The Victorian Age.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 86
 The Victoria Age
The Victoria Age
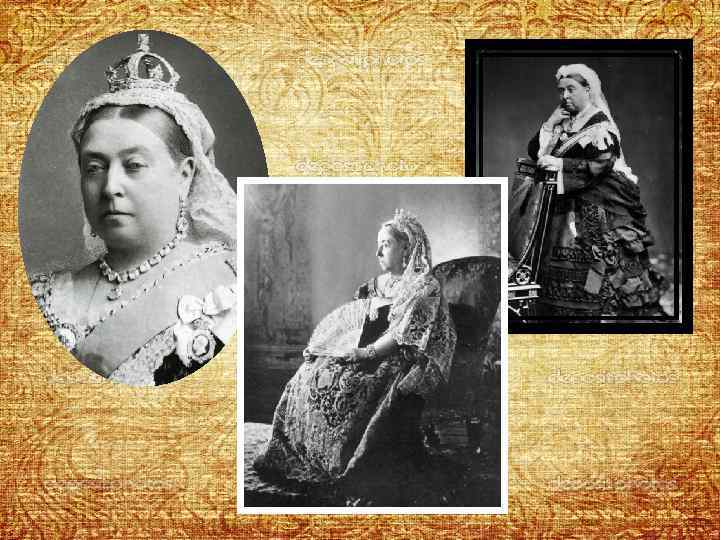
 Victorian Period • Period of Queen Victoria’s reign from 20 June 1837 (at 18) until her death on 22 January 1901 • It was the longest reign in British history • a period of peace, prosperity, refined sensibilities and national self-confidence for Britain
Victorian Period • Period of Queen Victoria’s reign from 20 June 1837 (at 18) until her death on 22 January 1901 • It was the longest reign in British history • a period of peace, prosperity, refined sensibilities and national self-confidence for Britain
 At 20 she married prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha who became not king, but Prince-
At 20 she married prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha who became not king, but Prince-
 • gave birth to nine children • arranged the marriages of children and grandchildren ‘the grandmother of Europe
• gave birth to nine children • arranged the marriages of children and grandchildren ‘the grandmother of Europe
 • Victoria maintained a sense of dignity and decorum that restored the average person’s high opinion of the monarchy after a series of horrible, ineffective leaders • After prince Albert’s death in 1861, the queen sank into a deep depression and wore black every day for the
• Victoria maintained a sense of dignity and decorum that restored the average person’s high opinion of the monarchy after a series of horrible, ineffective leaders • After prince Albert’s death in 1861, the queen sank into a deep depression and wore black every day for the

 The British Empire v. Large scale immigration to British colonies v. In 1857, Parliament took over the government of India and Queen Victoria became empress of India. v. British people saw the expansion of empire as a moral responsibility. v. Missionaries spread Christianity in India, Asia, and Africa.
The British Empire v. Large scale immigration to British colonies v. In 1857, Parliament took over the government of India and Queen Victoria became empress of India. v. British people saw the expansion of empire as a moral responsibility. v. Missionaries spread Christianity in India, Asia, and Africa.
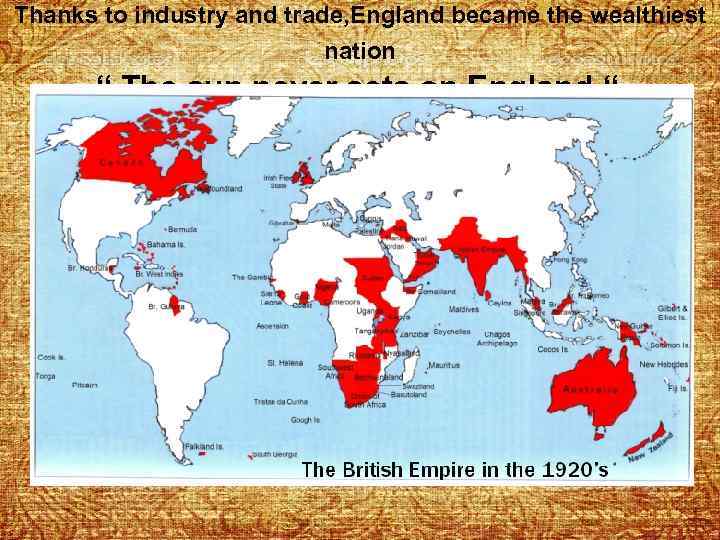 Thanks to industry and trade, England became the wealthiest nation “ The sun never sets on England “”
Thanks to industry and trade, England became the wealthiest nation “ The sun never sets on England “”
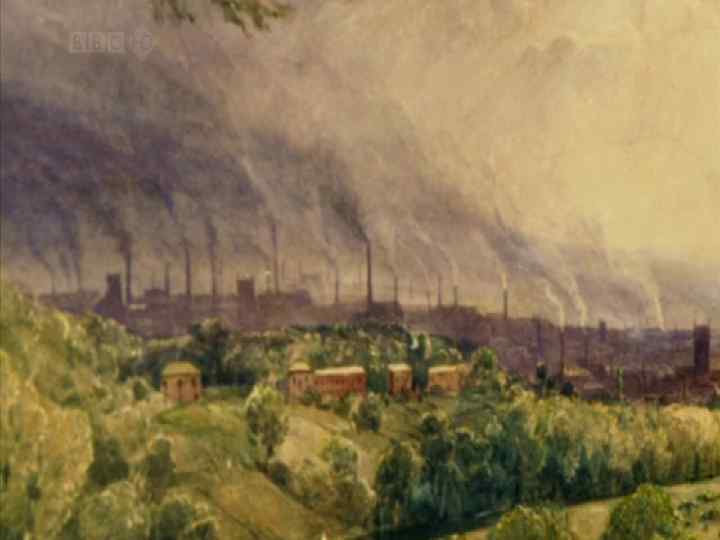
 The Industrial Revolution vpeople went into cities to search for better lives ► growth of the cities vboth unskilled and skilled people demanded work, so the wages were low ►hard life conditions. vpoverty and child labour emerged. vpollution in towns due to factory activity
The Industrial Revolution vpeople went into cities to search for better lives ► growth of the cities vboth unskilled and skilled people demanded work, so the wages were low ►hard life conditions. vpoverty and child labour emerged. vpollution in towns due to factory activity
 The old rural social pattern was changing under the impact of harsh industrialization
The old rural social pattern was changing under the impact of harsh industrialization

 The Age of Steam Railways, canals and steamships provided Britain with the transportation between Britain and its colonies.
