56ec538458f4565b32590ecd6885e422.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 THE STATE OF MATERNAL, NEONATAL AND CHILD HEALTH IN MALAWI AND AN ANALYSIS OF THE NATIONAL RESPONSE: A REVIEW OF CRITICAL ISSUES AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR MEETING GLOBAL TARGETS GROUP 3 Tutor: Marcio Estrada Paneque Emmanuel Calderón Espinosa (Mexico) Rocío Fernández Méndez (Spain) Alena Kulyapina (Russian Federation) Thidar Pyone (Myanmar) Rodrigo Sarmiento Suárez (Colombia) Liaquat Ali Shaikh (Pakistan) Mariela Silveira (Australia) Henock Taddese (Ethiopia) www. africatravelpictures. com
THE STATE OF MATERNAL, NEONATAL AND CHILD HEALTH IN MALAWI AND AN ANALYSIS OF THE NATIONAL RESPONSE: A REVIEW OF CRITICAL ISSUES AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR MEETING GLOBAL TARGETS GROUP 3 Tutor: Marcio Estrada Paneque Emmanuel Calderón Espinosa (Mexico) Rocío Fernández Méndez (Spain) Alena Kulyapina (Russian Federation) Thidar Pyone (Myanmar) Rodrigo Sarmiento Suárez (Colombia) Liaquat Ali Shaikh (Pakistan) Mariela Silveira (Australia) Henock Taddese (Ethiopia) www. africatravelpictures. com
 MNCH DEFINITION Maternal and child health (MCH) refers to the health of mothers, infants, children, and adolescents. It also refers to a profession within public health committed to promoting the health status and future challenges of this vulnerable population (Breslow, 2002) Using the concept Maternal Neonatal and Child Health, MNCH, emphasizes the specific consideration of the new-born.
MNCH DEFINITION Maternal and child health (MCH) refers to the health of mothers, infants, children, and adolescents. It also refers to a profession within public health committed to promoting the health status and future challenges of this vulnerable population (Breslow, 2002) Using the concept Maternal Neonatal and Child Health, MNCH, emphasizes the specific consideration of the new-born.
 “We know how to save the lives of mothers and children and yet, every year about nine million children die and half a million women die due to pregnancy-related causes. . . ” (World Health Organization, 2009) GLOBAL INFANT MORTALITY 2006: Under-five mortality rate of the developing world estimated at 80 per 1, 000 live births (plus underreported cases)* GLOBAL MATERNAL MORTALITY Around 500, 000 women die annually during childbirth or due to complications from pregnancy (99% in developing regions)* • MDG 2008 Report • Images: http: //www. worldmapper. org
“We know how to save the lives of mothers and children and yet, every year about nine million children die and half a million women die due to pregnancy-related causes. . . ” (World Health Organization, 2009) GLOBAL INFANT MORTALITY 2006: Under-five mortality rate of the developing world estimated at 80 per 1, 000 live births (plus underreported cases)* GLOBAL MATERNAL MORTALITY Around 500, 000 women die annually during childbirth or due to complications from pregnancy (99% in developing regions)* • MDG 2008 Report • Images: http: //www. worldmapper. org
