6edf59ee08ed8244c496930c5519a001.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 The Western Frontier and Industrialization The Western Frontier Industry and Railroads Big Business and Labor The Gilded Age Immigrants and Urbanization
The Western Frontier and Industrialization The Western Frontier Industry and Railroads Big Business and Labor The Gilded Age Immigrants and Urbanization
 The Western Frontier Prairie Problems § Native American and White cultures greatly differed § Owning land § Whites believed west was unsettled, but lure of striking it rich too strong § US Gov’t grants and restricts land for NA often § Massacre at Sand Creek- Troops attack Indian reservation § Treaty of Fort Laramie settle problems temporarily § Whites encroach on Indian land searching for gold § Custer’s Last Stand: NA lay in wait and ambush US troops § Many Americans wanted to assimilate NA- integrate into white culture § The Dawes Act: Broke up reservations, “Americanize” Indians
The Western Frontier Prairie Problems § Native American and White cultures greatly differed § Owning land § Whites believed west was unsettled, but lure of striking it rich too strong § US Gov’t grants and restricts land for NA often § Massacre at Sand Creek- Troops attack Indian reservation § Treaty of Fort Laramie settle problems temporarily § Whites encroach on Indian land searching for gold § Custer’s Last Stand: NA lay in wait and ambush US troops § Many Americans wanted to assimilate NA- integrate into white culture § The Dawes Act: Broke up reservations, “Americanize” Indians
 General Custer Sitting Bull
General Custer Sitting Bull
 The Western Frontier § NA still suffering starvation and poverty § Battle of Wounded Knee. US army rounds up hundreds of homeless NA § Took them to a camp and demanded they lay down arms § Someone fires shot and massacre ensues § Era of wide open range over
The Western Frontier § NA still suffering starvation and poverty § Battle of Wounded Knee. US army rounds up hundreds of homeless NA § Took them to a camp and demanded they lay down arms § Someone fires shot and massacre ensues § Era of wide open range over
 The Western Frontier The Great Plains § Railroads open west. Central Pacific and Union Pacific race to reach west coast § Homestead Act: free land to families headed west § Historians claimed frontier was closed and that parts of US had lost its lure § Prairie life tough- soddy and dugout homes § Little to no farming equipment- pressure to grow as much as possible to stay out of debt
The Western Frontier The Great Plains § Railroads open west. Central Pacific and Union Pacific race to reach west coast § Homestead Act: free land to families headed west § Historians claimed frontier was closed and that parts of US had lost its lure § Prairie life tough- soddy and dugout homes § Little to no farming equipment- pressure to grow as much as possible to stay out of debt
