da56b0631069c2464a2d02c7fbf33136.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

The Veil Nebula: a large, expanding cloud resulting from the explosion of a massive star (a supernova remnant). Life owes its existence to elements created in these massive stars and returned to space in these explosions to form new stars and planets. Light from the original supernova explosion likely reached Earth over 5, 000 years ago. Also known as the Cygnus Loop, the Veil Nebula now spans nearly 3

Homework #2 has been posted Questions 1 -16 are multiple choice. Answers to these questions are due on Oncourse by 5: 00 pm, Wednesday, September 22. Questions 17 – 20 require short written answers. These are due by the beginning of class on Thursday, September 23.

The Activities page of the class website now has a number of out-of-class activities posted. These activities count towards the activity points earned towards the final grade.
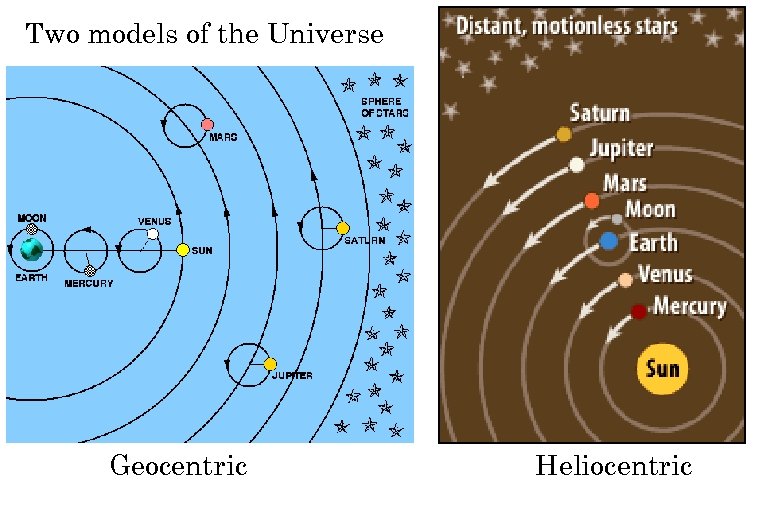
Two models of the Universe Geocentric Heliocentric

A hallmark of science is that theories are testable
Which model more accurately depicts nature? v Both make predictions for the apparent motions of the Sun, planets and stars. v The Heliocentric model, with modifications incorporating Kepler’s Laws, gives more accurate predictions v But, the Geocentric model might be made more accurate through appropriate modifications. v Need additional predictions that clearly differentiate between the two models. (need tests)

Contemporary with Kepler was Galileo Galilei (1564 -1642), the “founder of experimental science” ● ● First person known to point a telescope at the sky He wanted to connect the physics understood on earth with objects in the heaven His work got him in trouble with the Church and led to his house arrest for many years.

(Some of) Galileo’s Observations v Galileo saw craters and shadows cast by the mountains on the Moon (Moon had a landscape; it was a “place”, not a perfect heavenly body)

(Some of) Galileo’s Observations v Galileo saw craters and shadows cast by the mountains on the Moon (Moon had a landscape; it was a “place”, not a perfect heavenly body) v Sunspots (sun not “perfect”)

