106ee40f9932d76ccddbfd025eaec62e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 The UK experience: The Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine Dr Peter Fisher Clinical Director of Research Expert Advisor to National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE)
The UK experience: The Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine Dr Peter Fisher Clinical Director of Research Expert Advisor to National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE)
 University College London Hospitals • One of largest academic medical centres in UK • Medical school and specialist institutes, linked to University College London • 8 hospitals: • University College Hospital (general/acute) • Cancer Centre • Eastman Dental Hospital • Elizabeth Garret Anderson (gynaecology, obstetrics, children) • Heart Hospital • Hospital for Tropical Diseases • National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery • Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine The Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine peter. fisher@uclh. nhs. uk
University College London Hospitals • One of largest academic medical centres in UK • Medical school and specialist institutes, linked to University College London • 8 hospitals: • University College Hospital (general/acute) • Cancer Centre • Eastman Dental Hospital • Elizabeth Garret Anderson (gynaecology, obstetrics, children) • Heart Hospital • Hospital for Tropical Diseases • National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery • Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine The Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine peter. fisher@uclh. nhs. uk
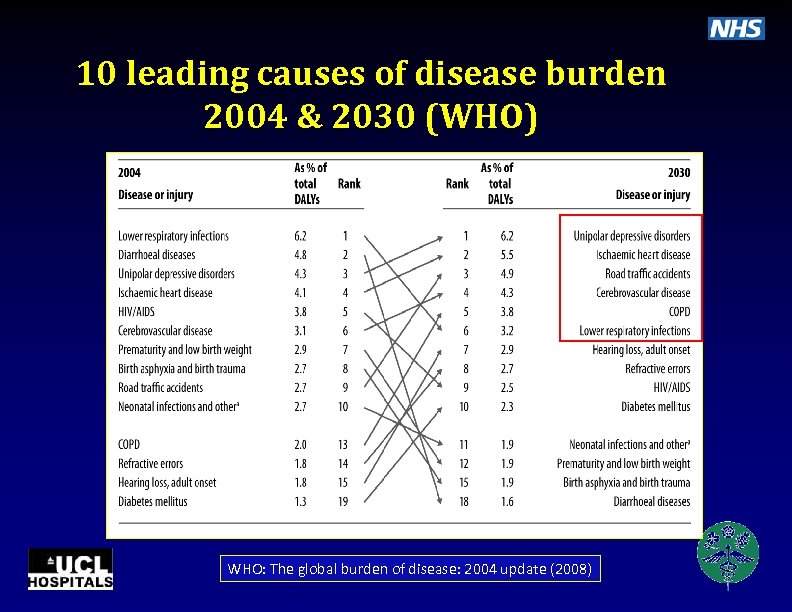 10 leading causes of disease burden 2004 & 2030 (WHO) WHO: The global burden of disease: 2004 update (2008)
10 leading causes of disease burden 2004 & 2030 (WHO) WHO: The global burden of disease: 2004 update (2008)
 Prevalence of mental disorder • Annual population prevalence in EU 38%: 165 m people • anxiety disorders (14%) • • • insomnia (7%) major depression (7%) somatoform (6%) alcohol and drug dependence (>4%) ADHD (5%) Dementia (1 -30%, depending on age) • 27% of total disease burden • Undertreated Wittchen HU et al. The size and burden of mental disorders and other disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011; 21: 655 -79
Prevalence of mental disorder • Annual population prevalence in EU 38%: 165 m people • anxiety disorders (14%) • • • insomnia (7%) major depression (7%) somatoform (6%) alcohol and drug dependence (>4%) ADHD (5%) Dementia (1 -30%, depending on age) • 27% of total disease burden • Undertreated Wittchen HU et al. The size and burden of mental disorders and other disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011; 21: 655 -79
