e90f2e4d99ebd8ebf4219fd810cbaba7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 The System Unit: Processing and Memory Chapter 2
The System Unit: Processing and Memory Chapter 2
 Inside the “box”
Inside the “box”
 Inside the System Unit System unit: The main case of a computer Holds the main hardware for a computer Main Circuit board (Motherboard) Storage devices Power supply Cooling fans CPU Memory Expansion Cards Other components such as CD/DVD drives 3
Inside the System Unit System unit: The main case of a computer Holds the main hardware for a computer Main Circuit board (Motherboard) Storage devices Power supply Cooling fans CPU Memory Expansion Cards Other components such as CD/DVD drives 3
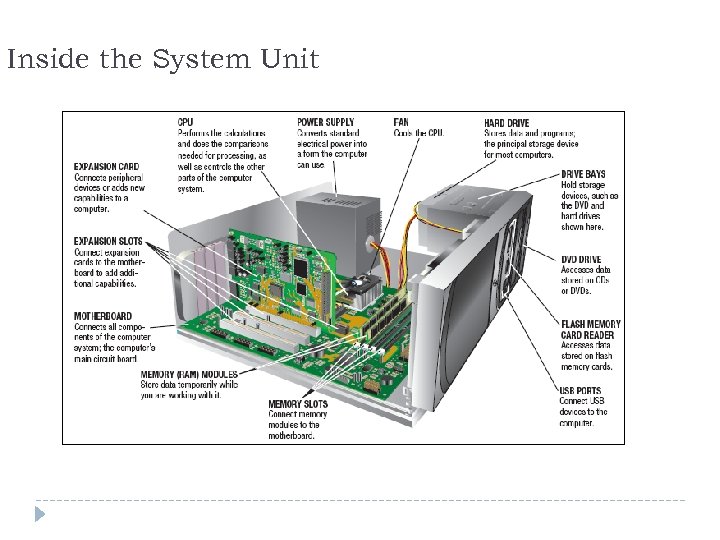 Inside the System Unit 4
Inside the System Unit 4
 The Motherboard Circuit board: A thin board containing computer chips and other electronic components Computer chip: A very small pieces of silicon or other semiconducting material onto which integrated circuits are embedded Motherboard or system board: The main circuit board inside the system unit All devices must connect to the motherboard External devices (monitors, keyboards, mice, printers) typically connect by plugging into a port exposed through the exterior of the system unit Wireless devices connect through a transceiver or wireless networking technology (like Bluetooth) 5
The Motherboard Circuit board: A thin board containing computer chips and other electronic components Computer chip: A very small pieces of silicon or other semiconducting material onto which integrated circuits are embedded Motherboard or system board: The main circuit board inside the system unit All devices must connect to the motherboard External devices (monitors, keyboards, mice, printers) typically connect by plugging into a port exposed through the exterior of the system unit Wireless devices connect through a transceiver or wireless networking technology (like Bluetooth) 5
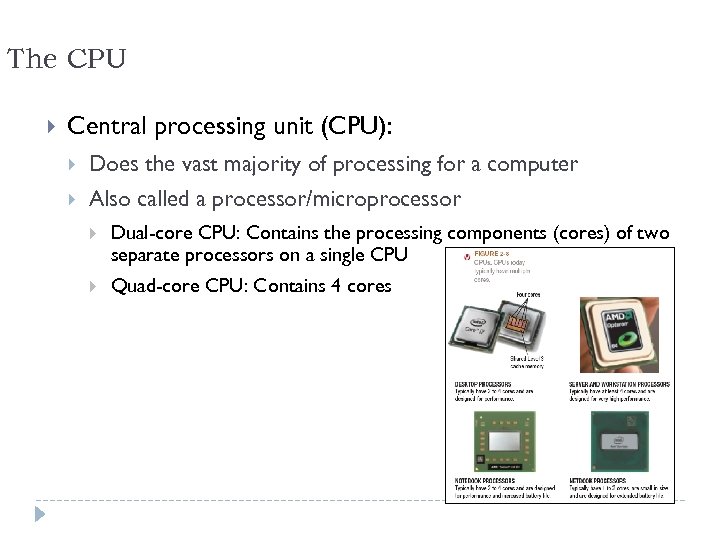 The CPU Central processing unit (CPU): Does the vast majority of processing for a computer Also called a processor/microprocessor Dual-core CPU: Contains the processing components (cores) of two separate processors on a single CPU Quad-core CPU: Contains 4 cores 6
The CPU Central processing unit (CPU): Does the vast majority of processing for a computer Also called a processor/microprocessor Dual-core CPU: Contains the processing components (cores) of two separate processors on a single CPU Quad-core CPU: Contains 4 cores 6
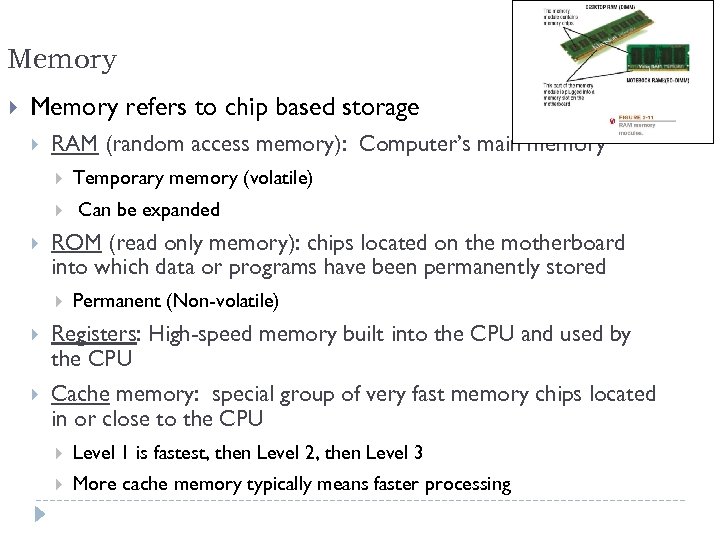 Memory refers to chip based storage RAM (random access memory): Computer’s main memory Temporary memory (volatile) Can be expanded ROM (read only memory): chips located on the motherboard into which data or programs have been permanently stored Permanent (Non-volatile) Registers: High-speed memory built into the CPU and used by the CPU Cache memory: special group of very fast memory chips located in or close to the CPU Level 1 is fastest, then Level 2, then Level 3 More cache memory typically means faster processing 7
Memory refers to chip based storage RAM (random access memory): Computer’s main memory Temporary memory (volatile) Can be expanded ROM (read only memory): chips located on the motherboard into which data or programs have been permanently stored Permanent (Non-volatile) Registers: High-speed memory built into the CPU and used by the CPU Cache memory: special group of very fast memory chips located in or close to the CPU Level 1 is fastest, then Level 2, then Level 3 More cache memory typically means faster processing 7
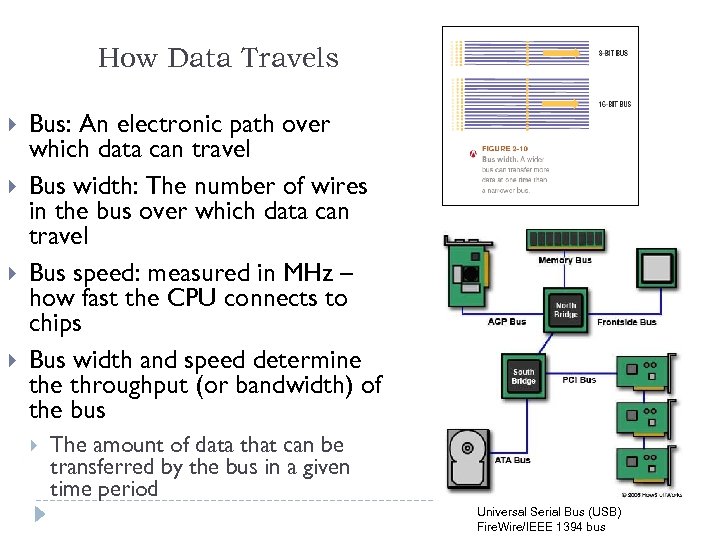 How Data Travels Bus: An electronic path over which data can travel Bus width: The number of wires in the bus over which data can travel Bus speed: measured in MHz – how fast the CPU connects to chips Bus width and speed determine throughput (or bandwidth) of the bus The amount of data that can be transferred by the bus in a given time period Universal Serial Bus (USB) Fire. Wire/IEEE 1394 bus 8
How Data Travels Bus: An electronic path over which data can travel Bus width: The number of wires in the bus over which data can travel Bus speed: measured in MHz – how fast the CPU connects to chips Bus width and speed determine throughput (or bandwidth) of the bus The amount of data that can be transferred by the bus in a given time period Universal Serial Bus (USB) Fire. Wire/IEEE 1394 bus 8
 Its all about “speed” and “timing” Computer has 2 clocks to keep things synchronized to perform at the best possible speed: CPU has its clock speed: Measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz) Higher CPU clock speed = more instructions processed per second System clock: Timing mechanism that synchronizes all of the computer’s operations on the motherboard Ticks like a metronome Number of ticks (cycles) per second = hertz (Hz) 1 MHz = 1 million ticks of the system clock per second Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition
Its all about “speed” and “timing” Computer has 2 clocks to keep things synchronized to perform at the best possible speed: CPU has its clock speed: Measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz) Higher CPU clock speed = more instructions processed per second System clock: Timing mechanism that synchronizes all of the computer’s operations on the motherboard Ticks like a metronome Number of ticks (cycles) per second = hertz (Hz) 1 MHz = 1 million ticks of the system clock per second Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition
 Fans, Heat Sinks, and Other Cooling Components Heat: A continuing problem for CPU and computer manufacturers Fans: Used on most personal computers Heat sinks: Small components typically made out of aluminum with fins that help to dissipate heat Water cooling systems: Cool the computer with liquid-filled tubes Notebook cooling stands 10
Fans, Heat Sinks, and Other Cooling Components Heat: A continuing problem for CPU and computer manufacturers Fans: Used on most personal computers Heat sinks: Small components typically made out of aluminum with fins that help to dissipate heat Water cooling systems: Cool the computer with liquid-filled tubes Notebook cooling stands 10
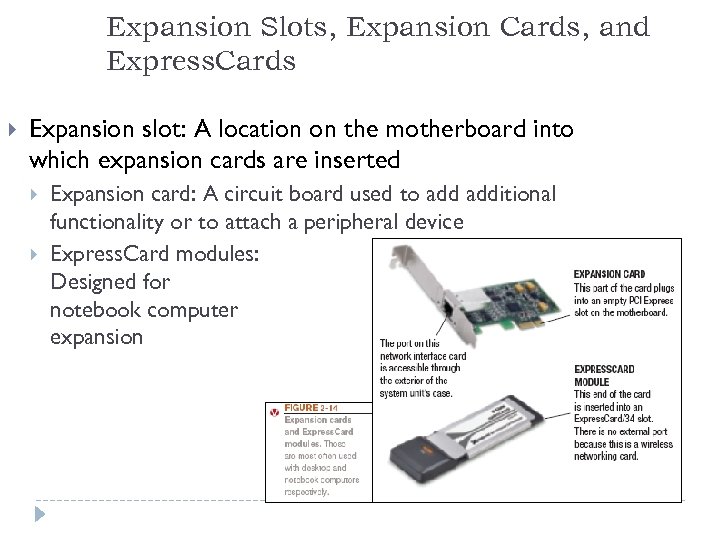 Expansion Slots, Expansion Cards, and Express. Cards Expansion slot: A location on the motherboard into which expansion cards are inserted Expansion card: A circuit board used to additional functionality or to attach a peripheral device Express. Card modules: Designed for notebook computer expansion 11
Expansion Slots, Expansion Cards, and Express. Cards Expansion slot: A location on the motherboard into which expansion cards are inserted Expansion card: A circuit board used to additional functionality or to attach a peripheral device Express. Card modules: Designed for notebook computer expansion 11
 Ports and Connectors Port: A connector on the exterior of a computer’s system unit to which a device may be attached – Monitor (VGA, DVI, HDMI) – SCSI – Network – Ir. DA – Modem – MIDI – USB – Flash memory card slots – Fire. Wire – Game – Keyboard – Audio – e. SATA 12
Ports and Connectors Port: A connector on the exterior of a computer’s system unit to which a device may be attached – Monitor (VGA, DVI, HDMI) – SCSI – Network – Ir. DA – Modem – MIDI – USB – Flash memory card slots – Fire. Wire – Game – Keyboard – Audio – e. SATA 12
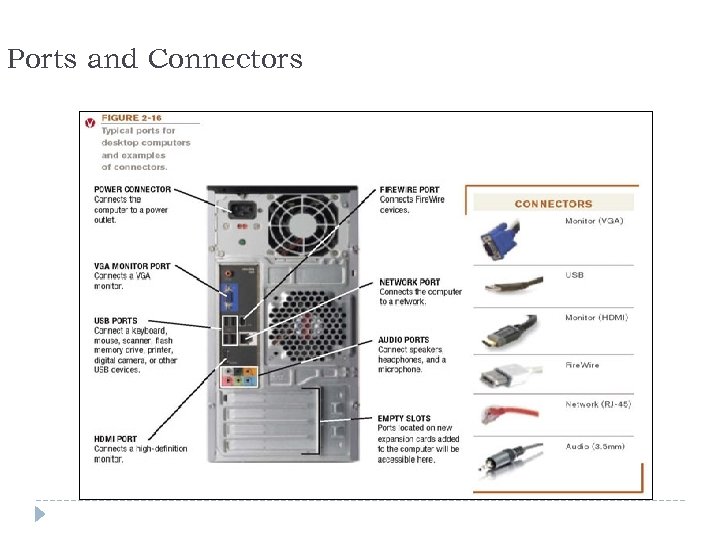 Ports and Connectors 13
Ports and Connectors 13
 Making Computers Faster and Better Now and in the Future Improving performance today Add more memory Perform system maintenance Uninstall programs properly Consider placing large files on external storage devices Delete temporary files Error check and defragment Scan for viruses and spyware Clean out dust once or twice a year Buy a larger or second hard drive Upgrade your Internet connection Upgrade your video graphics card Upgrade the CPU Replace the Motherboard (faster busses) 14
Making Computers Faster and Better Now and in the Future Improving performance today Add more memory Perform system maintenance Uninstall programs properly Consider placing large files on external storage devices Delete temporary files Error check and defragment Scan for viruses and spyware Clean out dust once or twice a year Buy a larger or second hard drive Upgrade your Internet connection Upgrade your video graphics card Upgrade the CPU Replace the Motherboard (faster busses) 14
 The “language” of the computer
The “language” of the computer
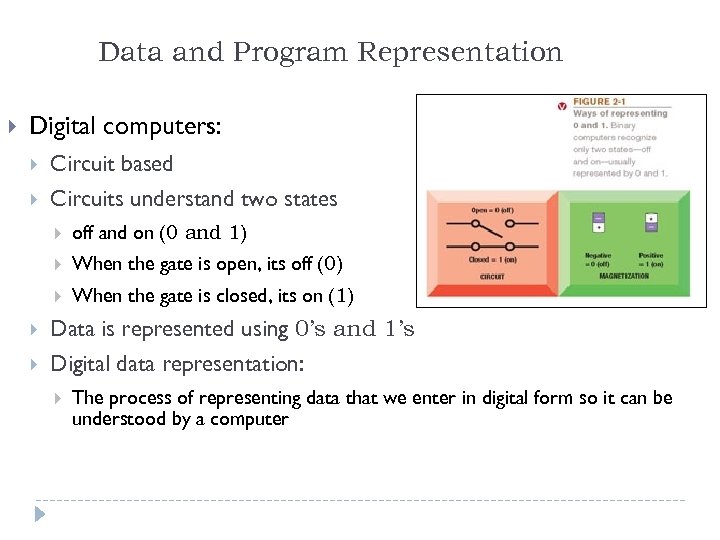 Data and Program Representation Digital computers: Circuit based Circuits understand two states off and on (0 and 1) When the gate is open, its off (0) When the gate is closed, its on (1) Data is represented using 0’s and 1’s Digital data representation: The process of representing data that we enter in digital form so it can be understood by a computer 16
Data and Program Representation Digital computers: Circuit based Circuits understand two states off and on (0 and 1) When the gate is open, its off (0) When the gate is closed, its on (1) Data is represented using 0’s and 1’s Digital data representation: The process of representing data that we enter in digital form so it can be understood by a computer 16
 The Binary Numbering System Numbering system: A way of representing numbers Decimal numbering system Uses 10 symbols (0 -9) Binary numbering system Uses only two symbols (1 and 0) to represent all possible numbers Used by computers 17
The Binary Numbering System Numbering system: A way of representing numbers Decimal numbering system Uses 10 symbols (0 -9) Binary numbering system Uses only two symbols (1 and 0) to represent all possible numbers Used by computers 17
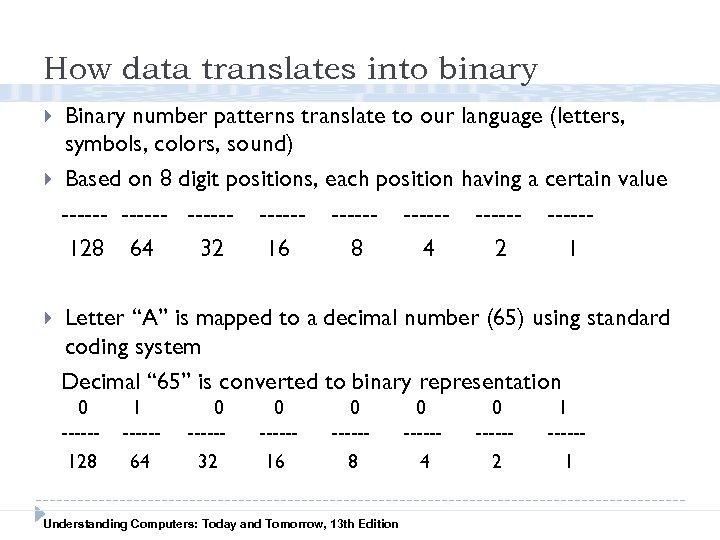 How data translates into binary Binary number patterns translate to our language (letters, symbols, colors, sound) Based on 8 digit positions, each position having a certain value ------ ------ -----128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Letter “A” is mapped to a decimal number (65) using standard coding system Decimal “ 65” is converted to binary representation 0 -----128 1 -----64 0 -----32 0 -----16 0 -----8 Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition 0 -----4 0 -----2 1 -----1
How data translates into binary Binary number patterns translate to our language (letters, symbols, colors, sound) Based on 8 digit positions, each position having a certain value ------ ------ -----128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Letter “A” is mapped to a decimal number (65) using standard coding system Decimal “ 65” is converted to binary representation 0 -----128 1 -----64 0 -----32 0 -----16 0 -----8 Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition 0 -----4 0 -----2 1 -----1
