THE US COURT SYSTEM In pictures with explanations



















![THE SENTENCE THE JUDGE IMPOSES A [JAIL] SENTENCE ON THE CONVICT/ SENTENCES THE CONVICT THE SENTENCE THE JUDGE IMPOSES A [JAIL] SENTENCE ON THE CONVICT/ SENTENCES THE CONVICT](https://present5.com/presentacii-2/20171208\9650-the_us_court_system.ppt\9650-the_us_court_system_25.jpg)







9650-the_us_court_system.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 THE US COURT SYSTEM In pictures with explanations Themis, the goddess of justice
THE US COURT SYSTEM In pictures with explanations Themis, the goddess of justice

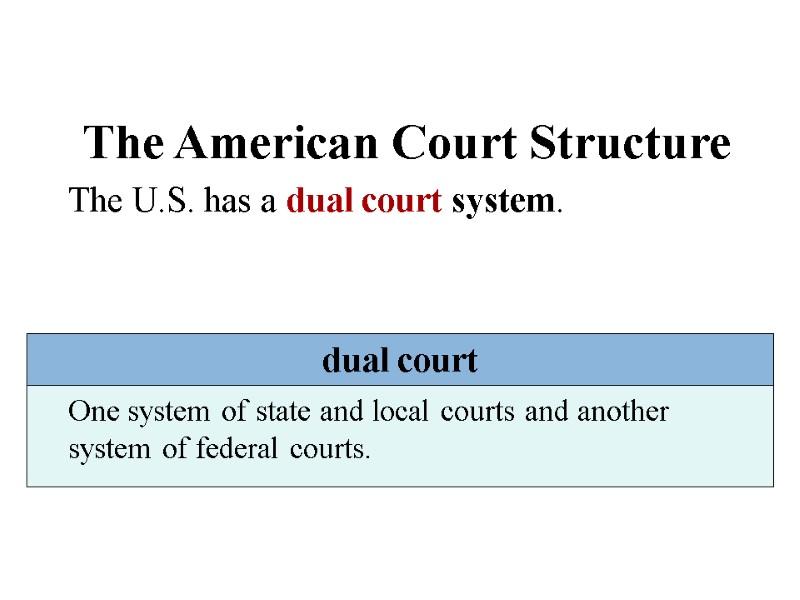
 The American Court Structure The U.S. has a dual court system. dual court One system of state and local courts and another system of federal courts.
The American Court Structure The U.S. has a dual court system. dual court One system of state and local courts and another system of federal courts.
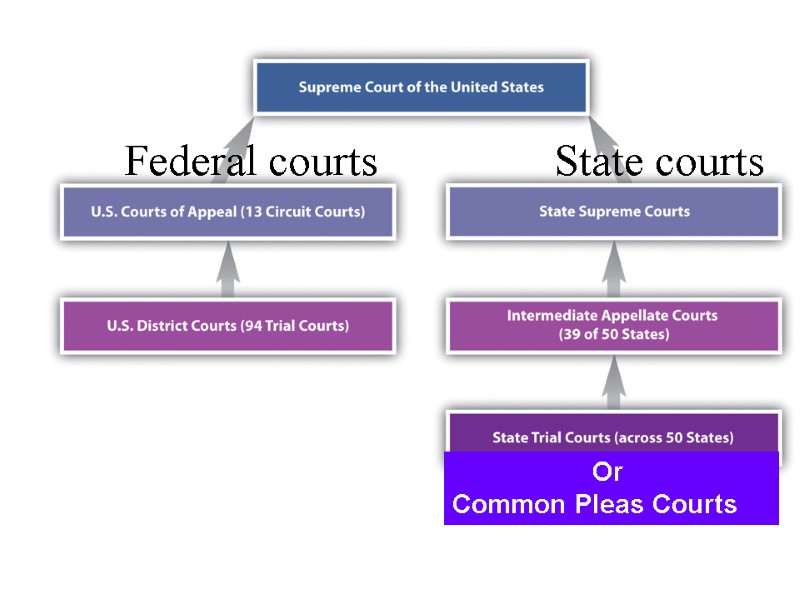
 Federal courts State courts Or Common Pleas Courts
Federal courts State courts Or Common Pleas Courts
 The American Court Structure The court’s jurisdiction is set by law and limited by territory and type of case. jurisdiction The authority of a court to hear and decide cases. Eg. Local jurisdiction Original jurisdiction General jurisdiction Criminal jurisdiction Civil jurisdiction etc
The American Court Structure The court’s jurisdiction is set by law and limited by territory and type of case. jurisdiction The authority of a court to hear and decide cases. Eg. Local jurisdiction Original jurisdiction General jurisdiction Criminal jurisdiction Civil jurisdiction etc

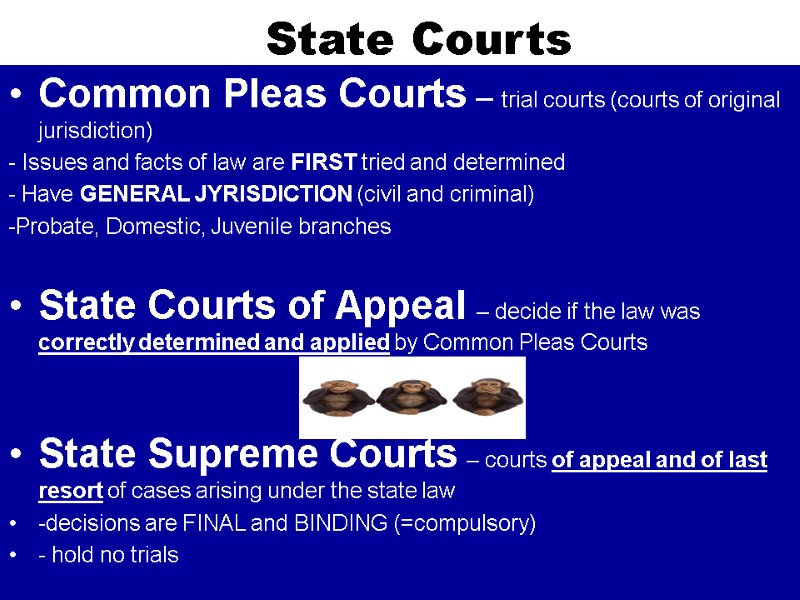
 Federal courts Common Pleas Courts – trial courts (courts of original jurisdiction) - Issues and facts of law are FIRST tried and determined - Have GENERAL JYRISDICTION (civil and criminal) -Probate, Domestic, Juvenile branches State Courts of Appeal – decide if the law was correctly determined and applied by Common Pleas Courts State Supreme Courts – courts of appeal and of last resort of cases arising under the state law -decisions are FINAL and BINDING (=compulsory) - hold no trials District Courts - cases heard by a JUDGE Issues and facts of law are FIRST tried and determined - Have GENERAL JYRISDICTION (civil and criminal) -Probate, Domestic, Juvenile branches - cases also include: Bank robbery Counterfeiting Moneylaundering Mail fraud Kidnapping Courts of Appeals – if the party loses the case, it appeals - decide if the law was correctly determined and applied by the District Court (review a case for errors of law, not of fact) - 3 judges sit as a panel to hear the case The US Supreme Court
Federal courts Common Pleas Courts – trial courts (courts of original jurisdiction) - Issues and facts of law are FIRST tried and determined - Have GENERAL JYRISDICTION (civil and criminal) -Probate, Domestic, Juvenile branches State Courts of Appeal – decide if the law was correctly determined and applied by Common Pleas Courts State Supreme Courts – courts of appeal and of last resort of cases arising under the state law -decisions are FINAL and BINDING (=compulsory) - hold no trials District Courts - cases heard by a JUDGE Issues and facts of law are FIRST tried and determined - Have GENERAL JYRISDICTION (civil and criminal) -Probate, Domestic, Juvenile branches - cases also include: Bank robbery Counterfeiting Moneylaundering Mail fraud Kidnapping Courts of Appeals – if the party loses the case, it appeals - decide if the law was correctly determined and applied by the District Court (review a case for errors of law, not of fact) - 3 judges sit as a panel to hear the case The US Supreme Court
 The US Supreme court 9 appointed judges decide cases considering federal law The court of last resort Revises the decision of the district court Decisions are binding (compulsory) Requires NO further court action, retrial, resentencing
The US Supreme court 9 appointed judges decide cases considering federal law The court of last resort Revises the decision of the district court Decisions are binding (compulsory) Requires NO further court action, retrial, resentencing

 State Courts Common Pleas Courts – trial courts (courts of original jurisdiction) - Issues and facts of law are FIRST tried and determined - Have GENERAL JYRISDICTION (civil and criminal) -Probate, Domestic, Juvenile branches State Courts of Appeal – decide if the law was correctly determined and applied by Common Pleas Courts State Supreme Courts – courts of appeal and of last resort of cases arising under the state law -decisions are FINAL and BINDING (=compulsory) - hold no trials