(Some of) Galileo’s Observations v Galileo saw craters and shadows cast by the mountains on the Moon (Moon had a landscape; it was a “place”, not a perfect heavenly body) v Sunspots (sun not “perfect”) v Rotation of sun
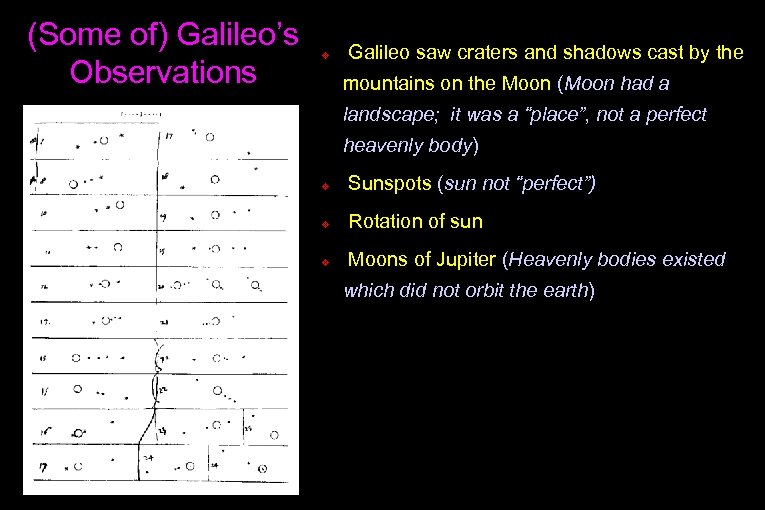
(Some of) Galileo’s Observations v Galileo saw craters and shadows cast by the mountains on the Moon (Moon had a landscape; it was a “place”, not a perfect heavenly body) v Sunspots (sun not “perfect”) v Rotation of sun v Moons of Jupiter (Heavenly bodies existed which did not orbit the earth)

(Some of) Galileo’s Observations v Galileo saw craters and shadows cast by the mountains on the Moon (Moon had a landscape; it was a “place”, not a perfect heavenly body) v Sunspots (sun not “perfect”) v Rotation of sun v Moons of Jupiter (Heavenly bodies existed which did not orbit the earth) v Phases of Venus: the two models of the Universe made two very different predictions.
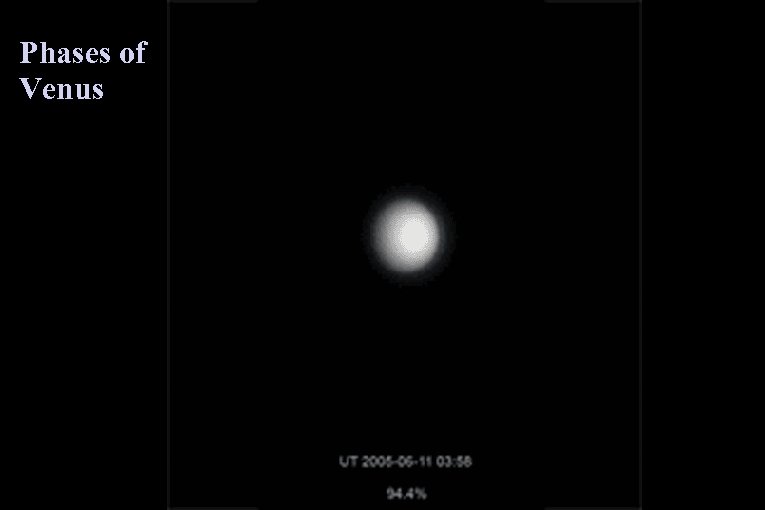

Phases of Venus
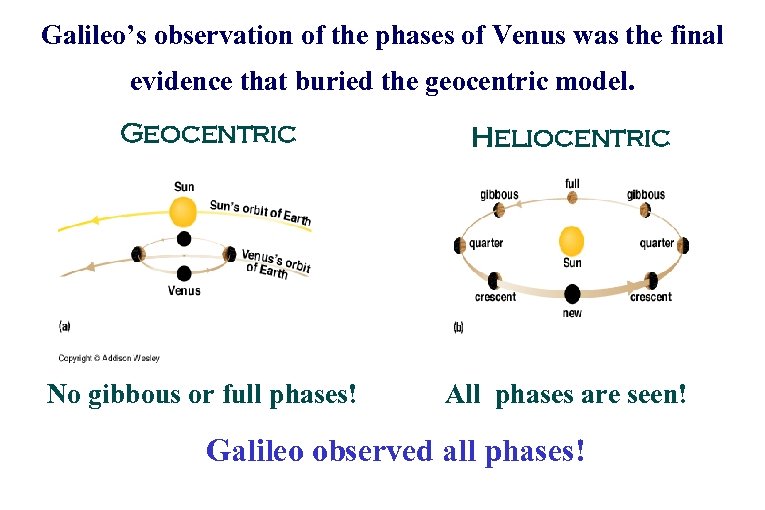
Galileo’s observation of the phases of Venus was the final evidence that buried the geocentric model. Geocentric Heliocentric No gibbous or full phases! All phases are seen! Galileo observed all phases!