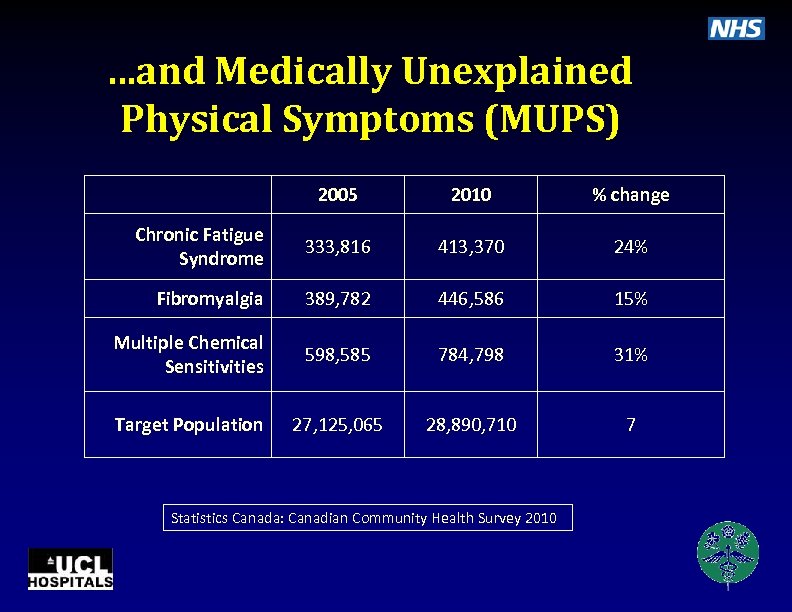 . . . and Medically Unexplained Physical Symptoms (MUPS) 2005 2010 % change Chronic Fatigue Syndrome 333, 816 413, 370 24% Fibromyalgia 389, 782 446, 586 15% Multiple Chemical Sensitivities 598, 585 784, 798 31% Target Population 27, 125, 065 28, 890, 710 7 Statistics Canada: Canadian Community Health Survey 2010
. . . and Medically Unexplained Physical Symptoms (MUPS) 2005 2010 % change Chronic Fatigue Syndrome 333, 816 413, 370 24% Fibromyalgia 389, 782 446, 586 15% Multiple Chemical Sensitivities 598, 585 784, 798 31% Target Population 27, 125, 065 28, 890, 710 7 Statistics Canada: Canadian Community Health Survey 2010
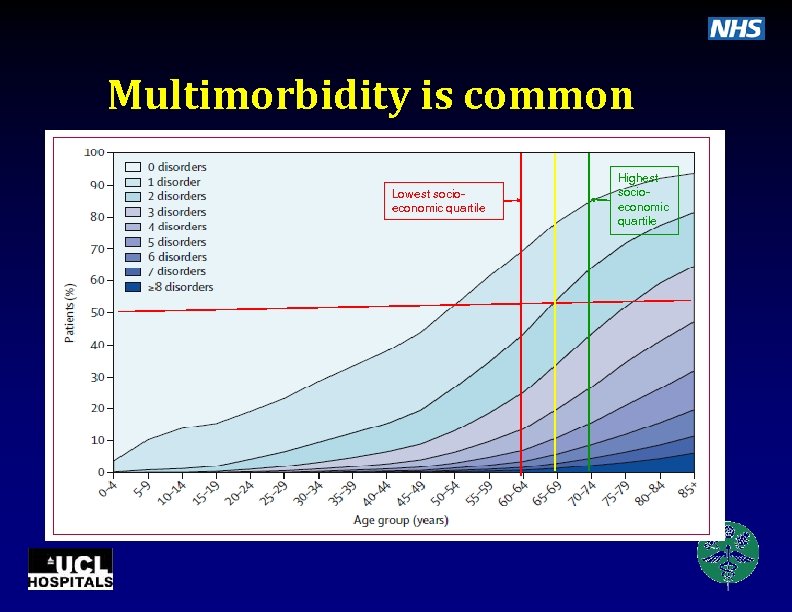 Multimorbidity is common • 40 morbidities ⅓ population of Scotland • • Highest socioeconomic quartile Lowest socio 42% > 1 morbidity economic quartile 23% multimorbid increases with age but absoute number higher in younger onset earlier in deprived areas particularly including mental health • Challenge single-disease framework • Personalised, continuity of care especially in deprived areas Barnett K et al. Epidemiology of multimorbidity and implications for health care, research, and medical education: a cross-sectional study. Lancet May 2012 DOI: 10. 1016/S 0140 -6736(12)60240 -2
Multimorbidity is common • 40 morbidities ⅓ population of Scotland • • Highest socioeconomic quartile Lowest socio 42% > 1 morbidity economic quartile 23% multimorbid increases with age but absoute number higher in younger onset earlier in deprived areas particularly including mental health • Challenge single-disease framework • Personalised, continuity of care especially in deprived areas Barnett K et al. Epidemiology of multimorbidity and implications for health care, research, and medical education: a cross-sectional study. Lancet May 2012 DOI: 10. 1016/S 0140 -6736(12)60240 -2
 Adverse drug events (ADEs) • Common • • • In USA 4. 6% of deaths, top 5 causes of death Hospitalized 6. 5% , almost double risk of death 4, 335, 990 outpatient attendances 107, 468 hospital admissions in 2005 9 17/1000 between 1995 -2005 • Expensive • Prolong hospital stays, increased resource utilization
Adverse drug events (ADEs) • Common • • • In USA 4. 6% of deaths, top 5 causes of death Hospitalized 6. 5% , almost double risk of death 4, 335, 990 outpatient attendances 107, 468 hospital admissions in 2005 9 17/1000 between 1995 -2005 • Expensive • Prolong hospital stays, increased resource utilization
 Adverse drug events (ADEs) • Associated Factors • age • number of medications • female gender Bourgeois FT et al. Adverse Drug Events in the Outpatient Setting: An 11 -Year National Analysis Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010 19 901– 910.