 SOME KEY MILESTONES IN MNCH AT THE GLOBAL LEVEL 1987 1948 1997 1999 2000 • THE UNIVERSAL DECLARATION OF HUMAN RIGHTS • INTERNATIONAL SAFE MOTHERHOOD CONFERENCE (Nairobi) • SAFE MOTHERHOOD INITIATIVE’S 10 TH ANNIVERSARY • De-emphasis training TBA • Maternal death as multisectoral problem • Comprehensive advocacy campaign increased visibility of &support for maternal health. • Making Pregnancy Safer project • MILLENIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS: 4 TH & 5 TH* 2003 • SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH as integral comp. of health rights 2005 • PARTNERSHIP FOR MATERNAL, NEWBORN AND CHILD HEALTH (PMNCH)*
SOME KEY MILESTONES IN MNCH AT THE GLOBAL LEVEL 1987 1948 1997 1999 2000 • THE UNIVERSAL DECLARATION OF HUMAN RIGHTS • INTERNATIONAL SAFE MOTHERHOOD CONFERENCE (Nairobi) • SAFE MOTHERHOOD INITIATIVE’S 10 TH ANNIVERSARY • De-emphasis training TBA • Maternal death as multisectoral problem • Comprehensive advocacy campaign increased visibility of &support for maternal health. • Making Pregnancy Safer project • MILLENIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS: 4 TH & 5 TH* 2003 • SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH as integral comp. of health rights 2005 • PARTNERSHIP FOR MATERNAL, NEWBORN AND CHILD HEALTH (PMNCH)*
 Consideration of MATERNAL, NEONATAL AND CHILD HEALTH (MNCH) amongst the key target areas in the Millennium Development Goals, MDGs of 2000 Goal-5: Improve Maternal Health Target: Reduce by three quarters, between 1990 and 2015, the maternal mortality ratio Goal-4: Reduce child mortality Target: Reduce by two thirds, between 1990 and 2015, the under-five mortality rate MDGs and images at: http: //www. undp. org/mdg/
Consideration of MATERNAL, NEONATAL AND CHILD HEALTH (MNCH) amongst the key target areas in the Millennium Development Goals, MDGs of 2000 Goal-5: Improve Maternal Health Target: Reduce by three quarters, between 1990 and 2015, the maternal mortality ratio Goal-4: Reduce child mortality Target: Reduce by two thirds, between 1990 and 2015, the under-five mortality rate MDGs and images at: http: //www. undp. org/mdg/
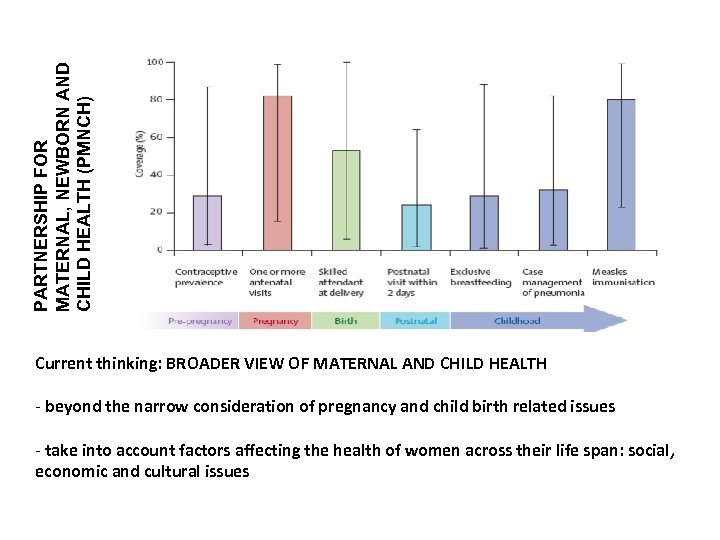 PARTNERSHIP FOR MATERNAL, NEWBORN AND CHILD HEALTH (PMNCH) Current thinking: BROADER VIEW OF MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH - beyond the narrow consideration of pregnancy and child birth related issues - take into account factors affecting the health of women across their life span: social, economic and cultural issues