The Age of Steam Railways, canals and steamships provided Britain with the transportation between Britain and its colonies.
 Britain dominated Global trade and expanded as a colonial empire in India, Australia, Africa and Brazil
Britain dominated Global trade and expanded as a colonial empire in India, Australia, Africa and Brazil
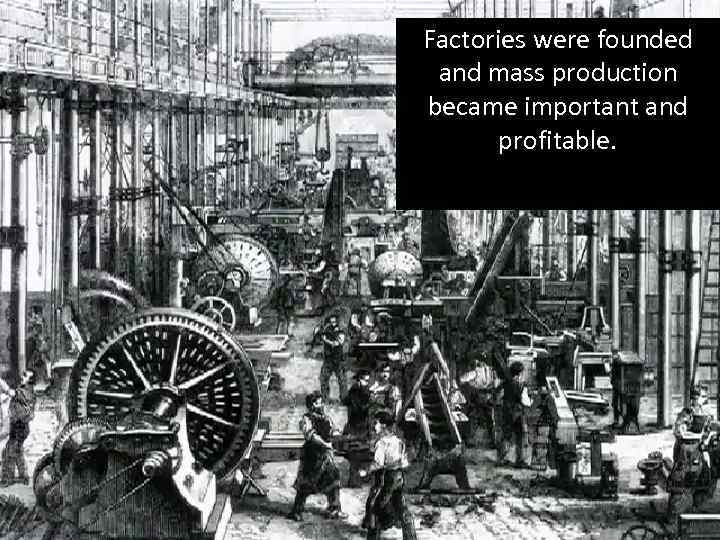 Factories were founded and mass production became important and profitable.
Factories were founded and mass production became important and profitable.
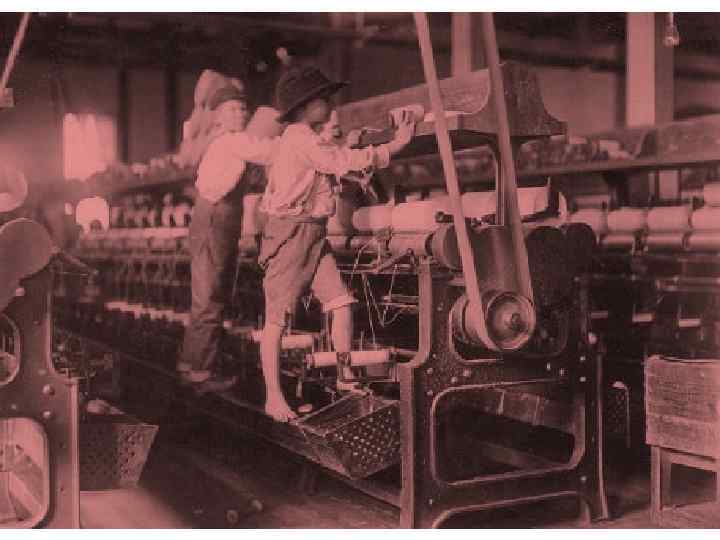
 Child Labour Children had to work long hours and under difficult conditions to help the family budget. (chimney sweepers, coal miners etc. )
Child Labour Children had to work long hours and under difficult conditions to help the family budget. (chimney sweepers, coal miners etc. )
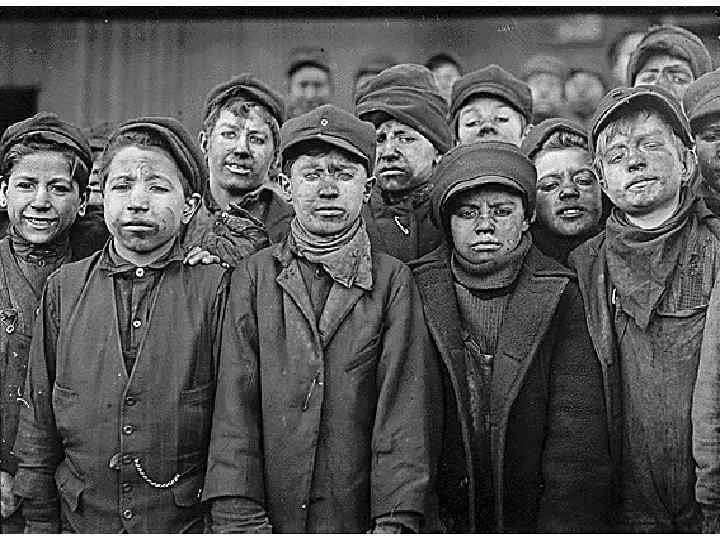
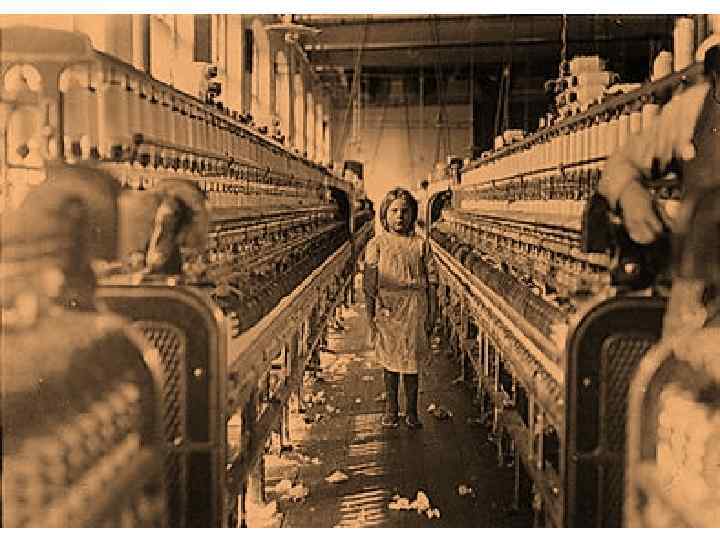


 victorian values • • moral responsibility, personal duty hard work, Decorum Respectability Chastity earnestness, domestic propriety not talking about sex punishing crime severely → only for one group of society
victorian values • • moral responsibility, personal duty hard work, Decorum Respectability Chastity earnestness, domestic propriety not talking about sex punishing crime severely → only for one group of society
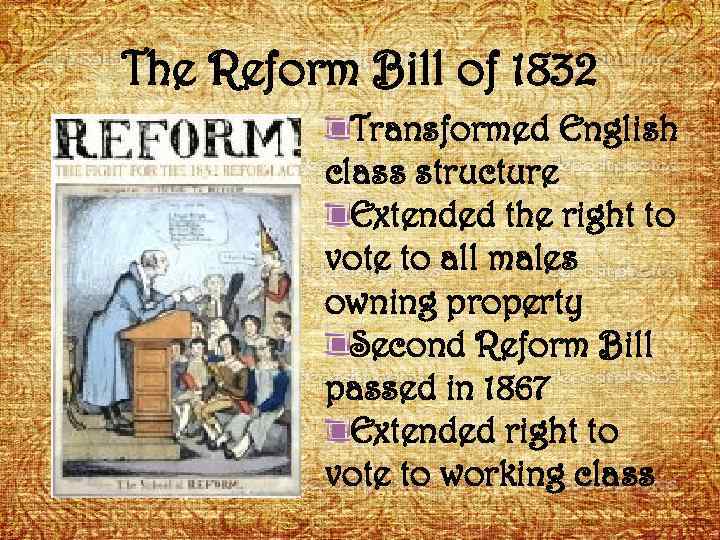 The Reform Bill of 1832 Transformed English class structure Extended the right to vote to all males owning property Second Reform Bill passed in 1867 Extended right to vote to working class
The Reform Bill of 1832 Transformed English class structure Extended the right to vote to all males owning property Second Reform Bill passed in 1867 Extended right to vote to working class
