2e21471cdfd3f527fe76640537ebcf65.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49

The United States Goes to War

B 4 our involvement in the war… what else is going on? • Double V Campaign – Against ____ abroad & against ____ at home • A. Phillip Randolph – Head of Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters – Black male industrialists • March on Washington • FDR’s response: Executive Order 8802 – Fair hiring practices for gov’t funded jobs.

Close Reading Activity • Brief summary of WWII • Read aloud • Circle things you don’t know or want to know more about • Underline important information _____ • Star the most important

So… how do we get involved?

Clash of Ideologies: Totalitarian Governments • Germany, Italy, and the Soviet Union. • Fascism – Germany’s Adolf Hitler and Italy’s Benito Mussolini. – These Gov’ts used terror to suppress individual rights – Places the importance of and to silence all forms of the nation above the oppression. value of the individual. – They controlled all aspects – Focused on the need to of everyday life. rebuilt Italy/Germany. – Different from communism, b/c it allows private business.
Where the heck is America? • Neutrality – The US will withhold weapons & loans from all nations at war. • Cash and Carry – Allies can buy war goods from the US and transport them in their own ships. • Lend-Lease Act – Allies could buy goods from the US on credit, in exchange for leases on military bases.

December 7, 1941 – Pearl Harbor • Hawaiian Island, Oahu • Right before 8: 00 am, 180 Japanese warplanes sailed overhead. • Most of the Pacific fleet was in an area less than 3 square miles. • 2, 400 Americans were killed and 1, 200 were wounded. • 300 warplanes damaged. • 18 warships sunk, (8/9 fleet battleship). • Japan lost 29 planes.

Pearl Harbor – Destroyed Battleships

Three days later, Germany and Italy declared war on the United States. Americans were part of another world conflict. Their contributions would make the differences between victory and defeat for the Allies.

Who’s side are you on? • Axis Powers: • Allied Powers: • Germany • Italy • Japan • • Great Britain Soviet Union (Russia) United States Gov’ts in exile – “Free French”

THE BIG THREE • US Alliance with Great Britain and the Soviet Union • Ideological differences • Common Enemy – Hitler • Stalin asked others to attack from France and open a second front to split the Nazi forces • Eastern Front took a heavy toll on the Soviet population • Allies attacked through Northern Africa

Early Allied Victory • November 1942, GB won a victory in El Alamein in Egypt. – They made Germans retreat west. • Eisenhower took US/GB troops in Morocco & Algeria and pushed east. • The two allied forces came together and posed an intimidating threat. – 240, 000 Germans/Italian surrendered.

General George Marshall • FDR’s Army Joint Chief of Staff • Orchestrated the “War in Europe!” • Later will win the Nobel Peace Prize for his “Marshall Plan. ”

North Africa • General George S. Patton – Allies • General Erwin Rommell “Desert Fox” – Axis (Nazi)

Hitler invades Soviet Union? !!? • Since 1924, Hitler had called for conquest of the Soviet Union. – He claimed Germany needed Lebensraum. • Living space – After the loss of the Battle of Britain, he launched an attack against the Soviet Union. • June 1941, 3. 6 million Germans poured across the Soviet (Baltic to Black Sea). • Soviets used “Scorched Earth” policy for defense.

• Stalin asked Roosevelt for help through the Lend. Lease Act. • Stalin asked the allies to please attack Western Europe. – Would make Hitler divide his troops. – Instead Churchill wanted to invade Italy the “soft under-belly of Europe. ” Stalin asks for Help!

Allies invade Italy • Allies, led by General George Patton, launch invasion of Sicily from North Africa. – Fell in 38 days. • Mussolini is denounced and arrested by the Italian government. • Italy announces declaration of war agaisnt Germany.

Peace out Mussolini… Here he is with his mistress

Battle of Stalingrad • September 1942 – Germany attacks, bombs! – Prolonged German offensive. • Mid Nov – got too cold for the Nazi’s – The Red Army was able to beat them! • They hold the city against unbelievable odds. • January 31, 1943 – 90, 000 surviving Germans surrendered. – Germany lost about 330, 000 • Turning point of the war in the East!!!!