PARTNERSHIP FOR MATERNAL, NEWBORN AND CHILD HEALTH (PMNCH) Current thinking: BROADER VIEW OF MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH - beyond the narrow consideration of pregnancy and child birth related issues - take into account factors affecting the health of women across their life span: social, economic and cultural issues
 Country situation, Malawi
Country situation, Malawi
 • Land-locked country, highest population density (105/km 2) in the southern part of Africa. • 12. 9 million people, 83% rural areas • Agriculture, the major source of livelihood • One of the poorest countries in the world with a GNI of 170 USD/capita • 65. 5% of its population live under the poverty line with a HDI rank of 165 out of 177 countries
• Land-locked country, highest population density (105/km 2) in the southern part of Africa. • 12. 9 million people, 83% rural areas • Agriculture, the major source of livelihood • One of the poorest countries in the world with a GNI of 170 USD/capita • 65. 5% of its population live under the poverty line with a HDI rank of 165 out of 177 countries
 Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi
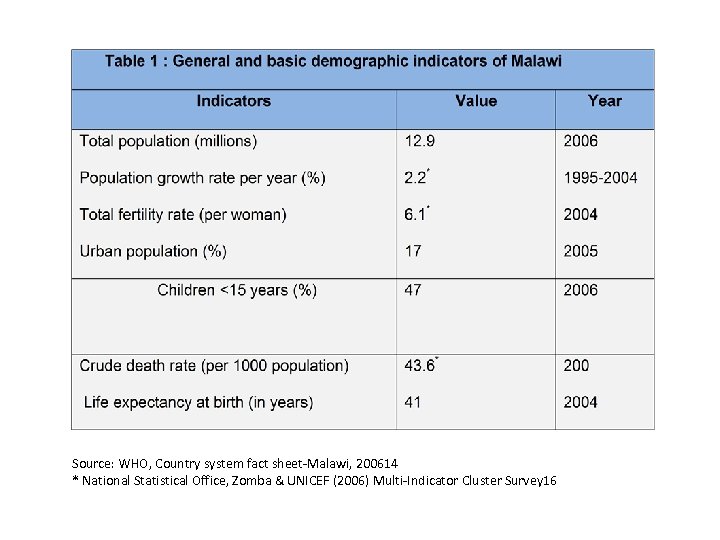 Source: WHO, Country system fact sheet-Malawi, 200614 * National Statistical Office, Zomba & UNICEF (2006) Multi-Indicator Cluster Survey 16
Source: WHO, Country system fact sheet-Malawi, 200614 * National Statistical Office, Zomba & UNICEF (2006) Multi-Indicator Cluster Survey 16
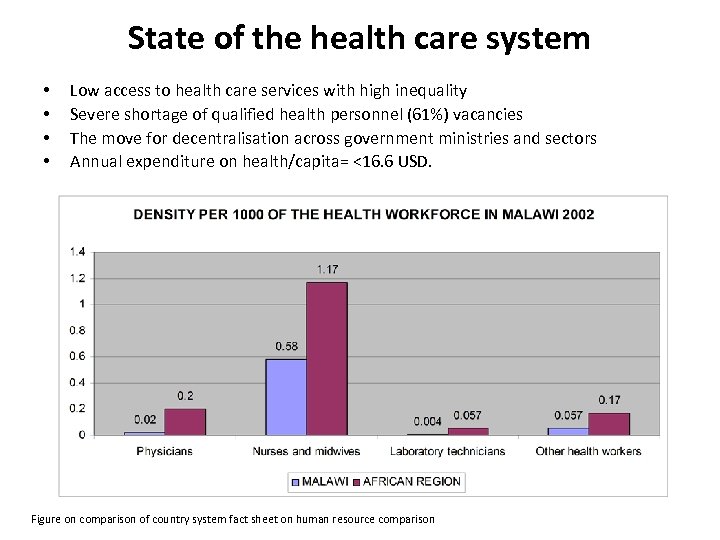 State of the health care system • • Low access to health care services with high inequality Severe shortage of qualified health personnel (61%) vacancies The move for decentralisation across government ministries and sectors Annual expenditure on health/capita= <16. 6 USD. Figure on comparison of country system fact sheet on human resource comparison
State of the health care system • • Low access to health care services with high inequality Severe shortage of qualified health personnel (61%) vacancies The move for decentralisation across government ministries and sectors Annual expenditure on health/capita= <16. 6 USD. Figure on comparison of country system fact sheet on human resource comparison
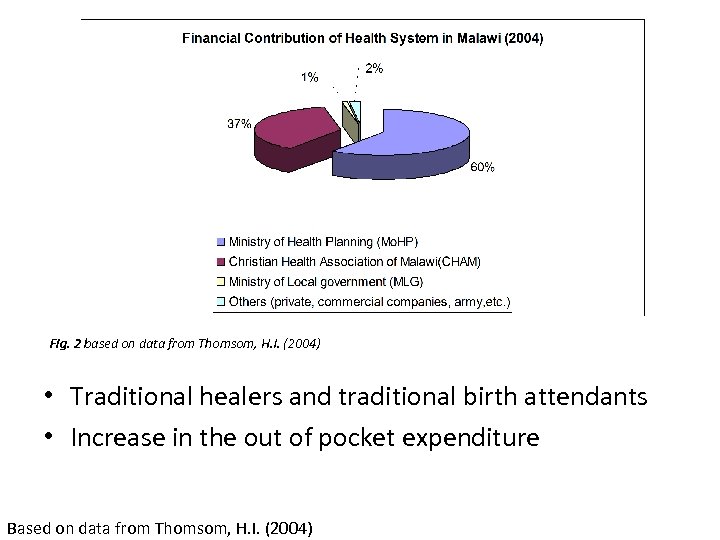 Fig. 2 based on data from Thomsom, H. I. (2004) • Traditional healers and traditional birth attendants • Increase in the out of pocket expenditure Based on data from Thomsom, H. I. (2004)
Fig. 2 based on data from Thomsom, H. I. (2004) • Traditional healers and traditional birth attendants • Increase in the out of pocket expenditure Based on data from Thomsom, H. I. (2004)
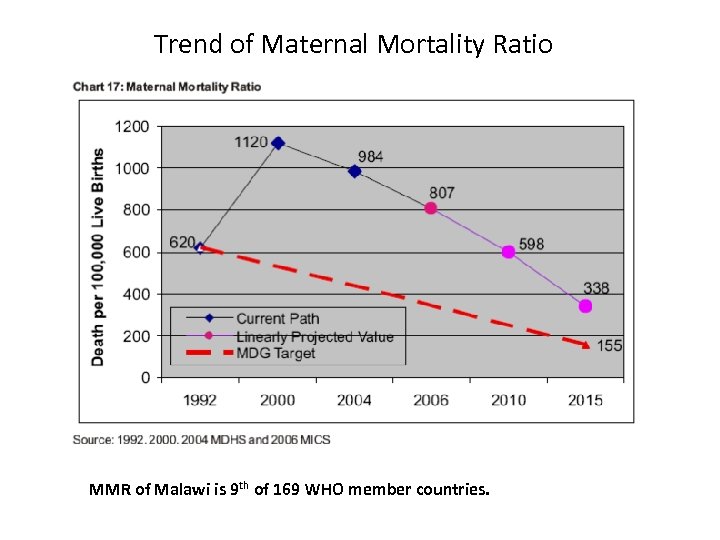 Trend of Maternal Mortality Ratio MMR of Malawi is 9 th of 169 WHO member countries.
