3112827d3f420ac489e1b91ef51bc912.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

The Visible PC Chapter 2 © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Overview • In this chapter, you will learn to – Describe how the PC works – Identify the essential tools of the trade and avoid electrostatic discharge (ESD) – Identify the major internal and external components of a PC – Identify the different connectors on a typical PC system unit © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
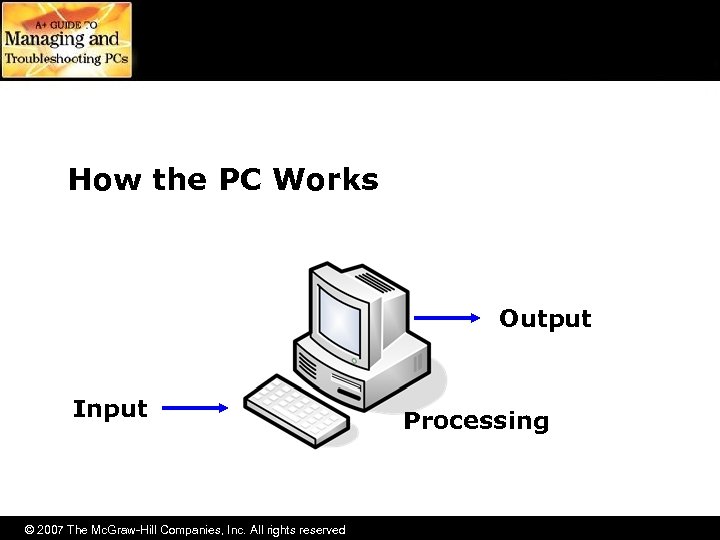
How the PC Works Output Input © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved Processing
How the PC Works • Software – Operating system (Windows, MAC OS X, Linux) – Applications (Power. Point, Word, Outlook, Internet Explorer) • Hardware – Pieces you can touch (mouse, monitor, motherboard, etc. ) © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
How the PC Works • Computer functions through four stages: – Input provides the computer with data • Keyboard and mouse – Processing occurs when the computer processes or manipulates your data – Output is provided as the result of processing your data • Monitor, printer, speakers – Storage is how you keep your data for later use • Hard drive, CD-ROM disc, floppy diskette © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
How the PC Works • The Art of the PC Technician – Hardware and software interact to accomplish the four stages – Your goal is to understand all the parts and how they interact in the various stages • By understanding how it works, you’re better able to fix it when it breaks Broken PC PC tech © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved Fixed PC

Tools of the Trade and ESD Avoidance © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

PC Tool Kit • The basic tech toolkit: a Phillips-head screwdriver – Most toolkits contain a few other items • It’s a good idea to include – Magnifying glass – Small flashlight © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Comp. TIA A+ Essentials IT Essentials © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Electrostatic Discharge • Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the passage of a static electrical charge into your PC or a PC component such as a RAM stick – Static electricity can destroy sensitive parts of a PC – ESD damage is much more prevalent in dry, cool environments © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Anti-static Tools • Anti-static wrist strap – Keeps you and the PC at the same electrical potential to prevent ESD • Anti-static mats – Used temporarily to place parts taken out of your PC • Anti-static bags – Used to store electrical components from your PC • Always unplug a PC when you work on it. Don’t just turn it off. © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