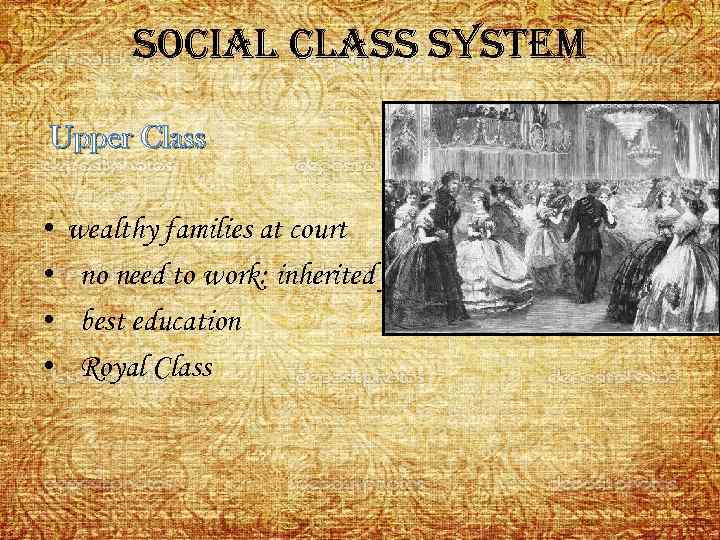 social class system Upper Class • • wealthy families at court no need to work: inherited fortune best education Royal Class
social class system Upper Class • • wealthy families at court no need to work: inherited fortune best education Royal Class
 Middle Class • largest class • benefitted the most from Industrial Revolution • Upper Middle Class • and Lower Middle Class
Middle Class • largest class • benefitted the most from Industrial Revolution • Upper Middle Class • and Lower Middle Class
 Working Class • Upper Working Class = skilled labour • Lower Working Class = unskilled labour • hostile to other classes • affected the worst by immigration
Working Class • Upper Working Class = skilled labour • Lower Working Class = unskilled labour • hostile to other classes • affected the worst by immigration
 Underclass • the “sunken people” • homeless, unskilled and ill
Underclass • the “sunken people” • homeless, unskilled and ill
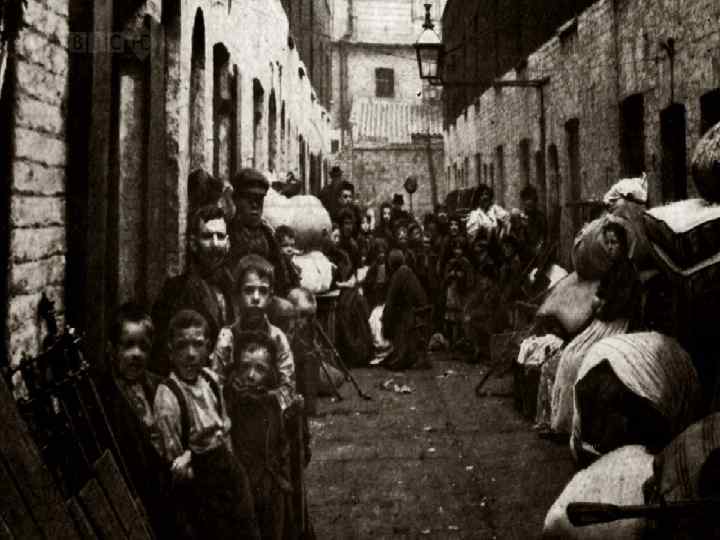
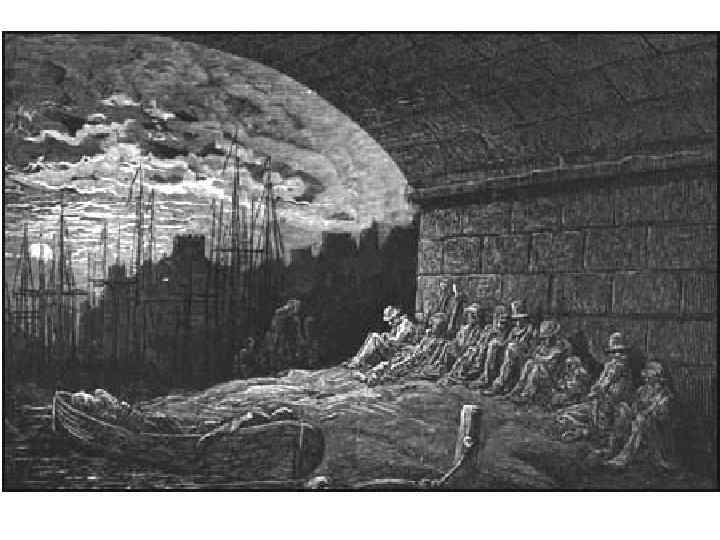
 The Time of Troubles 1830’s and 1840’s • • • Unemployment Poverty Rioting Slums in large cities Working conditions for women and children were terrible
The Time of Troubles 1830’s and 1840’s • • • Unemployment Poverty Rioting Slums in large cities Working conditions for women and children were terrible
 The Mid-Victorian Period 1848 -1870 A time of vprosperity vimprovement vstability voptimism
The Mid-Victorian Period 1848 -1870 A time of vprosperity vimprovement vstability voptimism
