 The unknown ‘shadow’. Supplementary education in Germany Thomas Koinzer Humboldt University Berlin Department of Educational Science Workshop The Worldwide Growth of Supplemental Education, University of Waterloo/On. , June 4 -6, 2010
The unknown ‘shadow’. Supplementary education in Germany Thomas Koinzer Humboldt University Berlin Department of Educational Science Workshop The Worldwide Growth of Supplemental Education, University of Waterloo/On. , June 4 -6, 2010
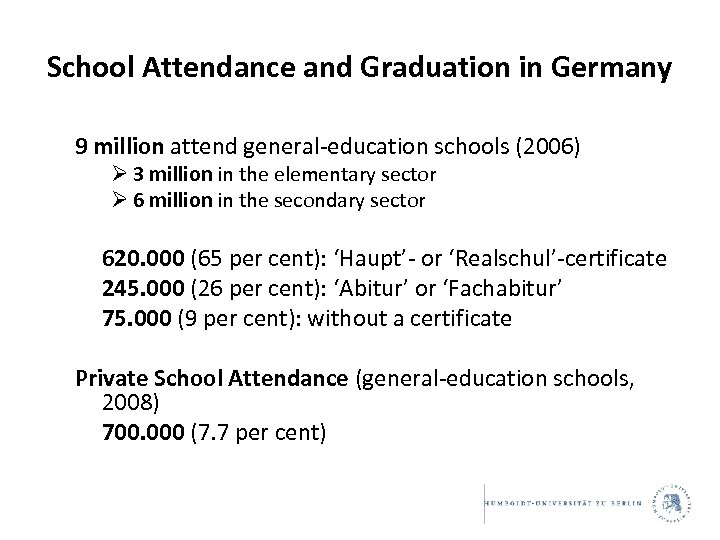 School Attendance and Graduation in Germany 9 million attend general-education schools (2006) Ø 3 million in the elementary sector Ø 6 million in the secondary sector 620. 000 (65 per cent): ‘Haupt’- or ‘Realschul’-certificate 245. 000 (26 per cent): ‘Abitur’ or ‘Fachabitur’ 75. 000 (9 per cent): without a certificate Private School Attendance (general-education schools, 2008) 700. 000 (7. 7 per cent)
School Attendance and Graduation in Germany 9 million attend general-education schools (2006) Ø 3 million in the elementary sector Ø 6 million in the secondary sector 620. 000 (65 per cent): ‘Haupt’- or ‘Realschul’-certificate 245. 000 (26 per cent): ‘Abitur’ or ‘Fachabitur’ 75. 000 (9 per cent): without a certificate Private School Attendance (general-education schools, 2008) 700. 000 (7. 7 per cent)
 Why take German pupils private lessons? Ø Poor school marks Ø Educational aspiration of parents Ø Methodology of German teachers
Why take German pupils private lessons? Ø Poor school marks Ø Educational aspiration of parents Ø Methodology of German teachers
 Cost Ø 942 and 1. 468 million Euros (U. S. -$ 1. 1 to 1. 8 billion) a year Ø 143 million Euros in the elementary, the remaining in the secondary sector Ø anticipated weekly attendance of 2 to 3 hours: annual cost is estimated between 900 and 1. 500 Euros (U. S. -$ 1. 120 to 1. 850) per subject and pupil 5
Cost Ø 942 and 1. 468 million Euros (U. S. -$ 1. 1 to 1. 8 billion) a year Ø 143 million Euros in the elementary, the remaining in the secondary sector Ø anticipated weekly attendance of 2 to 3 hours: annual cost is estimated between 900 and 1. 500 Euros (U. S. -$ 1. 120 to 1. 850) per subject and pupil 5
 Suppliers 70% by students, retired teachers etc. 30% by commercial suppliers: about 300 with 3, 000 contractors e. g. Ø Studienkreis Ø Schülerhilfe Ø Ø Ø ABACUS Nachhilfeinstitut Lernstudio Barbarossa Berlitz Germany ACADOMIA Keep. School KUMON Germany 7
Suppliers 70% by students, retired teachers etc. 30% by commercial suppliers: about 300 with 3, 000 contractors e. g. Ø Studienkreis Ø Schülerhilfe Ø Ø Ø ABACUS Nachhilfeinstitut Lernstudio Barbarossa Berlitz Germany ACADOMIA Keep. School KUMON Germany 7
 Literature • Klemm, K. /Klemm, A. , (2010): Ausgaben für Nachhilfe – teurer und unfairer Ausgleich für fehlende individuelle Förderung. Im Auftrag der Bertelsmann-Stiftung. Gütersloh: Bertelsmann-Stiftung. • Dohmen, D. et al. (2008): Was wissen wir über Nachhilfe. Sachstand und Auswertung der Forschungsliteratur zu Angebot, Nachfrage und Wirkungen, Berlin: Forschungsinstitut für Bildungs- und Sozialökonomie. • Jürgens, E. /Diekmann, M. (2007): Wirksamkeit und Nachhaltigkeit von Nachhilfeunterricht. Dargestellt am Beispiel des Studienkreises. Frankfurt am Main u. a. : Lang. • Schneider, T. (2004): Nachhilfe als Strategie zur Verwirklichung von Bildungszielen. Eine empirische Untersuchung mit Daten des Soziooekonomischen Panels (SOEP). In: DIW Discussion Papers No. 447, Oktober 2004. 8
Literature • Klemm, K. /Klemm, A. , (2010): Ausgaben für Nachhilfe – teurer und unfairer Ausgleich für fehlende individuelle Förderung. Im Auftrag der Bertelsmann-Stiftung. Gütersloh: Bertelsmann-Stiftung. • Dohmen, D. et al. (2008): Was wissen wir über Nachhilfe. Sachstand und Auswertung der Forschungsliteratur zu Angebot, Nachfrage und Wirkungen, Berlin: Forschungsinstitut für Bildungs- und Sozialökonomie. • Jürgens, E. /Diekmann, M. (2007): Wirksamkeit und Nachhaltigkeit von Nachhilfeunterricht. Dargestellt am Beispiel des Studienkreises. Frankfurt am Main u. a. : Lang. • Schneider, T. (2004): Nachhilfe als Strategie zur Verwirklichung von Bildungszielen. Eine empirische Untersuchung mit Daten des Soziooekonomischen Panels (SOEP). In: DIW Discussion Papers No. 447, Oktober 2004. 8