Trend of Maternal Mortality Ratio MMR of Malawi is 9 th of 169 WHO member countries.
 Childbirth: a joyful occasion or one of grief?
Childbirth: a joyful occasion or one of grief?
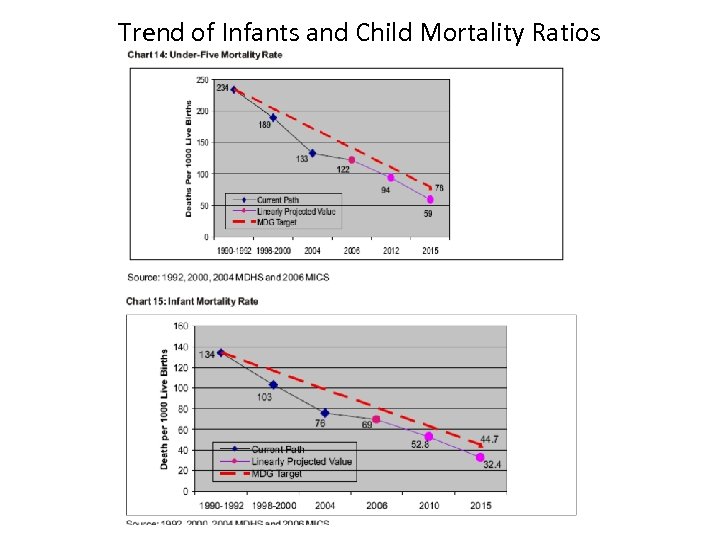 Trend of Infants and Child Mortality Ratios
Trend of Infants and Child Mortality Ratios
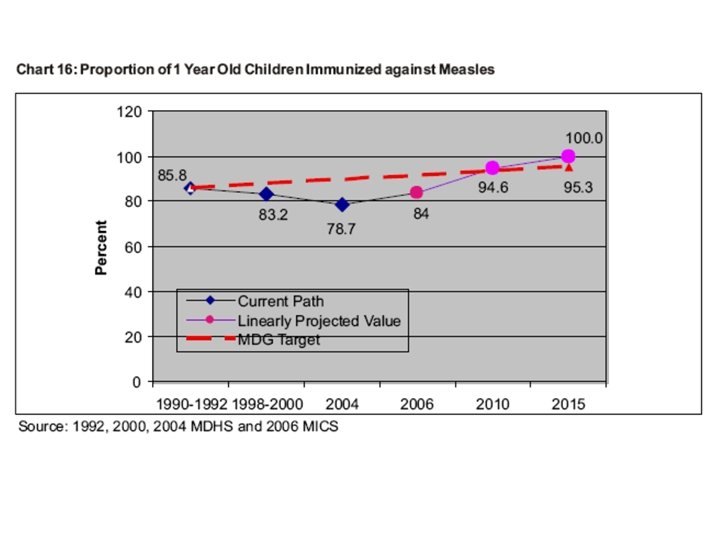
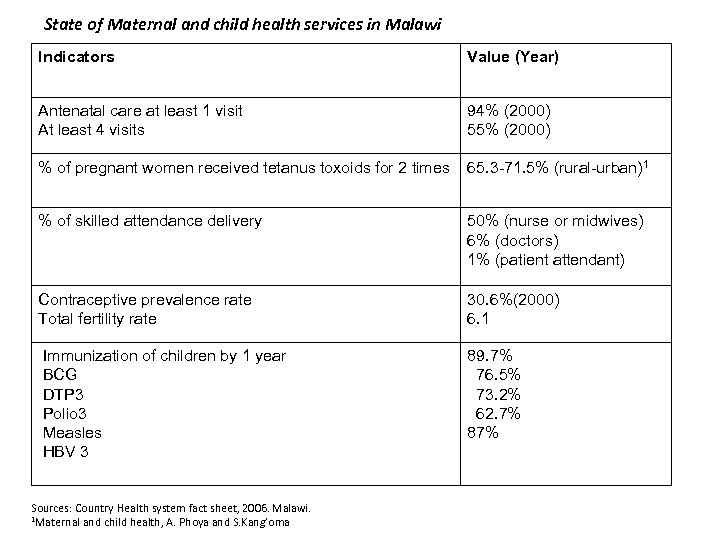 State of Maternal and child health services in Malawi Indicators Value (Year) Antenatal care at least 1 visit At least 4 visits 94% (2000) 55% (2000) % of pregnant women received tetanus toxoids for 2 times 65. 3 -71. 5% (rural-urban)1 % of skilled attendance delivery 50% (nurse or midwives) 6% (doctors) 1% (patient attendant) Contraceptive prevalence rate Total fertility rate 30. 6%(2000) 6. 1 Immunization of children by 1 year BCG DTP 3 Polio 3 Measles HBV 3 89. 7% 76. 5% 73. 2% 62. 7% 87% Sources: Country Health system fact sheet, 2006. Malawi. 1 Maternal and child health, A. Phoya and S. Kang’oma
State of Maternal and child health services in Malawi Indicators Value (Year) Antenatal care at least 1 visit At least 4 visits 94% (2000) 55% (2000) % of pregnant women received tetanus toxoids for 2 times 65. 3 -71. 5% (rural-urban)1 % of skilled attendance delivery 50% (nurse or midwives) 6% (doctors) 1% (patient attendant) Contraceptive prevalence rate Total fertility rate 30. 6%(2000) 6. 1 Immunization of children by 1 year BCG DTP 3 Polio 3 Measles HBV 3 89. 7% 76. 5% 73. 2% 62. 7% 87% Sources: Country Health system fact sheet, 2006. Malawi. 1 Maternal and child health, A. Phoya and S. Kang’oma
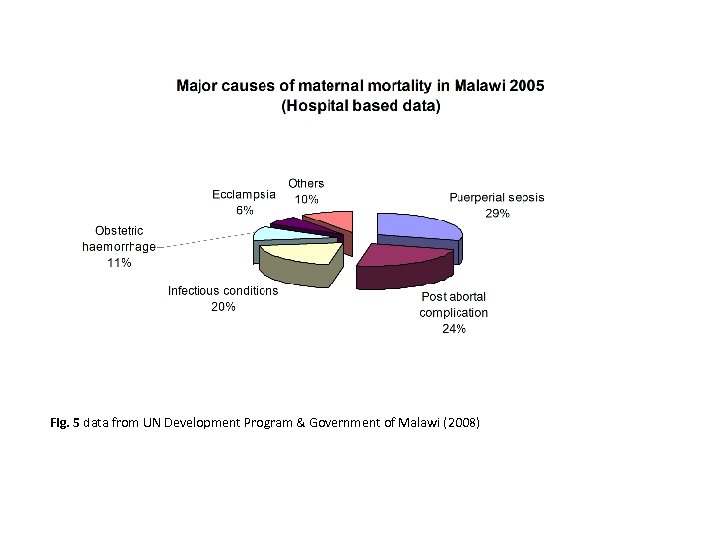 Fig. 5 data from UN Development Program & Government of Malawi (2008)
Fig. 5 data from UN Development Program & Government of Malawi (2008)
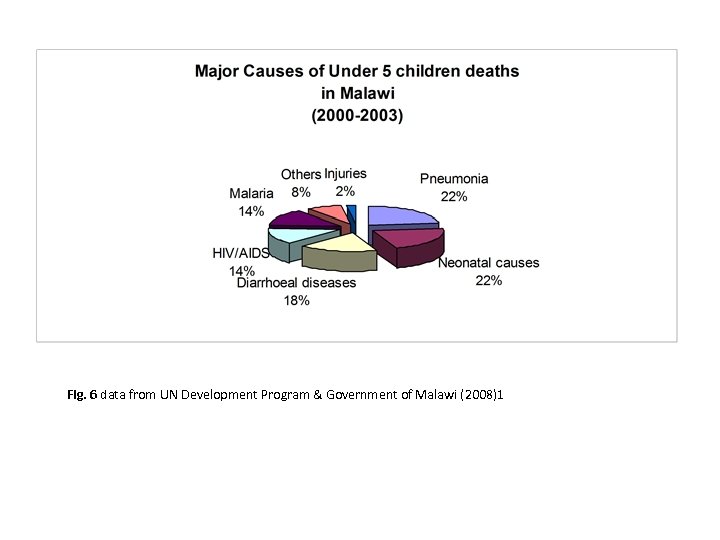 Fig. 6 data from UN Development Program & Government of Malawi (2008)1
Fig. 6 data from UN Development Program & Government of Malawi (2008)1