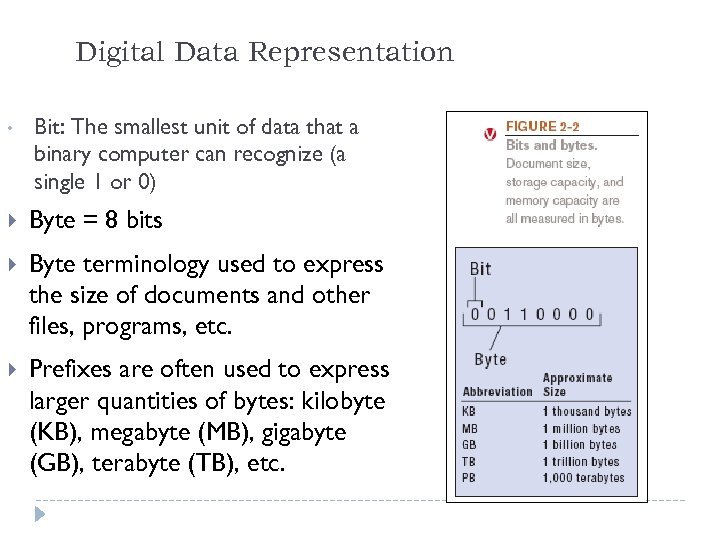 Digital Data Representation • Bit: The smallest unit of data that a binary computer can recognize (a single 1 or 0) Byte = 8 bits Byte terminology used to express the size of documents and other files, programs, etc. Prefixes are often used to express larger quantities of bytes: kilobyte (KB), megabyte (MB), gigabyte (GB), terabyte (TB), etc. 19
Digital Data Representation • Bit: The smallest unit of data that a binary computer can recognize (a single 1 or 0) Byte = 8 bits Byte terminology used to express the size of documents and other files, programs, etc. Prefixes are often used to express larger quantities of bytes: kilobyte (KB), megabyte (MB), gigabyte (GB), terabyte (TB), etc. 19
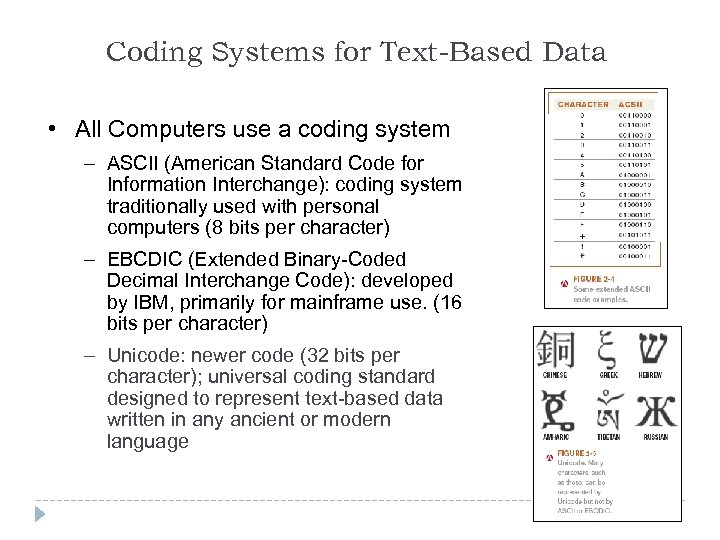 Coding Systems for Text-Based Data • All Computers use a coding system – ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange): coding system traditionally used with personal computers (8 bits per character) – EBCDIC (Extended Binary-Coded Decimal Interchange Code): developed by IBM, primarily for mainframe use. (16 bits per character) – Unicode: newer code (32 bits per character); universal coding standard designed to represent text-based data written in any ancient or modern language 20
Coding Systems for Text-Based Data • All Computers use a coding system – ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange): coding system traditionally used with personal computers (8 bits per character) – EBCDIC (Extended Binary-Coded Decimal Interchange Code): developed by IBM, primarily for mainframe use. (16 bits per character) – Unicode: newer code (32 bits per character); universal coding standard designed to represent text-based data written in any ancient or modern language 20
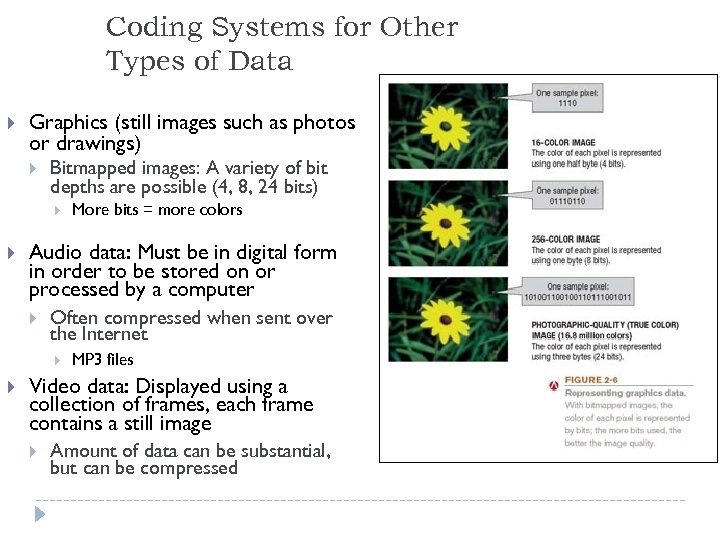 Coding Systems for Other Types of Data Graphics (still images such as photos or drawings) Bitmapped images: A variety of bit depths are possible (4, 8, 24 bits) Audio data: Must be in digital form in order to be stored on or processed by a computer Often compressed when sent over the Internet More bits = more colors MP 3 files Video data: Displayed using a collection of frames, each frame contains a still image Amount of data can be substantial, but can be compressed 21
Coding Systems for Other Types of Data Graphics (still images such as photos or drawings) Bitmapped images: A variety of bit depths are possible (4, 8, 24 bits) Audio data: Must be in digital form in order to be stored on or processed by a computer Often compressed when sent over the Internet More bits = more colors MP 3 files Video data: Displayed using a collection of frames, each frame contains a still image Amount of data can be substantial, but can be compressed 21
 Representing Programs: Machine Language Machine language: Binary-based language for representing computer programs the computer can execute directly Early programs were written in machine language. Today’s programs still need to be translated into machine language in order to be understood by the computer Most programs are written in other programming languages Language translators are used to translate the programs into machine language 22
Representing Programs: Machine Language Machine language: Binary-based language for representing computer programs the computer can execute directly Early programs were written in machine language. Today’s programs still need to be translated into machine language in order to be understood by the computer Most programs are written in other programming languages Language translators are used to translate the programs into machine language 22
 Storage Chapter 3
Storage Chapter 3
 Storage System Characteristics Consist of a storage device and a storage medium Medium is inserted into device to be used Storage devices are typically identified by letter 24
Storage System Characteristics Consist of a storage device and a storage medium Medium is inserted into device to be used Storage devices are typically identified by letter 24
 Storage System Characteristics Type: Location: Magnetic (conventional hard drives, tape) Optical (CD/DVD’s) Solid State: Electrons (flash memory media: USB, camera cards ) Local – internal or external Remote – somewhere else View: Logical file representation: Physical file representation: The user’s view of the way data is stored The actual physical way the data is stored on the storage media Storage Data can be stored randomly or sequentially 25
Storage System Characteristics Type: Location: Magnetic (conventional hard drives, tape) Optical (CD/DVD’s) Solid State: Electrons (flash memory media: USB, camera cards ) Local – internal or external Remote – somewhere else View: Logical file representation: Physical file representation: The user’s view of the way data is stored The actual physical way the data is stored on the storage media Storage Data can be stored randomly or sequentially 25
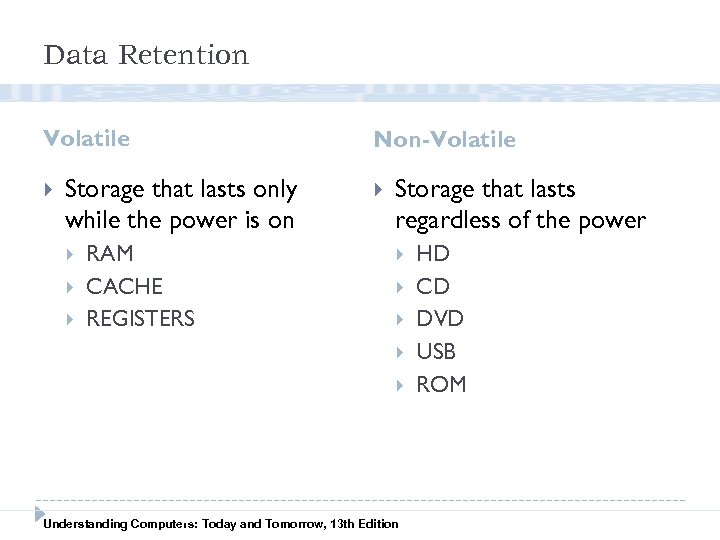 Data Retention Volatile Storage that lasts only while the power is on RAM CACHE REGISTERS Non-Volatile Storage that lasts regardless of the power 26 Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition HD CD DVD USB ROM
