5dac04903da7ec9dab6431b6335c16eb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 The Upper Paleolithic Period 40, 000 to 10, 000 ya
The Upper Paleolithic Period 40, 000 to 10, 000 ya
 The Upper Paleolithic l By 28 kya Neanderthals gone. l Humans expand into most of the world. l Art appears and spreads. l Numerous technological innovations occur. l Domestication of the Dog
The Upper Paleolithic l By 28 kya Neanderthals gone. l Humans expand into most of the world. l Art appears and spreads. l Numerous technological innovations occur. l Domestication of the Dog
 Summary of Chronology l Basal Paleolithic – 2. 5 to 1. 8 mya – Time of Homo habilis – Olduwan tools l Lower Paleolithic – 1. 8 m to 250 kya – Time of Homo erectus – Acheulean hand axes l Middle Paleolithic – 250 to 40 kya – Time of H. neanderthalensis – Mousterian tools The Upper Paleolithic 40 to 10 kya Chatelperronian Aurignacian Gravettian Solutrean Magdalenian
Summary of Chronology l Basal Paleolithic – 2. 5 to 1. 8 mya – Time of Homo habilis – Olduwan tools l Lower Paleolithic – 1. 8 m to 250 kya – Time of Homo erectus – Acheulean hand axes l Middle Paleolithic – 250 to 40 kya – Time of H. neanderthalensis – Mousterian tools The Upper Paleolithic 40 to 10 kya Chatelperronian Aurignacian Gravettian Solutrean Magdalenian
 Tool Industries l These are tool complexes that are associated and are useful time markers for the UP. – Chatelperronian = intermediate Mousterian to Aurignacian – Aurignacian 36 – 22 kya. Earliest “blade industry. ” – Gravettian 33 – 22 kya. Thinner, more finely made blades than Aurignacian. – Solutrean 22 – 18 kya. Extremely refined blade technology. – Magdalenian 18 – 10 kya. Final UP blade industry. ART.
Tool Industries l These are tool complexes that are associated and are useful time markers for the UP. – Chatelperronian = intermediate Mousterian to Aurignacian – Aurignacian 36 – 22 kya. Earliest “blade industry. ” – Gravettian 33 – 22 kya. Thinner, more finely made blades than Aurignacian. – Solutrean 22 – 18 kya. Extremely refined blade technology. – Magdalenian 18 – 10 kya. Final UP blade industry. ART.
 Two important definitions l Blades = flakes that are at least twice as long as they are wide. l Composite tools = ones formed from multiple materials. – E. g. , a spear has a stone point, wooden shaft, bone fore-shaft, sinew hafting, and resins.
Two important definitions l Blades = flakes that are at least twice as long as they are wide. l Composite tools = ones formed from multiple materials. – E. g. , a spear has a stone point, wooden shaft, bone fore-shaft, sinew hafting, and resins.