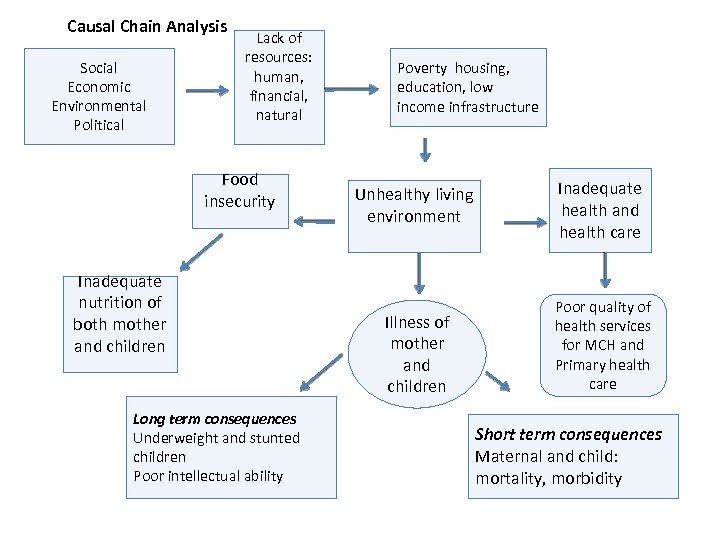 Causal Chain Analysis Social Economic Environmental Political Lack of resources: human, financial, natural Food insecurity Inadequate nutrition of both mother and children Long term consequences Underweight and stunted children Poor intellectual ability Poverty housing, education, low income infrastructure Unhealthy living environment Illness of mother and children Inadequate health and health care Poor quality of health services for MCH and Primary health care Short term consequences Maternal and child: mortality, morbidity
Causal Chain Analysis Social Economic Environmental Political Lack of resources: human, financial, natural Food insecurity Inadequate nutrition of both mother and children Long term consequences Underweight and stunted children Poor intellectual ability Poverty housing, education, low income infrastructure Unhealthy living environment Illness of mother and children Inadequate health and health care Poor quality of health services for MCH and Primary health care Short term consequences Maternal and child: mortality, morbidity
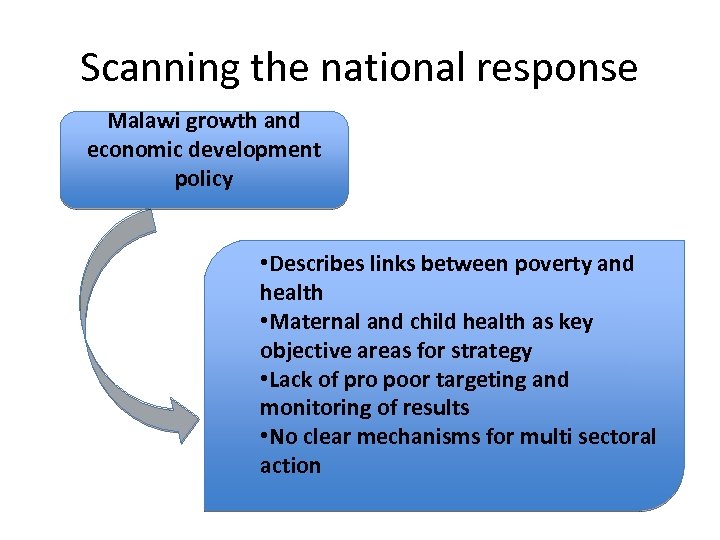 Scanning the national response Malawi growth and economic development policy • Describes links between poverty and health • Maternal and child health as key objective areas for strategy • Lack of pro poor targeting and monitoring of results • No clear mechanisms for multi sectoral action
Scanning the national response Malawi growth and economic development policy • Describes links between poverty and health • Maternal and child health as key objective areas for strategy • Lack of pro poor targeting and monitoring of results • No clear mechanisms for multi sectoral action
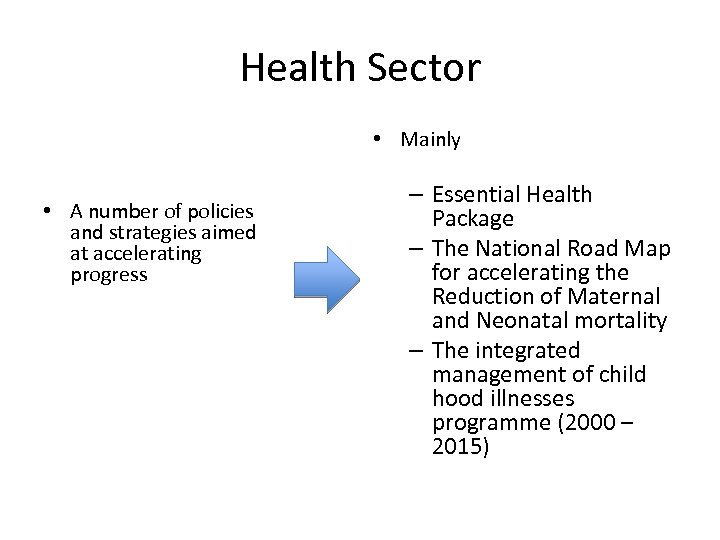 Health Sector • Mainly • A number of policies and strategies aimed at accelerating progress – Essential Health Package – The National Road Map for accelerating the Reduction of Maternal and Neonatal mortality – The integrated management of child hood illnesses programme (2000 – 2015)