 The Role of Women women’s duty was to create a place of peace where man could take refuge from the difficulties of modern life (congenial angel) The only occupation at which an unmarried middle-class woman could earn a living and maintain some claim to gentility was that of a governess.
The Role of Women women’s duty was to create a place of peace where man could take refuge from the difficulties of modern life (congenial angel) The only occupation at which an unmarried middle-class woman could earn a living and maintain some claim to gentility was that of a governess.
 Prostitution v. Bad working conditions and underemployment drove thousands of women into prostitution v. Beginning in the late 1840 s , major news organizations, clergymen, and single women became increasingly concerned about prostitution, which came to be known as “ The Great Social Evil ” v. I n his landmark study, “Prostitution “, William Acton reported that the police estimated there were 8, 600 in London alone in 1857 and this number is too much to ignore.
Prostitution v. Bad working conditions and underemployment drove thousands of women into prostitution v. Beginning in the late 1840 s , major news organizations, clergymen, and single women became increasingly concerned about prostitution, which came to be known as “ The Great Social Evil ” v. I n his landmark study, “Prostitution “, William Acton reported that the police estimated there were 8, 600 in London alone in 1857 and this number is too much to ignore.
 Queen’s College for Women was established
Queen’s College for Women was established
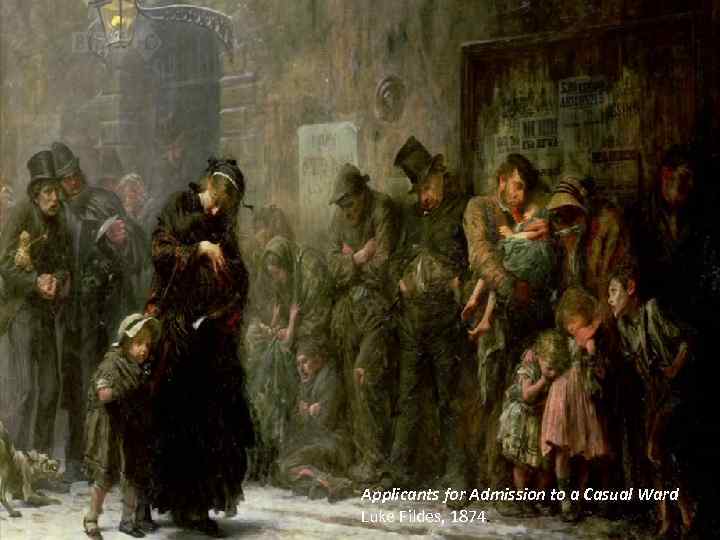

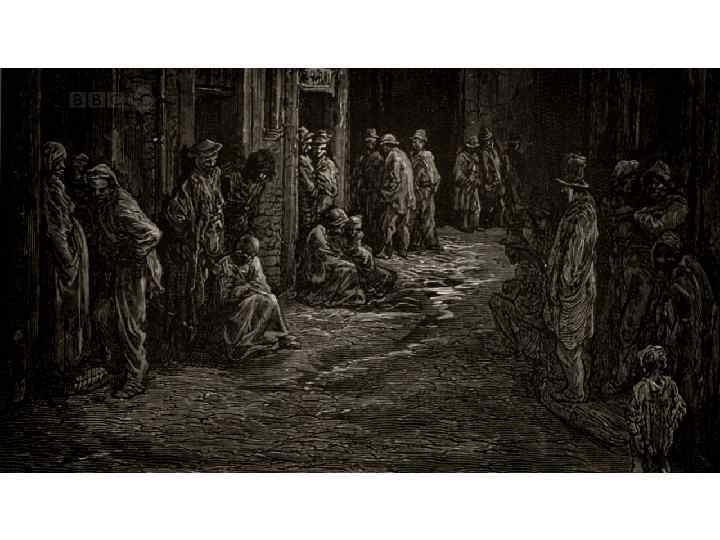
 Applicants for Admission to a Casual Ward Luke Fildes, 1874.
Applicants for Admission to a Casual Ward Luke Fildes, 1874.