State Courts Common Pleas Courts – trial courts (courts of original jurisdiction) - Issues and facts of law are FIRST tried and determined - Have GENERAL JYRISDICTION (civil and criminal) -Probate, Domestic, Juvenile branches State Courts of Appeal – decide if the law was correctly determined and applied by Common Pleas Courts State Supreme Courts – courts of appeal and of last resort of cases arising under the state law -decisions are FINAL and BINDING (=compulsory) - hold no trials
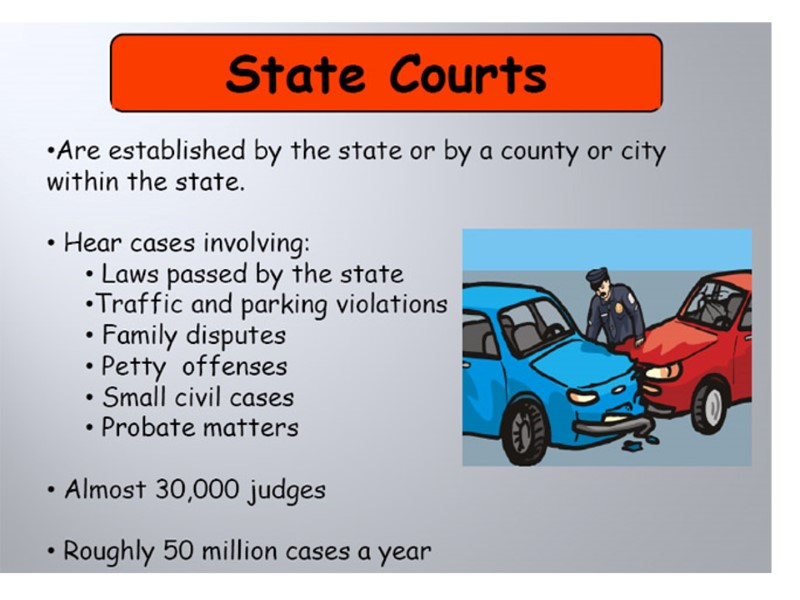
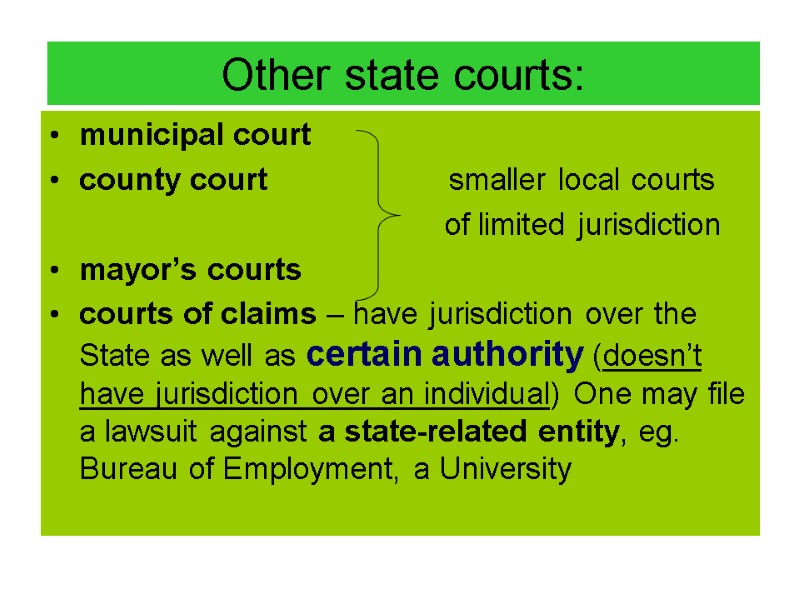
 Other state courts: municipal court county court smaller local courts of limited jurisdiction mayor’s courts courts of claims – have jurisdiction over the State as well as certain authority (doesn’t have jurisdiction over an individual) One may file a lawsuit against a state-related entity, eg. Bureau of Employment, a University
Other state courts: municipal court county court smaller local courts of limited jurisdiction mayor’s courts courts of claims – have jurisdiction over the State as well as certain authority (doesn’t have jurisdiction over an individual) One may file a lawsuit against a state-related entity, eg. Bureau of Employment, a University
 Felony Murder, manslaughter (unpremeditated), homicide Rape; Aggravated assault and/or battery; Arson; Robbery; Burglary;house breaking (depending on the scale of offence – it may also be considered misdemeanor) Manufacture, possession, selling of illegal drugs Grand larceny or grand theft, Kidnapping Embezzlement Bribery Forgery Fraud Swindling Vandalism on federal property
Felony Murder, manslaughter (unpremeditated), homicide Rape; Aggravated assault and/or battery; Arson; Robbery; Burglary;house breaking (depending on the scale of offence – it may also be considered misdemeanor) Manufacture, possession, selling of illegal drugs Grand larceny or grand theft, Kidnapping Embezzlement Bribery Forgery Fraud Swindling Vandalism on federal property
 Misdemeanour (petty offence) Petty theft/ larceny Prostitution, Public intoxication, Property damage Simple assault, Disorderly conduct Slander Blackmail Abuse of power Vandalism, Reckless driving, speeding Fraud, swindling Mugging Perjury Contempt of court