The Complete PC © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
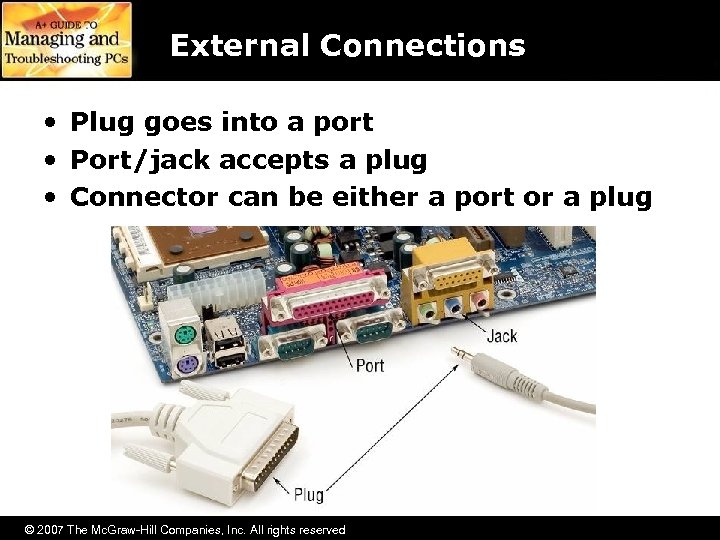
External Connections • Plug goes into a port • Port/jack accepts a plug • Connector can be either a port or a plug © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
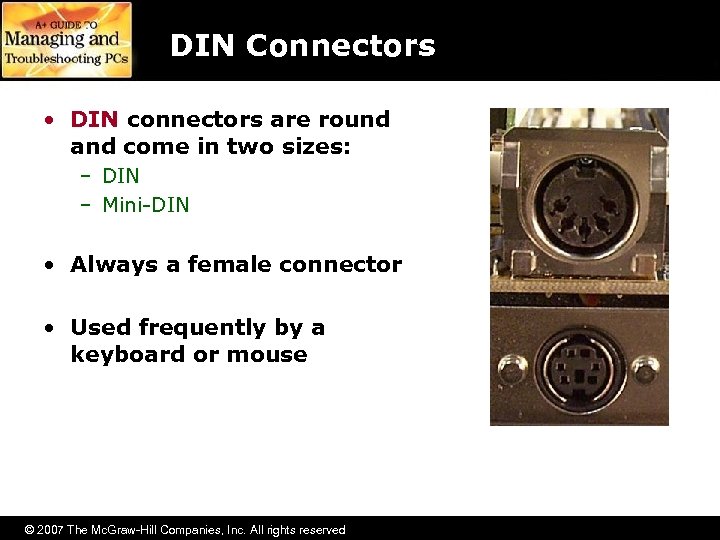
DIN Connectors • DIN connectors are round and come in two sizes: – DIN – Mini-DIN • Always a female connector • Used frequently by a keyboard or mouse © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

USB Connectors • Universal Serial Bus (USB) – Used by many devices today – Devices are hotswappable • You can insert or remove the device while the PC is powered on – USB B plugs into devices – USB A plugs into computers © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved USB B USB A

Fire. Wire Connectors • Fire. Wire connectors move data at incredibly high speeds – – Also known as IEEE 1394 Popular with video applications Uses 6 -wire connector (note the rounded edge) Hot-swappable © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