 CULTURAL CONTEXT ADAM SMITH: ’s economic ideas had great influence on Victorian thinking The Wealth of Nations (1776) CHARLES DARWIN’s theory of evolution The Origin of Species (1859) The theory of evolution led to a crisis of faith and spiritual doubt among so many people. JOHN STUART MILL a champion of individual rights - On Liberty (1869) a pioneer of women’s rights - The Subjection of Women (1869). attacked the tyranny of the majority who would deny liberty to individuals through public opinion.
CULTURAL CONTEXT ADAM SMITH: ’s economic ideas had great influence on Victorian thinking The Wealth of Nations (1776) CHARLES DARWIN’s theory of evolution The Origin of Species (1859) The theory of evolution led to a crisis of faith and spiritual doubt among so many people. JOHN STUART MILL a champion of individual rights - On Liberty (1869) a pioneer of women’s rights - The Subjection of Women (1869). attacked the tyranny of the majority who would deny liberty to individuals through public opinion.

 Impact on Victorian Literature: • The novelists of the 1840’s and the 1850’s responded to the industrial and political scene: – Charles Kingsley- The Water Babies – Elizabeth Gaskell – North and South; Life of Charlotte Bronte – Benjamin Disraeli- Sybil
Impact on Victorian Literature: • The novelists of the 1840’s and the 1850’s responded to the industrial and political scene: – Charles Kingsley- The Water Babies – Elizabeth Gaskell – North and South; Life of Charlotte Bronte – Benjamin Disraeli- Sybil
 Victorian Novel • Dominant form in Victorian literature • Seek to represent a large and comprehensive social world, with a variety of classes. • Victorian novels are realistic • Major theme: Place of the individual in society, the aspiration of the hero or heroine for love or social position • The protagonist’s search for fulfillment is emblematic of the human condition. • Was a principal form of entertainment • For the first time, women were major
Victorian Novel • Dominant form in Victorian literature • Seek to represent a large and comprehensive social world, with a variety of classes. • Victorian novels are realistic • Major theme: Place of the individual in society, the aspiration of the hero or heroine for love or social position • The protagonist’s search for fulfillment is emblematic of the human condition. • Was a principal form of entertainment • For the first time, women were major
 Charlotte Bronte (1816 -1855) • English author and eldest of the famed Bronte sisters • Pen Name: Currer Bell • Notable Work: Jane Eyre (1847)
Charlotte Bronte (1816 -1855) • English author and eldest of the famed Bronte sisters • Pen Name: Currer Bell • Notable Work: Jane Eyre (1847)
 Jane Eyre • Published on: 16 October 1847 by Smith Elder and Co. of London, England. • Genre: Gothic Fiction, Social Criticism, Bildungsroman • Themes: Morality, God and Religion, Social Class, Gender Relations, Love and Passion, Feminism, Atonement and Forgiveness, Search
Jane Eyre • Published on: 16 October 1847 by Smith Elder and Co. of London, England. • Genre: Gothic Fiction, Social Criticism, Bildungsroman • Themes: Morality, God and Religion, Social Class, Gender Relations, Love and Passion, Feminism, Atonement and Forgiveness, Search
 Jane Eyre (1847)
Jane Eyre (1847)
 Emily Bronte (1818 -1849) • English author and one of the famed Bronte sisters • Pen Name: Ellis Bell • Notable Work: Wuthering Heights (1847)
Emily Bronte (1818 -1849) • English author and one of the famed Bronte sisters • Pen Name: Ellis Bell • Notable Work: Wuthering Heights (1847)
 Wuthering Heights (1847) • Written on: Oct 1845 - June 1846 • Published on: 1847 • First and only published novel • Elements of passion, mystery and doomed love as well as social commentary have made Wuthering Heights
Wuthering Heights (1847) • Written on: Oct 1845 - June 1846 • Published on: 1847 • First and only published novel • Elements of passion, mystery and doomed love as well as social commentary have made Wuthering Heights
 Wuthering Heights Core theme: the destructive effect that jealousy and vengefulness have
Wuthering Heights Core theme: the destructive effect that jealousy and vengefulness have
 Charles Dickens (1812 -1870)
Charles Dickens (1812 -1870)
 His Life • Born February 7, 1812 • 1824 -- Dickens worked at Warren’s Blacking Warehouse • 1824 -- Mr. Dickens (Charles’ father) taken to debtors’ prison; family joins him Imprisoned from February – May • 1827 - Dickens family evicted from home for not paying rent • Charles is pulled out of private school • Charles, now 15, becomes law clerk and free-lance writer • At the beginning Dickens called himself ´Boz´, this was his pen-name. • He gave numerous talks across Europe and in America.
His Life • Born February 7, 1812 • 1824 -- Dickens worked at Warren’s Blacking Warehouse • 1824 -- Mr. Dickens (Charles’ father) taken to debtors’ prison; family joins him Imprisoned from February – May • 1827 - Dickens family evicted from home for not paying rent • Charles is pulled out of private school • Charles, now 15, becomes law clerk and free-lance writer • At the beginning Dickens called himself ´Boz´, this was his pen-name. • He gave numerous talks across Europe and in America.