Misdemeanour (petty offence) Petty theft/ larceny Prostitution, Public intoxication, Property damage Simple assault, Disorderly conduct Slander Blackmail Abuse of power Vandalism, Reckless driving, speeding Fraud, swindling Mugging Perjury Contempt of court
 Graffiti – a common form of misdemeanor vandalism
Graffiti – a common form of misdemeanor vandalism
 Legal procedure civil case Step 1 – you file a complaint (you claim legal rights against another person. A countercomplaint may be filed against you) NB. Should be carefully drafted, usu., by an attorney Plaintiff VS Defendant the party filing a complaint Step 2 – the defendant (against whom the complaint is filed) answers the complaint (point by point) Step 3 - The defendant is notified of the lawsuit (brought against him) - the summons (or SUNPOENA) is issued Step 4 – the hearings of the case are held Step 5 – the judge returns the verdict and decides upon punishment
Legal procedure civil case Step 1 – you file a complaint (you claim legal rights against another person. A countercomplaint may be filed against you) NB. Should be carefully drafted, usu., by an attorney Plaintiff VS Defendant the party filing a complaint Step 2 – the defendant (against whom the complaint is filed) answers the complaint (point by point) Step 3 - The defendant is notified of the lawsuit (brought against him) - the summons (or SUNPOENA) is issued Step 4 – the hearings of the case are held Step 5 – the judge returns the verdict and decides upon punishment
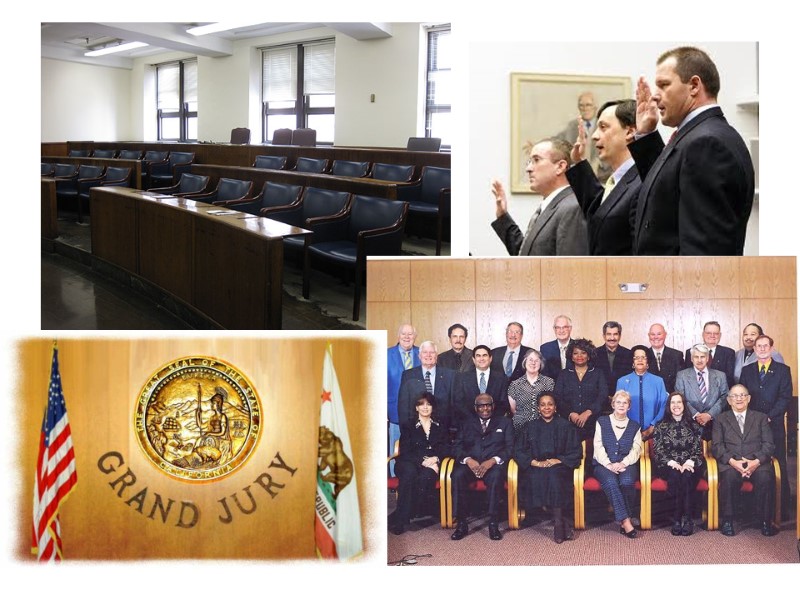
 Legal procedure criminal case 1. the police investigate the crime 2. the police bring criminal prosecution upon initiating a criminal case 3. the police issue a search or an arrest warrant 4. the suspect is detained 5. the case is brought to court i.e. a law-enforcement body (the prosecutor’s office): brings a [law]suit against smb (иск) sues smb/ brings a case against smb. Подать в суд brings an action against smb/ takes legal actions against smb/ (судебное разбирательство, тяжба) 6. the charge is brought against the suspect 7. the grand jury considers the case arrest/ search warrant A written order directing law enforcement officers to arrest/search a person.