Adverse drug events (ADEs) • Associated Factors • age • number of medications • female gender Bourgeois FT et al. Adverse Drug Events in the Outpatient Setting: An 11 -Year National Analysis Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010 19 901– 910.
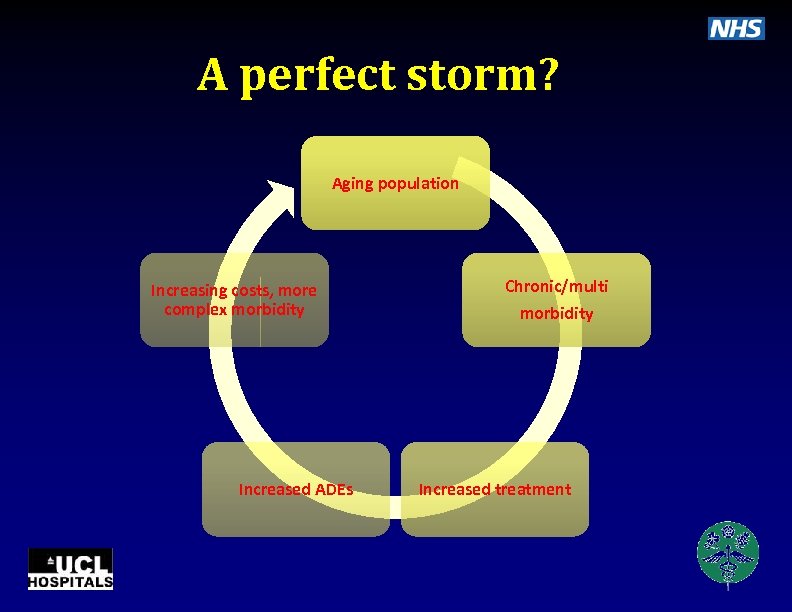 A perfect storm? Aging population Increasing costs, more complex morbidity Increased ADEs Chronic/multi morbidity Increased treatment
A perfect storm? Aging population Increasing costs, more complex morbidity Increased ADEs Chronic/multi morbidity Increased treatment
 Why integrate medicine? • chronic & multimorbid conditions v pandemic of iatrogenic illness • Reduce medication, treat person not disease • fiscal imperatives v expensive diagnostics & treatments • Effective economical whole person treatment • greater duration of life v greater duration of poor quality later life • Safe whole person long term treatments
Why integrate medicine? • chronic & multimorbid conditions v pandemic of iatrogenic illness • Reduce medication, treat person not disease • fiscal imperatives v expensive diagnostics & treatments • Effective economical whole person treatment • greater duration of life v greater duration of poor quality later life • Safe whole person long term treatments
 Why integrate medicine? • high-tech, high impact, high-cost interventions v caring, commitment, compassion • Revive the art of medicine • concordance v efficacy • Patient-friendly, culturally appropriate treatments • dependency on drugs and medical services v disillusionment and medical counterculture • Restore confidence in medicine
Why integrate medicine? • high-tech, high impact, high-cost interventions v caring, commitment, compassion • Revive the art of medicine • concordance v efficacy • Patient-friendly, culturally appropriate treatments • dependency on drugs and medical services v disillusionment and medical counterculture • Restore confidence in medicine
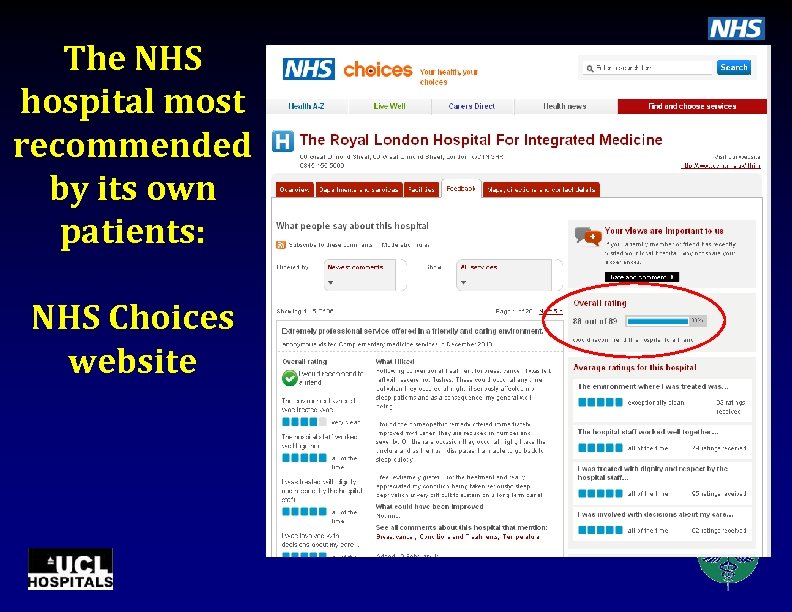 The NHS hospital most recommended by its own patients: NHS Choices website
The NHS hospital most recommended by its own patients: NHS Choices website
 The Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine: clinical services • Acupuncture • including high volume & training clinics • mostly western, some TCM • • • Allergy Children Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/ME Complementary Cancer General medicine • Including inflammatory and functional bowel • Podiatry Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
The Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine: clinical services • Acupuncture • including high volume & training clinics • mostly western, some TCM • • • Allergy Children Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/ME Complementary Cancer General medicine • Including inflammatory and functional bowel • Podiatry Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
