 30 -12: 30 Brussels Sándor Sipos Sector Manager Social Protection & Labor (HDNSP) Human Development Network (HDN)

Sizeable Disability Portfolio From 2002 -2006, 4% of all World Bank projects by number and 5% of new lending volume were projects with a disability component ($4. 9 bn) and 6% of Economic and Sector Work. In July 2004, 10% of projects in Europe & Central Asia had a Disability Component S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Implementing Inclusive Development Complementary twin track approach: – Economic – disability & MDGs – Legal – Human Rights relevance for development and International Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (ICRPD) – National Legislation S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Human Rights and the World Bank “There should be a clear understanding that in certain cases and under certain circumstances, Human Rights generate actionable legal obligations. Such obligations may arise from international treaties, or from rights enshrined in national laws. Here the Bank’s role is to support its Members to fulfill those obligations where they relate to Bank projects and policies” Ana Palacio, Senior Vice President World Bank Group General Counsel 2006

World Bank Action Items Mainstreaming Disability in WB Operations – Lending/Safeguards – Economic and Sector Work – Capacity: Awareness and Training Building Partnerships Inclusive Work Environment S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Lending and Analytical Work – Poverty Reduction Strategy Programs – Investment Lending – Technical Assistance – Project Monitoring & Evaluation - Results S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Policy Lending and Dialogue Poverty Reduction Strategy Papers – “Making PRSPs Inclusive” Handicap International and Cristoffel-Blindenmission (January 2006). Funded by Germany. Facilitated by World Bank, presented at December 2006 Berlin conference Developmental Policy Lending: Promoting Inclusive Policies – Legislation – Implementing Regulation – Specific Agreed Policy Measures S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006
Investment Project Cycle S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Africa – Multi-Country Demobilization & Reintegration Program – Multi-agency effort that supports the demobilization and reintegration of excombatants in the greater Great Lakes region of Central Africa. – The largest program of its kind in the world, MDRP currently targets an estimated 450, 000 ex-combatants in seven countries: Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Republic of Congo, Rwanda and Uganda. Support will also be extended to Namibia and Zimbabwe if and when appropriate. – MDRP provides assistance for medical rehabilitation based on the type and degree of disability. – Services typically include the provision of physical rehabilitation assistance (prosthesis and orthesis), counseling, vocational training and/or support for microenterprise activities. – Aims to reinforce key medical facilities – provide systematic prosthetic and physiotherapy services, including maintenance of prosthetic devices.
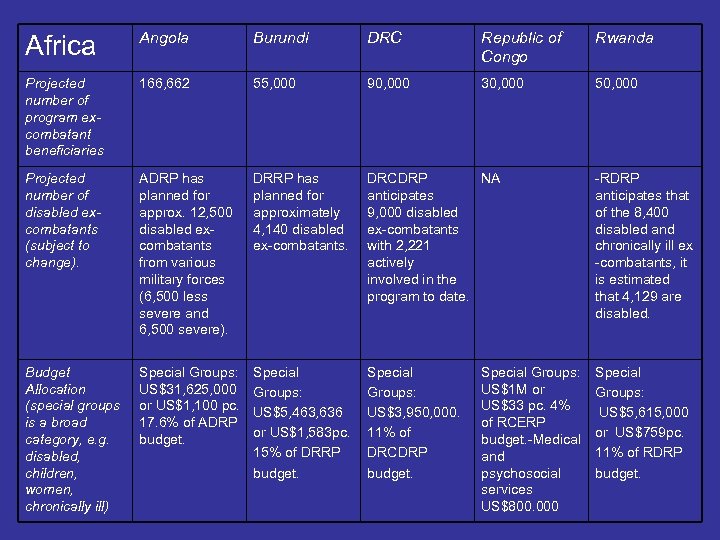
Africa Angola Burundi DRC Republic of Congo Rwanda Projected number of program excombatant beneficiaries 166, 662 55, 000 90, 000 30, 000 50, 000 Projected number of disabled excombatants (subject to change). ADRP has planned for approx. 12, 500 disabled excombatants from various military forces (6, 500 less severe and 6, 500 severe). DRRP has planned for approximately 4, 140 disabled ex-combatants. DRCDRP NA anticipates 9, 000 disabled ex-combatants with 2, 221 actively involved in the program to date. -RDRP anticipates that of the 8, 400 disabled and chronically ill ex -combatants, it is estimated that 4, 129 are disabled. Budget Allocation (special groups is a broad category, e. g. disabled, children, women, chronically ill) Special Groups: US$31, 625, 000 or US$1, 100 pc. 17. 6% of ADRP budget. Special Groups: US$5, 463, 636 or US$1, 583 pc. 15% of DRRP budget. Special Groups: US$3, 950, 000. 11% of DRCDRP budget. Special Groups: US$5, 615, 000 or US$759 pc. 11% of RDRP budget. Special Groups: US$1 M or US$33 pc. 4% of RCERP budget. -Medical and psychosocial services US$800. 000