Data Retention Volatile Storage that lasts only while the power is on RAM CACHE REGISTERS Non-Volatile Storage that lasts regardless of the power 26 Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition HD CD DVD USB ROM
 MAGNETIC STORAGE Hard Drives Tape Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition
MAGNETIC STORAGE Hard Drives Tape Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition
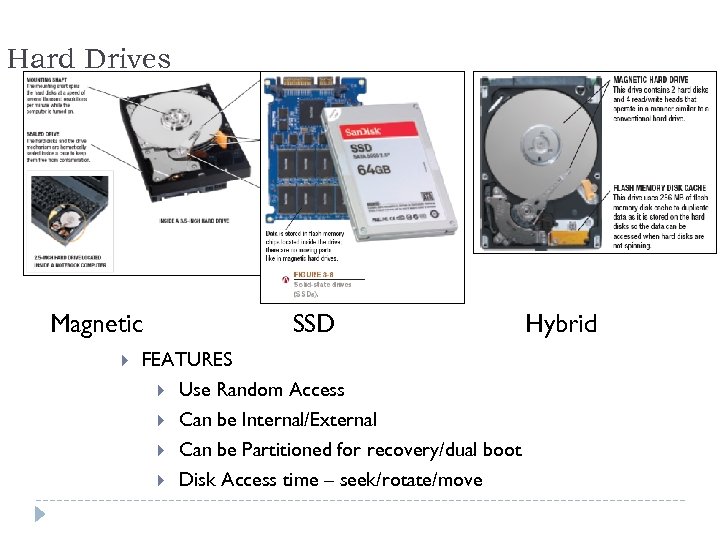 Hard Drives Magnetic SSD Hybrid FEATURES Use Random Access Can be Internal/External Can be Partitioned for recovery/dual boot Disk Access time – seek/rotate/move 28
Hard Drives Magnetic SSD Hybrid FEATURES Use Random Access Can be Internal/External Can be Partitioned for recovery/dual boot Disk Access time – seek/rotate/move 28
 Magnetic Tape Systems Magnetic tape: Plastic tape with a magnetizable surface that stores data as a series of magnetic spots Primarily used for backup and archival purposes Sequential access only Low cost per megabyte Most tapes today are in the form of cartridge tapes Read from and written to via a tape drive 29
Magnetic Tape Systems Magnetic tape: Plastic tape with a magnetizable surface that stores data as a series of magnetic spots Primarily used for backup and archival purposes Sequential access only Low cost per megabyte Most tapes today are in the form of cartridge tapes Read from and written to via a tape drive 29
 OPTICAL STORAGE CD’s DVD’s Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition
OPTICAL STORAGE CD’s DVD’s Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition
 Optical Discs Optical discs: store data optically (using laser beams) Types of discs: CD, DVD, or Blu-Ray Disc (BD) Burning: Process of Recording data onto disc CD discs: hold 650 MB DVD discs: hold 4. 7 GB (single-layer) – can be dual layer BD discs: hold 25 GB (single-layer) – can be dual layer CD discs: Use infrared lasers DVD discs: Use red lasers BD discs: Use blue-violet lasers Can be internal or external drives External drives typically USB 31
Optical Discs Optical discs: store data optically (using laser beams) Types of discs: CD, DVD, or Blu-Ray Disc (BD) Burning: Process of Recording data onto disc CD discs: hold 650 MB DVD discs: hold 4. 7 GB (single-layer) – can be dual layer BD discs: hold 25 GB (single-layer) – can be dual layer CD discs: Use infrared lasers DVD discs: Use red lasers BD discs: Use blue-violet lasers Can be internal or external drives External drives typically USB 31
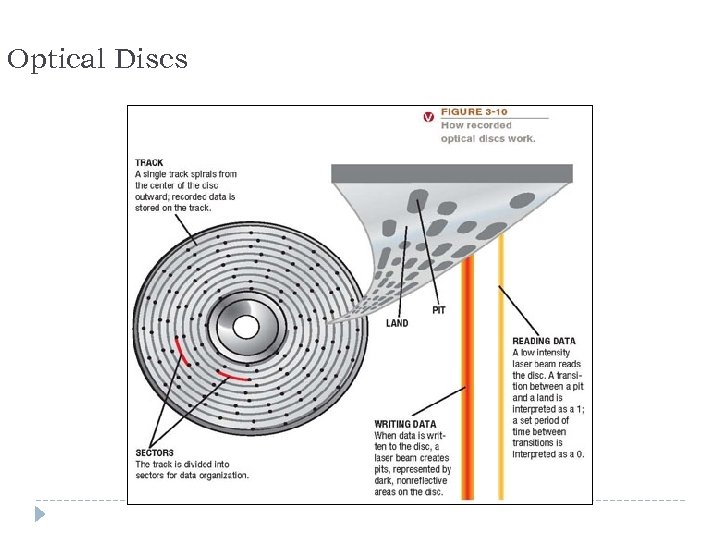 Optical Discs 32
Optical Discs 32
 Read-Only Discs (-ROM) Read-only disc: end in –ROM Can be read from, but not written to, by the user Surface is molded or stamped to represent the data CD-ROM (compact disc read-only memory) DVD-ROM (digital versatile disc read-only memory) BD-ROM (Blu-Ray disc read-only memory) Normally come pre-recorded Software programs Clip art and other graphics Music Movies Games (UMD, Wii, Xbox, etc. ) 33
Read-Only Discs (-ROM) Read-only disc: end in –ROM Can be read from, but not written to, by the user Surface is molded or stamped to represent the data CD-ROM (compact disc read-only memory) DVD-ROM (digital versatile disc read-only memory) BD-ROM (Blu-Ray disc read-only memory) Normally come pre-recorded Software programs Clip art and other graphics Music Movies Games (UMD, Wii, Xbox, etc. ) 33
 Recordable Discs (-R or +R) Recordable disc: End in –R or +R Can be written to ONCE, but cannot be erased and reused Reflectivity of surface is changed by a laser (burned in) CD-R discs DVD-R/DVD+R discs BD-R Used for back up, sending large files to others, creating custom music CDs, storing home movies, etc. 34
Recordable Discs (-R or +R) Recordable disc: End in –R or +R Can be written to ONCE, but cannot be erased and reused Reflectivity of surface is changed by a laser (burned in) CD-R discs DVD-R/DVD+R discs BD-R Used for back up, sending large files to others, creating custom music CDs, storing home movies, etc. 34
 Rewritable Discs (-RW or –RE) Rewritable disc: end in –RW or –RE Can be recorded on MANY TIMES - erased, and overwritten just like hard drives and USB’s CD-RW DVD-RW BD-RE Use phase-change technology where reflectivity of surface is changed by a laser and melted down for rewrite Heating and cooling process is used to change the reflectivity of the disc Can be changed back to erase the disc 35
Rewritable Discs (-RW or –RE) Rewritable disc: end in –RW or –RE Can be recorded on MANY TIMES - erased, and overwritten just like hard drives and USB’s CD-RW DVD-RW BD-RE Use phase-change technology where reflectivity of surface is changed by a laser and melted down for rewrite Heating and cooling process is used to change the reflectivity of the disc Can be changed back to erase the disc 35
 SOLID STATE Uses CHIP-BASED ELECTRON STORAGE USB’s, Memory cards (SD, x. D, CF, etc. ) Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition
SOLID STATE Uses CHIP-BASED ELECTRON STORAGE USB’s, Memory cards (SD, x. D, CF, etc. ) Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition
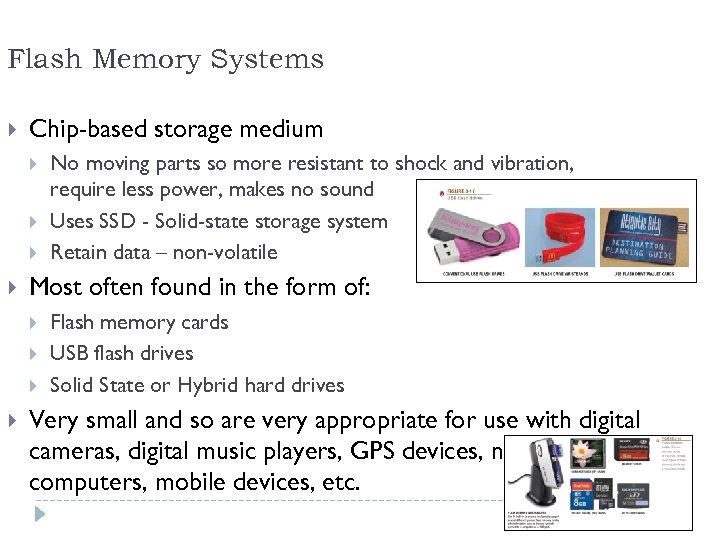 Flash Memory Systems Chip-based storage medium Most often found in the form of: No moving parts so more resistant to shock and vibration, require less power, makes no sound Uses SSD - Solid-state storage system Retain data – non-volatile Flash memory cards USB flash drives Solid State or Hybrid hard drives Very small and so are very appropriate for use with digital cameras, digital music players, GPS devices, notebook computers, mobile devices, etc. 37