 The Western Frontier Farmer and Populist Movement § Farmers in trouble-> crop prices low, mortgage farms to pay bills § Civil War greenbacks worthless now § RR charging high prices to transport grain and goods § Farmers organize the Grange- battle railroads and organize farm families
The Western Frontier Farmer and Populist Movement § Farmers in trouble-> crop prices low, mortgage farms to pay bills § Civil War greenbacks worthless now § RR charging high prices to transport grain and goods § Farmers organize the Grange- battle railroads and organize farm families
 The Western Frontier § From the Grange comes the Populist Political Party § Increase money supply § Federal loan program § 8 hr workday § By 1893 - full fledged depression § Republicans- industrialized North (Gold Standard) § Democrats- farmers from west and south (Bimettalism) § Williams Jennings Bryan- Cross of Gold Speech § Compared crucifixion of Jesus to Southerners and their economic plight § Republicans win election: William Mckinley
The Western Frontier § From the Grange comes the Populist Political Party § Increase money supply § Federal loan program § 8 hr workday § By 1893 - full fledged depression § Republicans- industrialized North (Gold Standard) § Democrats- farmers from west and south (Bimettalism) § Williams Jennings Bryan- Cross of Gold Speech § Compared crucifixion of Jesus to Southerners and their economic plight § Republicans win election: William Mckinley

 Industry and Railroads Expansion of Industry § Industrial Boom § Growing urban pop, natural resources, gov’t support of business § Oil Boom- Kerosene and eventually gasoline § Bessemer Steel- Turning iron into steel § Railroads, bridges, skyscrapers § Inventions § Edison: lightbulb-> need for electricity rises, allowed factories to choose any area, not just near rivers § Typewriter and telephone: growth of clerical jobs (women)
Industry and Railroads Expansion of Industry § Industrial Boom § Growing urban pop, natural resources, gov’t support of business § Oil Boom- Kerosene and eventually gasoline § Bessemer Steel- Turning iron into steel § Railroads, bridges, skyscrapers § Inventions § Edison: lightbulb-> need for electricity rises, allowed factories to choose any area, not just near rivers § Typewriter and telephone: growth of clerical jobs (women)
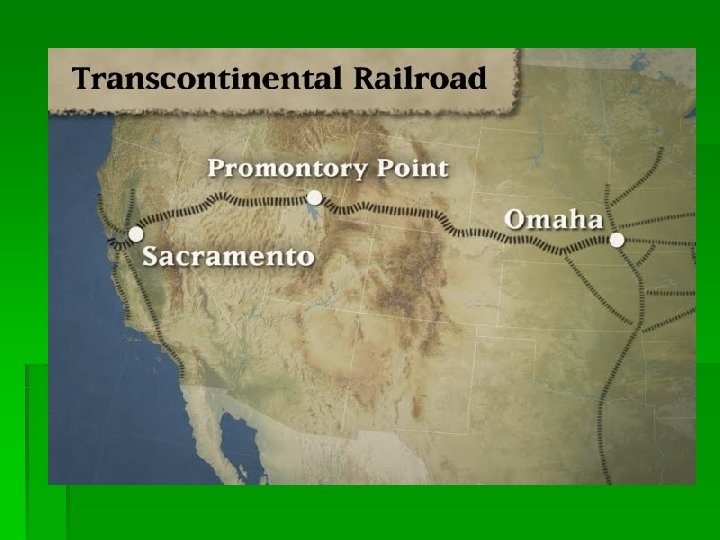
 Industry and Railroads Age of Railroads § Gov’t grants huge tracts of land for RR expansion § 1869: Promontory Point, Utah-> 1 st Transcontinental RR § Building RR caused death and illness, using immigrant labor China and Ireland § Unified the country, first use of time zones
Industry and Railroads Age of Railroads § Gov’t grants huge tracts of land for RR expansion § 1869: Promontory Point, Utah-> 1 st Transcontinental RR § Building RR caused death and illness, using immigrant labor China and Ireland § Unified the country, first use of time zones
 Industry and Railroads The Good and The Bad § New towns and communities § George Pullman- RR car builder; also built town for his workers->very controlled § Credit Mobilier Scandal § Union Pacific RR formed construction company § Ordered company to lay RR track 2 -3 times higher than necessary § Pocketed the profit
