IPCC_WG2AR5_SlideDeck.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 24

THE WORKING GROUP II CONTRIBUTION TO THE IPCC'S FIFTH ASSESSMENT REPORT

CLIMATE CHANGE 2014: IMPACTS, ADAPTATION, AND VULNERABILITY
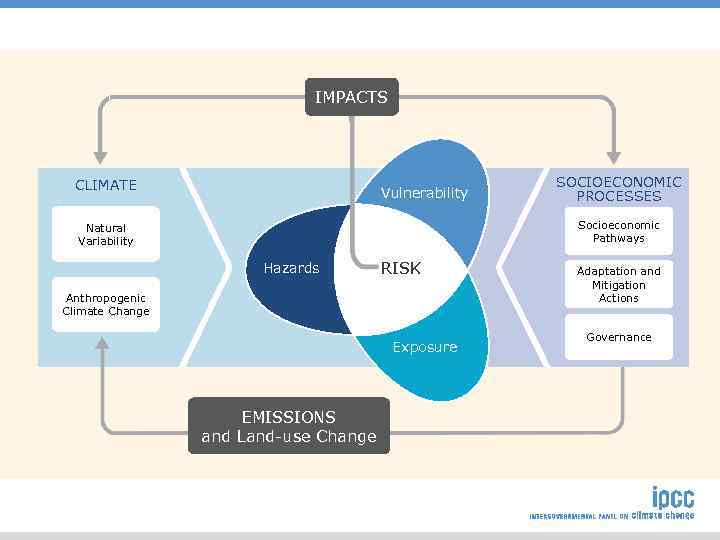
IMPACTS CLIMATE Vulnerability SOCIOECONOMIC PROCESSES Socioeconomic Pathways Natural Variability Hazards RISK Anthropogenic Climate Change Exposure EMISSIONS and Land-use Change Adaptation and Mitigation Actions Governance

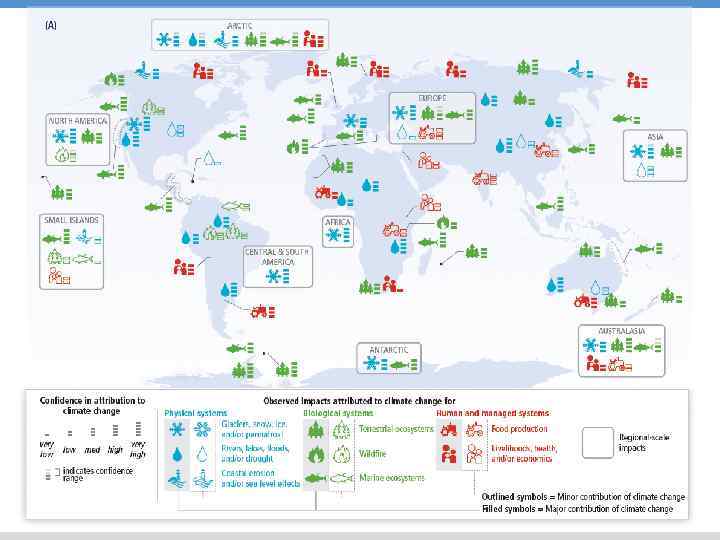
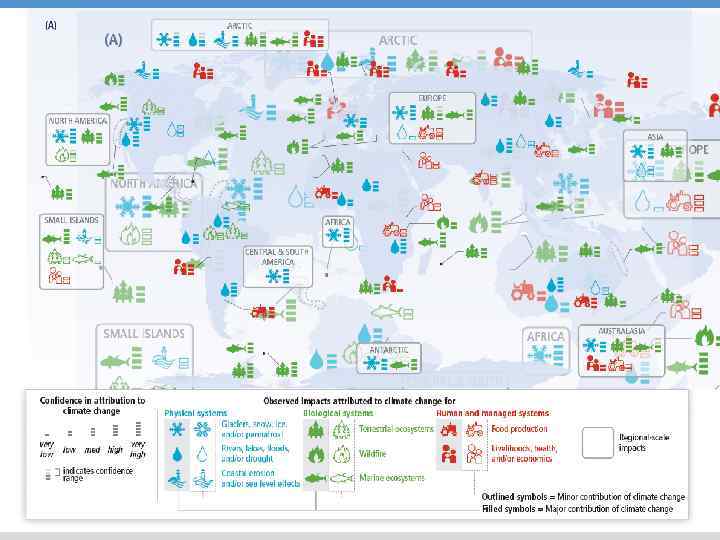
WIDESPREAD OBSERVED IMPACTS A CHANGING WORLD

