TheUnitedNations.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 The United Nations: logic of decision making.
The United Nations: logic of decision making.
 The United Nations Main Aims: Tolerance and friendship among all nation, racial or religious groups. Maintenance of peace
The United Nations Main Aims: Tolerance and friendship among all nation, racial or religious groups. Maintenance of peace
 When did it begin? § The United Nations is made up of 193 countries from around the world. It is often called the UN. § It was set up in 1945, after the Second World War, as a way of bringing people together and to avoid further wars. § It started with 51 countries. The United Kingdom is one of the original members. Germany did not join until 1973.
When did it begin? § The United Nations is made up of 193 countries from around the world. It is often called the UN. § It was set up in 1945, after the Second World War, as a way of bringing people together and to avoid further wars. § It started with 51 countries. The United Kingdom is one of the original members. Germany did not join until 1973.
 What does the UN do? § The UN aims to ensure that people don’t suffer from hunger and homelessness. § It has a special section called Unicef that tries to help children. § The UN has a convention on children's rights. They would like it to be followed by all countries, as a set of rules about the treatment of children.
What does the UN do? § The UN aims to ensure that people don’t suffer from hunger and homelessness. § It has a special section called Unicef that tries to help children. § The UN has a convention on children's rights. They would like it to be followed by all countries, as a set of rules about the treatment of children.
 Why is it important to have an organisation that is bigger than any one country? § Stops governments mistreating people § Helps stop wars between countries § Looks after all the world's young people
Why is it important to have an organisation that is bigger than any one country? § Stops governments mistreating people § Helps stop wars between countries § Looks after all the world's young people
 UN General Assembly - Deliberative assembly of all UN member states (each country has one vote) § may resolve non-compulsory § § § recommendations to states, or suggestions to the UNSC (not a Parliament) decides on the admission of new members, on proposal of the UNSC adopts the budget elects the non-permanent members of the UNSC, all members of ECOSOC, on the proposal of the UNSC the UN Secretary General, and the 15 judges of the ICJ
UN General Assembly - Deliberative assembly of all UN member states (each country has one vote) § may resolve non-compulsory § § § recommendations to states, or suggestions to the UNSC (not a Parliament) decides on the admission of new members, on proposal of the UNSC adopts the budget elects the non-permanent members of the UNSC, all members of ECOSOC, on the proposal of the UNSC the UN Secretary General, and the 15 judges of the ICJ
 UN Secretariat - Administrative organ of the UN - its chairman is the UN Secretary General § supports the other UN bodies administratively, e. g. in the organization of conferences, writing reports and studies, and the preparation of the budgetplan its chairperson - the UN Secretary General - is elected by the UN General Assembly for a five-year mandate and is the most important representative of the UN Outside its headquarters in New York City, the organization has three main offices in Geneva, Nairobi, and Vienna
UN Secretariat - Administrative organ of the UN - its chairman is the UN Secretary General § supports the other UN bodies administratively, e. g. in the organization of conferences, writing reports and studies, and the preparation of the budgetplan its chairperson - the UN Secretary General - is elected by the UN General Assembly for a five-year mandate and is the most important representative of the UN Outside its headquarters in New York City, the organization has three main offices in Geneva, Nairobi, and Vienna
 UN Secretary-General § Assumed office 1 January 2007 § Minister of Foreign Affairs and Trade In office 17 January 2004 – 1 December 2006
UN Secretary-General § Assumed office 1 January 2007 § Minister of Foreign Affairs and Trade In office 17 January 2004 – 1 December 2006