Industry and Railroads The Good and The Bad § New towns and communities § George Pullman- RR car builder; also built town for his workers->very controlled § Credit Mobilier Scandal § Union Pacific RR formed construction company § Ordered company to lay RR track 2 -3 times higher than necessary § Pocketed the profit
 Industry and Railroads Farmers vs. Railroads § Farmers mad: misuse land, fix prices, no consistent prices § Congress passes Interstate Commerce Act § Fed. Supervises inter-state activity (RR) § Corporate corruption, funds mismanagement, over building and competition lead to national financial probs
Industry and Railroads Farmers vs. Railroads § Farmers mad: misuse land, fix prices, no consistent prices § Congress passes Interstate Commerce Act § Fed. Supervises inter-state activity (RR) § Corporate corruption, funds mismanagement, over building and competition lead to national financial probs
 Big Business and Labor Carnegie’s Innovations § Carnegie Steel Company § Make better products cheaper § Offered stock in his company § Vertical Integration- buy out his suppliers (coal fields, iron mines, RR lines) § Horizontal Integration- buy out competing companies § Carnegie adhered to Social Darwinism- laissez faire policy, strong win, weak go home
Big Business and Labor Carnegie’s Innovations § Carnegie Steel Company § Make better products cheaper § Offered stock in his company § Vertical Integration- buy out his suppliers (coal fields, iron mines, RR lines) § Horizontal Integration- buy out competing companies § Carnegie adhered to Social Darwinism- laissez faire policy, strong win, weak go home
 Andrew Carnegie John D. Rockefellar
Andrew Carnegie John D. Rockefellar
 Big Business and Labor Fewer Control More § Mergers, stockholders, and trustees controlled wealth of nation § John D. Rockefeller- Standard Oil Company § Paid low wages, price gouging § Nicknames “Robber Baron” § Gov’t passes Sherman Antitrust Act: illegal to form a trust that interfered with free trade b/t states or countries § South lags- tobacco, furniture, and textile industries flourish
Big Business and Labor Fewer Control More § Mergers, stockholders, and trustees controlled wealth of nation § John D. Rockefeller- Standard Oil Company § Paid low wages, price gouging § Nicknames “Robber Baron” § Gov’t passes Sherman Antitrust Act: illegal to form a trust that interfered with free trade b/t states or countries § South lags- tobacco, furniture, and textile industries flourish
 Big Business and Labor Unions § Laborers join together to improve conditions § Injuries, poor ventilation, 7 day work weeks § Early Unions: National Labor Union, Knights of Labor § Activists turn to Socialism- gov’t controls business- equal distribution of wealth § Industrial Workers of the World – Wobblies
Big Business and Labor Unions § Laborers join together to improve conditions § Injuries, poor ventilation, 7 day work weeks § Early Unions: National Labor Union, Knights of Labor § Activists turn to Socialism- gov’t controls business- equal distribution of wealth § Industrial Workers of the World – Wobblies