DB Connectors • DB connectors have a slight D-shape – Male DB connectors have pins – Female DB connectors have sockets – Oldest type of connector in the PC © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
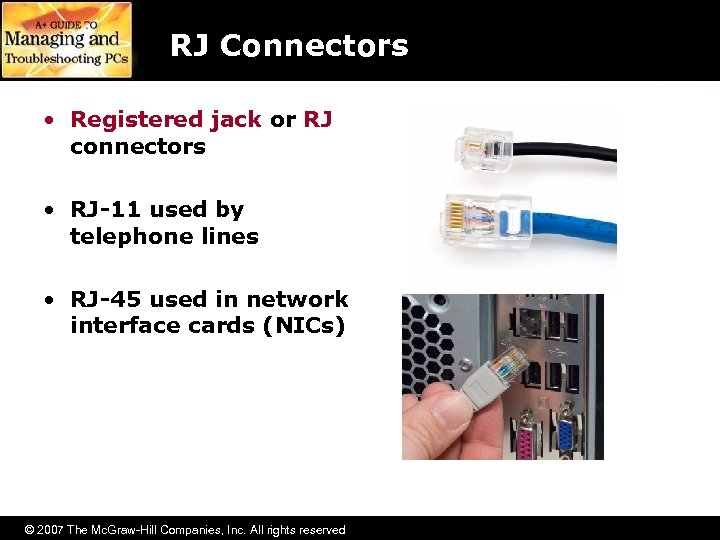
RJ Connectors • Registered jack or RJ connectors • RJ-11 used by telephone lines • RJ-45 used in network interface cards (NICs) © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Audio Connectors • Audio connectors are used on sound cards – Used to connect speakers, microphones, and other audio devices © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
Devices and Their Connectors © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
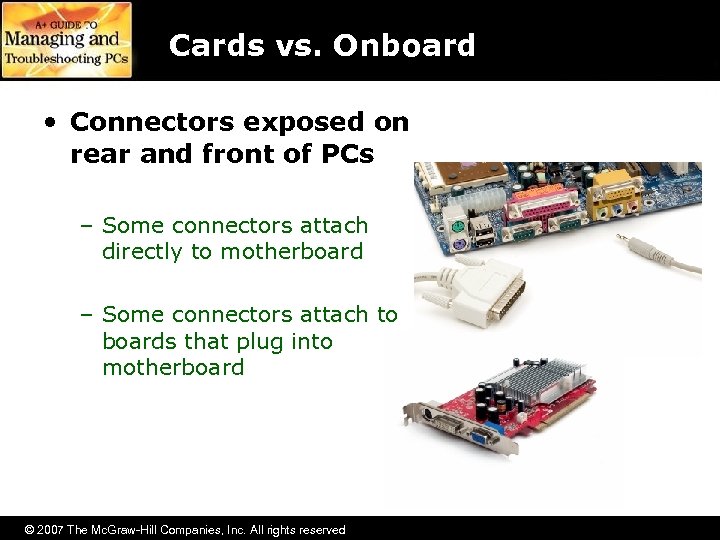
Cards vs. Onboard • Connectors exposed on rear and front of PCs – Some connectors attach directly to motherboard – Some connectors attach to boards that plug into motherboard © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Keyboard • Keyboards connect into dedicated mini-DIN (usually purple) or USB • Plugs and ports usually purple © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Video Cards • Video cards connect to monitors – S-Video connector (left) – Digital video interface (DVI) connector (center) – 15 -pin female DB connector (right) – Newer High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Sound Cards • Sound cards – – – Convert digital information into sound Convert sound from a microphone into digital data Mini-audio jacks for speakers and microphones DB-15 connector for a joystick or musical instrument Newer Sony/Phillips Digital Interface Format (S/PDIF) © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Network Cards • Networks: groups of PCs connected together – Network interface cards (NICs) typically on motherboard (can be expansion card) – Typical connector is RJ-45 © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Mouse • A mouse enables you to select graphical items on a screen – Connects through mini. DIN port (usually light green) or USB port (most common) – Trackball may be used instead of mouse © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