WIDESPREAD OBSERVED IMPACTS A CHANGING WORLD
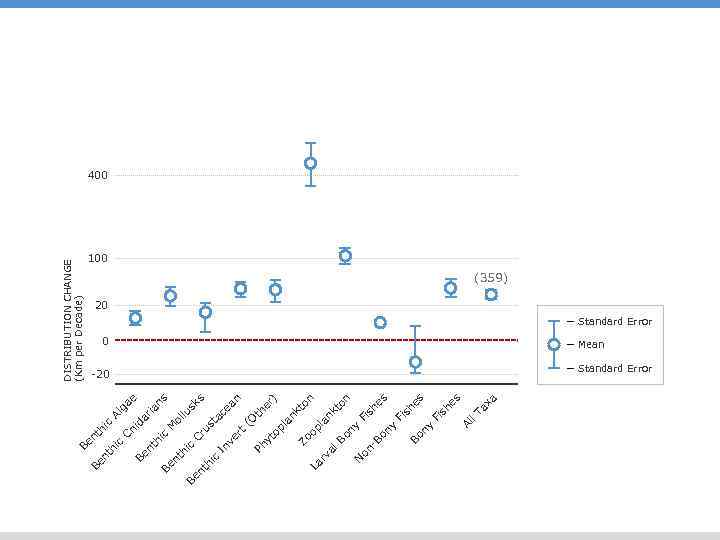
a ax l. T s es he Fi sh es n kt o Fi sh Al ny Bo y ny on -B on N Bo n to nk er ) th la n op Zo la yt op (O an s s sk ce us ta Cr ia n ol lu M ve rt Ph In hi c rv al La c hi nt Be ae Al g ar id Cn nt hi c c hi c nt Be hi nt Be Be DISTRIBUTION CHANGE (Km per Decade) 400 100 (359) 20 Standard Error 0 Mean -20 Standard Error
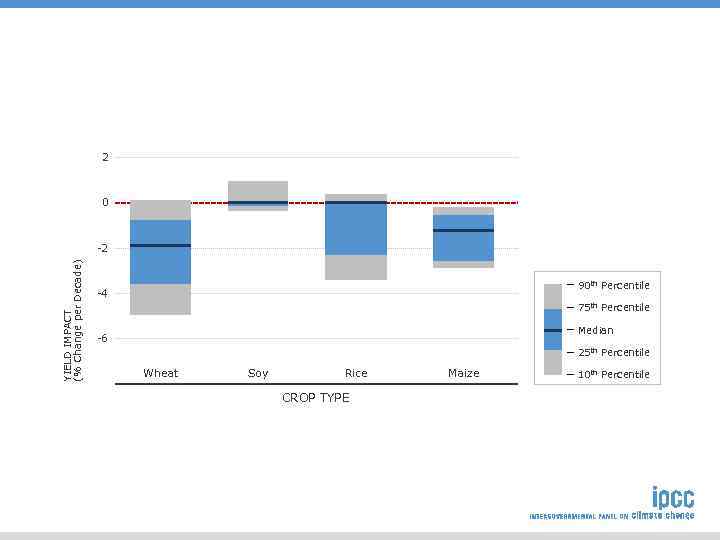
2 0 YIELD IMPACT (% Change per Decade) -2 90 th Percentile -4 75 th Percentile Median -6 25 th Percentile Wheat Soy Rice CROP TYPE Maize 10 th Percentile