 Big Business and Labor Strikers Violence § Haymarket Affair- Bomb thrown into strike line in Chicago § Pullman Strike. Depression and low wages force strike, Pullman Co. hires “scabs” § Many companies blacklisted strikers, yet union numbers grew
Big Business and Labor Strikers Violence § Haymarket Affair- Bomb thrown into strike line in Chicago § Pullman Strike. Depression and low wages force strike, Pullman Co. hires “scabs” § Many companies blacklisted strikers, yet union numbers grew
 The Gilded Age Political Machines § Weak city gov’t and ruthless Social Darwinist theory, cities receptive to new power structure: Political Machine § Organized group that controls activities of a political party § Offer services to voters and business in exchange for political or financial support § Political Boss: controlled city like a major
The Gilded Age Political Machines § Weak city gov’t and ruthless Social Darwinist theory, cities receptive to new power structure: Political Machine § Organized group that controls activities of a political party § Offer services to voters and business in exchange for political or financial support § Political Boss: controlled city like a major
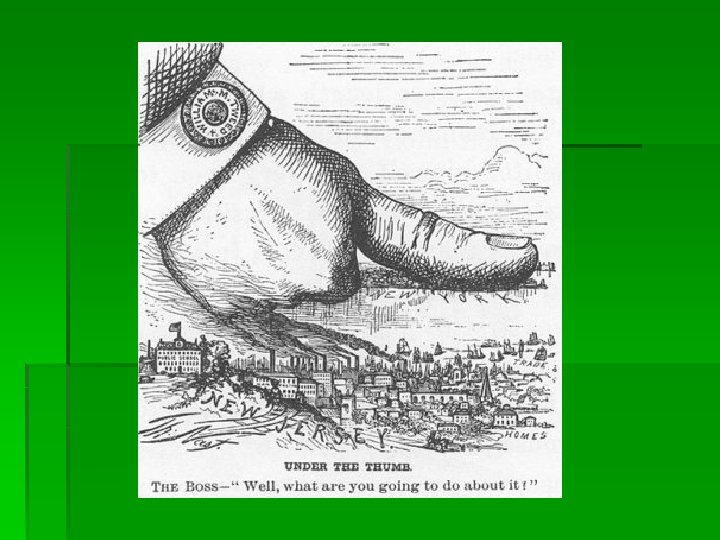
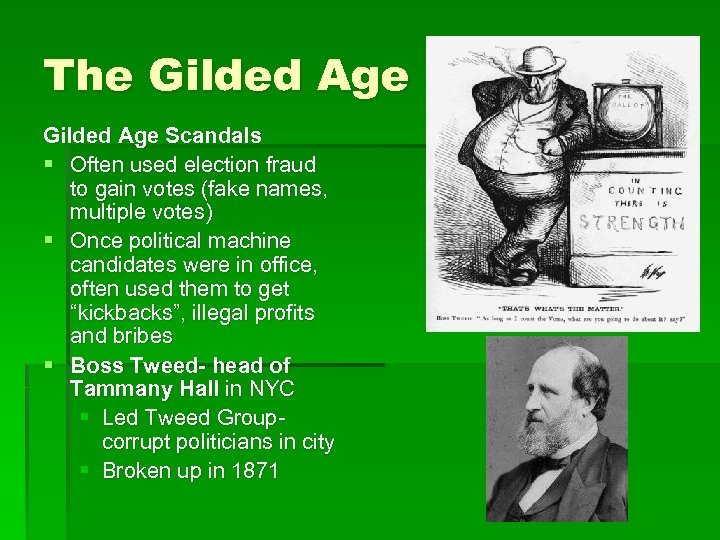 The Gilded Age Scandals § Often used election fraud to gain votes (fake names, multiple votes) § Once political machine candidates were in office, often used them to get “kickbacks”, illegal profits and bribes § Boss Tweed- head of Tammany Hall in NYC § Led Tweed Groupcorrupt politicians in city § Broken up in 1871
The Gilded Age Scandals § Often used election fraud to gain votes (fake names, multiple votes) § Once political machine candidates were in office, often used them to get “kickbacks”, illegal profits and bribes § Boss Tweed- head of Tammany Hall in NYC § Led Tweed Groupcorrupt politicians in city § Broken up in 1871
 The Gilded Age Civil Service Replaces Patronage § Complaints about patronage- giving gov’t jobs to people who helped a candidate get elected § Reformers press for adoption of merit system § Civil Service (gov’t jobs) go to those who are most qualified § Presidents Hayes, Garfield, and Arthur further reforms § Garfield assassinated § Pendleton Civil Service Act- enforced merit system § Big Business ensure that foreign tariffs would remain low by “buying” candidates in office
The Gilded Age Civil Service Replaces Patronage § Complaints about patronage- giving gov’t jobs to people who helped a candidate get elected § Reformers press for adoption of merit system § Civil Service (gov’t jobs) go to those who are most qualified § Presidents Hayes, Garfield, and Arthur further reforms § Garfield assassinated § Pendleton Civil Service Act- enforced merit system § Big Business ensure that foreign tariffs would remain low by “buying” candidates in office
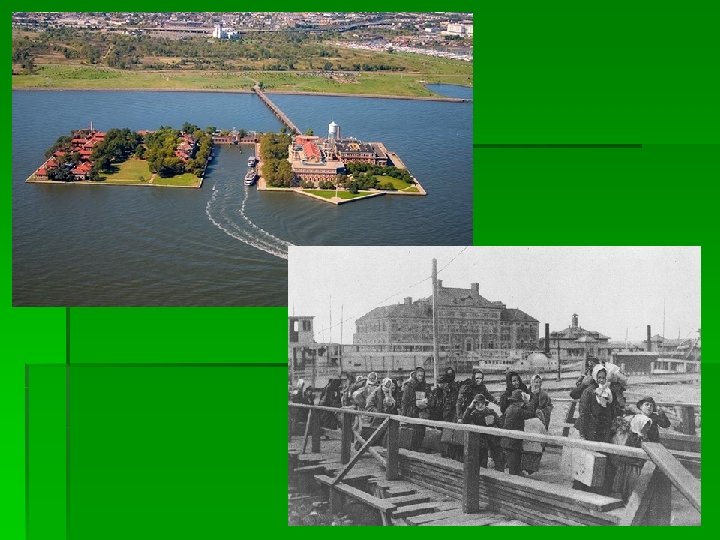