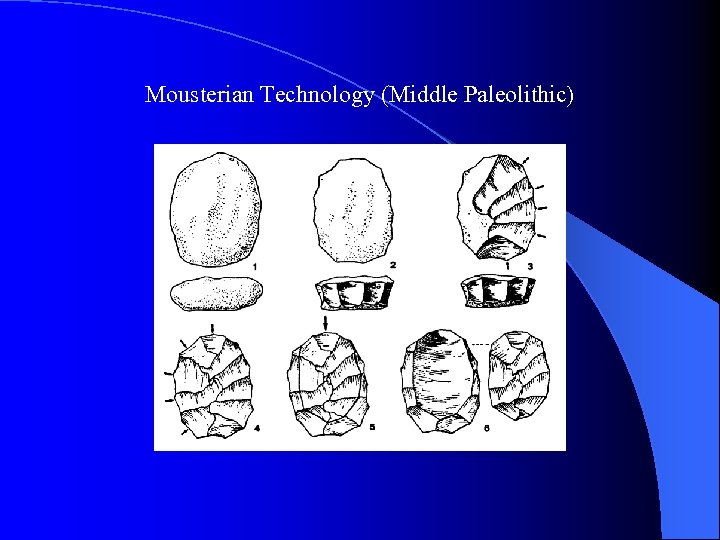 Mousterian Technology (Middle Paleolithic)
Mousterian Technology (Middle Paleolithic)
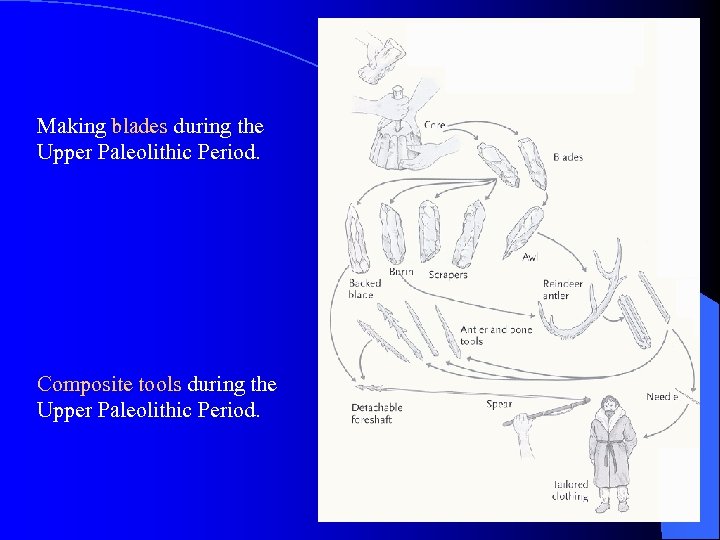 Making blades during the Upper Paleolithic Period. Composite tools during the Upper Paleolithic Period.
Making blades during the Upper Paleolithic Period. Composite tools during the Upper Paleolithic Period.
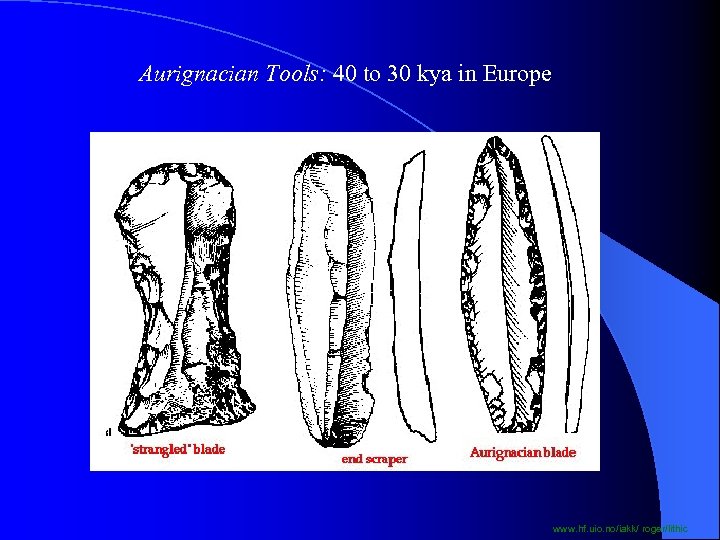 Aurignacian Tools: 40 to 30 kya in Europe www. hf. uio. no/iakk/ roger/lithic
Aurignacian Tools: 40 to 30 kya in Europe www. hf. uio. no/iakk/ roger/lithic
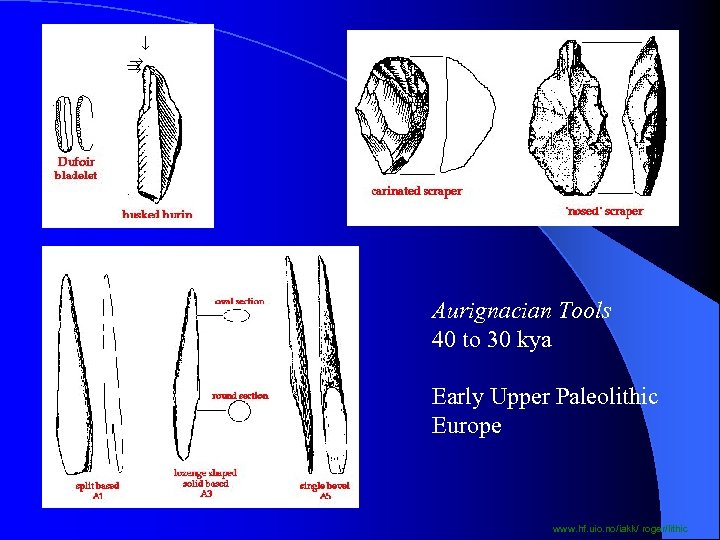 Aurignacian Tools 40 to 30 kya Early Upper Paleolithic Europe www. hf. uio. no/iakk/ roger/lithic
Aurignacian Tools 40 to 30 kya Early Upper Paleolithic Europe www. hf. uio. no/iakk/ roger/lithic
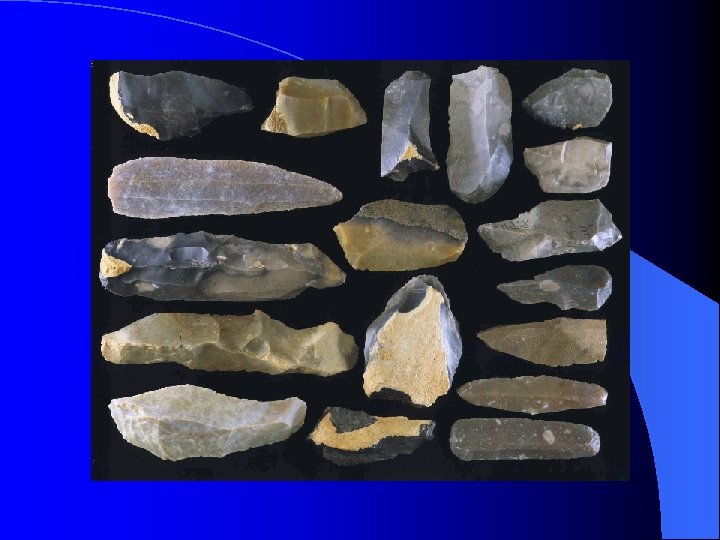

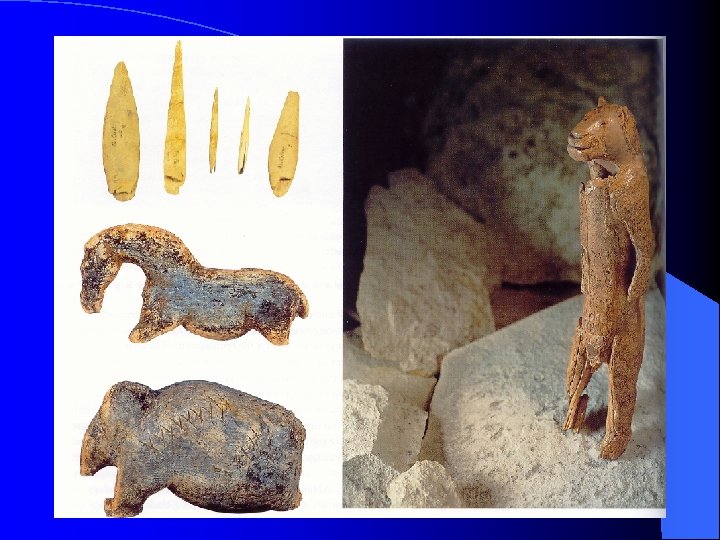
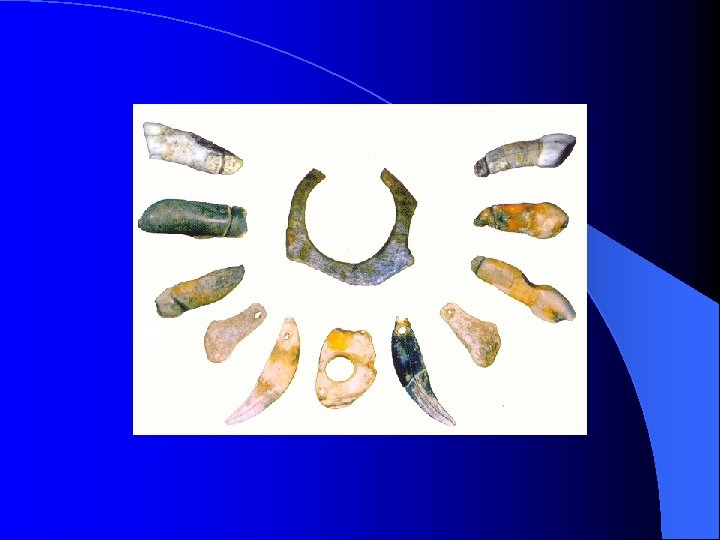
 Other Features of the Aurignacian Diverse, efficient, flexible tool kit. l Beads & Jewelry made from mammal bones & teeth. l Bone needles & awls suggesting tailored clothing. l Portable art of engraved bone and ivory l – Southern Germany: Vogelherd Cave & Hohlenstein Stadel. – Grotte du Renne, France.