With Galileo’s observations, the revolution begun by Copernicus was nearly complete… Ø The structure of the universe had been totally changed. Ø The motions of the planets were understood, at least from a geometrical perspective. Ø Earth was no longer a “special” place in the universe. Ø The crowning achievement was yet to come discovering the laws of nature and that naturally led to the newly determined structure.

Sir Isaac Newton (1642 -1727) Invented calculus Invented the reflecting telescope Connected gravity and planetary forces
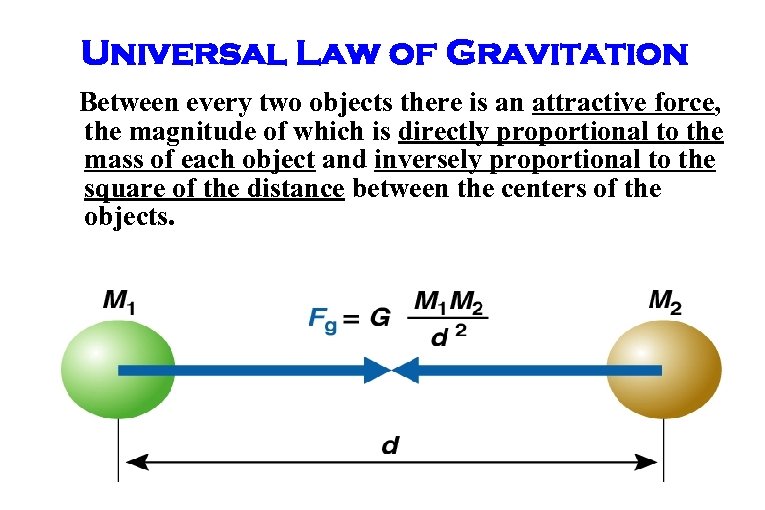
Universal Law of Gravitation Between every two objects there is an attractive force, the magnitude of which is directly proportional to the mass of each object and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centers of the objects.
This force is always attractive and it applies to ALL objects possessing mass!
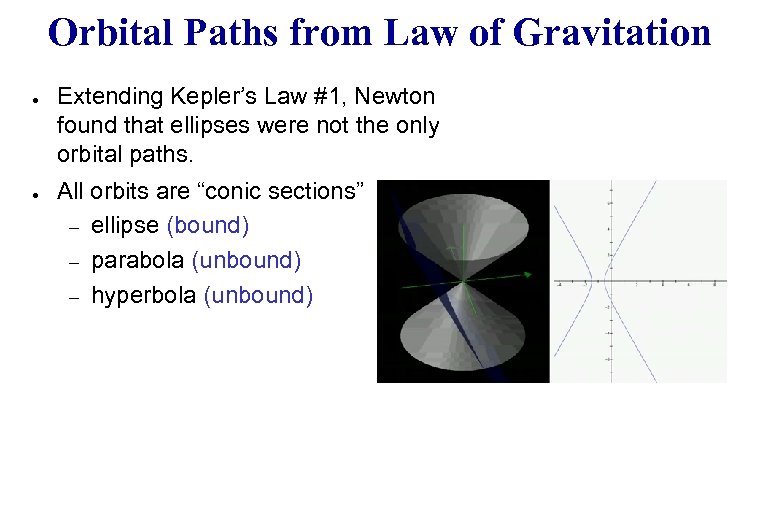
Orbital Paths from Law of Gravitation ● ● Extending Kepler’s Law #1, Newton found that ellipses were not the only orbital paths. All orbits are “conic sections” – ellipse (bound) – parabola (unbound) – hyperbola (unbound)
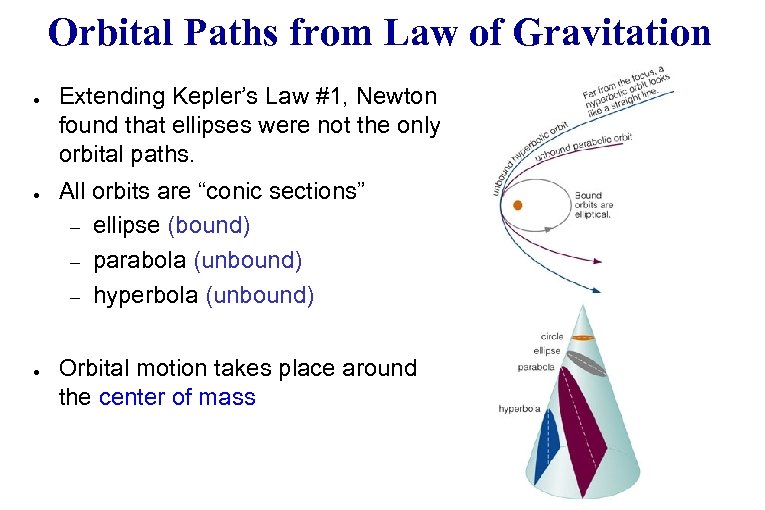
Orbital Paths from Law of Gravitation ● ● ● Extending Kepler’s Law #1, Newton found that ellipses were not the only orbital paths. All orbits are “conic sections” – ellipse (bound) – parabola (unbound) – hyperbola (unbound) Orbital motion takes place around the center of mass

