d1319e6ae7a1aa1dfc239566eb2cda6e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 The Stealth Geriatrician: How to learn what you need to know from your patients Tiffany Shubert, MPT Anthony Caprio, MD
The Stealth Geriatrician: How to learn what you need to know from your patients Tiffany Shubert, MPT Anthony Caprio, MD
 Course Objectives n n Identify four key risk factors for falling in older adults Perform a comprehensive geriatric functional assessment Evaluate the need for referral “Build a Team” – Determine disciplines and community resources to aid in patient health management
Course Objectives n n Identify four key risk factors for falling in older adults Perform a comprehensive geriatric functional assessment Evaluate the need for referral “Build a Team” – Determine disciplines and community resources to aid in patient health management
 Who is going to fall?
Who is going to fall?
 How will you identify who will fall?
How will you identify who will fall?
 A comprehensive geriatric assessment uncovers falls risk
A comprehensive geriatric assessment uncovers falls risk
 What you can find in your comprehensive exam If you take their shoes off!
What you can find in your comprehensive exam If you take their shoes off!
 Introducing Mrs. Jones
Introducing Mrs. Jones
 Chief Complaint n It depends on who you ask: n Patient: “No complaints, I feel fine” n Daughter: “Difficulty getting around the house, I am afraid she may fall” n MD: “Blood pressure should be better controlled”
Chief Complaint n It depends on who you ask: n Patient: “No complaints, I feel fine” n Daughter: “Difficulty getting around the house, I am afraid she may fall” n MD: “Blood pressure should be better controlled”
 History of Present Illness n What do you want to know? n Changes in medications n Trips to the opthamologist n Trips to the ER n Changes in mood/activity levels n Previous falls n Consult with family members
History of Present Illness n What do you want to know? n Changes in medications n Trips to the opthamologist n Trips to the ER n Changes in mood/activity levels n Previous falls n Consult with family members
 Past Medical History Hypertension Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Chronic Renal Insufficiency Anxiety/Depression “Dizziness” Osteoporosis
Past Medical History Hypertension Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Chronic Renal Insufficiency Anxiety/Depression “Dizziness” Osteoporosis
 Medication List n n n Metoprolol Hydrochlorothiazide Digoxin Warfarin Sertraline n n n Diazepam Zolpidem Meclizine Fosinopril Alendronate
Medication List n n n Metoprolol Hydrochlorothiazide Digoxin Warfarin Sertraline n n n Diazepam Zolpidem Meclizine Fosinopril Alendronate
 Medication Review n > 4 Drugs = Increased risk of falls n Red Flags – Classes that increase falls risk n Benzodiazepines (short and long-acting agents) n Antidepressants (tricyclics and SSRIs) n Antipsychotics n Anticonvulsants n Opioids n Antispasmodics n Over the counter medications
Medication Review n > 4 Drugs = Increased risk of falls n Red Flags – Classes that increase falls risk n Benzodiazepines (short and long-acting agents) n Antidepressants (tricyclics and SSRIs) n Antipsychotics n Anticonvulsants n Opioids n Antispasmodics n Over the counter medications
 Social History n What do you want to know? n Living Situation n Type of house? Stairs? ADLs, IADLs Social Supports n Economic Status n Smoke/Drink n Current Activity Level n Fear of Falling n
Social History n What do you want to know? n Living Situation n Type of house? Stairs? ADLs, IADLs Social Supports n Economic Status n Smoke/Drink n Current Activity Level n Fear of Falling n
 Review of Systems n Systems vs. Syndromes Organ-based review may give you limited information n Geriatric syndromes encompass multiple organ systems n n Falls Dizziness, Vision, hearing n Cardiovascular n Orthopedic problems, arthritis, neuropathy n Depression, cognitive impairment n
Review of Systems n Systems vs. Syndromes Organ-based review may give you limited information n Geriatric syndromes encompass multiple organ systems n n Falls Dizziness, Vision, hearing n Cardiovascular n Orthopedic problems, arthritis, neuropathy n Depression, cognitive impairment n
 Activities of Daily Living: Ask or Observe n ADLs n IADLS n Transferring n Transportation n Toileting n Use the phone n Bathing n Buy groceries n Dressing n Meal preparation n Continence n Housework n Feeding n Medication n Pay bills