 RLHIM: clinical services 2 • • • Weight loss Insomnia Integrated facial pain Integrated antenatal Musculoskeletal medicine Rheumatology Skin Stress & mood disorder Women's Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
RLHIM: clinical services 2 • • • Weight loss Insomnia Integrated facial pain Integrated antenatal Musculoskeletal medicine Rheumatology Skin Stress & mood disorder Women's Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
 RLHIM: innovation • • • 1950’s 1 st NHS Complementary Cancer Service 1977 1 st NHS Acupuncture Service 1995 1 st NHS Musculoskeletal medicine service 2005 1 st NHS Group acupuncture service 2005 1 st UK course on Integrated Medicine for doctors 2006 1 st NHS Integrated antenatal service 2007 1 st Integrated allergy service 2008 1 st NHS Herbal clinic 2009 1 st Integrated weight loss service 2010 1 st Integrated insomnia service 2012 Complementary Cancer Care in UK’s largest cancer centre
RLHIM: innovation • • • 1950’s 1 st NHS Complementary Cancer Service 1977 1 st NHS Acupuncture Service 1995 1 st NHS Musculoskeletal medicine service 2005 1 st NHS Group acupuncture service 2005 1 st UK course on Integrated Medicine for doctors 2006 1 st NHS Integrated antenatal service 2007 1 st Integrated allergy service 2008 1 st NHS Herbal clinic 2009 1 st Integrated weight loss service 2010 1 st Integrated insomnia service 2012 Complementary Cancer Care in UK’s largest cancer centre
 What problems do GPs face? Effectiveness Gaps • A clinical area where available treatments are not fully effective or satisfactory, for any reason. • Never previously researched Top 5 EGs % GPs reporting Musculoskeletal problems Depression Eczema Chronic pain Irritable bowel syndrome 91 45 36 32 32 Fisher P et al. Effectiveness gaps: A new concept for evaluating health service and research needs applied to complementary and alternative medicine. J Alt Comp Med, 2004; 10: 627– 632.
What problems do GPs face? Effectiveness Gaps • A clinical area where available treatments are not fully effective or satisfactory, for any reason. • Never previously researched Top 5 EGs % GPs reporting Musculoskeletal problems Depression Eczema Chronic pain Irritable bowel syndrome 91 45 36 32 32 Fisher P et al. Effectiveness gaps: A new concept for evaluating health service and research needs applied to complementary and alternative medicine. J Alt Comp Med, 2004; 10: 627– 632.
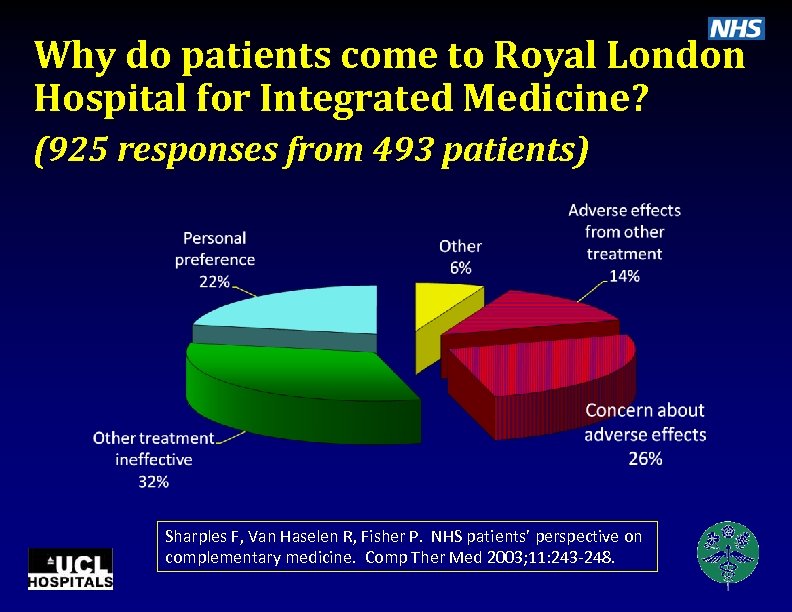 Why do patients come to Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine? (925 responses from 493 patients) Sharples F, Van Haselen R, Fisher P. NHS patients’ perspective on complementary medicine. Comp Ther Med 2003; 11: 243 -248.