The Center of Mass In Kepler's Laws, the Sun is fixed at a point in space (a focus of an ellipse) and the planet revolves around it. Why is the Sun privileged? Kepler had mystical ideas about the Sun, endowing it with almost god-like qualities that justified its special place. Newton demonstrated that the Sun does not occupy a privileged postion and in the process he modified Kepler's 3 rd Law.
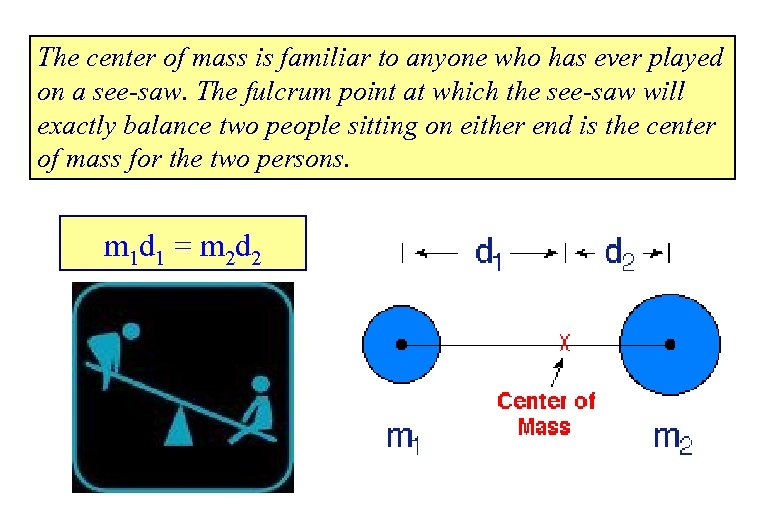
The center of mass is familiar to anyone who has ever played on a see-saw. The fulcrum point at which the see-saw will exactly balance two people sitting on either end is the center of mass for the two persons. m 1 d 1 = m 2 d 2
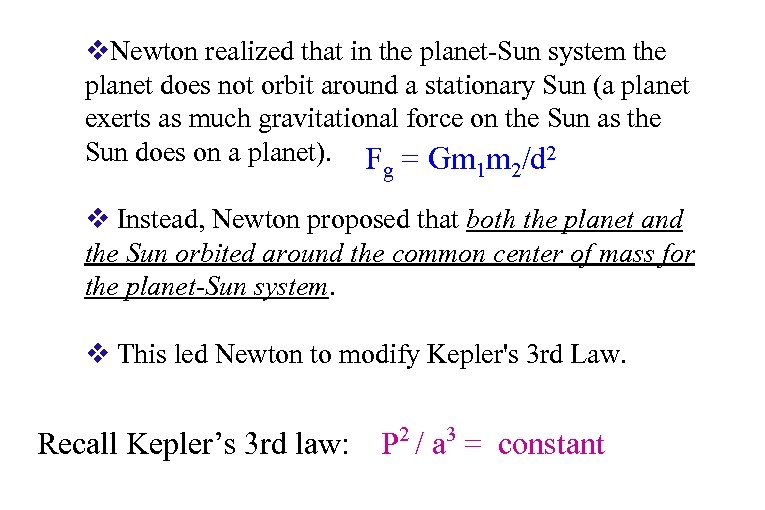
