d8c13d355cd14bdb92798d079c281ac5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 The toilet is over there
The toilet is over there
 Stalin's Death. 1953. 73 years of age, had suffered a cerebral hemorrhage and died at 9: 50 p. m. on March 5, 1953.
Stalin's Death. 1953. 73 years of age, had suffered a cerebral hemorrhage and died at 9: 50 p. m. on March 5, 1953.
 • Stalin's body washed by a nurse and then carried via a white car to the Kremlin mortuary. There, an autopsy was performed. After the autopsy was completed, Stalin's body was given to the embalmers to prepare it for the three days it would lay-in-state.
• Stalin's body washed by a nurse and then carried via a white car to the Kremlin mortuary. There, an autopsy was performed. After the autopsy was completed, Stalin's body was given to the embalmers to prepare it for the three days it would lay-in-state.
 Thousands of people lined up in the snow to see it. The crowds were so dense and chaotic outside that some people were trampled underfoot, others rammed against traffic lights, and some others choked to death. It is estimated that 500 people lost their lives while trying to get a glimpse of Stalin's corpse.
Thousands of people lined up in the snow to see it. The crowds were so dense and chaotic outside that some people were trampled underfoot, others rammed against traffic lights, and some others choked to death. It is estimated that 500 people lost their lives while trying to get a glimpse of Stalin's corpse.
 The body was then ceremoniously taken to Lenin's tomb on the Red Square in Moscow.
The body was then ceremoniously taken to Lenin's tomb on the Red Square in Moscow.

 His usual fistbanging has resulted in his wrist watch falling off his arm. When he picked it up from the ground, he saw his shoes, which he had taken of his feet earlier because the stiff new leather was bothering him. He instantly decided that a shoe would make for much better banging than his wrist. And so, out of purely practical reasons, the shoe banging resulted. Khrushchev's shoe became yet another symbol of the Cold War. An era of rhetorics and tensions, topped with a dash of propaganda.
His usual fistbanging has resulted in his wrist watch falling off his arm. When he picked it up from the ground, he saw his shoes, which he had taken of his feet earlier because the stiff new leather was bothering him. He instantly decided that a shoe would make for much better banging than his wrist. And so, out of purely practical reasons, the shoe banging resulted. Khrushchev's shoe became yet another symbol of the Cold War. An era of rhetorics and tensions, topped with a dash of propaganda.
 Events • 1961 Communist Fidel Castro took over Cuba.
Events • 1961 Communist Fidel Castro took over Cuba.
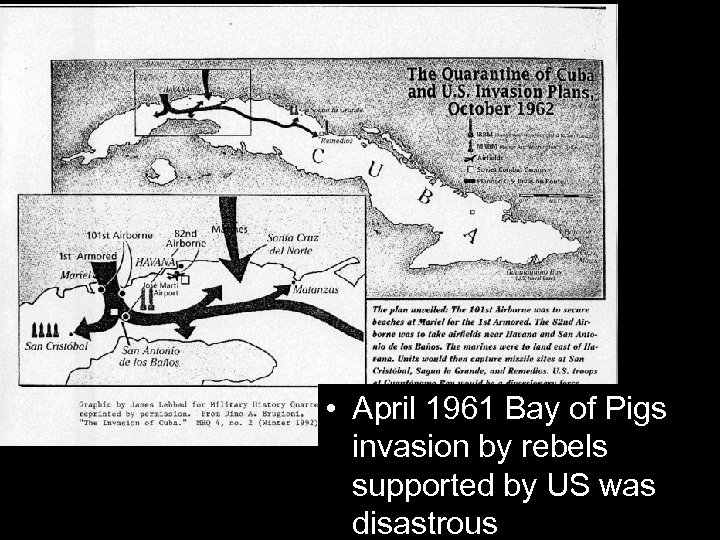 • April 1961 Bay of Pigs invasion by rebels supported by US was disastrous
• April 1961 Bay of Pigs invasion by rebels supported by US was disastrous
 IRBM – Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile MRBM – Medium Range Ballistic Missile • Soviet missiles on Cuba
IRBM – Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile MRBM – Medium Range Ballistic Missile • Soviet missiles on Cuba
 • Soviet Union’s leader Khrushchev refused to remove missiles
• Soviet Union’s leader Khrushchev refused to remove missiles
 • Kennedy ordered a naval blockade, trade blockade and threatened invasion.
• Kennedy ordered a naval blockade, trade blockade and threatened invasion.