Flash Memory Systems Chip-based storage medium Most often found in the form of: No moving parts so more resistant to shock and vibration, require less power, makes no sound Uses SSD - Solid-state storage system Retain data – non-volatile Flash memory cards USB flash drives Solid State or Hybrid hard drives Very small and so are very appropriate for use with digital cameras, digital music players, GPS devices, notebook computers, mobile devices, etc. 37
 Flash Memory Systems 38
Flash Memory Systems 38
 Smart Cards Smart card: Credit card-sized piece of plastic that contains some computer circuitry (processor, memory, and storage) Stores small amount of data (about 64 KB or less) Commonly used to store prepaid amounts of digital cash or personal information Smart card readers are built into or attached to a computer, keyboard, vending machine, or other device Some smart cards store biometric data Can be used in conjunction with encryption and other security technologies 39
Smart Cards Smart card: Credit card-sized piece of plastic that contains some computer circuitry (processor, memory, and storage) Stores small amount of data (about 64 KB or less) Commonly used to store prepaid amounts of digital cash or personal information Smart card readers are built into or attached to a computer, keyboard, vending machine, or other device Some smart cards store biometric data Can be used in conjunction with encryption and other security technologies 39
 Holographic Storage Holographic storage: Store data as holograms Emerging type of 3 D storage technology Uses two blue laser beams to store data in three dimensions Reference beam Signal beam Potential initial applications for holographic data storage systems include: High-speed digital libraries Image processing for medical, video, and military purposes Any other applications in which data needs to be stored or retrieved quickly in large quantities but rarely changed 40
Holographic Storage Holographic storage: Store data as holograms Emerging type of 3 D storage technology Uses two blue laser beams to store data in three dimensions Reference beam Signal beam Potential initial applications for holographic data storage systems include: High-speed digital libraries Image processing for medical, video, and military purposes Any other applications in which data needs to be stored or retrieved quickly in large quantities but rarely changed 40
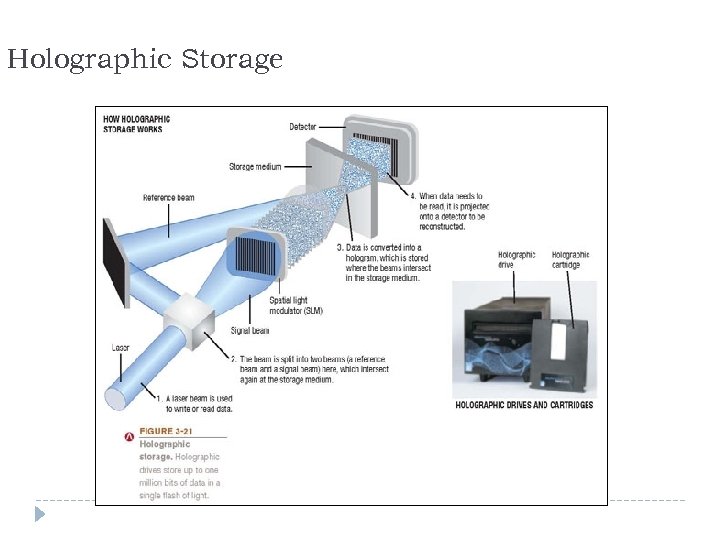 Holographic Storage 41
Holographic Storage 41
 RAID (redundant arrays of independent discs): Method of storing data on two or more hard drives that work together to do the job of a larger drive Usually involves recording redundant copies of stored data Helps to increase fault tolerance Different levels of RAID: RAID 0 = disk striping (spread files over two or more hard drives) RAID 1 = disk mirroring (duplicate copy) Other level use a combination or striping and mirroring 42
RAID (redundant arrays of independent discs): Method of storing data on two or more hard drives that work together to do the job of a larger drive Usually involves recording redundant copies of stored data Helps to increase fault tolerance Different levels of RAID: RAID 0 = disk striping (spread files over two or more hard drives) RAID 1 = disk mirroring (duplicate copy) Other level use a combination or striping and mirroring 42
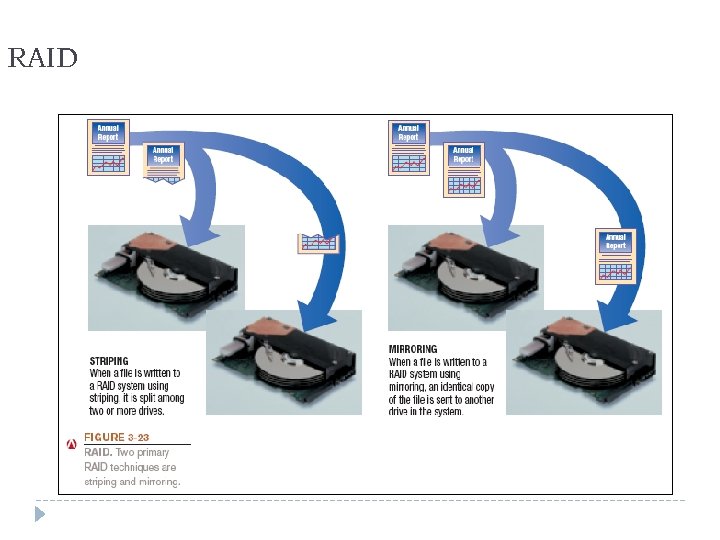 RAID 43
RAID 43
 REMOTE STORAGE Cloud, NAS, SAN (could be magnetic, tape, electrons) Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition
REMOTE STORAGE Cloud, NAS, SAN (could be magnetic, tape, electrons) Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition
 Other Types of Storage Systems Remote storage: Using a storage device not directly a part of the computer being used Cloud storage: Accessed via the Internet Network attached storage (NAS) Via Web sites (Flickr, Facebook, Google Docs, etc. ) Via online storage sites (Box. net, Sky. Drive, etc. ) Storage device is connected directly to a network Storage Area Network (SAN) A whole network of hard drives, connected to a central computer To use a storage area network, you must have access to the central computer 45
Other Types of Storage Systems Remote storage: Using a storage device not directly a part of the computer being used Cloud storage: Accessed via the Internet Network attached storage (NAS) Via Web sites (Flickr, Facebook, Google Docs, etc. ) Via online storage sites (Box. net, Sky. Drive, etc. ) Storage device is connected directly to a network Storage Area Network (SAN) A whole network of hard drives, connected to a central computer To use a storage area network, you must have access to the central computer 45
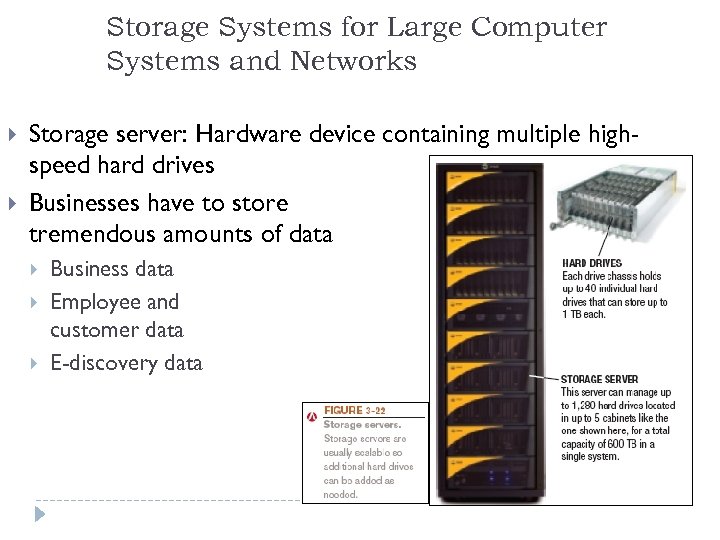 Storage Systems for Large Computer Systems and Networks Storage server: Hardware device containing multiple highspeed hard drives Businesses have to store tremendous amounts of data Business data Employee and customer data E-discovery data 46
Storage Systems for Large Computer Systems and Networks Storage server: Hardware device containing multiple highspeed hard drives Businesses have to store tremendous amounts of data Business data Employee and customer data E-discovery data 46
 Input and Output Chapter 4
Input and Output Chapter 4