v. Newton realized that in the planet-Sun system the planet does not orbit around a stationary Sun (a planet exerts as much gravitational force on the Sun as the Sun does on a planet). F = Gm m /d 2 g 1 2 v Instead, Newton proposed that both the planet and the Sun orbited around the common center of mass for the planet-Sun system. v This led Newton to modify Kepler's 3 rd Law. Recall Kepler’s 3 rd law: P 2 / a 3 = constant
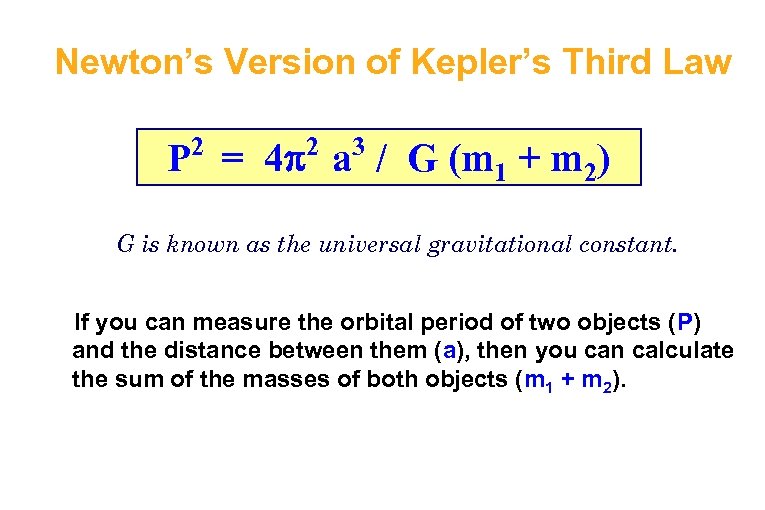
Newton’s Version of Kepler’s Third Law 2 2 3 P = 4 a / G (m 1 + m 2) G is known as the universal gravitational constant. If you can measure the orbital period of two objects (P) and the distance between them (a), then you can calculate the sum of the masses of both objects (m 1 + m 2).

