2935235bf1b7369b4ea280ae72e3e1b7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

THE US NATIONAL VIRTUAL OBSERVATORY Technology Open House 2004 The National Virtual Observatory Bob Hanisch Gretchen Greene Wil O’Mullane 2 Dec 2004 1

Abstract Technology Open House 2004 The National Virtual Observatory has been under development for three years, and is now at the point of making its first release of applications software and tools to the astronomy community. The team will describe the main technology development areas of the VO and demonstrate some of the tools that will be released for general community use in conjunction with the January AAS meeting. We will also briefly describe the software development toolkit that we assembled for the NVO Summer School, which includes software libraries and sample code for VO-compatible data publication and retrieval. 2 Dec 2004 2
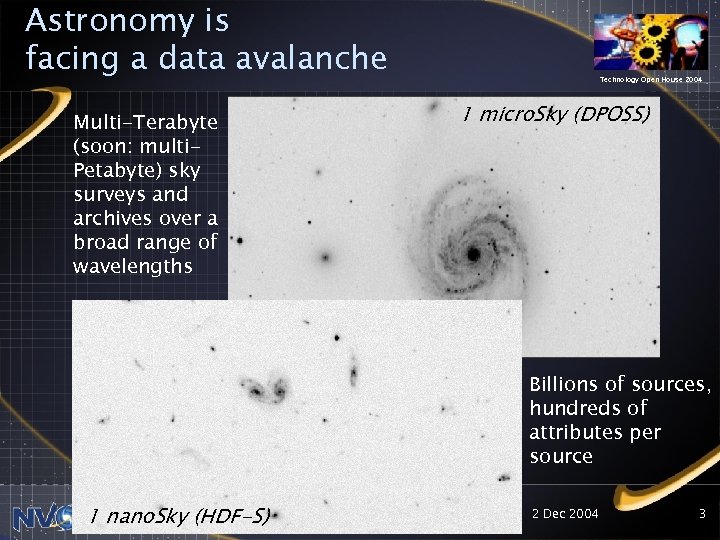
Astronomy is facing a data avalanche Multi-Terabyte (soon: multi. Petabyte) sky surveys and archives over a broad range of wavelengths Technology Open House 2004 1 micro. Sky (DPOSS) Billions of sources, hundreds of attributes per source 1 nano. Sky (HDF-S) 2 Dec 2004 3

The changing face of observational astronomy Technology Open House 2004 • Large digital sky surveys are becoming dominant source of data in astronomy: > 100 TB, growing rapidly – SDSS, 2 MASS, DPOSS, GSC, FIRST, NVSS, RASS, IRAS, QUEST, GALEX, SST; CMBR experiments; Microlensing experiments; NEAT, LONEOS, and other searches for Solar system objects – Digital libraries: ADS, astro-ph, NED, CDS, NSSDC – Observatory archives: HST, CXO, space and ground-based – Future: Pan. STARRS, LSST, and other synoptic surveys; astrometric missions, GW detectors • Data sets orders of magnitude larger, more complex, more homogeneous than in the past • Roughly 1 TB/Sky/band/epoch – Human Genome is < 1 GB, Library of Congress ~ 20 TB 2 Dec 2004 4

Toward a “new astronomy” Technology Open House 2004 • Past: Observations of small, carefully selected samples (often with a priori prejudices) of objects in one or a few wavelength bands • Future: Multi-wavelength data for millions of objects, allowing us to – Discover significant patterns from the analysis of statistically rich and unbiased image/catalog databases (e. g. , Gunn-Peterson effect in high-z quasars) – Understand complex astrophysical systems via confrontation between data and sophisticated numerical simulation • Discovering new phenomena and patterns in these datasets will require simultaneous access to multi-wavelength archives, advanced visualization and statistical analysis tools 2 Dec 2004 5