Legal procedure criminal case 1. the police investigate the crime 2. the police bring criminal prosecution upon initiating a criminal case 3. the police issue a search or an arrest warrant 4. the suspect is detained 5. the case is brought to court i.e. a law-enforcement body (the prosecutor’s office): brings a [law]suit against smb (иск) sues smb/ brings a case against smb. Подать в суд brings an action against smb/ takes legal actions against smb/ (судебное разбирательство, тяжба) 6. the charge is brought against the suspect 7. the grand jury considers the case arrest/ search warrant A written order directing law enforcement officers to arrest/search a person.
 grand jury Generally a group of 12 to 23 citizens The primary purpose of the grand jury is to determine whether there is probable cause to believe that the accused committed the crime, i.e. Whether to TRY him or NOT
grand jury Generally a group of 12 to 23 citizens The primary purpose of the grand jury is to determine whether there is probable cause to believe that the accused committed the crime, i.e. Whether to TRY him or NOT

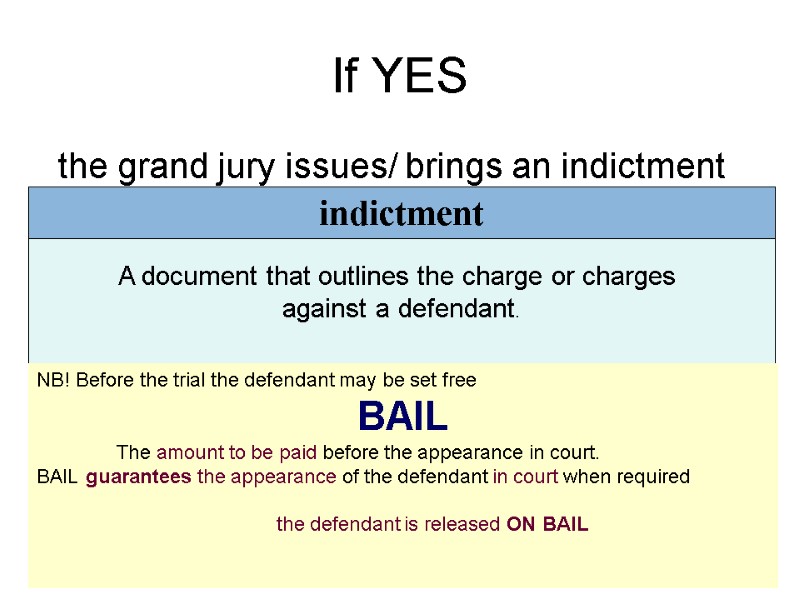
 If YES the grand jury issues/ brings an indictment A document that outlines the charge or charges against a defendant. A document that outlines the charge or charges against a defendant. indictment NB! Before the trial the defendant may be set free BAIL The amount to be paid before the appearance in court. BAIL guarantees the appearance of the defendant in court when required the defendant is released ON BAIL
If YES the grand jury issues/ brings an indictment A document that outlines the charge or charges against a defendant. A document that outlines the charge or charges against a defendant. indictment NB! Before the trial the defendant may be set free BAIL The amount to be paid before the appearance in court. BAIL guarantees the appearance of the defendant in court when required the defendant is released ON BAIL
 About 90 percent of criminal defendants plead guilty to the charges against them, in an arrangement called : Plea Bargaining (соглашение о признании вины обвиняемым) Depending on The seriousness of the offense The defendant’s criminal record The defendant may be allowed to plead guilty to a lesser offense. A defendant who pleads guilty may receive a lighter sentence without trial. A defendant may plead guilty to one charge in exchange for the prosecutor’s promise to drop another charge.