A Universe of Matter and Energy What is matter? What is energy?

Matter – material such as rocks, water, air; “stuff” composed of atoms Energy – makes or has the potential to make matter move! The history of the universe, including biological organisms, is based upon the interplay between matter and energy.

Three Basic Types of Energy • kinetic – energy of motion • potential – stored energy; e. g. , chemical, gravitational, electrical, etc. • radiative – energy transported by light (electromagetic radiation)
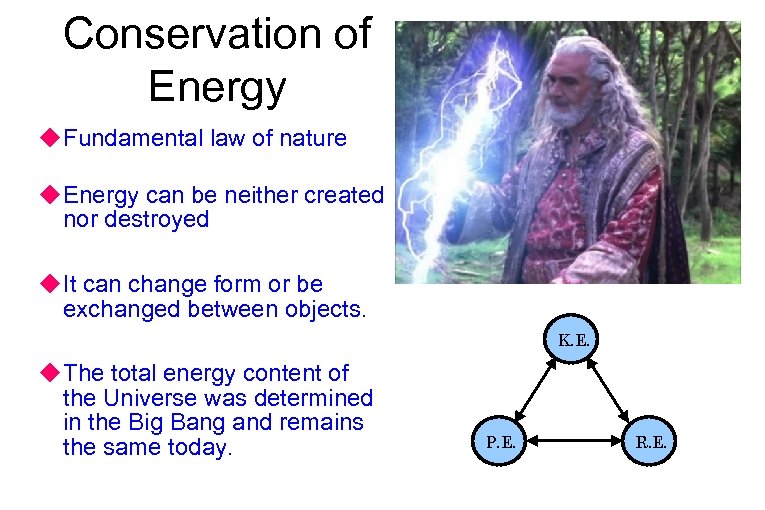
Conservation of Energy u Fundamental law of nature u Energy can be neither created nor destroyed u It can change form or be exchanged between objects. K. E. u The total energy content of the Universe was determined in the Big Bang and remains the same today. P. E. R. E.