Why do patients come to Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine? (925 responses from 493 patients) Sharples F, Van Haselen R, Fisher P. NHS patients’ perspective on complementary medicine. Comp Ther Med 2003; 11: 243 -248.
 The Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine: therapies • acupuncture • • mostly western, some TCM aromatherapy autogenic training cognitive behaviour therapy cranio-sacral therapy graded exercise homeopathy nutritional medicine • exclusion, supplements, nutraceuticals Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
The Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine: therapies • acupuncture • • mostly western, some TCM aromatherapy autogenic training cognitive behaviour therapy cranio-sacral therapy graded exercise homeopathy nutritional medicine • exclusion, supplements, nutraceuticals Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
 RLHIM: therapies 2 • • lifestyle management occupational therapy physiotherapy phytotherapy • • shiatsu spinal manipulation sublingual immunotherapy wet needling • standardised extracts • western mixtures • Chinese an aspiration Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
RLHIM: therapies 2 • • lifestyle management occupational therapy physiotherapy phytotherapy • • shiatsu spinal manipulation sublingual immunotherapy wet needling • standardised extracts • western mixtures • Chinese an aspiration Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
 Dimensions of integration • System • Normal NHS system • Common electronic patient records • Governance and evaluation • professionals trained in CM, subject to discipline • Culture of evaluation • Guidelines • eg National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidelines for low back pain recommend acupuncture and manipulation Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
Dimensions of integration • System • Normal NHS system • Common electronic patient records • Governance and evaluation • professionals trained in CM, subject to discipline • Culture of evaluation • Guidelines • eg National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidelines for low back pain recommend acupuncture and manipulation Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
 Dimensions of integration: professionalism
Dimensions of integration: professionalism
 Dimensions of integration: information and education • • Education and training: integrated and ‘hands-on’ Specialist advice NICE External Expert Panel Complementary and Alternative Medicine Library and Information Service (CAMLIS) • Physical and online Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
Dimensions of integration: information and education • • Education and training: integrated and ‘hands-on’ Specialist advice NICE External Expert Panel Complementary and Alternative Medicine Library and Information Service (CAMLIS) • Physical and online Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
 Dimensions of integration: hands-on training
Dimensions of integration: hands-on training
 Complementary and Alternative Medicine Library and Information Service (CAMLIS) www. cam. nhs. uk
Complementary and Alternative Medicine Library and Information Service (CAMLIS) www. cam. nhs. uk
 Models of integration • Fully integrated: • integrated Chronic Pain Service with dental hospital • integrated antenatal service with UCLH midwives • Unique services: Allergy and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome • UCLH’s only services for under-provided conditions: • guideline recommended treatments & CM. Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