 UN Security Council - For international security issues § responsible for the § § § maintenance of international peace and security the most powerful organ of the UN, as it may adopt compulsory resolutions its decisions include peacekeeping- and peace enforcement-missions, as well as non-military pressure mediums, such as trade embargos has 15 members: five permanent members with veto power, and ten elected members
UN Security Council - For international security issues § responsible for the § § § maintenance of international peace and security the most powerful organ of the UN, as it may adopt compulsory resolutions its decisions include peacekeeping- and peace enforcement-missions, as well as non-military pressure mediums, such as trade embargos has 15 members: five permanent members with veto power, and ten elected members
 International Court of Justice - Universal court for international law (based in The Hague) § decides disputes between states that recognize its jurisdiction and creates legal opinions § the 15 judges are elected by the UN General Assembly for nine years. It renders judgement with relative majority. § parties on the ICJ can only be countries, however no international organizations and other subjects of international law (not to be confused with the ICC)
International Court of Justice - Universal court for international law (based in The Hague) § decides disputes between states that recognize its jurisdiction and creates legal opinions § the 15 judges are elected by the UN General Assembly for nine years. It renders judgement with relative majority. § parties on the ICJ can only be countries, however no international organizations and other subjects of international law (not to be confused with the ICC)
 UN Economic and Social Council - For global economical and social affairs § responsible for cooperation between states on economic and social fields (raising the general standard of living, solve economic, social and health problems, promotion of human rights, culture and education, as well as humanitarian aid) § therefore it has established numerous functional and regional commissions § also coordinates the cooperation with the numerous specialized agencies of the United Nations § has 54 members, who are elected by the UN General Assembly to serve staggered three-year mandates
UN Economic and Social Council - For global economical and social affairs § responsible for cooperation between states on economic and social fields (raising the general standard of living, solve economic, social and health problems, promotion of human rights, culture and education, as well as humanitarian aid) § therefore it has established numerous functional and regional commissions § also coordinates the cooperation with the numerous specialized agencies of the United Nations § has 54 members, who are elected by the UN General Assembly to serve staggered three-year mandates
 UN Trusteeship Council - Was administering trust territories (currently not active) - § was originally designed to manage colonial possessions that were earlier League of Nations mandates § is inactive since 1994, with the last trust territory (Palau) attaining independence in 1994
UN Trusteeship Council - Was administering trust territories (currently not active) - § was originally designed to manage colonial possessions that were earlier League of Nations mandates § is inactive since 1994, with the last trust territory (Palau) attaining independence in 1994
 The UN Family § Consists if 17 independent organizations also known § § § as “specialized agencies” which are linked to the UN through cooperative agreements They have wide-ranging international responsibilities in the economic, social, cultural, educational, and health-related fields All these organizations have their own governing bodies, budgets, and secretariats. Together, they provide technical assistance and other forms of practical help in virtually all economic and social areas
The UN Family § Consists if 17 independent organizations also known § § § as “specialized agencies” which are linked to the UN through cooperative agreements They have wide-ranging international responsibilities in the economic, social, cultural, educational, and health-related fields All these organizations have their own governing bodies, budgets, and secretariats. Together, they provide technical assistance and other forms of practical help in virtually all economic and social areas
 . . . .
. . . .
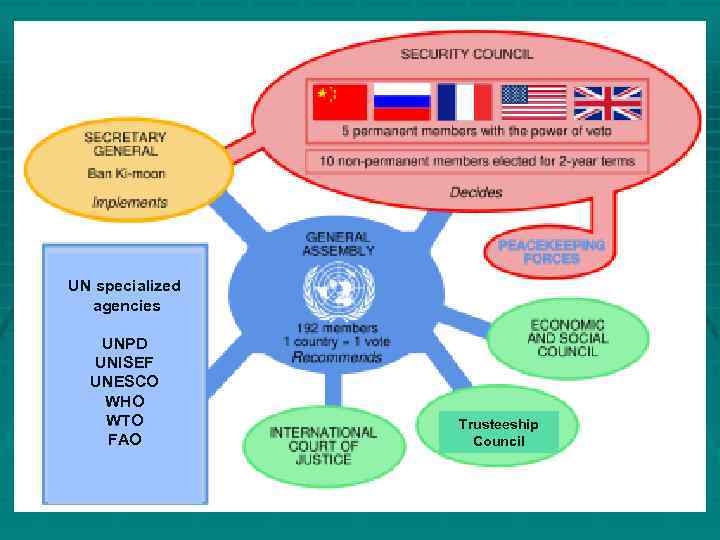 UN specialized agencies UNPD UNISEF UNESCO WHO WTO FAO Trusteeship Council
UN specialized agencies UNPD UNISEF UNESCO WHO WTO FAO Trusteeship Council
 Thanks for your attention.
Thanks for your attention.