Motivation Technology Open House 2004 • National Academy of Sciences Decadal Survey recommended NVO as highest priority small (<$100 M) project “ Several small initiatives recommended by the committee span both ground and space. The first among them—the National Virtual Observatory (NVO)—is the committee’s top priority among the small initiatives. The NVO will provide a “virtual sky” based on the enormous data sets being created now and the even larger ones proposed for the future. It will enable a new mode of research for professional astronomers and will provide to the public an unparalleled opportunity for education and discovery. ” —Astronomy and Astrophysics in the New Millennium, p. 14 2 Dec 2004 6

History Technology Open House 2004 • 1990 s: NASA establishes wavelength-oriented science archive centers; multiple large ground-based digital sky survey projects initiated (following 1988 Astrophysics Data System report) • April 1999, Decadal Survey Panel on Theory, Computation, and Data Discovery met in Los Alamos – Szalay, Prince, and Alcock coin the name “National Virtual Observatory” • November 1999, NVO organizational workshop at JHU • February 2000, 2 nd NVO workshop at NOAO-Tucson • June 2000, conference held at Caltech, “Towards a Virtual Observatory” • June 2000, ad hoc steering committee formed • February 2001, AASC/NAS report “Astronomy and Astrophysics in the New Millennium” released • April 2001, proposal submitted to NSF ITR program, 17 collaborating organizations, led by A. Szalay (JHU) • September 2001, NSF announces proposal selection • January 2003, first NVO science prototypes shown at Seattle AAS 2 Dec 2004 7

What is the Virtual Observatory… and what it is not… Technology Open House 2004 The VO is: • A set of international standards to share complex data • A modular set of tools to work with distributed data • A simple environment to publish data to • An essential part of the research astronomer’s toolkit • A catalyst for world-wide access to astronomical archives • A vehicle for education and public outreach The VO is not: • A replacement for building new telescopes and instruments • A centralized repository for data • A data quality enforcement organization 2 Dec 2004 8

Who is the National Virtual Observatory? Technology Open House 2004 • US NVO development project, funded by NSF Information Technology Program and managed by NSF Astronomy Division, is entering 4 th year of 5 -year project • Funding is $10 M+ over the 5 years • 17 organizations (astro, CS, IT) involved – JHU (PI Alex Szalay), STSc. I, Caltech (Astronomy, IPAC, CACR), HEASARC, SAO, NRAO, NOAO, NCSA, SDSC, FNAL, USNO, et al. • Collaboration being extended to Gemini Science Archive, LSST, Keck 2 Dec 2004 9

International collaboration Technology Open House 2004 • NVO is co-founder of the International Virtual Observatory Alliance • IVOA now has 15 member projects • Adopted a standards process based on W 3 C • Forum for technical development, working groups, discussion and sharing of experience http: //ivoa. net 2 Dec 2004 10

Exposure Technology Open House 2004 • NVO Summer School (Sept. 2004, Aspen) trained 40 students and software developers in VO tools and technology • Special Session scheduled for January 2005 AAS meeting: Astronomical Research with the Virtual Observatory; includes several papers based on Summer School projects (environments of radio galaxies, starburst galaxies) • IAU Joint Discussion on Future Large Telescopes and the Virtual Observatory (July 2003, Sydney) • IAU Symposium being proposed for 2006 (Prague) 2 Dec 2004 11

Science prototypes Technology Open House 2004 • Science demonstrations show capabilities of new infrastructure, motivate and guide technical developments. For example: – Data discovery, multi-λ comparisons – Search for brown dwarfs – Galaxy morphologies in clusters – Globular cluster simulations 2 Dec 2004 12

Science results Technology Open House 2004 • Padovani et al. (2004)) demonstrates that VO tools are mature enough to produce cutting-edge science results by exploiting astronomical data beyond classical identification limits (R 25) 2 Dec 2004 13

Science results Technology Open House 2004 • Mc. Glynn et al. (2004) classified all unidentified ROSAT WGACAT objects using VO data access methods to crosscorrelate multiwavelength catalogs – Technique applied to find candidate X-ray binaries and now to SDSS photometric catalog • More than 400 papers related to “virtual observatory” in ADS 2 Dec 2004 14