Other Features of the Aurignacian Diverse, efficient, flexible tool kit. l Beads & Jewelry made from mammal bones & teeth. l Bone needles & awls suggesting tailored clothing. l Portable art of engraved bone and ivory l – Southern Germany: Vogelherd Cave & Hohlenstein Stadel. – Grotte du Renne, France.


 Tool Industries l These are tool complexes that are associated and are useful time markers for the UP. – Chatelperronian = intermediate Mousterian to Aurignacian – Aurignacian 36 – 22 kya. Earliest “blade industry. ” – Gravettian 33 – 22 kya. Thinner, more finely made blades than Aurignacian. – Solutrean 22 – 18 kya. Extremely refined blade technology. – Magdalenian 18 – 10 kya. Final UP blade industry. ART.
Tool Industries l These are tool complexes that are associated and are useful time markers for the UP. – Chatelperronian = intermediate Mousterian to Aurignacian – Aurignacian 36 – 22 kya. Earliest “blade industry. ” – Gravettian 33 – 22 kya. Thinner, more finely made blades than Aurignacian. – Solutrean 22 – 18 kya. Extremely refined blade technology. – Magdalenian 18 – 10 kya. Final UP blade industry. ART.
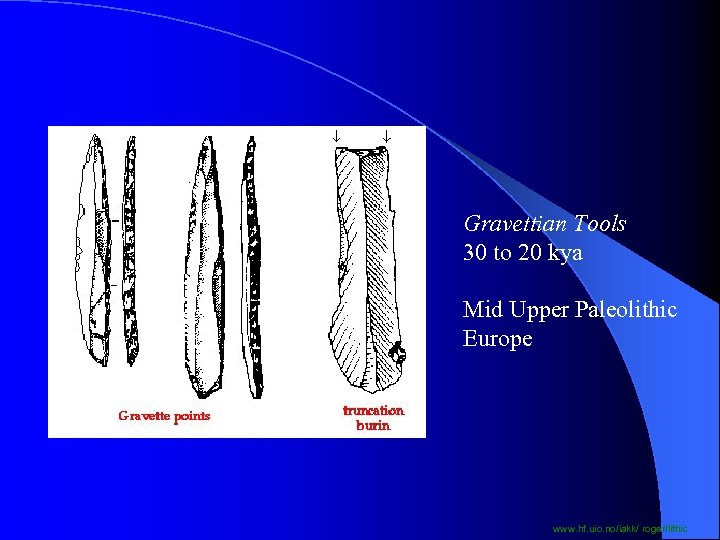 Gravettian Tools 30 to 20 kya Mid Upper Paleolithic Europe www. hf. uio. no/iakk/ roger/lithic
Gravettian Tools 30 to 20 kya Mid Upper Paleolithic Europe www. hf. uio. no/iakk/ roger/lithic
 Two Important Gravettian Sites l Dolni Vestonice 27 kya (Czech Republic) – Complex campsite. l Kostenki 27 kya (Russia). – Nine pit houses – Hearths in centers of huts – Storage pits cut into permafrost
Two Important Gravettian Sites l Dolni Vestonice 27 kya (Czech Republic) – Complex campsite. l Kostenki 27 kya (Russia). – Nine pit houses – Hearths in centers of huts – Storage pits cut into permafrost
 Dolni Vestonice
Dolni Vestonice
 Dolni Vestonice
Dolni Vestonice
 Kostenki
Kostenki
 Bone-framed house
Bone-framed house
 Implications of Sites l People becoming a bit more sedentary l Diet, however, still hunting & gathering – Find large herbivore remains – Small mammals remains – Some fish bones