About 90 percent of criminal defendants plead guilty to the charges against them, in an arrangement called : Plea Bargaining (соглашение о признании вины обвиняемым) Depending on The seriousness of the offense The defendant’s criminal record The defendant may be allowed to plead guilty to a lesser offense. A defendant who pleads guilty may receive a lighter sentence without trial. A defendant may plead guilty to one charge in exchange for the prosecutor’s promise to drop another charge.
 I swear to tell the truth and nothing but the truth The JURY swears/ is sworn in by the bailiff or the judge
I swear to tell the truth and nothing but the truth The JURY swears/ is sworn in by the bailiff or the judge
 The JURY (12) A group of citizens called to hear a trial To decide the factual questions of guilt or innocence NB! CRIMINAL TRIAL – UNANIMOUS DECISION Bring in/ return/ deliver the verdict (guilty – not guilty to the charge)
The JURY (12) A group of citizens called to hear a trial To decide the factual questions of guilt or innocence NB! CRIMINAL TRIAL – UNANIMOUS DECISION Bring in/ return/ deliver the verdict (guilty – not guilty to the charge)
 The judge Determines the legal questions that arise during the trial Explains legal issues to the jurors Rules out/ overrules or sustains an objection Admits or doesn't admit smth. as evidence Determines the sentence
The judge Determines the legal questions that arise during the trial Explains legal issues to the jurors Rules out/ overrules or sustains an objection Admits or doesn't admit smth. as evidence Determines the sentence
 Parties to the criminal lawsuit Prosecutor (the State) = Attorney for the prosecution/ prosecuting attorney Witnesses for the prosecution (present evidence) The defendant Attorney for the defense (may be court-appointed=district attorney) Witnesses for the defense (present evidence) Direct, circumstantial, (irr)relevant, material, incompetent, (in)admissible, corroborative, irrefutable, presumptive, documentary, first hand etc…
Parties to the criminal lawsuit Prosecutor (the State) = Attorney for the prosecution/ prosecuting attorney Witnesses for the prosecution (present evidence) The defendant Attorney for the defense (may be court-appointed=district attorney) Witnesses for the defense (present evidence) Direct, circumstantial, (irr)relevant, material, incompetent, (in)admissible, corroborative, irrefutable, presumptive, documentary, first hand etc…
![>THE SENTENCE THE JUDGE IMPOSES A [JAIL] SENTENCE ON THE CONVICT/ SENTENCES THE CONVICT >THE SENTENCE THE JUDGE IMPOSES A [JAIL] SENTENCE ON THE CONVICT/ SENTENCES THE CONVICT](https://present5.com/presentacii-2/20171208\9650-the_us_court_system.ppt\9650-the_us_court_system_25.jpg) THE SENTENCE THE JUDGE IMPOSES A [JAIL] SENTENCE ON THE CONVICT/ SENTENCES THE CONVICT TO: - DEATH -A PENITENTIARY TERM -TO … YEARS IMPRISONMENT - … MONTHS IMPRISONMENT/ LIFE IMPRISONMENT - HARD LABOR -MANUAL LABOR -PROBATION (AN OFFENDER IS PLACED ON OR GRANTED PROBATION) THE CONVICT may be released ON PAROLE ??? Who is eligible for PAROLE??? PROBATION - PUBLIC SERVICE WORK -NO ALCOHOL/DRUGS -A FINE - GOOD BRHAVIOUR -MENTAL THERAPY REPORTS TO PROBATION OFFICER
THE SENTENCE THE JUDGE IMPOSES A [JAIL] SENTENCE ON THE CONVICT/ SENTENCES THE CONVICT TO: - DEATH -A PENITENTIARY TERM -TO … YEARS IMPRISONMENT - … MONTHS IMPRISONMENT/ LIFE IMPRISONMENT - HARD LABOR -MANUAL LABOR -PROBATION (AN OFFENDER IS PLACED ON OR GRANTED PROBATION) THE CONVICT may be released ON PAROLE ??? Who is eligible for PAROLE??? PROBATION - PUBLIC SERVICE WORK -NO ALCOHOL/DRUGS -A FINE - GOOD BRHAVIOUR -MENTAL THERAPY REPORTS TO PROBATION OFFICER

 Who is speaking?
Who is speaking?
 What is it?
What is it?
 And what is this?
And what is this?
 Name the instrument
Name the instrument
 Where are the defendants?
Where are the defendants?
 Who is speaking? and what? Name the people in the picture
Who is speaking? and what? Name the people in the picture