Europe and Central Asia – Romania – Pension Reforms Support: A component of the Social Sector Development Project supports the rehabilitation of the disabled by strengthening the capacity of the National institute for Medical Expertise and Work Capacity Recovery. It is also bolstering the local medical expertise offices of the National House of Pensions and Other Social Insurances Rights (CNPAS) ($50 million, of which $6. 32 million targets the disabled) – Social Inclusion Project: Assist governmental implementation of Joint Inclusion Memorandum through assistance given to the existing or emerging programs that address the needs of the vulnerable and/or disadvantaged groups of Roma, People with Disabilities, youth at risk and victims o f domestic violence in four components: • Priority Interventions Program • Inclusive Early Childhood Education of Roma • Social Assistance Programs • Capacity Building for Roma Social Inclusion S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Europe and Central Asia cont. – Lithuania – School Access for Children with Disabilities: A Lithuania Education Improvement Project is making 62 schools accessible to disabled children and is fully renovating the Vilnius School for the Deaf as well as providing teacher training. ($25. 29 million) – Turkey – Teacher Training: Training 6, 678 Special Education Teachers in schools, reaching 150, 000 students of which 35, 000 were students with disabilities – Visually and Hearing impaired primary school children are receiving specialized equipment through phase 2 of a Basic Education project. The project is building 70 special education primary schools and installing 770 computers. Special educational materials and teacher training will cover 1, 340 preschool classrooms. S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

East Asia & Pacific Region – Vietnam – Primary Education for Disadvantaged Children Project combined project funds of US$ 243 million for technical support to improve administrative planning and management; enhanced delivery of acceptable quality education; linkages to communities; National level child development report and policy on inclusive education and accessible schools – introduce disability questions on census – HIV/AIDS project run by young people with disabilities received support from the Bank. This project is a fully mainstreamed project with young people with disabilities raising awareness S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

East Asia & Pacific Region cont. – Cambodia, Indonesia, Mongolia and Vietnam – Building administrative capacity and develop an inclusive Educational Management Information Systems (EMIS) – Indonesia – BNPP trust funds for baseline data collection on children with disabilities in the education sector; envisioned that there will be some policy directives supporting inclusive education as a result of this study – Thailand – JSDF post Tsunami reconstruction work – Philippines – Social Expenditure Management Project: component of social assistance for disadvantaged groups (US$25 m) – Development Marketplace (DM) support for access to justice for the Deaf; Several other DM competitions to distributed grants to various stakeholders working on independent living. S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

East Asia & Pacific Region cont. – Region-wide – Access to Information: All Public Information Centers (PICs) in region ensuring accessible information; Supported the translation of the UNESCO toolkit on embracing diversity into at least three languages in the region. accessible PIC resulted in an increase use of the centers by people with disabilities in Philippines – Transport: project addresses disability from the perspective of prevention and road safety. S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Middle East & North Africa Region – Egypt – Social Protection Initiative Project - Disability Component – Project Objective – Develop and test integrated programs for children with disabilities and youth at risk through a range of providers, and to use the experience of these programs to develop a new strategy for improving services. – Main Results – Exposure to new inclusive approaches – Awareness of issues for policy formulation

Middle East & North Africa cont. Main Outputs – A total of 36 subprojects were developed with an average cost of approximately US$100, 000 per subproject. – 1, 028 facilities were rehabilitated to adapt the infrastructure to the needs of disabled children. – Numerous resource materials were developed to support future interventions Institutional Development – Impact on Ministry of Insurance and Social Affairs – Impact on the service providers and the communities – Impact future international collaborations S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