VULNERABILITY AND EXPOSURE AROUND THE WORLD

VULNERABILITY AND EXPOSURE AROUND THE WORLD

ADAPTATION IS ALREADY OCCURING

ADAPTATION IS ALREADY OCCURING

CLIMATE CHANGE REDUCING AND MANAGING RISKS

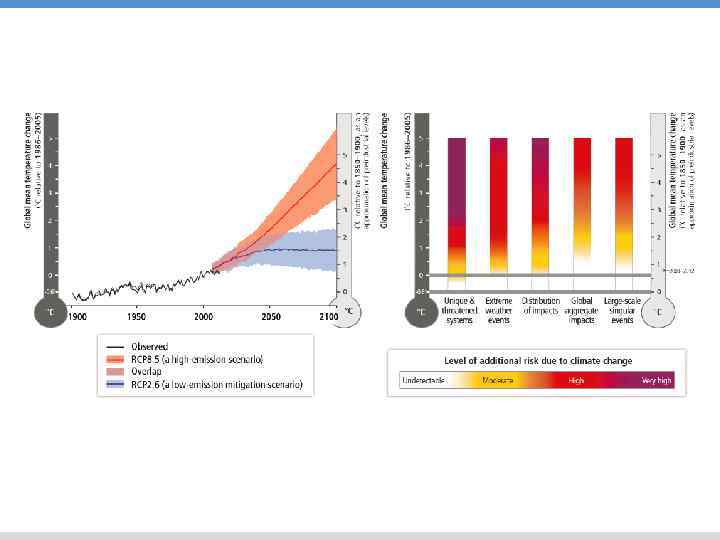
INCREASING MAGNITUDES OF WARMING INCREASE THE LIKELIHOOD OF SEVERE AND PERVASIVE IMPACTS
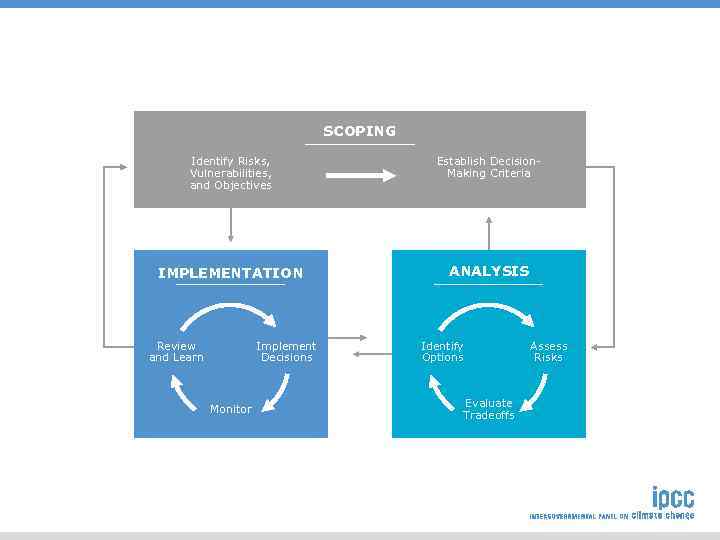
SCOPING Identify Risks, Vulnerabilities, and Objectives Establish Decision. Making Criteria IMPLEMENTATION ANALYSIS Review and Learn Implement Decisions Monitor Identify Options Evaluate Tradeoffs Assess Risks