D-Day • General Dwight D. Eisenhower - leading officer • Largest amphibious attack in history • June 6, 1944 • Operation Overlord • D-Day = Designated Day • 2 million troops involved (largest invasion force ever assembled) • First waves experienced high casualty rates • Eventually liberated Paris and Belgium
Battle of the Bulge • December 1944 – General Patton brought 250, 000 soldiers. • Nazi troops squeezed b/w Soviets and Allies • Hitler launched a surprise offensive in a weakened part of the line • Created a “bulge” in the front line. • Hitler was defeated again • Largest battle in Western Europe during WWII. – Out of 600, 000 GI’s 80, 000 killed. – German loss: 100, 000 • One more nail in the coffin. • Nazi leaders knew that the end was near.

Yalta Conference • The Big Three planned for the post war world & agreed that: • Germany would be divided. • Part of Poland would go to the Soviet Union. • Soviet Union would declare war on Japan 2 to 3 months after defeating Germany. • Stalin didn’t allow free elections and was slow to enter the war with Japan. • This would cause problems b/t them and the US which would lead to the Cold War.

Allied Victory in Europe • After “Bulge, ” Allies closed in on Berlin. • Allies met at Yalta to discuss terms of German surrender. • Berlin ended up under Soviet control. (Uh, oh). • Hitler committed suicide at the beginning of May in 1945. • VE DAY = Victory in Europe! – May 8, 1945 • Discovery of the “death” camps.

• Germany signs unconditional surrender. – May 1, 1945 Hitler kills himself. – May 8, 1945 Germany surrenders. • War in Europe is over! – May 8, 1945



The Potsdam Conference • New Big Three: – Stalin (still), Clement Attlee (replaces Churchill), and Harry Truman (no more FDR). – They finalized plans for administration of Europe. – Germany and Berlin were divided into four zones of occupation. – Administered by Big Three countries plus France. – Free elections to be held later for selfdetermination. – Now… time to focus on the Pacific!

America in the Pacific • Battle of Midway – June 4, 1942; fought by air. – Sunk 4 Japanese carriers, 250 planes. • Japan can no longer launch an offensive, allies can. • Battle of Guadalcanal – First taste of Japanese jungle for the Allies. • Battle of Iwo Jima – One of the bloodiest, 74 days long. • 110, 000 US vs. 25, 000 Jap – Enemy fought until the last man, only 216 taken prisoner. – 27 medals of Honor awarded. • Island hopping commences!
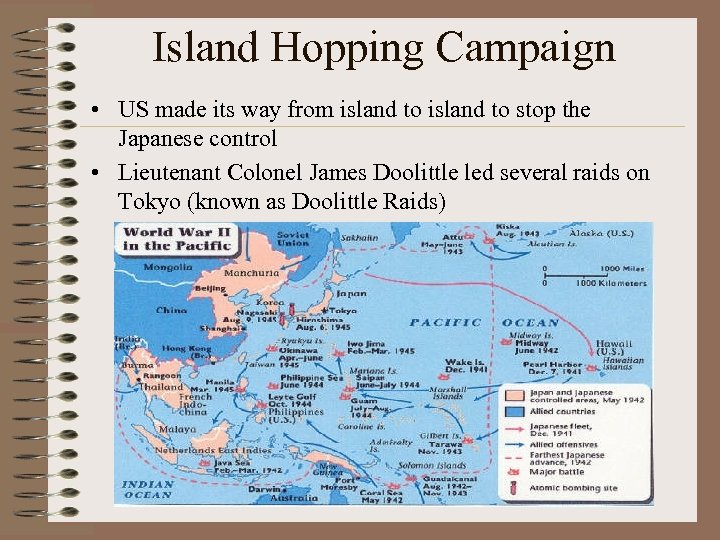
Island Hopping Campaign • US made its way from island to stop the Japanese control • Lieutenant Colonel James Doolittle led several raids on Tokyo (known as Doolittle Raids)