 Learning Objectives Inputs –get data INTO the computer 1. Describe the characteristics and purpose of a computer input devices Outputs – get data OUT of the computer 2. Describe the characteristics and purpose of a computer output devices 48
Learning Objectives Inputs –get data INTO the computer 1. Describe the characteristics and purpose of a computer input devices Outputs – get data OUT of the computer 2. Describe the characteristics and purpose of a computer output devices 48
 Input: Keyboards Keyboard: An input device used to enter characters at the location marked by the insertion point or cursor Can be wired or wireless Built in or slide-out keyboard Pen or touch input (on-screen keyboard) Voice input Most computers today are designed to be used with a keyboard Typically contains: Standard alphanumeric keys Numeric keypad Function keys Delete and Backspace keys Control and Alternate keys Arrow directional keys and special keys 49
Input: Keyboards Keyboard: An input device used to enter characters at the location marked by the insertion point or cursor Can be wired or wireless Built in or slide-out keyboard Pen or touch input (on-screen keyboard) Voice input Most computers today are designed to be used with a keyboard Typically contains: Standard alphanumeric keys Numeric keypad Function keys Delete and Backspace keys Control and Alternate keys Arrow directional keys and special keys 49
 Input: Pointing Devices Pointing devices: Used to select and manipulate objects Used to input data Used to issue commands to the computer Common types of pointing devices: Mouse Pen/stylus/digital pen Optical or laser mice track with light 3 D mice Signature capture Touch screen 50
Input: Pointing Devices Pointing devices: Used to select and manipulate objects Used to input data Used to issue commands to the computer Common types of pointing devices: Mouse Pen/stylus/digital pen Optical or laser mice track with light 3 D mice Signature capture Touch screen 50
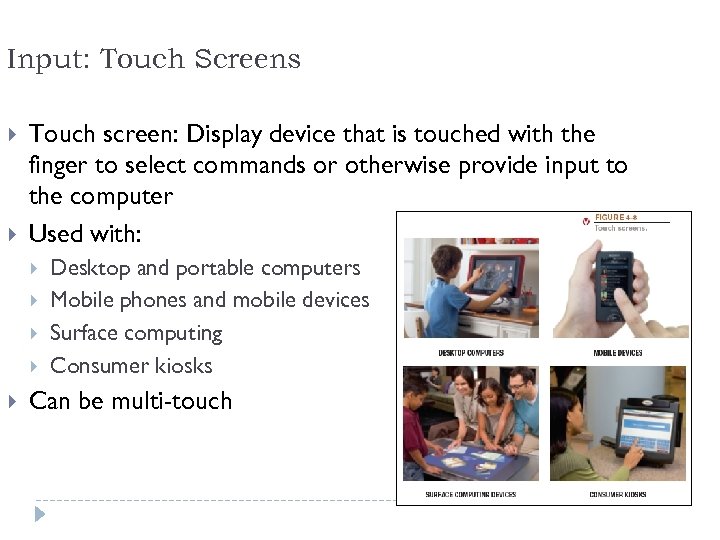 Input: Touch Screens Touch screen: Display device that is touched with the finger to select commands or otherwise provide input to the computer Used with: Desktop and portable computers Mobile phones and mobile devices Surface computing Consumer kiosks Can be multi-touch 51
Input: Touch Screens Touch screen: Display device that is touched with the finger to select commands or otherwise provide input to the computer Used with: Desktop and portable computers Mobile phones and mobile devices Surface computing Consumer kiosks Can be multi-touch 51
 Input: Other Pointing Devices Other pointing devices: Joysticks, gamepads, and other gaming devices Trackballs Buttons and wheels Touch pads 52
Input: Other Pointing Devices Other pointing devices: Joysticks, gamepads, and other gaming devices Trackballs Buttons and wheels Touch pads 52
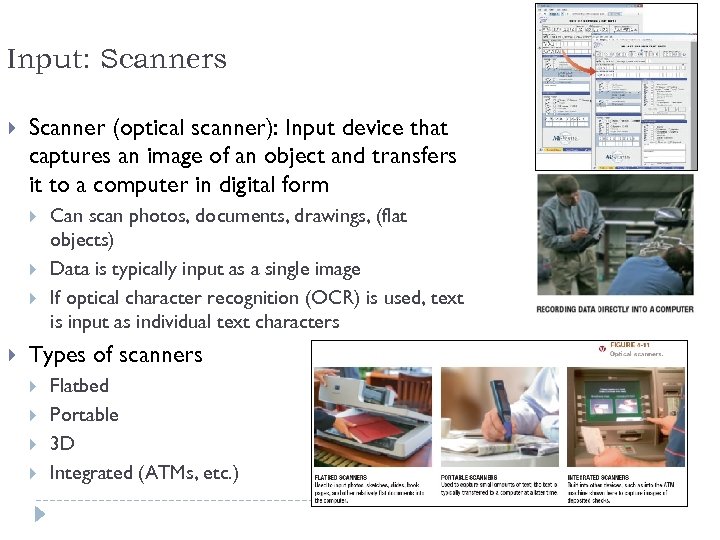 Input: Scanners Scanner (optical scanner): Input device that captures an image of an object and transfers it to a computer in digital form Can scan photos, documents, drawings, (flat objects) Data is typically input as a single image If optical character recognition (OCR) is used, text is input as individual text characters Types of scanners Flatbed Portable 3 D Integrated (ATMs, etc. ) 53
Input: Scanners Scanner (optical scanner): Input device that captures an image of an object and transfers it to a computer in digital form Can scan photos, documents, drawings, (flat objects) Data is typically input as a single image If optical character recognition (OCR) is used, text is input as individual text characters Types of scanners Flatbed Portable 3 D Integrated (ATMs, etc. ) 53
 Input: Barcode Readers Barcode: Data is displayed as a set of bars, and is read by a special machine, called a Barcode reader Common types Universal Product Code (UPC) ISBN Code 39 Intelligent mail code 2 D (QR) – hold more data 54
Input: Barcode Readers Barcode: Data is displayed as a set of bars, and is read by a special machine, called a Barcode reader Common types Universal Product Code (UPC) ISBN Code 39 Intelligent mail code 2 D (QR) – hold more data 54
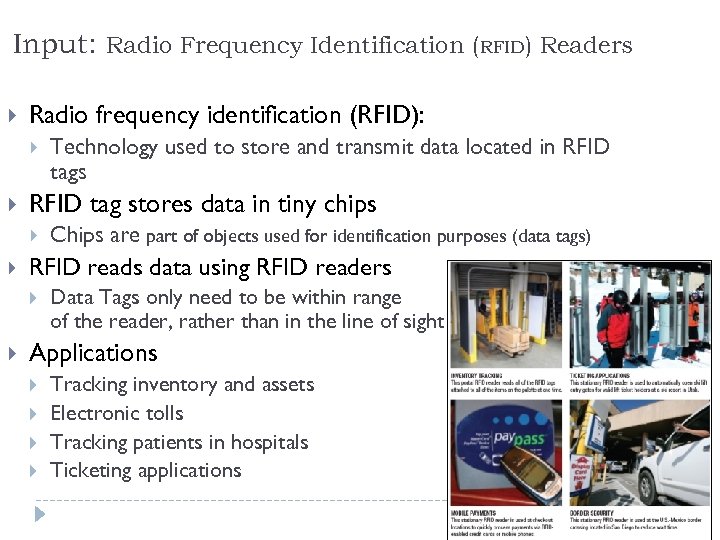 Input: Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Readers Radio frequency identification (RFID): RFID tag stores data in tiny chips Chips are part of objects used for identification purposes (data tags) RFID reads data using RFID readers Technology used to store and transmit data located in RFID tags Data Tags only need to be within range of the reader, rather than in the line of sight Applications Tracking inventory and assets Electronic tolls Tracking patients in hospitals Ticketing applications 55
Input: Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Readers Radio frequency identification (RFID): RFID tag stores data in tiny chips Chips are part of objects used for identification purposes (data tags) RFID reads data using RFID readers Technology used to store and transmit data located in RFID tags Data Tags only need to be within range of the reader, rather than in the line of sight Applications Tracking inventory and assets Electronic tolls Tracking patients in hospitals Ticketing applications 55