 Married: Catherine (Hogarth) Dickens April 2, 1836 10 Children
Married: Catherine (Hogarth) Dickens April 2, 1836 10 Children

 Main Works • • • • The Pickwick Papers The Adventures of Oliver Twist The Old Curiosity Shop A Christmas Carol Dombey and Son David Copperfield Bleak House Hard Times: For These Times Little Dorrit A Tale of Two Cities Great Expectations Our Mutual Friend The Mystery of Edwin Drood (never completed by Dickens)
Main Works • • • • The Pickwick Papers The Adventures of Oliver Twist The Old Curiosity Shop A Christmas Carol Dombey and Son David Copperfield Bleak House Hard Times: For These Times Little Dorrit A Tale of Two Cities Great Expectations Our Mutual Friend The Mystery of Edwin Drood (never completed by Dickens)
 David Copperfield • Published on: 1850 Full title: The Personal History, Adventures, Experience and Observation of David Copperfield the Younger of Blunderstone Rookery
David Copperfield • Published on: 1850 Full title: The Personal History, Adventures, Experience and Observation of David Copperfield the Younger of Blunderstone Rookery
 His Social Conscience • He crusaded for children’s rights. • He was an advocate of child labor laws to protect children. • He opposed cruelty, deprivation, and corporal punishment of children. • He protested a greedy, uncaring, materialistic society through such works as A Christmas Carol
His Social Conscience • He crusaded for children’s rights. • He was an advocate of child labor laws to protect children. • He opposed cruelty, deprivation, and corporal punishment of children. • He protested a greedy, uncaring, materialistic society through such works as A Christmas Carol
 Charles Dickens’ End 1870 – Dickens died He is buried in the Poets’ Corner in Westminster Abbey in London Dickens’ epitaph: “He was a sympathizer to the poor, the suffering, and the oppressed; and by his death, one of England’s greatest writers is lost to the world. ”
Charles Dickens’ End 1870 – Dickens died He is buried in the Poets’ Corner in Westminster Abbey in London Dickens’ epitaph: “He was a sympathizer to the poor, the suffering, and the oppressed; and by his death, one of England’s greatest writers is lost to the world. ”
 William Makepeace Thackeray (1811 -1863)
William Makepeace Thackeray (1811 -1863)
 “Life is a mirror. When you smile in front of it, it will also smile and so will it when you cry to it. ” W. M. Thackeray
“Life is a mirror. When you smile in front of it, it will also smile and so will it when you cry to it. ” W. M. Thackeray
 His Life • born in Calcutta, India to well -to-do parents • sent to England after his father died • education: Trinity College, Cambridge • became addicted to gambling • left Cambridge without a degree and heavily in debt
His Life • born in Calcutta, India to well -to-do parents • sent to England after his father died • education: Trinity College, Cambridge • became addicted to gambling • left Cambridge without a degree and heavily in debt
 • started his career as a hard working journalist • many absurd pen names: – George Savage Fitz. Boodle – Michael Angelo Titmarsh – Théophile Wagstaff – C. J. Yellowplush – Esq.
• started his career as a hard working journalist • many absurd pen names: – George Savage Fitz. Boodle – Michael Angelo Titmarsh – Théophile Wagstaff – C. J. Yellowplush – Esq.
 Major Works • Vanity Fair, 1847 • Pendennis, 1850 • Henry Esmond, 1852 • The Newcomes, 1853 -55
Major Works • Vanity Fair, 1847 • Pendennis, 1850 • Henry Esmond, 1852 • The Newcomes, 1853 -55
 Thackeray is 1. a realist. • paints life as he has seen it. • his stories are accurate and true to life form his precise and thorough • his satire: observation • rich knowledge of social life and of the human heart aim: to produce impression in all his novels. – caustic • his humour: 2. a moralist. • His 3. a satirist. a moral – subtle
Thackeray is 1. a realist. • paints life as he has seen it. • his stories are accurate and true to life form his precise and thorough • his satire: observation • rich knowledge of social life and of the human heart aim: to produce impression in all his novels. – caustic • his humour: 2. a moralist. • His 3. a satirist. a moral – subtle
 Vanity Fair (1847 -1848) • the first major work published under his own name • appeared in monthly installments • sub-titled ‘A Novel without a Hero
Vanity Fair (1847 -1848) • the first major work published under his own name • appeared in monthly installments • sub-titled ‘A Novel without a Hero
 Death Thackeray died suddenly on Christmas Eve 1863. Just before his death he had reconciled with Dickens.
Death Thackeray died suddenly on Christmas Eve 1863. Just before his death he had reconciled with Dickens.
 Thomas Hardy (1840 -1928) “Some blessed Hope, whereof he knew And I was unaware. ”
Thomas Hardy (1840 -1928) “Some blessed Hope, whereof he knew And I was unaware. ”
 His Life • Born in Higher Bockhampton, Dorset on June 2, 1840. • Eldest child of builder, Thomas Hardy II and his wife, Jemima Hand. • attended local school until he was apprenticed to a Dorchester architect at 15. • After six years apprenticeship, went to London in 1861. • read widely in London and became interested in fiction and poetry while practicing architecture.
His Life • Born in Higher Bockhampton, Dorset on June 2, 1840. • Eldest child of builder, Thomas Hardy II and his wife, Jemima Hand. • attended local school until he was apprenticed to a Dorchester architect at 15. • After six years apprenticeship, went to London in 1861. • read widely in London and became interested in fiction and poetry while practicing architecture.
 • returned to Dorset as an architect and builder. • 1871 published his first novel. • due to their subject matter his novels were widely condemned in the papers and in critical writing • after Jude, Hardy writes only poetry and some drama
• returned to Dorset as an architect and builder. • 1871 published his first novel. • due to their subject matter his novels were widely condemned in the papers and in critical writing • after Jude, Hardy writes only poetry and some drama
 Major Themes in Hardy • Man’s impotence against greater forces—of nature, of society, of his own impulses. • A shaken, if not completely fractured view of the relationship between humans and God. • “meliorism”(Hardy’s term) that is the belief that the word CAN be made better by human effort • Naturalism • An overwhelming feeling of irony
Major Themes in Hardy • Man’s impotence against greater forces—of nature, of society, of his own impulses. • A shaken, if not completely fractured view of the relationship between humans and God. • “meliorism”(Hardy’s term) that is the belief that the word CAN be made better by human effort • Naturalism • An overwhelming feeling of irony
 Main Works • • Under the Greenwood Tree 1872 A Pair of Blue Eyes 1873 Far from the Madding Crowd 1874 The Return of the Native 1878 The Mayor of Casterbridge 1886 Tess of the D’Urbervilles 1891 Jude the Obscure 1896
Main Works • • Under the Greenwood Tree 1872 A Pair of Blue Eyes 1873 Far from the Madding Crowd 1874 The Return of the Native 1878 The Mayor of Casterbridge 1886 Tess of the D’Urbervilles 1891 Jude the Obscure 1896
 Victorian poetry vless subjective than the romantic. v. Poets sought new ways of telling stories in verse v. An interest in the past, both the classical and the medieval (mythological and historical allusions). v. The use of dramatic monologue. v. The themes are more realistic (child labor, the rights of women, science and religion) vmostly pictorial, heavily relying on visual imagery. v. The elegy is one of the most popular poetic forms (a form of poetry that laments the dead or the past). voften characterized by doubt and psychological conflicts.