Turning Point in the Pacific • Had to gain control of the skies and waters of the Pacific – The Battle of Coral Sea was the 1 st major battle for US in the Pacific. • Battle of Midway in June of 1942 was THE turning point • Faced many Kamikazes

KAMIKAZES • Japanese suicide squadrons • Aircrafts were loaded with explosives • Flew directly into US naval vessels killing themselves in an effort to stop the American advance • Altogether, they sank about 40 ships

Battle of Iwo Jima • US Island hopping Dangers other than battle included: 1. Monsoons 2. Malaria 3. Heat 4. Earthquakes 5. Jungle Conditions • Iwo Jima: – US 6, 800 killed and 23, 000 wounded
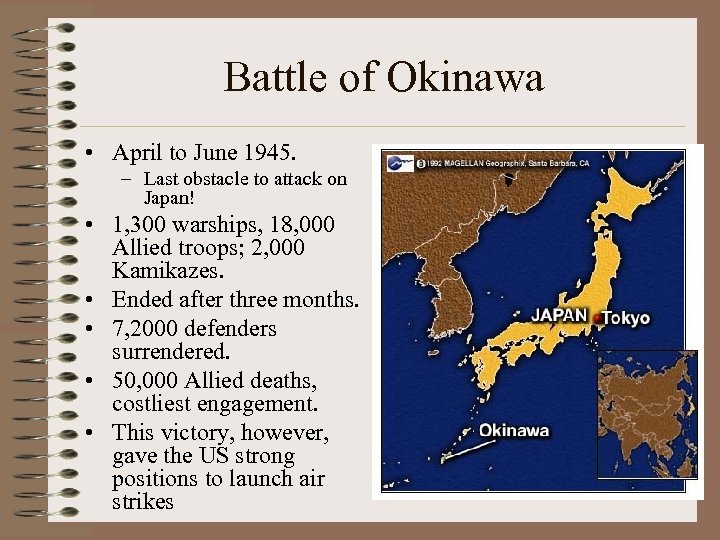
Battle of Okinawa • April to June 1945. – Last obstacle to attack on Japan! • 1, 300 warships, 18, 000 Allied troops; 2, 000 Kamikazes. • Ended after three months. • 7, 2000 defenders surrendered. • 50, 000 Allied deaths, costliest engagement. • This victory, however, gave the US strong positions to launch air strikes
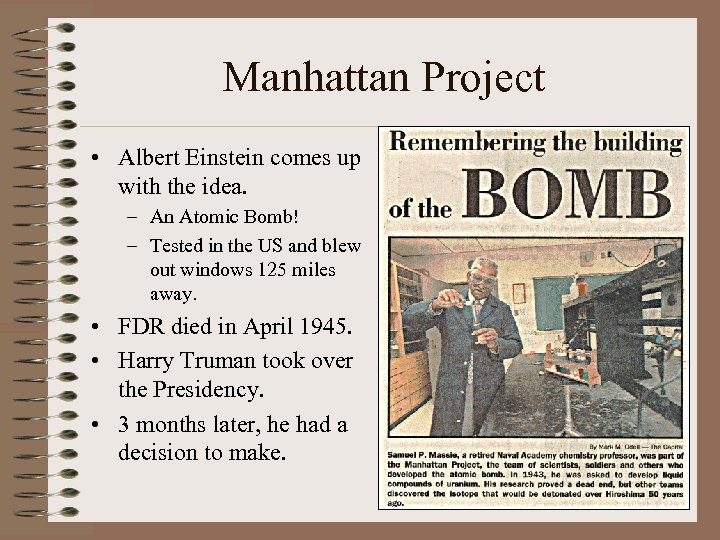
Manhattan Project • Albert Einstein comes up with the idea. – An Atomic Bomb! – Tested in the US and blew out windows 125 miles away. • FDR died in April 1945. • Harry Truman took over the Presidency. • 3 months later, he had a decision to make.

1953, Las Vegas – A mom and her son watch the mushroom cloud after an atomic bomb test 75 miles away.