Health Sector • Mainly • A number of policies and strategies aimed at accelerating progress – Essential Health Package – The National Road Map for accelerating the Reduction of Maternal and Neonatal mortality – The integrated management of child hood illnesses programme (2000 – 2015)
 . . . Health Sector • Main lines of action of policies and strategies. – Decentralisation of health infrastructure – Health infrastructure development – Health personnel training and deployment – Enhancing access to basic drugs and equipments – Community health Workers – link PHC with community
. . . Health Sector • Main lines of action of policies and strategies. – Decentralisation of health infrastructure – Health infrastructure development – Health personnel training and deployment – Enhancing access to basic drugs and equipments – Community health Workers – link PHC with community
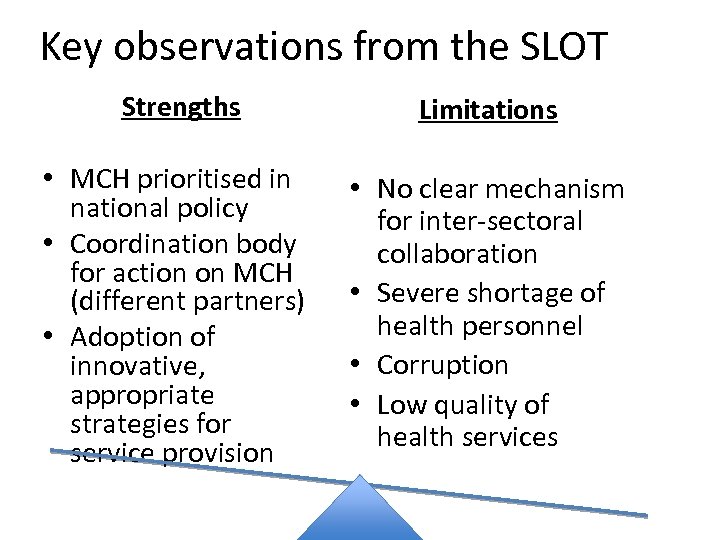 Key observations from the SLOT Strengths Limitations • MCH prioritised in national policy • Coordination body for action on MCH (different partners) • Adoption of innovative, appropriate strategies for service provision • No clear mechanism for inter-sectoral collaboration • Severe shortage of health personnel • Corruption • Low quality of health services
Key observations from the SLOT Strengths Limitations • MCH prioritised in national policy • Coordination body for action on MCH (different partners) • Adoption of innovative, appropriate strategies for service provision • No clear mechanism for inter-sectoral collaboration • Severe shortage of health personnel • Corruption • Low quality of health services
 SOME LIMITATIONS Malawi: 115 th in world ranking (index 2. 8) http: //www. transparency. org. uk/
SOME LIMITATIONS Malawi: 115 th in world ranking (index 2. 8) http: //www. transparency. org. uk/