Victorian poetry vless subjective than the romantic. v. Poets sought new ways of telling stories in verse v. An interest in the past, both the classical and the medieval (mythological and historical allusions). v. The use of dramatic monologue. v. The themes are more realistic (child labor, the rights of women, science and religion) vmostly pictorial, heavily relying on visual imagery. v. The elegy is one of the most popular poetic forms (a form of poetry that laments the dead or the past). voften characterized by doubt and psychological conflicts.
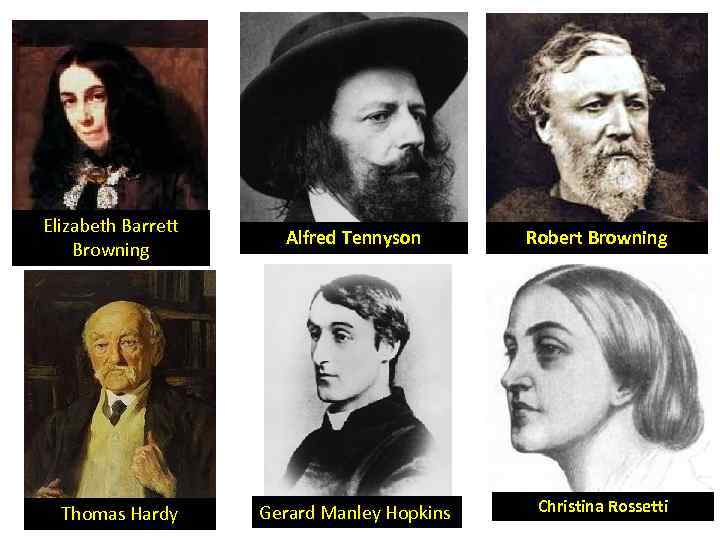 Elizabeth Barrett Browning Thomas Hardy Alfred Tennyson Gerard Manley Hopkins Robert Browning Christina Rossetti
Elizabeth Barrett Browning Thomas Hardy Alfred Tennyson Gerard Manley Hopkins Robert Browning Christina Rossetti
 Alfred Lord Tennyson (6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) • Leading poet of Victorian age and the Poet Laureate of the era • began to write poetry at an early age in the style of Lord Byron. • published Poems, Chiefly Lyrical, in 1830, which included the popular "Mariana".
Alfred Lord Tennyson (6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) • Leading poet of Victorian age and the Poet Laureate of the era • began to write poetry at an early age in the style of Lord Byron. • published Poems, Chiefly Lyrical, in 1830, which included the popular "Mariana".
 • His poem In Memoriam is most famous. • Themes: problems of religious faith, social change and political power. • the 2 nd most quoted writer after Shakespeare. “Tis better to have loved and lost , Than never to have loved at all”, “Theirs not to reason why, Theirs but to do and die
• His poem In Memoriam is most famous. • Themes: problems of religious faith, social change and political power. • the 2 nd most quoted writer after Shakespeare. “Tis better to have loved and lost , Than never to have loved at all”, “Theirs not to reason why, Theirs but to do and die
 Ulysses and the Sirens J. M. W. Waterhouse , 1891
Ulysses and the Sirens J. M. W. Waterhouse , 1891
 Robert Browning (1812 -1889) • Raised the DRAMATIC MONOLOGUE • Playwright and master of dramatic dialogue poetry • “A Death in the Desert”, “My Last Dutchess”, and “A Grammarian’s Funeral”
Robert Browning (1812 -1889) • Raised the DRAMATIC MONOLOGUE • Playwright and master of dramatic dialogue poetry • “A Death in the Desert”, “My Last Dutchess”, and “A Grammarian’s Funeral”
 Elizabeth Barrett Browning (1806 -1861) • With Robert, one of literature’s greatest love affairs. • One of the most prominent poets of the Victorian Era • Notable Work: How Do I Love Thee? (Sonnet 43)
Elizabeth Barrett Browning (1806 -1861) • With Robert, one of literature’s greatest love affairs. • One of the most prominent poets of the Victorian Era • Notable Work: How Do I Love Thee? (Sonnet 43)
 How Do I Love Thee? (Sonnet 43) • How do I love thee? Let me count the ways. I love thee to the depth and breadth and height My soul can reach, when feeling out of sight For the ends of Being and ideal Grace. I love thee to the level of everyday's Most quiet need, by sun and candlelight. I love thee freely, as men strive for Right; I love thee purely, as they turn from Praise. I love thee with the passion put to use In my old griefs, and with my childhood's faith. I love thee with a love I seemed to lose With my lost saints, —I love thee with the breath,
How Do I Love Thee? (Sonnet 43) • How do I love thee? Let me count the ways. I love thee to the depth and breadth and height My soul can reach, when feeling out of sight For the ends of Being and ideal Grace. I love thee to the level of everyday's Most quiet need, by sun and candlelight. I love thee freely, as men strive for Right; I love thee purely, as they turn from Praise. I love thee with the passion put to use In my old griefs, and with my childhood's faith. I love thee with a love I seemed to lose With my lost saints, —I love thee with the breath,
 Dante Gabriel Rossetti (12 May 1828 – 9 April 1882) • an artist, poet, illustrator, and translator of the pre. Raphaelite movement. • his art was characterized by its sensuality and its medieval revivalism. • wrote a poem specifically for a piece of his artwork, or the other way around.