 Immigrants and Urbanization Life in a New Land § Seek better life- refuge from famine, religious/political persecution, rising population § In 50 yrs, ~20 million Europeans immigrate § Chinese and Japanese seek gold (1898 - US annex Hawaii) § Almost all immigrants travel by steamship- disease spreads § Pass inspection at Ellis Island- 5 hrs; Angel Island on West Coast § Ethnic communities grow-> friction increases
Immigrants and Urbanization Life in a New Land § Seek better life- refuge from famine, religious/political persecution, rising population § In 50 yrs, ~20 million Europeans immigrate § Chinese and Japanese seek gold (1898 - US annex Hawaii) § Almost all immigrants travel by steamship- disease spreads § Pass inspection at Ellis Island- 5 hrs; Angel Island on West Coast § Ethnic communities grow-> friction increases

 Immigrants and Urbanization Immigrant Restrictions § America becomes melting pot § Anti-immigrant feelings emerge->Nativism (Favoritism to native born Americans) § Right immigrants VS Wrong Immigrants § Chinese Exclusion Act- stopped Chinese immigration for 10 yrs § 1907 - Japan agrees to “Gentlemen’s Agreement”Limit Japanese immigration to US, if US promises to stop segregating US schools
Immigrants and Urbanization Immigrant Restrictions § America becomes melting pot § Anti-immigrant feelings emerge->Nativism (Favoritism to native born Americans) § Right immigrants VS Wrong Immigrants § Chinese Exclusion Act- stopped Chinese immigration for 10 yrs § 1907 - Japan agrees to “Gentlemen’s Agreement”Limit Japanese immigration to US, if US promises to stop segregating US schools

 Immigrants and Urbanization § Rapid growth of cities due to tech and industry boom § Immigrants settle in cities - cheap/convenient § Ethnic neighborhoods become overcrowded § Tension b/t blacks and immigrants- compete for jobs
Immigrants and Urbanization § Rapid growth of cities due to tech and industry boom § Immigrants settle in cities - cheap/convenient § Ethnic neighborhoods become overcrowded § Tension b/t blacks and immigrants- compete for jobs
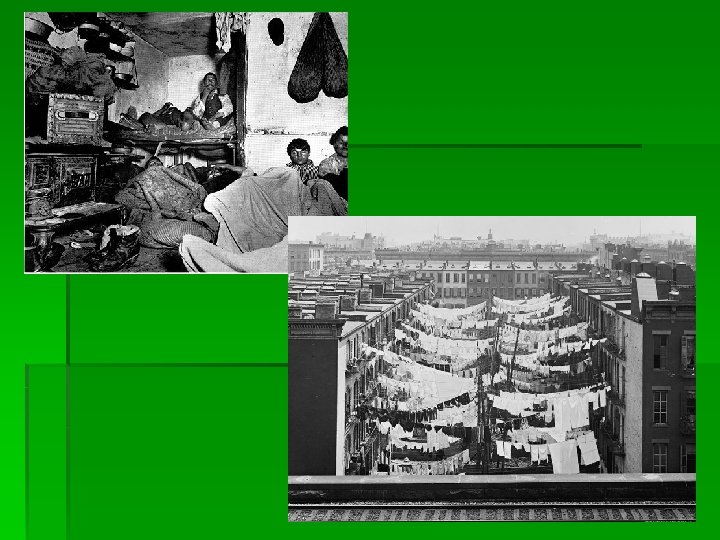
 Immigrants and Urbanization Urban Problems § Housing: Tenements overcrowded and diseased § Transportation: Street cars, subways § Water: no indoor plumbing, unsafe drinking water § Constant threat of fire (little water and wood buildings) § High crime and poor sanitation
Immigrants and Urbanization Urban Problems § Housing: Tenements overcrowded and diseased § Transportation: Street cars, subways § Water: no indoor plumbing, unsafe drinking water § Constant threat of fire (little water and wood buildings) § High crime and poor sanitation

 Immigrants and Urbanization Reform § Social welfare programs develop § Settlement houses- community centers § Run by middle class, college educated women § Jane Addams: Hull House
Immigrants and Urbanization Reform § Social welfare programs develop § Settlement houses- community centers § Run by middle class, college educated women § Jane Addams: Hull House