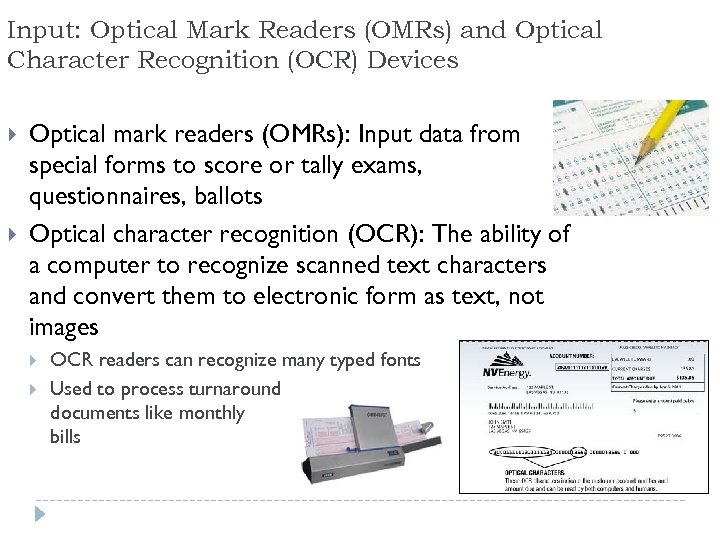 Input: Optical Mark Readers (OMRs) and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Devices Optical mark readers (OMRs): Input data from special forms to score or tally exams, questionnaires, ballots Optical character recognition (OCR): The ability of a computer to recognize scanned text characters and convert them to electronic form as text, not images OCR readers can recognize many typed fonts Used to process turnaround documents like monthly bills 56
Input: Optical Mark Readers (OMRs) and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Devices Optical mark readers (OMRs): Input data from special forms to score or tally exams, questionnaires, ballots Optical character recognition (OCR): The ability of a computer to recognize scanned text characters and convert them to electronic form as text, not images OCR readers can recognize many typed fonts Used to process turnaround documents like monthly bills 56
 Input: Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) Readers Magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) readers: Read MICR characters Used primarily for banking MICR readers read the special magnetic characters and sort/process checks Can be used for remote deposit 57
Input: Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) Readers Magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) readers: Read MICR characters Used primarily for banking MICR readers read the special magnetic characters and sort/process checks Can be used for remote deposit 57
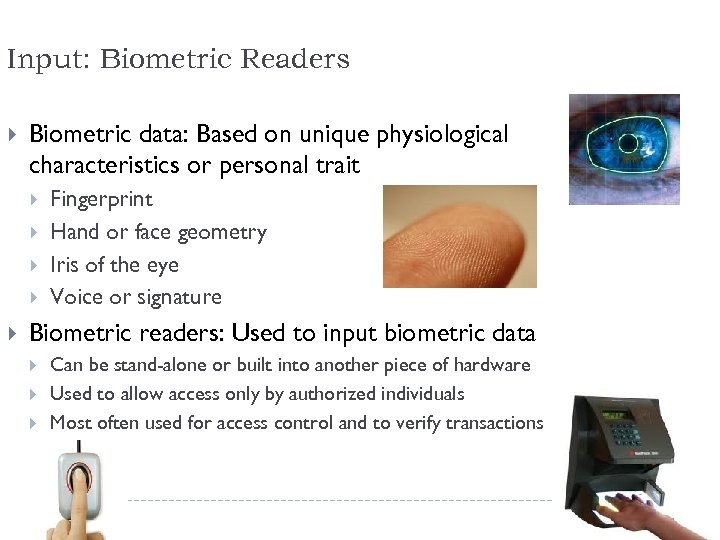 Input: Biometric Readers Biometric data: Based on unique physiological characteristics or personal trait Fingerprint Hand or face geometry Iris of the eye Voice or signature Biometric readers: Used to input biometric data Can be stand-alone or built into another piece of hardware Used to allow access only by authorized individuals Most often used for access control and to verify transactions 58
Input: Biometric Readers Biometric data: Based on unique physiological characteristics or personal trait Fingerprint Hand or face geometry Iris of the eye Voice or signature Biometric readers: Used to input biometric data Can be stand-alone or built into another piece of hardware Used to allow access only by authorized individuals Most often used for access control and to verify transactions 58
 Input: Digital Still Cameras Digital cameras: Record images on digital storage medium rather than film Can either be still cameras or video cameras Integrated into many portable computers and mobile phones. Digital still cameras Available in a wide variety of sizes and capabilities Primary appeal is images immediately available Camera quality is measured in megapixels Typically use flash memory for storage 59
Input: Digital Still Cameras Digital cameras: Record images on digital storage medium rather than film Can either be still cameras or video cameras Integrated into many portable computers and mobile phones. Digital still cameras Available in a wide variety of sizes and capabilities Primary appeal is images immediately available Camera quality is measured in megapixels Typically use flash memory for storage 59
 Input: Digital Video Cameras Digital video cameras Digital camcorders PC video cameras (PC cams, Web cam) Store images on digital media (flash memory, DVDs, hard drives, etc. ) Applications: Surveillance video cameras Video conferences and Webinars Face recognition systems 60
Input: Digital Video Cameras Digital video cameras Digital camcorders PC video cameras (PC cams, Web cam) Store images on digital media (flash memory, DVDs, hard drives, etc. ) Applications: Surveillance video cameras Video conferences and Webinars Face recognition systems 60
 Input: Audio input: The process of entering audio data into the computer Voice input: Inputting spoken words and converting them to digital form Via microphone or headset Recorded for narrations, podcasts, etc. To provide spoken instructions to computer (speech recognition systems) Music input systems are used to input music Microphones, keyboard controllers, etc. using MIDI 61
Input: Audio input: The process of entering audio data into the computer Voice input: Inputting spoken words and converting them to digital form Via microphone or headset Recorded for narrations, podcasts, etc. To provide spoken instructions to computer (speech recognition systems) Music input systems are used to input music Microphones, keyboard controllers, etc. using MIDI 61
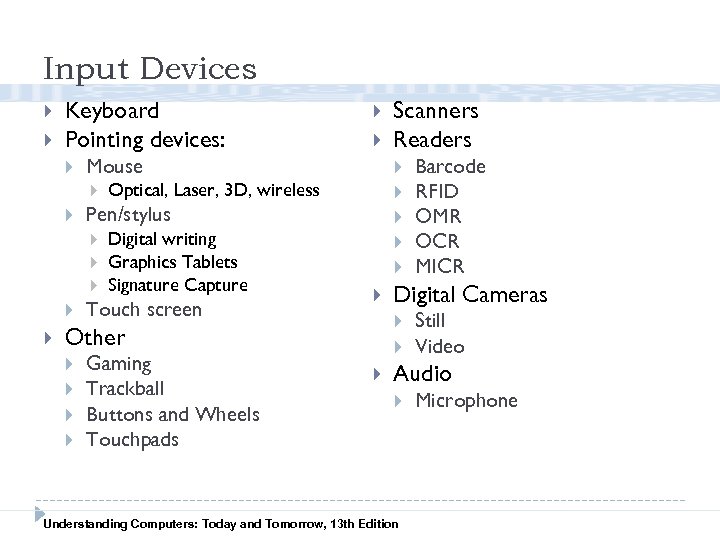 Input Devices Keyboard Pointing devices: Optical, Laser, 3 D, wireless Digital writing Graphics Tablets Signature Capture Touch screen Gaming Trackball Buttons and Wheels Touchpads Barcode RFID OMR OCR MICR Digital Cameras Other Scanners Readers Pen/stylus Mouse Still Video Audio Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition Microphone
Input Devices Keyboard Pointing devices: Optical, Laser, 3 D, wireless Digital writing Graphics Tablets Signature Capture Touch screen Gaming Trackball Buttons and Wheels Touchpads Barcode RFID OMR OCR MICR Digital Cameras Other Scanners Readers Pen/stylus Mouse Still Video Audio Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition Microphone
 Output: Display Devices Display device: Presents output visually Monitor: Display device for a desktop computer Laptops, Notebooks, Tablets, phones, gaming devices, e. Book readers: built in display screens Digital frames: photo frames, billboards 63