Hiroshima/Nagasaki Little Boy and Fat Man

Little Boy and Fat Man • Little Boy was the first nuclear weapon used in warfare. It exploded approximately 1, 800 feet over Hiroshima, Japan, on the morning of August 6, 1945, with a force equal to 13, 000 tons of TNT. Immediate deaths were between 70, 000 to 130, 000. • Little Boy was dropped from a B-29 bomber piloted by U. S. Army Air Force Col. Paul W. Tibbets had named the plane Enola Gay after his mother the night before the atomic attack. • Fat Man was the second nuclear weapon used in warfare. Dropped on Nagasaki, Japan, on August 9, 1945, Fat Man devastated more than two square miles of the city and caused approximately 45, 000 immediate deaths. • Major Charles W. Sweeney piloted the B-29, #77 that dropped Fat Man. After the nuclear mission, #77 was christened Bockscar after its regular Command Pilot, Fred Bock. • While Little Boy was a uranium gun-type device, Fat Man was a more complicated and powerful plutonium implosion weapon that exploded with a force equal to 20 kilotons of TNT.

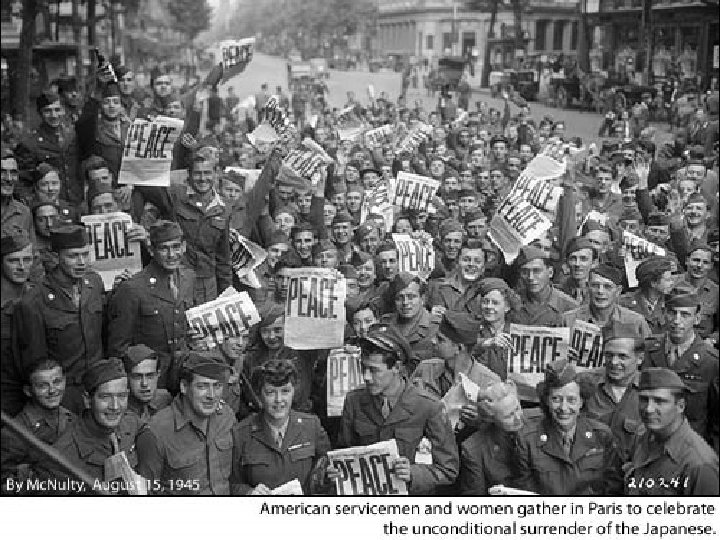
A-Bomb • On August 6, 1945 US dropped the first A-bomb on Hiroshima • Japan still does not surrender • On August 9 th, 1945 US dropped the second Abomb on Nagasaki • On August 14, 1945 Japan surrenders unconditionally; VJ Day

Devastation Innocents

Nagasaki
Pikadon • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=e. EOZ 1 s. Bpp. Ws


Effects of the War • • • Holocaust Nuremberg Trials Japanese War Criminals Unbelievable death & destruction US Home front : – Japanese Interment Camps • Korematsu v. United States (intro activity tomorrow) – Wartime Economy boost – Women (“Rosie the Riveter, ” and Minorities join the market economy, only to be booted out AGAIN after the war. – Women’s Baseball (A League of their Own!)
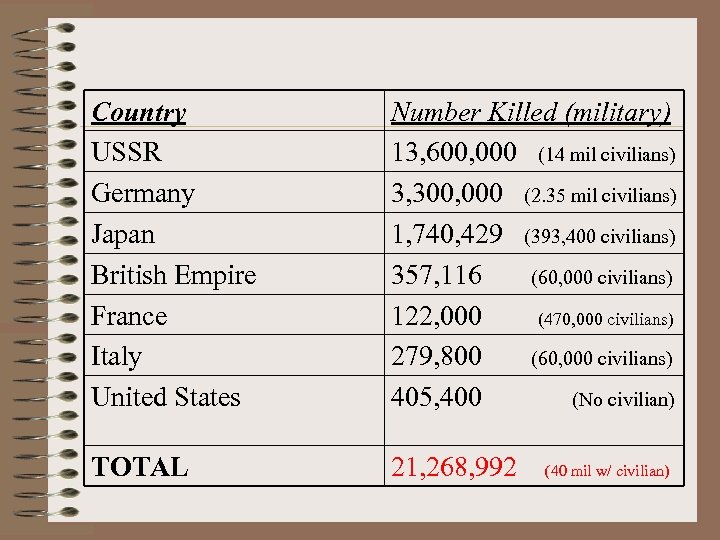
Country USSR Germany Japan British Empire France Italy United States Number Killed (military) 13, 600, 000 (14 mil civilians) 3, 300, 000 (2. 35 mil civilians) 1, 740, 429 (393, 400 civilians) 357, 116 (60, 000 civilians) 122, 000 (470, 000 civilians) 279, 800 (60, 000 civilians) 405, 400 (No civilian) TOTAL 21, 268, 992 (40 mil w/ civilian)