Models of integration • Fully integrated: • integrated Chronic Pain Service with dental hospital • integrated antenatal service with UCLH midwives • Unique services: Allergy and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome • UCLH’s only services for under-provided conditions: • guideline recommended treatments & CM. Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
 Models of integration 2 • Colocated services: in UCLH’s main centres • cancer • children • Cost effective services for ‘effectiveness gap’ conditions: • group acupuncture • knee, low back, headache, facial pain • group Cognitive Behaviour Therapy, Autogenic Training • insomnia, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia • Informal: Contacts, ad-hoc referrals etc Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
Models of integration 2 • Colocated services: in UCLH’s main centres • cancer • children • Cost effective services for ‘effectiveness gap’ conditions: • group acupuncture • knee, low back, headache, facial pain • group Cognitive Behaviour Therapy, Autogenic Training • insomnia, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia • Informal: Contacts, ad-hoc referrals etc Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine
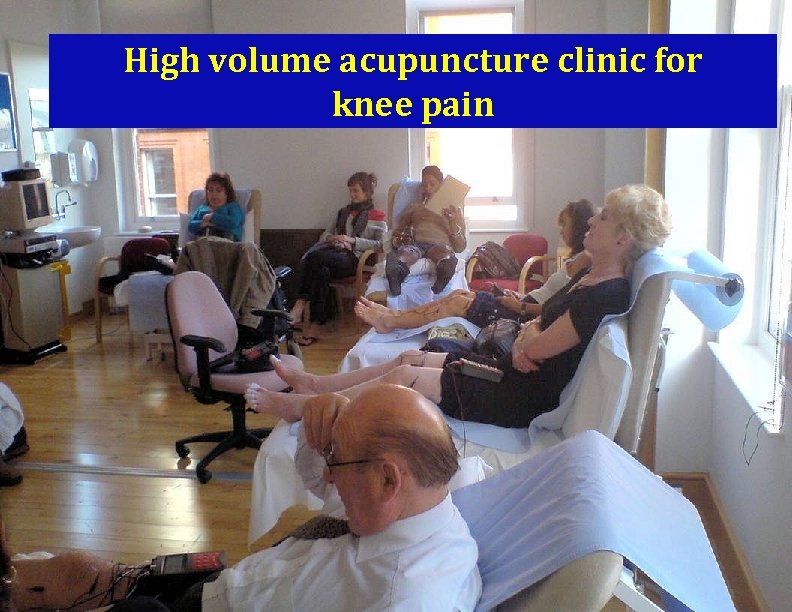 High volume acupuncture clinic for knee pain
High volume acupuncture clinic for knee pain
 Constraints to Integration • Coordinated hostile media campaign • NHS provision • Regulation • Scepticism • colleagues, particularly academic and older • Financial • but often saves money
Constraints to Integration • Coordinated hostile media campaign • NHS provision • Regulation • Scepticism • colleagues, particularly academic and older • Financial • but often saves money
 The Challenges: • Commissioners ‘Low priority’ treatments • evidence of clinical/cost effectiveness limited • grommets, tonsillectomy… varicocoele, refashioning scars…. • Complementary medicine of all types • ‘Referral management’ • Slow, bureaucratic, often refused
The Challenges: • Commissioners ‘Low priority’ treatments • evidence of clinical/cost effectiveness limited • grommets, tonsillectomy… varicocoele, refashioning scars…. • Complementary medicine of all types • ‘Referral management’ • Slow, bureaucratic, often refused
 Commissioning challenges: clinical pathways • Category 1 based on authoritative guidelines • Approximately 60% of patient attendances • Category 2 • Complementary cancer care • Category 3 require individual approval
Commissioning challenges: clinical pathways • Category 1 based on authoritative guidelines • Approximately 60% of patient attendances • Category 2 • Complementary cancer care • Category 3 require individual approval
 NHS Commissioning ‘Category 1’ based on authoritative guidelines Stress & Mood Disorder Group Acupuncture Chronic Headache Non-Organic Insomnia Group Acupuncture Knee Pain Cognitive Behavioural Therapy Perennial Allergic Rhinitis Irritable Bowel Syndrome Hayfever Fibromyalgia Syndrome Weight Loss Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Facial Pain Chronic low back pain
NHS Commissioning ‘Category 1’ based on authoritative guidelines Stress & Mood Disorder Group Acupuncture Chronic Headache Non-Organic Insomnia Group Acupuncture Knee Pain Cognitive Behavioural Therapy Perennial Allergic Rhinitis Irritable Bowel Syndrome Hayfever Fibromyalgia Syndrome Weight Loss Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Facial Pain Chronic low back pain