RISKS OF CLIMATE CHANGE INCREASE WITH CONTINUED HIGH EMISSIONS
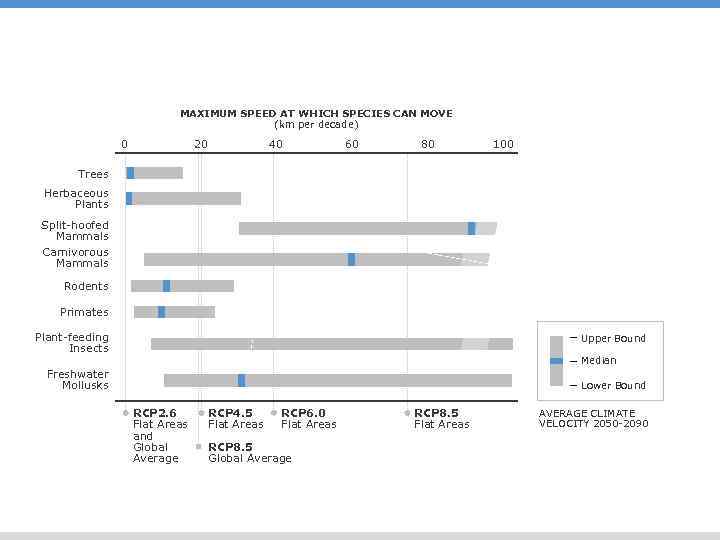
MAXIMUM SPEED AT WHICH SPECIES CAN MOVE (km per decade) 0 20 40 60 80 100 Trees Herbaceous Plants Split-hoofed Mammals Carnivorous Mammals Rodents Primates Plant-feeding Insects Upper Bound Median Freshwater Mollusks Lower Bound RCP 2. 6 Flat Areas and Global Average RCP 4. 5 Flat Areas RCP 6. 0 Flat Areas RCP 8. 5 Global Average RCP 8. 5 Flat Areas AVERAGE CLIMATE VELOCITY 2050 -2090
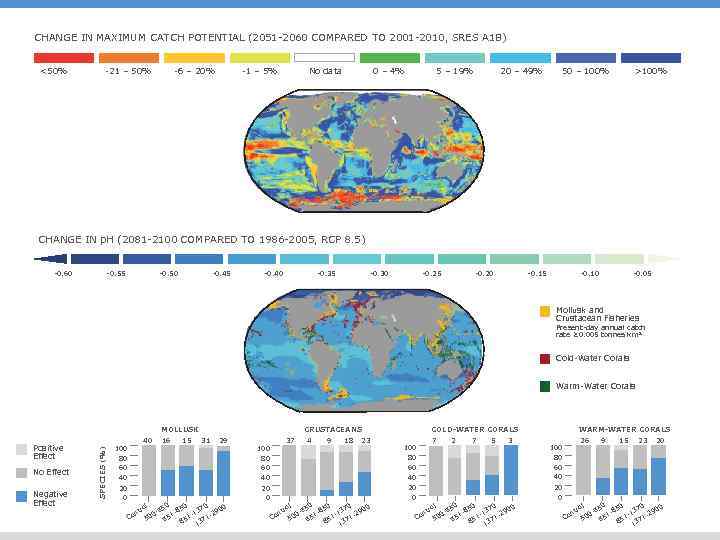
CHANGE IN MAXIMUM CATCH POTENTIAL (2051 -2060 COMPARED TO 2001 -2010, SRES A 1 B) <50% -21 – 50% -6 – 20% -1 – 5% No data 0 – 4% 5 – 19% 20 – 49% 50 – 100% >100% CHANGE IN p. H (2081 -2100 COMPARED TO 1986 -2005, RCP 8. 5) -0. 60 -0. 55 -0. 50 -0. 45 -0. 40 -0. 35 -0. 30 -0. 25 -0. 20 -0. 15 -0. 10 -0. 05 Mollusk and Crustacean Fisheries Present-day annual catch rate ≥ 0. 005 tonnes km 2 Cold-Water Corals Warm-Water Corals Positive Effect No Effect Negative Effect SPECIES (%) MOLLUSK 40 100 16 15 CRUSTACEANS 31 29 37 100 4 9 18 23 COLD-WATER CORALS 7 100 2 7 5 3 WARM-WATER CORALS 26 100 80 60 40 40 20 0 23 20 40 20 0 15 80 60 40 9 20 0 Co l 0 0 0 50 ro 65 37 290 0 - 51 -8 1 -1 150 6 85 137 nt l 0 0 0 50 65 tro 37 290 0 - 51 -8 1 -1 150 6 85 137 n Co l 0 0 0 50 ro 65 37 290 0 - 51 -8 1 -1 150 6 85 137 nt Co
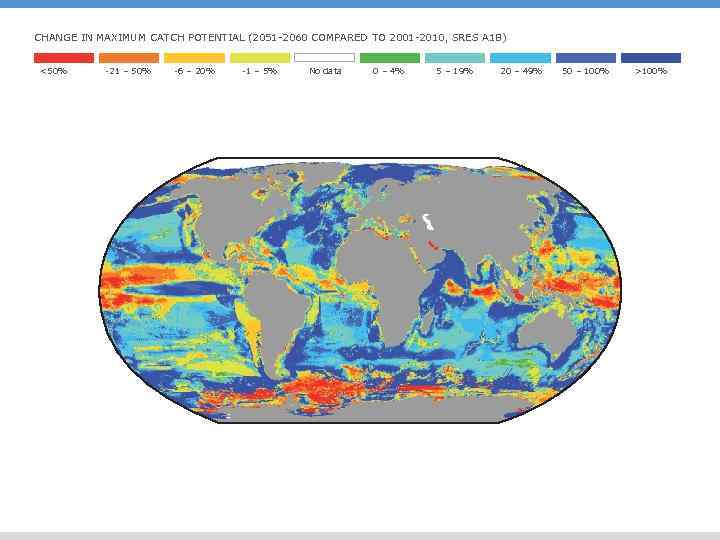
CHANGE IN MAXIMUM CATCH POTENTIAL (2051 -2060 COMPARED TO 2001 -2010, SRES A 1 B) <50% -21 – 50% -6 – 20% -1 – 5% No data 0 – 4% 5 – 19% 20 – 49% 50 – 100% >100%
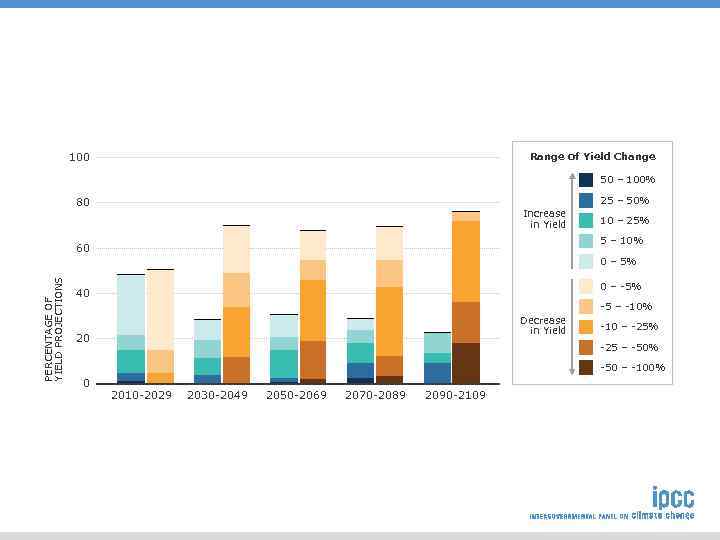
Range of Yield Change 100 50 – 100% 25 – 50% 80 Increase in Yield 10 – 25% 5 – 10% 60 PERCENTAGE OF YIELD PROJECTIONS 0 – 5% 0 – -5% 40 -5 – -10% Decrease in Yield 20 -10 – -25% -25 – -50% -50 – -100% 0 2010 -2029 2030 -2049 2050 -2069 2070 -2089 2090 -2109