THE WAR IS OVER!
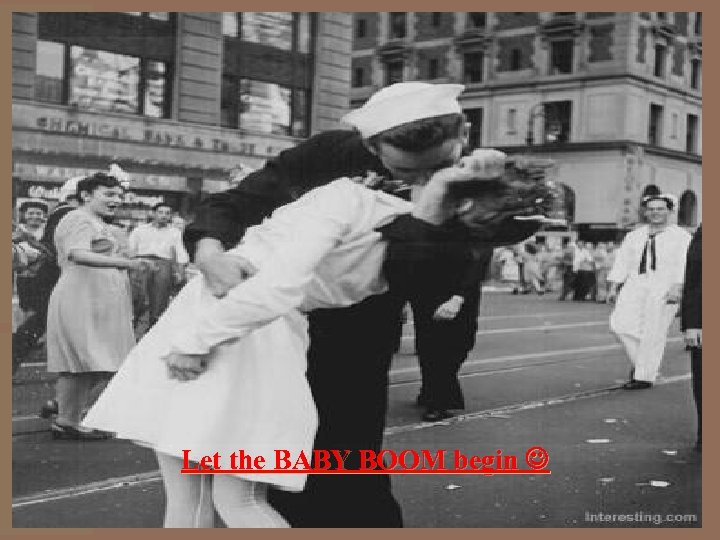

Let the BABY BOOM begin

What we’ve learned so far: SSUSH 19 The student will identify the origins, major developments, and the domestic impact of World War II, especially the growth of the federal government. • Element: SSUSH 19. a • Explain A. Philip Randolph's proposed march on Washington, D. C. and President Franklin D. Roosevelt's response. • Element: SSUSH 19. b • Explain the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor and the internment of Japanese-Americans. • Element: SSUSH 19. c • Explain major events including the lend-lease program, the Battle of Midway, D-Day, and the fall of Berlin. • Element: SSUSH 19. d • Describe war mobilization, as indicated by rationing, war-time conversion, and the role of women in war industries. • Element: SSUSH 19. e • Describe Los Alamos and the scientific, economic, and military implications of developing the atomic bomb. • Element: SSUSH 19. f • Compare the geographic locations of the European theater and the Pacific theater and the difficulties the U. S. faced in delivering weapons, food, and medical supplies to troops.

What else we have to learn before the ATA and PA: • • • SSUSH 20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. Element: SSUSH 20. a Describe the creation of the Marshall Plan, U. S. commitment to Europe, the Truman Doctrine, and the origins and implications of the containment policy. Element: SSUSH 20. b Explain the impact of the new communist regime in China, the outbreak of the Korean War, & how these events contributed to the rise of Senator Joseph Mc. Carthy. SSUSH 21 The student will explain economic growth and its impact on the United States 1945 -1970. Element: SSUSH 21. a Describe the baby boom and the impact as shown by Levittown and the Interstate Highway Act. Element: SSUSH 21. d Describe the impact of competition with the USSR as evidenced by the launch of Sputnik I and President Eisenhower's actions.

LET’S TAKE A CLOSER LOOK AT WHAT IS HAPPENING AT HOME DURING THE WAR.
2e21471cdfd3f527fe76640537ebcf65.ppt