Implications of Sites l People becoming a bit more sedentary l Diet, however, still hunting & gathering – Find large herbivore remains – Small mammals remains – Some fish bones
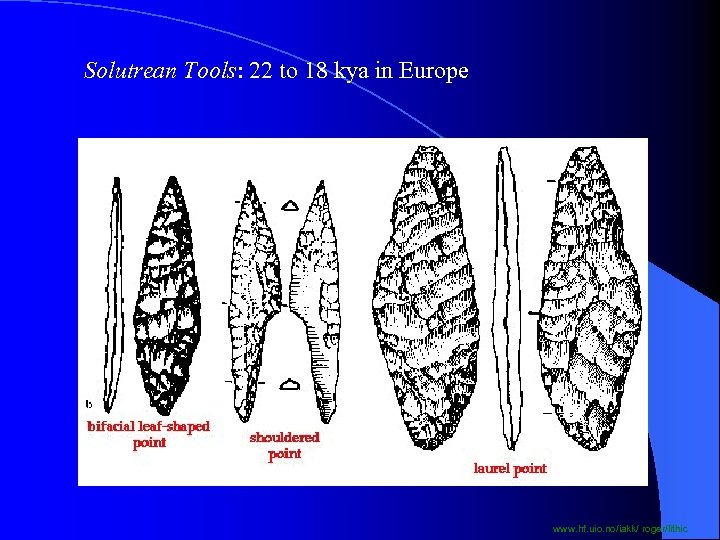 Solutrean Tools: 22 to 18 kya in Europe www. hf. uio. no/iakk/ roger/lithic
Solutrean Tools: 22 to 18 kya in Europe www. hf. uio. no/iakk/ roger/lithic

 The Dog l Domestication = an organism relying on humans for survival & reproduction. l Dogs come from wolves, which are pack animals. l Dogs have abilities that humans don’t have.
The Dog l Domestication = an organism relying on humans for survival & reproduction. l Dogs come from wolves, which are pack animals. l Dogs have abilities that humans don’t have.
 The Venus Figurines l Portable art that appeared during the Upper Paleolithic period. l Female figures carved from soft stone or mammoth bone. l Thought to symbolize fertility.
The Venus Figurines l Portable art that appeared during the Upper Paleolithic period. l Female figures carved from soft stone or mammoth bone. l Thought to symbolize fertility.