Dante Gabriel Rossetti (12 May 1828 – 9 April 1882) • an artist, poet, illustrator, and translator of the pre. Raphaelite movement. • his art was characterized by its sensuality and its medieval revivalism. • wrote a poem specifically for a piece of his artwork, or the other way around.
 Christina Rossetti (1830 – 1894) • a great female poet of the era. • most famous for her poem Goblin Market • published widely until her death, especially in the pre. Raphaelite magazine “The Germ”
Christina Rossetti (1830 – 1894) • a great female poet of the era. • most famous for her poem Goblin Market • published widely until her death, especially in the pre. Raphaelite magazine “The Germ”
 Matthew Arnold (24 December 1822 – 15 April 1888) • one of the first modern poets of the Victorian Era. • the superintendent of England’s schools for many years and was highly revered. • famous for his imagery involving the ocean and also themes involving women. • Themes: sorrowful, disillusioned pessimism over the human plight in rapidly changing times
Matthew Arnold (24 December 1822 – 15 April 1888) • one of the first modern poets of the Victorian Era. • the superintendent of England’s schools for many years and was highly revered. • famous for his imagery involving the ocean and also themes involving women. • Themes: sorrowful, disillusioned pessimism over the human plight in rapidly changing times
 Victorian Drama Oscar Wilde (1856 -1900) George Bernard Shaw (1856 -1950)
Victorian Drama Oscar Wilde (1856 -1900) George Bernard Shaw (1856 -1950)
 Oscar Wilde (1854 -1900) • born in Dublin in 1854 • a disciple of Walter Pater, theorist of aestheticism. • a fashionable dandy. • died in Paris in 1900. • one of the most successful playwrights of late Victorian London
Oscar Wilde (1854 -1900) • born in Dublin in 1854 • a disciple of Walter Pater, theorist of aestheticism. • a fashionable dandy. • died in Paris in 1900. • one of the most successful playwrights of late Victorian London
 Works The Happy Prince and Other Tales (1888) The Picture of Dorian Gray (1890) Lord Arthur Saville’s Crime and Other Stories (1891) Lady Windermere’s Fan (1892) Salomé (1893) A Woman of No Importance (1893) An Ideal Husband (1895) The Importance of Being Earnest (1895) The Ballad of Reading Gaol (1898) De Profundis (1905)
Works The Happy Prince and Other Tales (1888) The Picture of Dorian Gray (1890) Lord Arthur Saville’s Crime and Other Stories (1891) Lady Windermere’s Fan (1892) Salomé (1893) A Woman of No Importance (1893) An Ideal Husband (1895) The Importance of Being Earnest (1895) The Ballad of Reading Gaol (1898) De Profundis (1905)
 Père Lachaise Cemetery, Paris
Père Lachaise Cemetery, Paris
 Witty Wilde "One should always be in love. That is the reason one should never marry. " -- “A Woman of No Importance” "To love oneself is the beginning of a life-long romance. “ “An Ideal Husband” "One should never trust a woman who tells one her real age. A woman who would tell one that, would tell one anything. “ “A Woman of No Importance” "A man who moralizes is usually a hypocrite, and a woman who moralizes is invariably plain. “ “Lady Windermere's Fan” "Young men want to be faithful and are not; old men want to be faithless and cannot. “ “The Picture of Dorian Gray”
Witty Wilde "One should always be in love. That is the reason one should never marry. " -- “A Woman of No Importance” "To love oneself is the beginning of a life-long romance. “ “An Ideal Husband” "One should never trust a woman who tells one her real age. A woman who would tell one that, would tell one anything. “ “A Woman of No Importance” "A man who moralizes is usually a hypocrite, and a woman who moralizes is invariably plain. “ “Lady Windermere's Fan” "Young men want to be faithful and are not; old men want to be faithless and cannot. “ “The Picture of Dorian Gray”
 The Ballad of Reading Gaol “And all men kill the thing they love, By all let this be heard, Some do it with a bitter look, Some with a flattering word, The coward does it with a kiss, The brave man with a sword!”
The Ballad of Reading Gaol “And all men kill the thing they love, By all let this be heard, Some do it with a bitter look, Some with a flattering word, The coward does it with a kiss, The brave man with a sword!”
 George Bernard Shaw (1856 -1950) born in Dublin, Ireland • • 1876 moved to London • did not return to Ireland for nearly thirty years • wrote prose, completing five novels before any of them was published. • educated himself, mostly at the British Museum reading books
George Bernard Shaw (1856 -1950) born in Dublin, Ireland • • 1876 moved to London • did not return to Ireland for nearly thirty years • wrote prose, completing five novels before any of them was published. • educated himself, mostly at the British Museum reading books
 • Together with friends founded the Fabian Society (socialist ideas) • the only person ever to have won both a Nobel Prize (for Literature in 1925) and an Academy Award (Best Screenplay for Pygmalion in 1938) • Died in 1950 at the age of 94 due to a fall from a ladder
• Together with friends founded the Fabian Society (socialist ideas) • the only person ever to have won both a Nobel Prize (for Literature in 1925) and an Academy Award (Best Screenplay for Pygmalion in 1938) • Died in 1950 at the age of 94 due to a fall from a ladder
 Works 63 plays, most of them full-length. • Widowers' Houses 1892 • Man and Superman 1902 • Mrs Warren’s Profession 1893 • Three Plays for Puritans (published 1901) • John Bull's Other Island 1904 • Major Barbara 1905 • Pygmalion 1912 -13 • Heartbreak House 1919 • Saint Joan 1923
Works 63 plays, most of them full-length. • Widowers' Houses 1892 • Man and Superman 1902 • Mrs Warren’s Profession 1893 • Three Plays for Puritans (published 1901) • John Bull's Other Island 1904 • Major Barbara 1905 • Pygmalion 1912 -13 • Heartbreak House 1919 • Saint Joan 1923