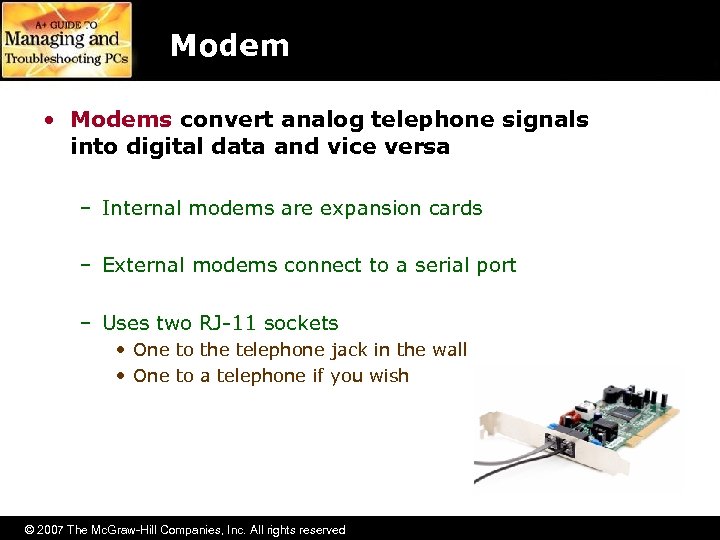
Modem • Modems convert analog telephone signals into digital data and vice versa – Internal modems are expansion cards – External modems connect to a serial port – Uses two RJ-11 sockets • One to the telephone jack in the wall • One to a telephone if you wish © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Serial Ports • Serial ports are used to add external devices to a PC – Accept and transmit serial data – Male DB-9 or DB-25 – Largely replaced by USB © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Printer • Printers output data from the PC onto paper – Historically used a female DB-25 – Today printers almost exclusively use a USB or Fire. Wire port © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Joystick • Joysticks are used almost exclusively to play games on the computer – Originally designed as an input device to be used like a mouse – Connector typically orange – Most joysticks now use USB © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Inside the System Unit © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Case • The case houses all of the internal components – Protects internal components – External connections in front and rear – Provides access to storage devices such as CDs © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
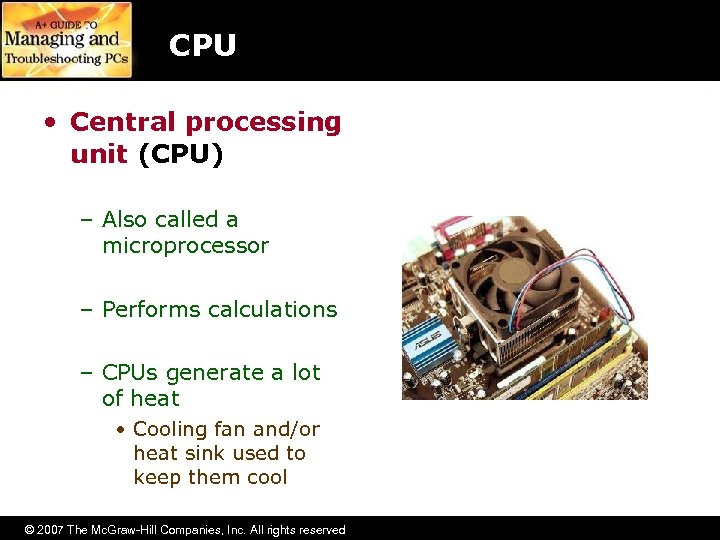
CPU • Central processing unit (CPU) – Also called a microprocessor – Performs calculations – CPUs generate a lot of heat • Cooling fan and/or heat sink used to keep them cool © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
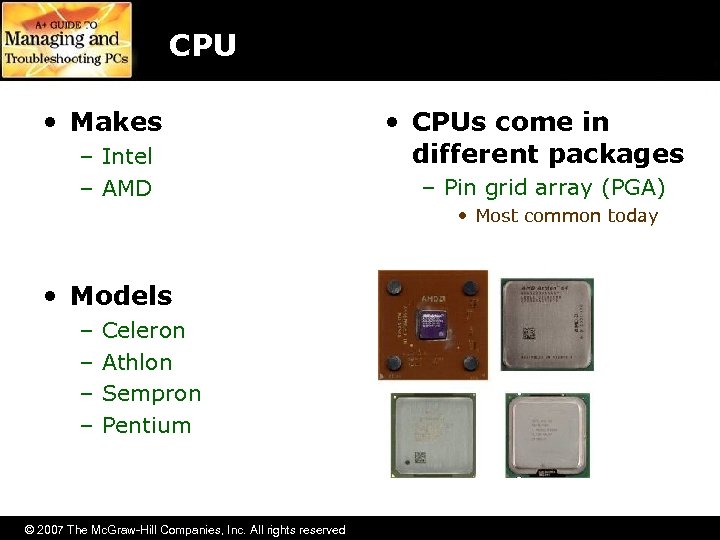
CPU • Makes – Intel – AMD • CPUs come in different packages – Pin grid array (PGA) • Most common today • Models – – Celeron Athlon Sempron Pentium © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
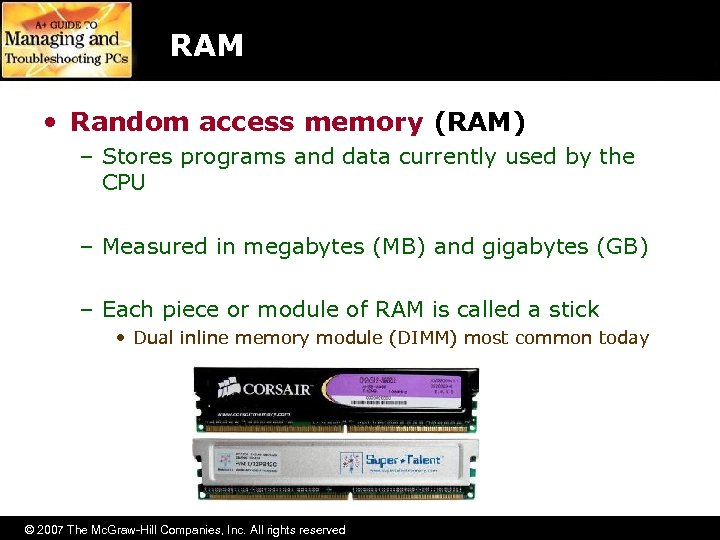