Activities of Daily Living: Ask or Observe n ADLs n IADLS n Transferring n Transportation n Toileting n Use the phone n Bathing n Buy groceries n Dressing n Meal preparation n Continence n Housework n Feeding n Medication n Pay bills
 Physical Exam Findings n n General Impression Vital Signs n n n HEENT n n n Bilateral cataracts, difficulty reading magazine and wall poster CV n n BP sitting 140/90, HR 88 BP standing 110/80, HR 100 Grade II/VI systolic murmur (right upper sternal border) MS Neuro
Physical Exam Findings n n General Impression Vital Signs n n n HEENT n n n Bilateral cataracts, difficulty reading magazine and wall poster CV n n BP sitting 140/90, HR 88 BP standing 110/80, HR 100 Grade II/VI systolic murmur (right upper sternal border) MS Neuro
 Pain n Pain assessment n Pain management
Pain n Pain assessment n Pain management
 Functional Assessment: Timed Up and Go
Functional Assessment: Timed Up and Go
 Functional Assessment: Walking Speed
Functional Assessment: Walking Speed
 Gait Speed: Mrs. Jones
Gait Speed: Mrs. Jones
 Functional Assessment: Timed Chair Rise
Functional Assessment: Timed Chair Rise
 Functional Assessment: Chair Rise Mrs. Jones
Functional Assessment: Chair Rise Mrs. Jones
 Functional Assessment: Balance
Functional Assessment: Balance
 Functional Assessment: Observation
Functional Assessment: Observation
 Quick Functional Scan
Quick Functional Scan
 Functional Assessment n What Do You Learn? n How Do You Assess? n Referral
Functional Assessment n What Do You Learn? n How Do You Assess? n Referral
 Cognitive Assessment n Mini Mental State Exam n Clock Draw Test
Cognitive Assessment n Mini Mental State Exam n Clock Draw Test
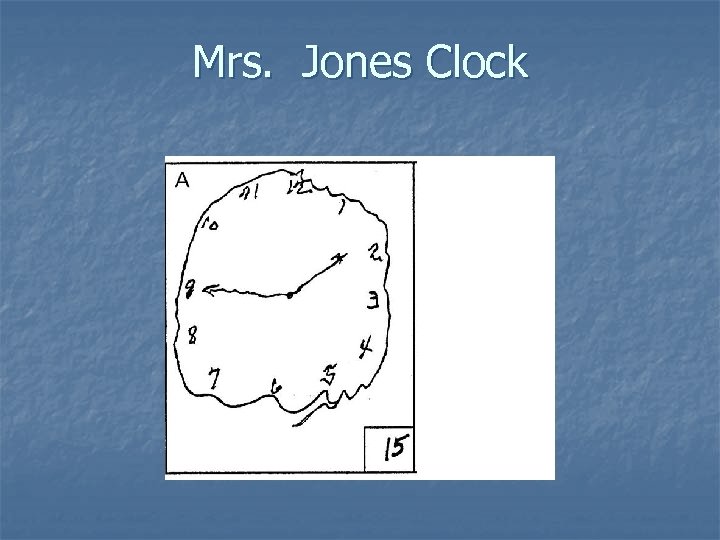 Mrs. Jones Clock
Mrs. Jones Clock
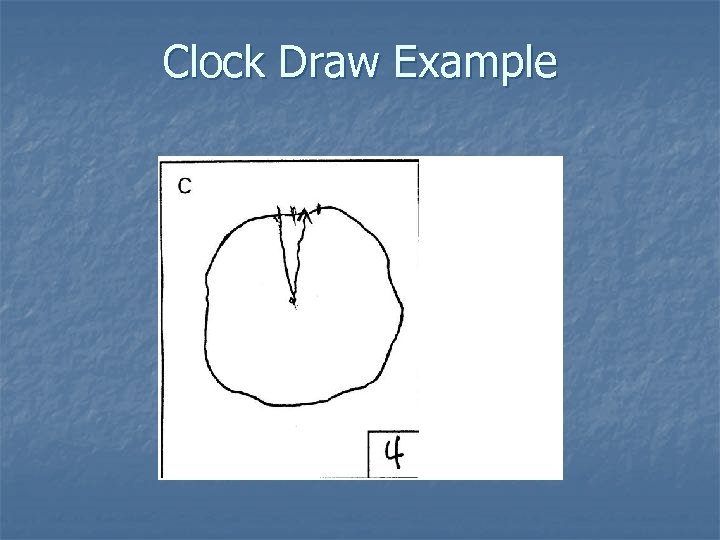 Clock Draw Example
Clock Draw Example
 Home Safety Evaluation n Use an environmental assessment sheet n Occupational therapy n Financial difficulties may be culprit
Home Safety Evaluation n Use an environmental assessment sheet n Occupational therapy n Financial difficulties may be culprit
 Labs n Volume depletion n Drug effects and levels n n n B 12, TSH Occult Infections n n PT/INR Digoxin Neuropathy n n CBC (anemia) Chemistries (BUN, Cr, Na) UA, CBC Vitamin D level
Labs n Volume depletion n Drug effects and levels n n n B 12, TSH Occult Infections n n PT/INR Digoxin Neuropathy n n CBC (anemia) Chemistries (BUN, Cr, Na) UA, CBC Vitamin D level
 Assessment: Mrs. Jones n What are the problems? n History of falls n 3 of the 4 risk factors for falls n Leg muscle weakness, poor walking, polypharmacy n Orthostatic Hypotension n Osteoporosis
Assessment: Mrs. Jones n What are the problems? n History of falls n 3 of the 4 risk factors for falls n Leg muscle weakness, poor walking, polypharmacy n Orthostatic Hypotension n Osteoporosis
 Plan: Mrs. Jones n What will you do about it? Fix orthostasis n Address osteoporosis n Modify medications n n Who will you refer to? Occupational Therapy for a home safety eval n Physical Therapy for leg strengthening, gait training, and assessment for assistive device n Consult with pharmacy about current medication list and insurance coverage n
Plan: Mrs. Jones n What will you do about it? Fix orthostasis n Address osteoporosis n Modify medications n n Who will you refer to? Occupational Therapy for a home safety eval n Physical Therapy for leg strengthening, gait training, and assessment for assistive device n Consult with pharmacy about current medication list and insurance coverage n
 Synthesis n n Evaluating major risk factors for falls is fundamental to a geriatric assessment A functional assessment will identify individuals at risk for falls A functional assessment can (and should) be done with your older patients Refer to other disciplines to best manage complex older adults
Synthesis n n Evaluating major risk factors for falls is fundamental to a geriatric assessment A functional assessment will identify individuals at risk for falls A functional assessment can (and should) be done with your older patients Refer to other disciplines to best manage complex older adults
 Practice n Today – work with Carol Woods Residents n n Physical, Cognitive, and Medication Assessment On the wards Perform at least one mini-Mental and clock draw n Shadow a physical therapist and perform 1 -2 functional assessments n Identify which of your patients are at risk for falls n
Practice n Today – work with Carol Woods Residents n n Physical, Cognitive, and Medication Assessment On the wards Perform at least one mini-Mental and clock draw n Shadow a physical therapist and perform 1 -2 functional assessments n Identify which of your patients are at risk for falls n