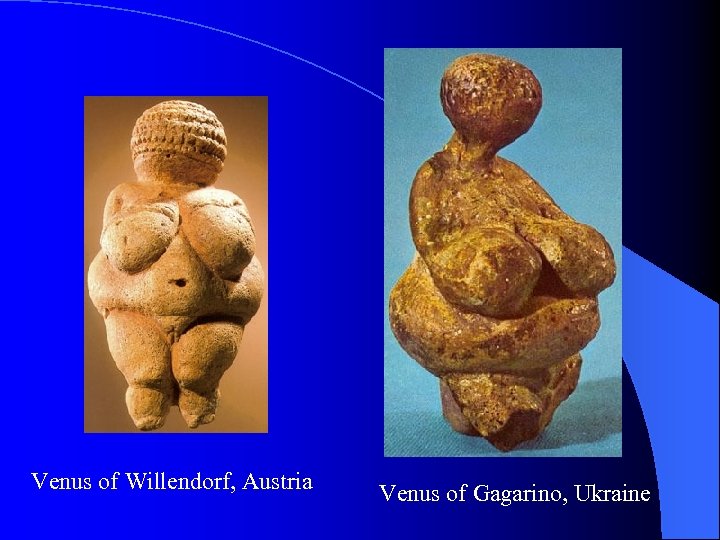 Venus of Willendorf, Austria Venus of Gagarino, Ukraine
Venus of Willendorf, Austria Venus of Gagarino, Ukraine
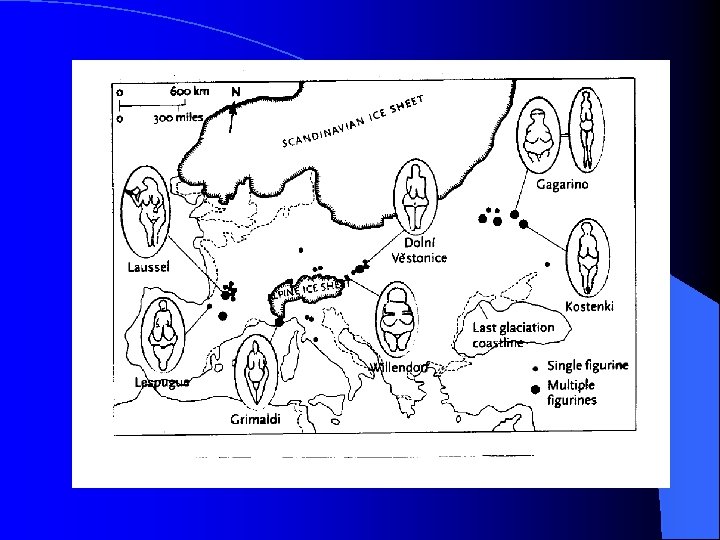
 Implication of Figurines l Suggest communication and interaction over long distances. l Suggest symbolic thinking.
Implication of Figurines l Suggest communication and interaction over long distances. l Suggest symbolic thinking.
 Cave Painting l Painters used charcoal & red ochre l Lascaux: (France) emphasis on animal paintings; human renderings are simple. l Altamira: (Spain) use of natural features of the cave to enhance animal art. l Chauvet Cave: (discovered 1994).
Cave Painting l Painters used charcoal & red ochre l Lascaux: (France) emphasis on animal paintings; human renderings are simple. l Altamira: (Spain) use of natural features of the cave to enhance animal art. l Chauvet Cave: (discovered 1994).
 Chauvet Cave 33 – 20 kya l Large cave galleries l Compositional groupings of herbivores & predators. l Find rare species not depicted in other caves: rhino, lion, long-eared owl, & hyena. l Appear to be stylistically unified (same culture).
Chauvet Cave 33 – 20 kya l Large cave galleries l Compositional groupings of herbivores & predators. l Find rare species not depicted in other caves: rhino, lion, long-eared owl, & hyena. l Appear to be stylistically unified (same culture).