Technology development Technology Open House 2004 • Resource registries • Data models • Content description (UCDs) • Data access layer (SIAP, SSAP, cone search) • VO Query Language (ADQL, Open. Sky. Query) • VOTable • Grid and Web Services Activities can be followed on IVOA web (http: //ivoa. net) 2 Dec 2004 15

Software toolkit Technology Open House 2004 • Assembled software development toolkit for NVO Summer School – – AXIS (Java web services) ANT (Java-based software build tool) Mirage, Topcat, VOPlot applications Sample data files • STSc. I Web Services course (http: //chart. stsci. edu/twiki/bin/view/Main/ STWeb. Services. Cource) • See http: //us-vo. org/summerschool/proceedings/software/index. html • Summer School proceedings available at http: //usvo. org/summer-school/proceedings/index. cfm 2 Dec 2004 16

Capabilities Technology Open House 2004 • Tools and applications available at http: //us-vo. org/ • Data location and access • • – Resource registry (yellow pages) has thousands of catalogs and archives and is easily extended – Data. Scope uses registry to locate data and allow user to display or download data of interest; can cache results on popular objects or for transient events Spectrum and filter database and analysis tools HST/MAST VO services Catalog cross-correlation (test version) SDSS web services Dynamic source-list generation and cross-correlation Visualization of tabular, spectral, and imaging data Source classification Try these yourself at http: //chart. stsci. edu/twiki/bin/view/Main/AASJanuary 2005 2 Dec 2004 17

Future VO-enabled science Technology Open House 2004 • January 2005: software release in conjunction with AAS, international data access through standard registries – Applications you have just seen • January 2005 AVO demos focusing on dynamic generation of SEDs for galaxies and comparisons with stellar spectral evolution models, and search for stars in transition from AGB to PN (unidentified IR sources); see • Tera. Grid-based analyses (CPU time already allocated): standard “sky atlas” spatial sampling and data federation, galaxy SED fitting, image mosaicing, quasar spectral modeling, N-point correlation function for SDSS galaxies, CMB modeling 2 Dec 2004 18

Future VO-enabled science Technology Open House 2004 • NVO applications for 2005 -2006 TBD in consultation with Science Steering Committee – – – Dynamic time series analysis, period fitting “VO-Google” Fast data inventory service Flux-recovery service Image registration and subtraction services VO integration with legacy software systems (web service interfaces, data access) – Datamining and data federation on increasingly large, distributed databases 2 Dec 2004 19

STSc. I/JHU activities Technology Open House 2004 • NVO project management • Technical development – Resource metadata and registry services – Open. Sky. Nodes (GALEX, HDF, UDF, GOODS) – HST/MAST catalog and image services with VOTable support and direct links to VOPlot – Links to/from the literature, ADS • Collaboration with GOODS team on catalog and image cutout services • Collaboration with JHU/SDSS personnel; joint technical discussions, augmented by co-location in Bloomberg building • Subscribe to nvo@stsci. edu (majordomo) 2 Dec 2004 20

Ear to the ground Technology Open House 2004 • NSF and NASA working to create joint program; draft RFP could be available as soon as next spring – Agency support is firm, but not unwavering • Continuing to build community support from the ground up – – Demonstrations Software releases Summer School EPO partnerships 2 Dec 2004 21

Next steps Technology Open House 2004 • Submitted white paper “The National Virtual Observatory: From Framework to Facility” to NSF and NASA this past summer – Suggests responsibilities and scope for eventual NVO operational (distributed) facility – Suggests smaller, tighter collaboration – Describes several possible management models, advocates management by consortium – Urges creation of joint NSF/NASA/other program to provide single point of contact for funding 2 Dec 2004 22

Summary Technology Open House 2004 • $10 M committed in US, >$40 M worldwide, to VO development • Active international community is working and meeting regularly to establish the VO • Major archives and catalogs available through VO and more coming • Refereed research papers utilizing VO now beginning to appear 2 Dec 2004 23

Technology Open House 2004 2 Dec 2004 24
2935235bf1b7369b4ea280ae72e3e1b7.ppt