South Asia Region Principles – Mainstreaming in inclusive development – Two country focus (Pakistan and India), others on demand – Build on existing momentum Strategy – Operationalizing – mainstreaming through prevention and inclusion – Improving data and information – Awareness and Outreach S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Pakistan – Earthquake Disability Project: $5 million grant from IBRD surplus to support community-based rehabilitation through contracting NGOs – Two JSDF grants: $1. 6 million for Handicap International and Milestone (national DPO) for establishing resource and information centers for community based rehabilitation and independent living S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

India – Andhra Pradesh Rural Poverty Reduction Program – The project targeted 560 disadvantaged mandals in 16 districts based on levels of human, economic, and infrastructural development indicators. The disabled were then specifically selected, and the targeting was facilitated by NGOs/DPOs, as well as by the Self Help Groups of the disabled themselves. – Interventions: providing surgical corrections and assistive devices, family support programs, training para-professionals in community based rehabilitation (CBR), reviving defunct rehabilitation centers and establishing bridge residential schools for disabled children, micro credit loans, small enterprise development, and vocational training – People with Disabilities in India: From Commitments to Outcomes, Draft June 2006 S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Regional Lessons Learned – Inclusive development is a multi-stakeholder responsibility – NGOs, made more effective as delivery of services to the vulnerable children, through a “contracting” rather than “grant” approach – Robust monitoring and evaluation (M&E) system is essential for learning and accountability – A learning and innovation lending instrument (LIL) is effective to pilot and test initiatives, and to build consensus – Field-based management provides effective, quick response – Use range of providers to help develop a new strategy for improving services S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Safeguards – Mandatory Safeguard Reviews and Clearance apply to all Bank managed investment lending in ten priority areas – Borrower responsibility – Bank conducts due diligence – Decentralized Regional Function (down to the task team for low- and medium-risk projects) – Centralized coordination/dispute resolution mechanism – Objectives of Safeguard Policies – Ensure that Environmental and Social issues are evaluated in decision making – Reduce and Manage Project Technical Risks – Provide a mechanism for Consultation and Disclosure of Information S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

No Direct Disability Safeguard Most Relevant Safeguards/Entry Points – Environmental Assessment – Involuntary Resettlement – Indigenous Peoples – Disclosure and Consultation S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Disability: What Safeguards Can Do – Pilot and later mainstream process innovations (public consultation, environmental protection clauses, …. . ) – Reminders of National Laws – Introduce Universal Design – Prevent further disabilities S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Disability: What Safeguards Cannot Do – Create a new disabilities policy – Extend disabilities concerns beyond project scope if there is no national requirement/legislation – Create stand-alone disabilities access projects S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006
Operational Toolkit and Compendium of Country Access Laws S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Main Themes of Analytical Work - Disability Data Collection and Poverty Analysis Inclusive Education Access to Health Services Youth Leadership Access to Microfinance Information and Communication Technologies Social Protection: Social Insurance and Assistance Accessibility of Infrastructure HIV/AIDS International Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities - Post-conflict and Natural Disasters - Employment S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Awareness raising and training on inclusion of disability Cross-sectoral awareness raising and training – World Bank Management & Operational Staff in Headquarters and Country Offices – Civil Society – Client Countries S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Building Partnerships WB role: facilitating and leveraging – Washington City Group on Data – Development Grant Facility to support workshops and testing – Direct collaboration – Global Partnership for Disability and Development (GPDD) – WHO on Disability Report – ILO on law and policies S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Inclusive Work Environment Working Group on Organizational Issues – HR policies and practices – Physical accessibility of HQ, Country Offices and Public Information Centers (PICs) – Assistive technologies – Disability Accommodation Fund S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Disability Structure at the WB Human Development Network Social Protection & Labor Sector Disability & Development (D&D) Team Regional Counterparts Regional Disability Working Group Coordinators Network Counterparts Legal, Infrastructure, Environmentally and Socially Sustainable Development, Information Solutions Group, Development Economics S. Sipos The World Bank November 26, 2006

Human Development Network Social Protection (HDNSP) www. worldbank. org/sp HDNSP Disability & Development (D&D) www. worldbank. org/disability Global Partnership on Disability and Development (GPDD) www. worldbank. org/disability/gpdd
6593712a3b38e4b88c2932474a7b10a9.ppt