 Opportunities Threats • Democratisation (1994) and decentralisation (1998) • Political commitment (Health Expenditure 9. 64 %) • Considerable international aid (% of aid? ) • Low empowerment of women • Recurrent drought • Global economic crisis • Multi faceted effects of HIV/AIDS
Opportunities Threats • Democratisation (1994) and decentralisation (1998) • Political commitment (Health Expenditure 9. 64 %) • Considerable international aid (% of aid? ) • Low empowerment of women • Recurrent drought • Global economic crisis • Multi faceted effects of HIV/AIDS
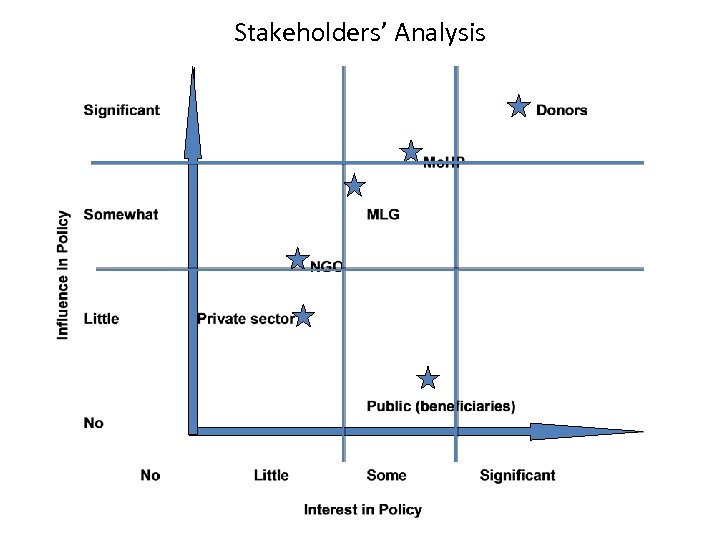 Stakeholders’ Analysis
Stakeholders’ Analysis
 Main conclusion points • Observed lag in maternal mortality rate • Attempts at a multi sectoral approach – lack of follow through in practice and evaluating outcome • Enhanced focus and action in the health sector, but structural challenges
Main conclusion points • Observed lag in maternal mortality rate • Attempts at a multi sectoral approach – lack of follow through in practice and evaluating outcome • Enhanced focus and action in the health sector, but structural challenges
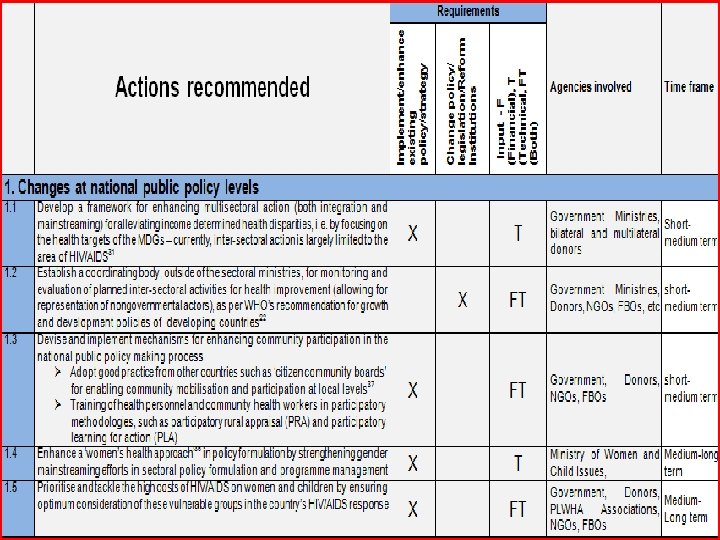
 Main recommendation points – Public Policy Level • Develop a framework for enhancing multisectoral action • Mechanisms for enhancing community participation • Enhance the ‘woman’s health approach’ – gender mainstreaming
Main recommendation points – Public Policy Level • Develop a framework for enhancing multisectoral action • Mechanisms for enhancing community participation • Enhance the ‘woman’s health approach’ – gender mainstreaming
 Main recommendation points – Public Policy Level • Actively target the women and children cost of HIV/AIDS • Step up anti corruption action
Main recommendation points – Public Policy Level • Actively target the women and children cost of HIV/AIDS • Step up anti corruption action