 Cuban missile crisis Part 1 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=5 ZY m. CQu 5 oyk
Cuban missile crisis Part 1 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=5 ZY m. CQu 5 oyk
 • For 10 days the world was on the brink of nuclear war.
• For 10 days the world was on the brink of nuclear war.
 • 28 October Khrushchev removed the missiles and the crisis was over
• 28 October Khrushchev removed the missiles and the crisis was over
 How Close did the Soviets Come to Pulling the Trigger? It was the most dangerous moment of the Cold War. At about 5 p. m. on Oct. 27, 1962, a Soviet submarine armed with a nuclear warhead found itself trapped and being bombarded by a US warship patrolling off Cuba. One of the Soviet captains gave the order to prepare to fire. .
How Close did the Soviets Come to Pulling the Trigger? It was the most dangerous moment of the Cold War. At about 5 p. m. on Oct. 27, 1962, a Soviet submarine armed with a nuclear warhead found itself trapped and being bombarded by a US warship patrolling off Cuba. One of the Soviet captains gave the order to prepare to fire. .
 It was the most dangerous moment of the Cold War. At about 5 p. m. on Oct. 27, 1962, a Soviet submarine armed with a nuclear warhead found itself trapped and being bombarded by a US warship patrolling off Cuba One of the Soviet captains gave the order to prepare to fire. But a cooler-headed officer persuaded him to wait for instructions from Moscow before unleashing a nuclear attack.
It was the most dangerous moment of the Cold War. At about 5 p. m. on Oct. 27, 1962, a Soviet submarine armed with a nuclear warhead found itself trapped and being bombarded by a US warship patrolling off Cuba One of the Soviet captains gave the order to prepare to fire. But a cooler-headed officer persuaded him to wait for instructions from Moscow before unleashing a nuclear attack.
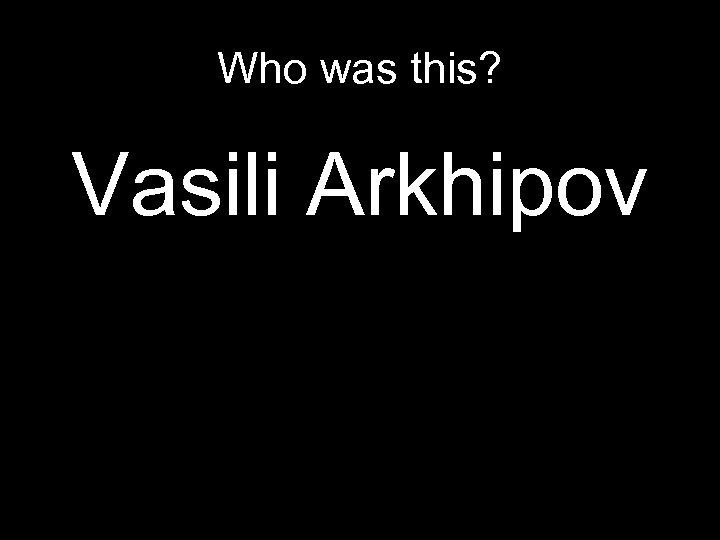 Who was this? Vasili Arkhipov
Who was this? Vasili Arkhipov
 CAUSES Remember A U 3 • 1. Arms Race – In 1960 s USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics) had less than half of US missiles – USSR worried about US missiles in Turkey because near Soviet Union cities – USA stationed missiles in Turkey because of their alliance – Khrushchev also felt that he should find allies and build missile sites near the USA
CAUSES Remember A U 3 • 1. Arms Race – In 1960 s USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics) had less than half of US missiles – USSR worried about US missiles in Turkey because near Soviet Union cities – USA stationed missiles in Turkey because of their alliance – Khrushchev also felt that he should find allies and build missile sites near the USA
 • 2. USSR Missiles in Cuba – 1960 USSR placed nuclear missiles on Cuba as protection and reduce USA advantage – Threat to US cities – less than 150 km away
• 2. USSR Missiles in Cuba – 1960 USSR placed nuclear missiles on Cuba as protection and reduce USA advantage – Threat to US cities – less than 150 km away