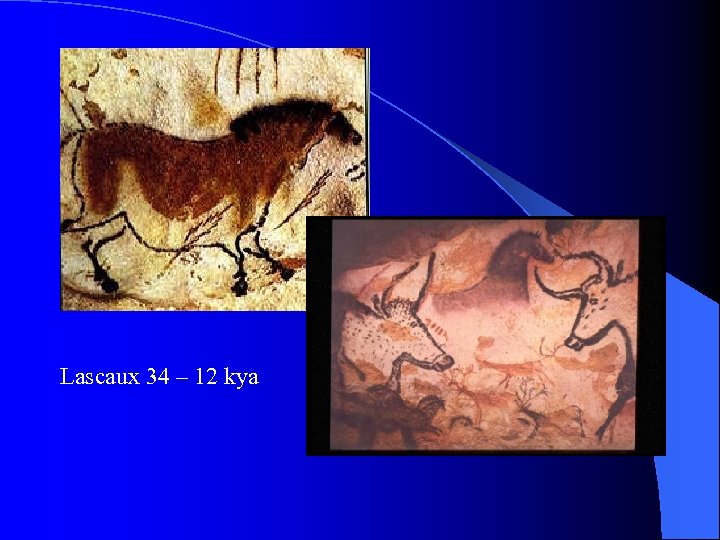 Lascaux 34 – 12 kya
Lascaux 34 – 12 kya
 Chauvet Cave, France 33 - 20 kya
Chauvet Cave, France 33 - 20 kya
 The Magdalenian 20 – 10 kya. l Stone/bone tool industry becomes more diverse. – Microlithic blades. – New weapons (e. g. , harpoon). l Large scale climate change occurred (deglaciation). l Sites were occupied for longer than during Gravettian (more sedentary). l – Important sites: Madeliene Rockshelter, Laugerie Haute – People lived there for entire seasons, not year round.
The Magdalenian 20 – 10 kya. l Stone/bone tool industry becomes more diverse. – Microlithic blades. – New weapons (e. g. , harpoon). l Large scale climate change occurred (deglaciation). l Sites were occupied for longer than during Gravettian (more sedentary). l – Important sites: Madeliene Rockshelter, Laugerie Haute – People lived there for entire seasons, not year round.
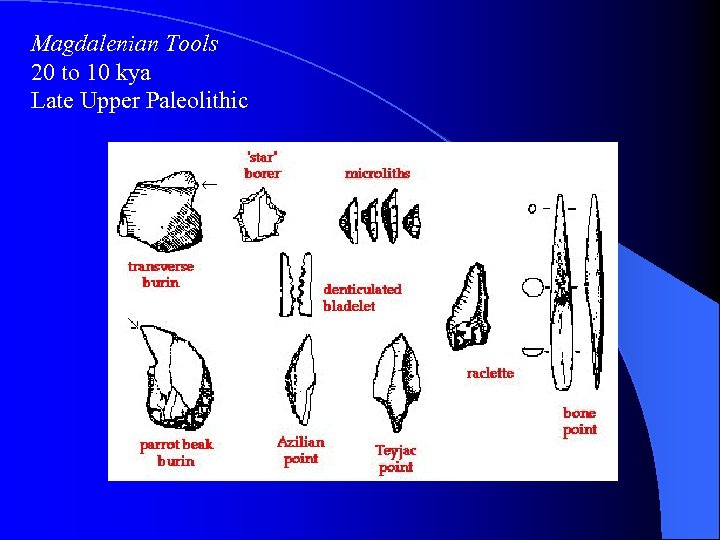 Magdalenian Tools 20 to 10 kya Late Upper Paleolithic
Magdalenian Tools 20 to 10 kya Late Upper Paleolithic
 Mezhirich, Russia Magdalenian
Mezhirich, Russia Magdalenian
 Summary of Upper Paleolithic l Diet became gradually more diverse l People became gradually less mobile l Artwork proliferates l Climate warms, deglaciation during Magdalenian l Sets the stage for more regionalization and diversification during the Mesolithic
Summary of Upper Paleolithic l Diet became gradually more diverse l People became gradually less mobile l Artwork proliferates l Climate warms, deglaciation during Magdalenian l Sets the stage for more regionalization and diversification during the Mesolithic
 The Mesolithic The transition from foraging to farming
The Mesolithic The transition from foraging to farming

 The Mesolithic l Starts at roughly 10 kya in many areas l Ends when agriculture is firmly established l The last ice age is definitely over – Climate becoming gradually warmer l Diet continues to change l Patterns of the Mesolithic are widespread
The Mesolithic l Starts at roughly 10 kya in many areas l Ends when agriculture is firmly established l The last ice age is definitely over – Climate becoming gradually warmer l Diet continues to change l Patterns of the Mesolithic are widespread
 Diet is diverse l Find all kinds of fishing equipment l Ground-stone tools l Diverse projectile weapons from many materials l Some cultivation is apparent – Cultigens are plants that are cultivated but this does not equal domestication.