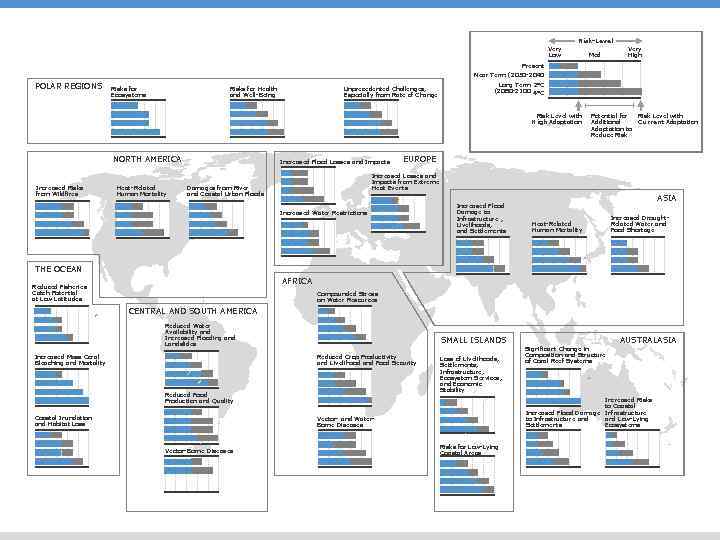
Risk-Level Very Low Med Very High Present Near Term (2030 -2040 POLAR REGIONS Risks for Ecosystems Risks for Health and Well-Being Unprecedented Challenges, Especially from Rate of Change Long Term 2°C (2080 -2100 4°C Risk Level with High Adaptation NORTH AMERICA Increased Risks from Wildfires Heat-Related Human Mortality Increased Flood Losses and Impacts Potential for Additional Adaptation to Reduce Risk Level with Current Adaptation EUROPE Increased Losses and Impacts from Extreme Heat Events Damages from River and Coastal Urban Floods Increased Water Restrictions Increased Flood Damage to Infrastructure , Livelihoods, and Settlements ASIA Heat-Related Human Mortality Increased Drought. Related Water and Food Shortage THE OCEAN AFRICA Reduced Fisheries Catch Potential at Low Latitudes Compounded Stress on Water Resources r CENTRAL AND SOUTH AMERICA Reduced Water Availability and Increased Flooding and Landslides Increased Mass Coral Bleaching and Mortality SMALL ISLANDS Reduced Crop Productivity and Livelihood and Food Security Reduced Food Production and Quality Coastal Inundation and Habitat Loss of Livelihoods, Settlements, Infrastructure, Ecosystem Services, and Economic Stability Increased Risks to Coastal Increased Flood Damage Infrastructure and Low-Lying to Infrastructure and Ecosystems Settlements Vector- and Water. Borne Diseases Vector-Borne Diseases AUSTRALASIA Significant Change in Composition and Structure of Coral Reef Systems Risks for Low-Lying Coastal Areas

EFFECTIVE CLIMATE CHANGE ADAPTATION A MORE VIBRANT WORLD
IPCC_WG2AR5_SlideDeck.pptx