Kinetic Energy (K. E. ): energy of motion K. E. = 1/2 mv 2 (m is mass, v is velocity)
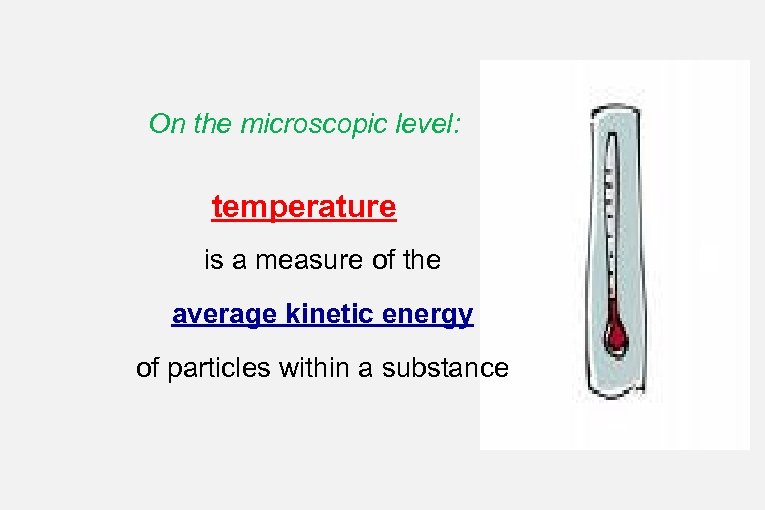
On the microscopic level: temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles within a substance
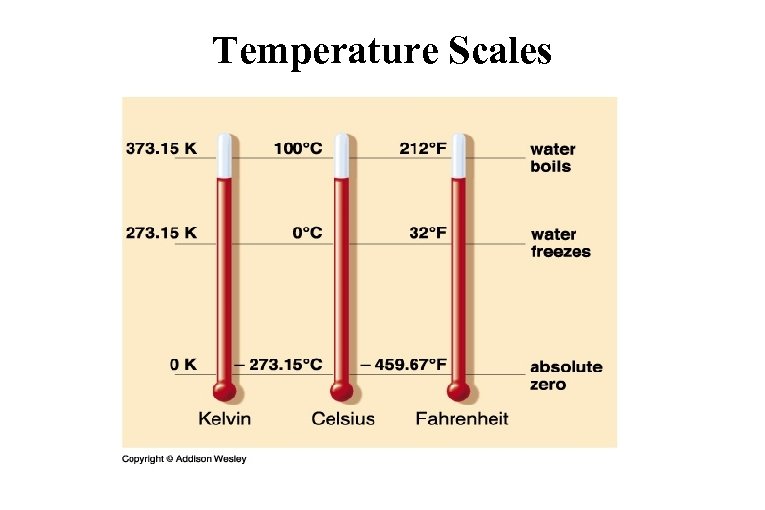
Temperature Scales
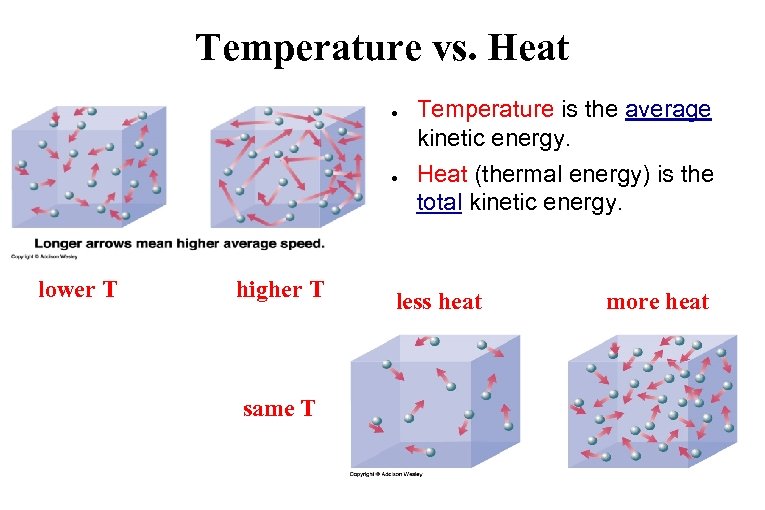
Temperature vs. Heat ● ● lower T higher T same T Temperature is the average kinetic energy. Heat (thermal energy) is the total kinetic energy. less heat more heat
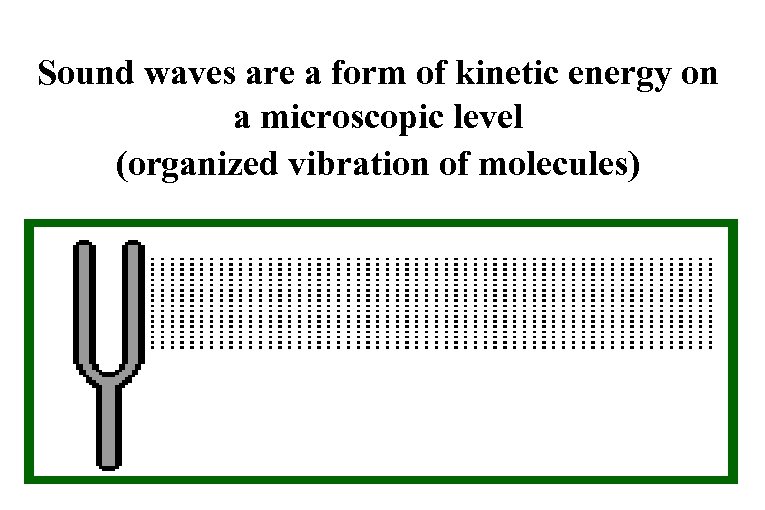
Sound waves are a form of kinetic energy on a microscopic level (organized vibration of molecules)