 . . . Recommendations – Health Sector • Strengthen SWaps • Strengthen the Emergency Human Resources Programme • Bolster efforts aimed at unsafe abortion – legislation • Scale up innovative, good practice – Kangaroo Mother care • Improve logistical management
. . . Recommendations – Health Sector • Strengthen SWaps • Strengthen the Emergency Human Resources Programme • Bolster efforts aimed at unsafe abortion – legislation • Scale up innovative, good practice – Kangaroo Mother care • Improve logistical management
 . . . Recommendations – Health Sector • Strengthen IEC/BCC for tackling cultural barriers • Sustainable means to health care financing • Strengthen partnerships with Global Actors – PMNCH • Actively monitor, reflect, and share lessons learnt
. . . Recommendations – Health Sector • Strengthen IEC/BCC for tackling cultural barriers • Sustainable means to health care financing • Strengthen partnerships with Global Actors – PMNCH • Actively monitor, reflect, and share lessons learnt
 MCH lecture Thematic Review of MNCH and setting agreed Population Approach and triangulation. MCH Review, milestones, current thinking and mechanisms National Context Regional context Global & response Actors Current thinking National response Key Findings Review vis-a-vis International Protocols Situation Analysis Major causes, trends and health system SLOT of Policy and Programmes Stakeholder Analysis matrix Conclusion Framework for actions
MCH lecture Thematic Review of MNCH and setting agreed Population Approach and triangulation. MCH Review, milestones, current thinking and mechanisms National Context Regional context Global & response Actors Current thinking National response Key Findings Review vis-a-vis International Protocols Situation Analysis Major causes, trends and health system SLOT of Policy and Programmes Stakeholder Analysis matrix Conclusion Framework for actions
 MERÇI DE VOTRE COLLABORASON
MERÇI DE VOTRE COLLABORASON