 NICE Guideline Low Back Pain • 1. 4 Manual therapy • 1. 4. 1 Consider offering a course of manual therapy, including spinal manipulation, maximum of 9 sessions over up to 12 weeks • 1. 5 Other non-pharmacological therapies • • • 1. 5. 1 Do not offer laser therapy 1. 5. 2 Do not offer interferential therapy 1. 5. 3 Do not offer therapeutic ultrasound 1. 5. 4 Do not offer transcutaneous electrical nerve simulation (TENS) 1. 5. 5 Do not offer lumbar supports 1. 5. 6 Do not offer traction • 1. 6 Invasive procedures • 1. 6. 1 Consider offering a course of acupuncture maximum of 10 sessions over up to 12 weeks • 1. 6. 2 Do not offer injections of therapeutic substances http: //guidance. nice. org. uk/CG 88
NICE Guideline Low Back Pain • 1. 4 Manual therapy • 1. 4. 1 Consider offering a course of manual therapy, including spinal manipulation, maximum of 9 sessions over up to 12 weeks • 1. 5 Other non-pharmacological therapies • • • 1. 5. 1 Do not offer laser therapy 1. 5. 2 Do not offer interferential therapy 1. 5. 3 Do not offer therapeutic ultrasound 1. 5. 4 Do not offer transcutaneous electrical nerve simulation (TENS) 1. 5. 5 Do not offer lumbar supports 1. 5. 6 Do not offer traction • 1. 6 Invasive procedures • 1. 6. 1 Consider offering a course of acupuncture maximum of 10 sessions over up to 12 weeks • 1. 6. 2 Do not offer injections of therapeutic substances http: //guidance. nice. org. uk/CG 88
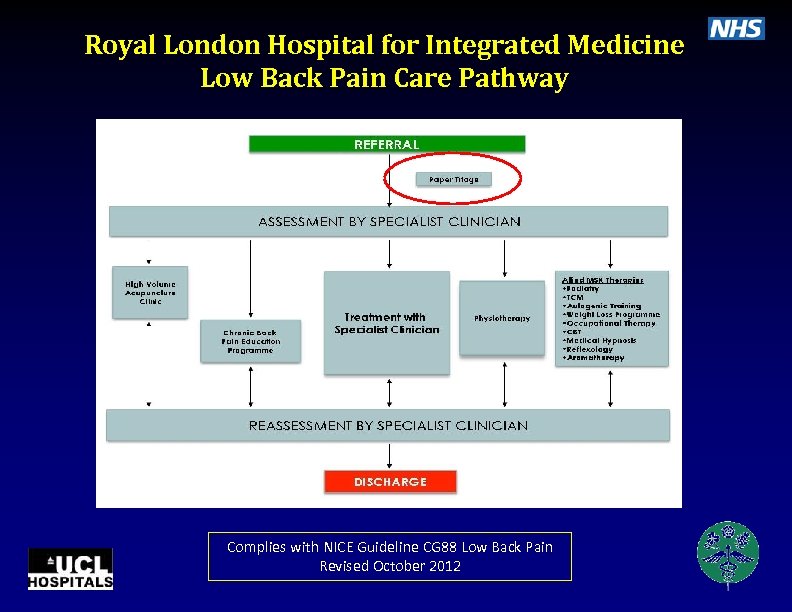 Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine Low Back Pain Care Pathway Complies with NICE Guideline CG 88 Low Back Pain Revised October 2012
Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine Low Back Pain Care Pathway Complies with NICE Guideline CG 88 Low Back Pain Revised October 2012
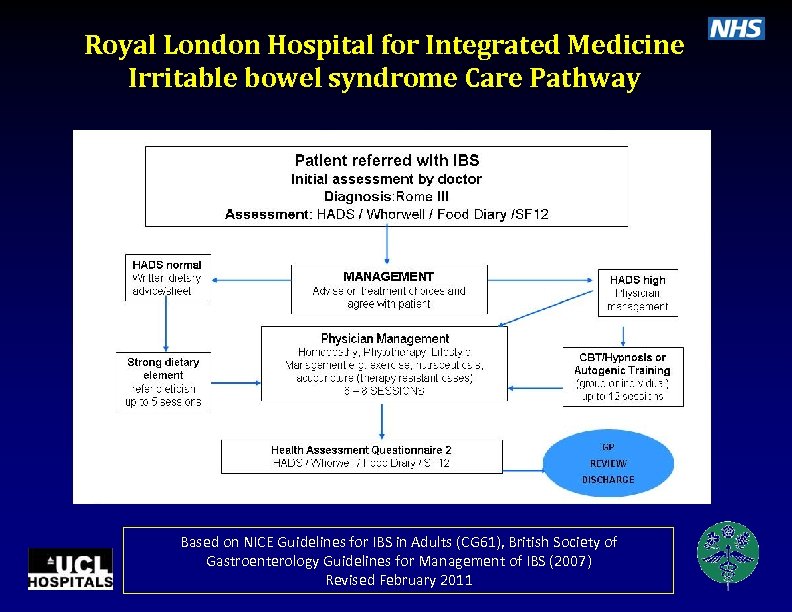 Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine Irritable bowel syndrome Care Pathway Based on NICE Guidelines for IBS in Adults (CG 61), British Society of Gastroenterology Guidelines for Management of IBS (2007) Revised February 2011
Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine Irritable bowel syndrome Care Pathway Based on NICE Guidelines for IBS in Adults (CG 61), British Society of Gastroenterology Guidelines for Management of IBS (2007) Revised February 2011
 Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine Complementary Cancer Care Pathway • category 2: Not requiring prior approval, not guideline based
Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine Complementary Cancer Care Pathway • category 2: Not requiring prior approval, not guideline based
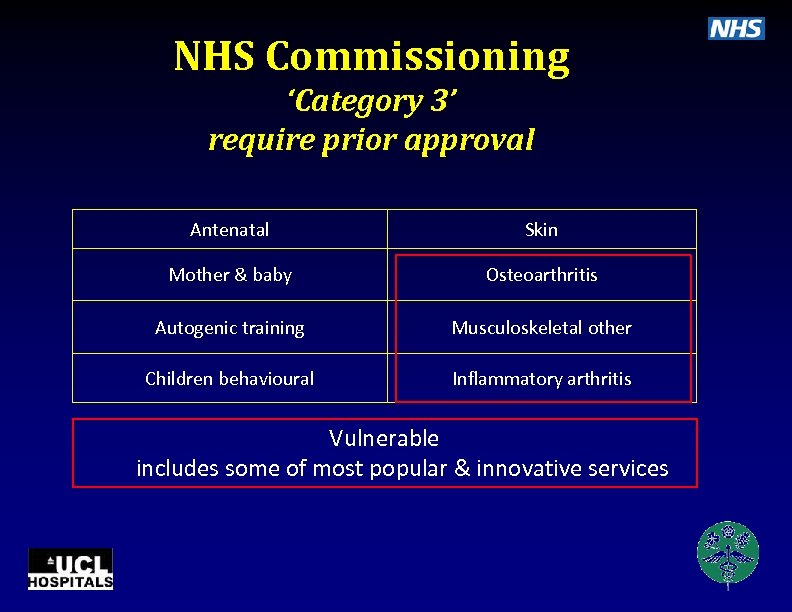 NHS Commissioning ‘Category 3’ require prior approval Antenatal Skin Mother & baby Osteoarthritis Autogenic training Musculoskeletal other Children behavioural Inflammatory arthritis Vulnerable includes some of most popular & innovative services
NHS Commissioning ‘Category 3’ require prior approval Antenatal Skin Mother & baby Osteoarthritis Autogenic training Musculoskeletal other Children behavioural Inflammatory arthritis Vulnerable includes some of most popular & innovative services