 • 3. US fear of Communist threat (Domino Theory) – Fidel Castro’s Cuba – only 90 miles off coast of America. / Close relationship with USSR (oil, machinery and money in return for sugar)/ Cuba nationalises American companies – accepted USSR help because feared US invasion – USA thought Castro was going to spread Communism to rest of South America – USA provided funding and training to exiled Cuban rebels who wanted to overthrow Castro government
• 3. US fear of Communist threat (Domino Theory) – Fidel Castro’s Cuba – only 90 miles off coast of America. / Close relationship with USSR (oil, machinery and money in return for sugar)/ Cuba nationalises American companies – accepted USSR help because feared US invasion – USA thought Castro was going to spread Communism to rest of South America – USA provided funding and training to exiled Cuban rebels who wanted to overthrow Castro government
 Backyard Fallout Shelter in the 1960 s
Backyard Fallout Shelter in the 1960 s
 IMPACT/RESULTS/CONSEQUENCES /SIGNIFICANCE/OUTCOME • Better US-Soviet relations – was the closest the world came to a nuclear war. An example of brinkmanship (the practice of doing something dangerous that almost leads countries to the brink of war, without actually starting one) – 1963 direct hotline linked for US and USSR leaders in case of emergency – Both sides supported disarmament and need to limit nuclear arms build-up – US missiles in Turkey and Italy removed
IMPACT/RESULTS/CONSEQUENCES /SIGNIFICANCE/OUTCOME • Better US-Soviet relations – was the closest the world came to a nuclear war. An example of brinkmanship (the practice of doing something dangerous that almost leads countries to the brink of war, without actually starting one) – 1963 direct hotline linked for US and USSR leaders in case of emergency – Both sides supported disarmament and need to limit nuclear arms build-up – US missiles in Turkey and Italy removed

 – 1963 USA, Soviet Union and Great Britain signed Nuclear Test Ban Treaty • only allowed nuclear tests to be carried out underground – Both realized importance of preventing other countries getting nuclear weapons • 1969 Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons Treaty signed • Could not give their nuclear technology to other countries – Led to more stable superpower relations • MAD (Mutually Assured Destruction) – both did not want to start a nuclear war • Tried to solve their problems without using nuclear weapons
– 1963 USA, Soviet Union and Great Britain signed Nuclear Test Ban Treaty • only allowed nuclear tests to be carried out underground – Both realized importance of preventing other countries getting nuclear weapons • 1969 Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons Treaty signed • Could not give their nuclear technology to other countries – Led to more stable superpower relations • MAD (Mutually Assured Destruction) – both did not want to start a nuclear war • Tried to solve their problems without using nuclear weapons

 • Cuba remained a Communist state – Fidel Castro remained in power – Soviet Union removed missiles – promised it would still help Cuba if attacked – Made USA promise it would not invade Cuba
• Cuba remained a Communist state – Fidel Castro remained in power – Soviet Union removed missiles – promised it would still help Cuba if attacked – Made USA promise it would not invade Cuba
 • Khrushchev’s fall from power – Removal of missiles from Cuba – Criticized by other members in Soviet government – Oct 1964 removed as leader and not allowed to leave his house until 1971 when he died. • Kennedy became the hero of the Western world
• Khrushchev’s fall from power – Removal of missiles from Cuba – Criticized by other members in Soviet government – Oct 1964 removed as leader and not allowed to leave his house until 1971 when he died. • Kennedy became the hero of the Western world
 • Tense Soviet-Chinese relations – After Soviet Union removed missiles from Cuba, China accuse it of being weak – ‘paper tiger’ – China claimed to be true leader of Communist movement – Divided international Communist movement
• Tense Soviet-Chinese relations – After Soviet Union removed missiles from Cuba, China accuse it of being weak – ‘paper tiger’ – China claimed to be true leader of Communist movement – Divided international Communist movement
 Cuban missile crisis Part 2 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=q. YVZp 1 ZFtm. U
Cuban missile crisis Part 2 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=q. YVZp 1 ZFtm. U