Output: Display Devices Display device: Presents output visually Monitor: Display device for a desktop computer Laptops, Notebooks, Tablets, phones, gaming devices, e. Book readers: built in display screens Digital frames: photo frames, billboards 63
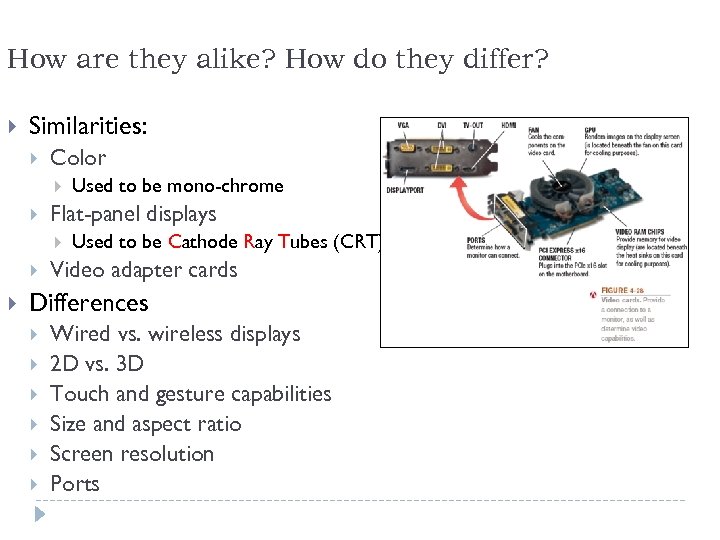 How are they alike? How do they differ? Similarities: Color Flat-panel displays Used to be mono-chrome Used to be Cathode Ray Tubes (CRT) Video adapter cards Differences Wired vs. wireless displays 2 D vs. 3 D Touch and gesture capabilities Size and aspect ratio Screen resolution Ports 64
How are they alike? How do they differ? Similarities: Color Flat-panel displays Used to be mono-chrome Used to be Cathode Ray Tubes (CRT) Video adapter cards Differences Wired vs. wireless displays 2 D vs. 3 D Touch and gesture capabilities Size and aspect ratio Screen resolution Ports 64
 Output: Flat-Panel Display Technologies LCD (Liquid crystal displays): Use charged liquid crystals between sheets of glass or plastic LED (Light emitting diode): Used in displays as well as a variety of consumer products UHD/SUHD: High-Def: 4 K displays Uses layers of organic material OLED (Organic Light emitting diode) – Emit visible light when current is applied FOLED (Flexible OLED) – bendable display device TOLED (Transparent OLED) – transparent display device PHOLED (Phosphorescent OLED) – uses phosphorescence Plasma: Use layers of gas to display images 65
Output: Flat-Panel Display Technologies LCD (Liquid crystal displays): Use charged liquid crystals between sheets of glass or plastic LED (Light emitting diode): Used in displays as well as a variety of consumer products UHD/SUHD: High-Def: 4 K displays Uses layers of organic material OLED (Organic Light emitting diode) – Emit visible light when current is applied FOLED (Flexible OLED) – bendable display device TOLED (Transparent OLED) – transparent display device PHOLED (Phosphorescent OLED) – uses phosphorescence Plasma: Use layers of gas to display images 65
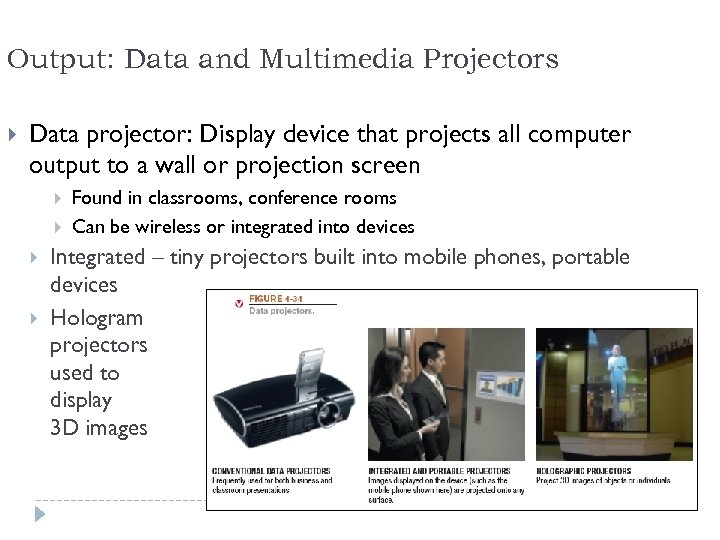 Output: Data and Multimedia Projectors Data projector: Display device that projects all computer output to a wall or projection screen Found in classrooms, conference rooms Can be wireless or integrated into devices Integrated – tiny projectors built into mobile phones, portable devices Hologram projectors used to display 3 D images 66
Output: Data and Multimedia Projectors Data projector: Display device that projects all computer output to a wall or projection screen Found in classrooms, conference rooms Can be wireless or integrated into devices Integrated – tiny projectors built into mobile phones, portable devices Hologram projectors used to display 3 D images 66
 Output: Printers: Produce hard copy Printer characteristics Printing technology used Impact vs. nonimpact Color vs. black and white Personal vs. network printers Print resolution -measured in dots per inch (dpi) Print speed (measured in pages per minute (PPM)) Connection (USB, Ethernet, Wi-Fi, etc. ) Multifunction capabilities 67
Output: Printers: Produce hard copy Printer characteristics Printing technology used Impact vs. nonimpact Color vs. black and white Personal vs. network printers Print resolution -measured in dots per inch (dpi) Print speed (measured in pages per minute (PPM)) Connection (USB, Ethernet, Wi-Fi, etc. ) Multifunction capabilities 67
 Output: Ink-Jet Printers Ink-jet printer: Sprays droplets of ink to produce images on paper Usually print in color Quality not quite as good as a laser printer Use ink-jet cartridges 68
Output: Ink-Jet Printers Ink-jet printer: Sprays droplets of ink to produce images on paper Usually print in color Quality not quite as good as a laser printer Use ink-jet cartridges 68
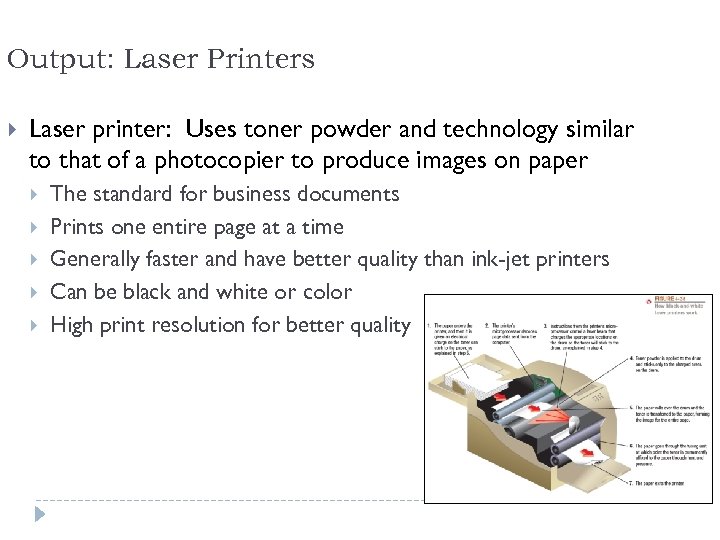 Output: Laser Printers Laser printer: Uses toner powder and technology similar to that of a photocopier to produce images on paper The standard for business documents Prints one entire page at a time Generally faster and have better quality than ink-jet printers Can be black and white or color High print resolution for better quality 69
Output: Laser Printers Laser printer: Uses toner powder and technology similar to that of a photocopier to produce images on paper The standard for business documents Prints one entire page at a time Generally faster and have better quality than ink-jet printers Can be black and white or color High print resolution for better quality 69
 Output: Special-Purpose Printers Photo printers Barcode, label, and postage printers Portable printers Plotters and wide-format ink -jet printers 3 -D printers 70
Output: Special-Purpose Printers Photo printers Barcode, label, and postage printers Portable printers Plotters and wide-format ink -jet printers 3 -D printers 70
 Output: Audio output: Output in the form of voice, music, and other audible sounds Speakers Headphones and headsets Earphones and earbuds 71
Output: Audio output: Output in the form of voice, music, and other audible sounds Speakers Headphones and headsets Earphones and earbuds 71
 Output Devices Display Devices Monitor Display Screens Projector Printers Sound Systems Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition Speakers Headphones/Buds
Output Devices Display Devices Monitor Display Screens Projector Printers Sound Systems Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow, 13 th Edition Speakers Headphones/Buds