 ‘Musculoskeletal other’ approval criteria • Commissioners will only fund Integrated Medical treatment for Musculoskeletal and Rheumatology • pain and/or disability significantly restricting work, everyday living • AND • Inadequate response to at least 2 treatments including: • physiotherapy and exercise, weight loss, simple analgesic, low dose antidepressant, NSAID, corticosteroid DMARD or biological agent • Heavy use of health services • >4 primary and secondary care consultations in previous 6 months, >6 in previous 12 months • Medically unexplained physical syndrome after extensive medical investigations and causing significant distress
‘Musculoskeletal other’ approval criteria • Commissioners will only fund Integrated Medical treatment for Musculoskeletal and Rheumatology • pain and/or disability significantly restricting work, everyday living • AND • Inadequate response to at least 2 treatments including: • physiotherapy and exercise, weight loss, simple analgesic, low dose antidepressant, NSAID, corticosteroid DMARD or biological agent • Heavy use of health services • >4 primary and secondary care consultations in previous 6 months, >6 in previous 12 months • Medically unexplained physical syndrome after extensive medical investigations and causing significant distress
 Summary • Responsive to need • services offering range of therapies • Integrated in depth • Dimensions • Service models • Guidelines, evidence, pathways • Patient preference
Summary • Responsive to need • services offering range of therapies • Integrated in depth • Dimensions • Service models • Guidelines, evidence, pathways • Patient preference
 Keys to success 1) Patient-centredness 2) Quality & Safety 3) practitioners, medicinal products, processes Patient-centredness 4) quality assurance: audit, governance Patient-centredness 3) Innovation responsive to need, guidelines etc 4) Integration best of complementary and conventional The Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine peter. fisher@uclh. nhs. uk
Keys to success 1) Patient-centredness 2) Quality & Safety 3) practitioners, medicinal products, processes Patient-centredness 4) quality assurance: audit, governance Patient-centredness 3) Innovation responsive to need, guidelines etc 4) Integration best of complementary and conventional The Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine peter. fisher@uclh. nhs. uk
 International Congress for Complementary Medicine Research London 11 - 13 April 2013 www. iccmr 2013. com
International Congress for Complementary Medicine Research London 11 - 13 April 2013 www. iccmr 2013. com
 • Global sustainability of healthcare for chronic conditions • Global Pandemic of long term conditions: 35/58 million deaths annually worldwide • 80% of consultations in industrialised countries • Multimorbidity/polypharmacy/iatrogenic illness. • Ecofootprint of pharmaceutical industry • Underexploited resources of traditional/complementary/integrated medicine International Congress for Complementary Medicine Research London 11 - 13 April 2013 www. iccmr 2013. com
• Global sustainability of healthcare for chronic conditions • Global Pandemic of long term conditions: 35/58 million deaths annually worldwide • 80% of consultations in industrialised countries • Multimorbidity/polypharmacy/iatrogenic illness. • Ecofootprint of pharmaceutical industry • Underexploited resources of traditional/complementary/integrated medicine International Congress for Complementary Medicine Research London 11 - 13 April 2013 www. iccmr 2013. com
 Thank you for your attention peter. fisher@uclh. nhs. uk
Thank you for your attention peter. fisher@uclh. nhs. uk