RAM • Random access memory (RAM) – Stores programs and data currently used by the CPU – Measured in megabytes (MB) and gigabytes (GB) – Each piece or module of RAM is called a stick • Dual inline memory module (DIMM) most common today © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
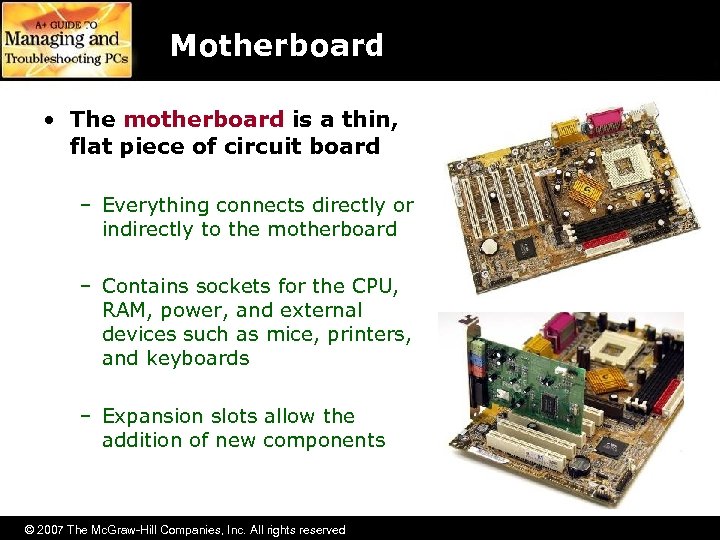
Motherboard • The motherboard is a thin, flat piece of circuit board – Everything connects directly or indirectly to the motherboard – Contains sockets for the CPU, RAM, power, and external devices such as mice, printers, and keyboards – Expansion slots allow the addition of new components © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Power Supply • Provides electrical power to PC components – Uses 110 VAC power from the wall outlet – Has power connectors for the motherboard and other devices – Uses a fan to keep itself and the PC cool inside – Safety Alert • High voltage capacitor holds power after unplugged © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Floppy Drive • The floppy drive uses floppy diskettes to store data – Connects to the computer via a ribbon cable – Connects to the floppy controller on the motherboard – Uses a connector from the power supply © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
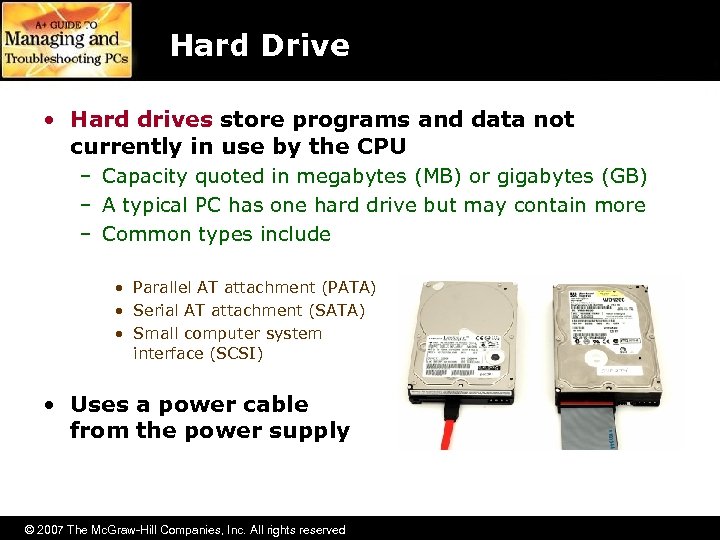
Hard Drive • Hard drives store programs and data not currently in use by the CPU – Capacity quoted in megabytes (MB) or gigabytes (GB) – A typical PC has one hard drive but may contain more – Common types include • Parallel AT attachment (PATA) • Serial AT attachment (SATA) • Small computer system interface (SCSI) • Uses a power cable from the power supply © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

Optical Media • Two groups – CD • Stores about 700 MB • CD-ROM (read only) • CD-R, CD-RW (allows writing to CD) – DVD • Stores about 4 GB of data • DVD-ROM, DVD+R, DVD+RW, DVD-RW © 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved

© 2007 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
3112827d3f420ac489e1b91ef51bc912.ppt