Diet is diverse l Find all kinds of fishing equipment l Ground-stone tools l Diverse projectile weapons from many materials l Some cultivation is apparent – Cultigens are plants that are cultivated but this does not equal domestication.
 Widespread l This diet pattern can be seen from England to Japan l There are 35, 000 Mesolithic sites along the coast of Japan l Let’s discuss one site, Nittano (Japan) – Constantly occupied from 6 to 5 kya
Widespread l This diet pattern can be seen from England to Japan l There are 35, 000 Mesolithic sites along the coast of Japan l Let’s discuss one site, Nittano (Japan) – Constantly occupied from 6 to 5 kya
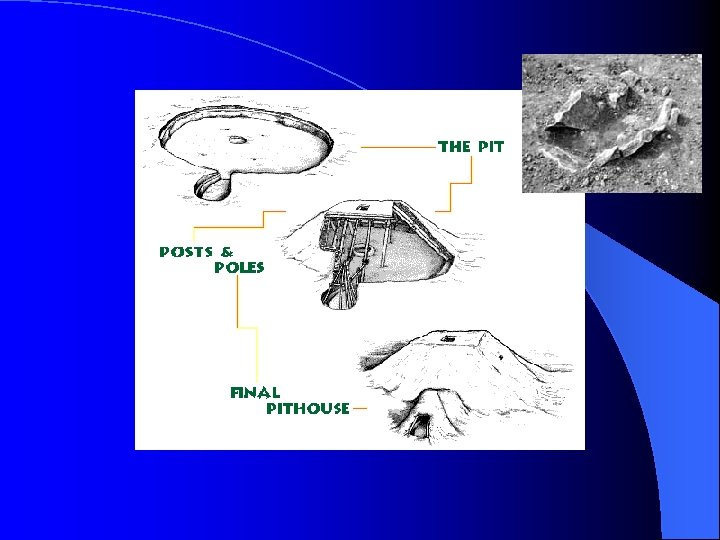
 Nittano l There were roughly 4 to 8 pithouses at any one time (they were often rebuilt) l These houses had stone-lined hearths l It is thought that people settled here year-round l Intensification of architecture is important
Nittano l There were roughly 4 to 8 pithouses at any one time (they were often rebuilt) l These houses had stone-lined hearths l It is thought that people settled here year-round l Intensification of architecture is important
 Broad Spectrum Revolution l BSR refers to the way people adapted around 15 kya in the Middle East & 12 kya in Europe. During the Mesolithic, many plants & animals were hunted, gathered, collected, caught, & fished. l Farming and life as we know it grows out of the BSR.
Broad Spectrum Revolution l BSR refers to the way people adapted around 15 kya in the Middle East & 12 kya in Europe. During the Mesolithic, many plants & animals were hunted, gathered, collected, caught, & fished. l Farming and life as we know it grows out of the BSR.
 BSR & Mesolithic l Star Carr (England) l Vedbaek (Denmark) l Nittano (Japan) l Elands Bay (South Africa) l Mount Sandel (Ireland) l It really is broad!
BSR & Mesolithic l Star Carr (England) l Vedbaek (Denmark) l Nittano (Japan) l Elands Bay (South Africa) l Mount Sandel (Ireland) l It really is broad!