Applying what we’ve learned - pizza vs. soup caution in the kitchen

Potential Energy: Energy that is “stored” within an object and that has the potential of being released in a different form
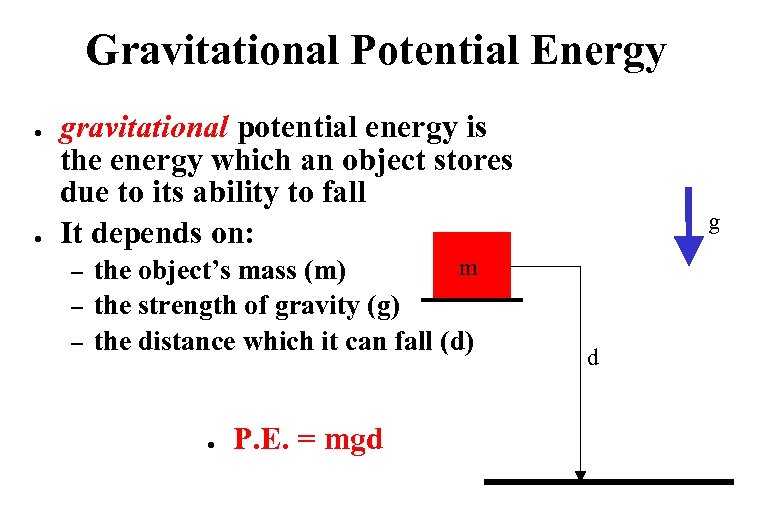
Gravitational Potential Energy ● ● gravitational potential energy is the energy which an object stores due to its ability to fall It depends on: – – – m the object’s mass (m) the strength of gravity (g) the distance which it can fall (d) ● P. E. = mgd g d
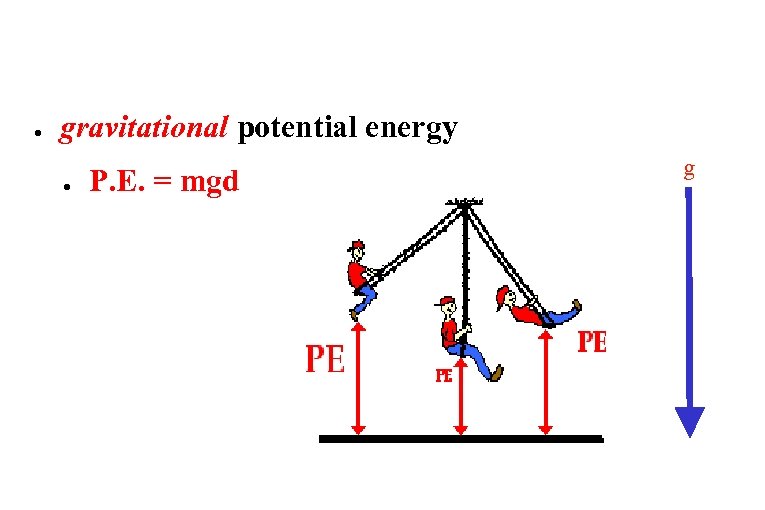
● gravitational potential energy ● P. E. = mgd g

Mass-Energy Potential Energy ● ● mass-energy: energy is stored in matter itself this mass-energy is what would be released if an amount of mass, m, were converted into energy E = mc 2 [ c = 3 x 108 m/s is the speed of light]

Chemical Potential Energy ● Chemical potential energy: energy stored chemical bounds

There are many additional examples of potential energy. e. g. , stretched springs, …

Energy, while conserved, can be transformed from one type of energy to another Potential Kinetic
Potential Kinetic

Kinetic Potential
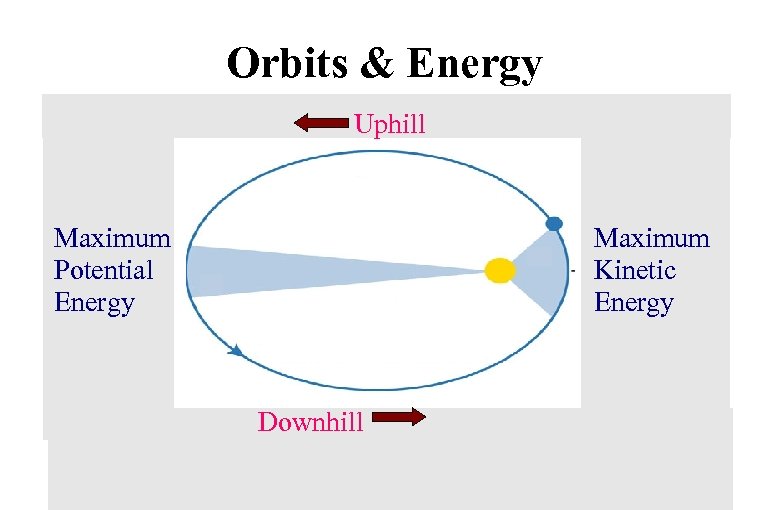
Orbits & Energy Uphill Maximum Potential Energy Maximum Kinetic Energy Downhill
da56b0631069c2464a2d02c7fbf33136.ppt