282cff7a2ccaee4e218c8cac8e6b7760.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 8

The Standards Based Integration Company Systems Integration Specialists Company, Inc. What is the Semantic Utility Architecture John Gillerman, SISCO IEC WG 16 Montreal 9/2006 © Copyright 2006 SISCO, Inc.

Problem Statement The exact data exchanged (messages) and the business processes used in energy markets varies across different geographic/political regions. l Data exchanged and business processes in an energy market susceptible to change as business conditions change l Utilities may operate in more than one market each of which may be slightly different. l 2 © Copyright 2005 SISCO, Inc.
Problem Statement l Today, software architecture typically based on a data and process model that is homogeneous and fixed. § Cannot base architecture on a single homogeneous information model such as the CIM (as it exists today) l 3 How a MOS is designed and integrated into the utility needs to be flexible © Copyright 2005 SISCO, Inc.
The Semantic Utility Architecture Assumes that data and process models differ across MOS deployments l Data and process models are configured at the time of system deployment l Based on explicitly modeling heterogeneous information model and configurable business processes l § Requires the use of technology that can model heterogeneous information models and processes. q 4 A heterogeneous information model is one that includes overlapping, conflicting, and/or disjoint information © Copyright 2005 SISCO, Inc.
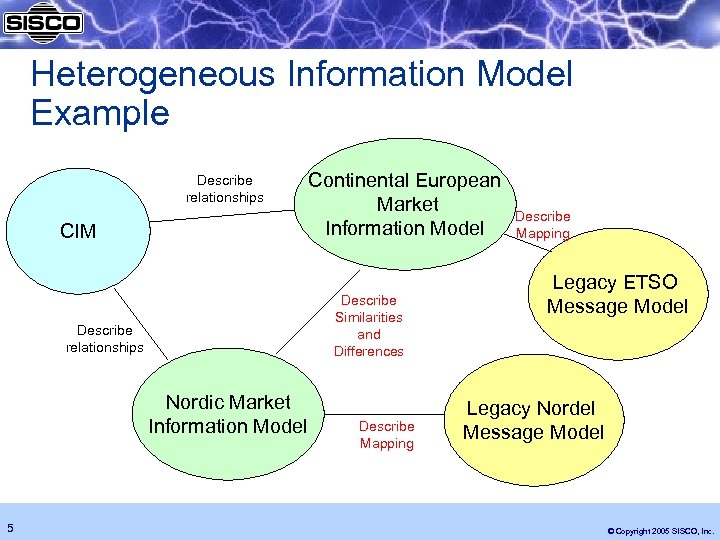
Heterogeneous Information Model Example Describe relationships CIM Describe Similarities and Differences Describe relationships Nordic Market Information Model 5 Continental European Market Information Model Describe Mapping Legacy ETSO Message Model Legacy Nordel Message Model © Copyright 2005 SISCO, Inc.

Proposed Solutions l Drive Business Process off of configurable process script § Most modern integration environments support business process workflow scripting § Use market independent service definitions for added flexibility l Drive data model off of an explicit description of the heterogeneous models § Describe relationship from 61970 CIM to Market IM’s § Describe similarities and differences between Market IM’s § Describe mapping to legacy messaging models § This last two require a technology such as OWL that can describe heterogeneous semantics 6 © Copyright 2005 SISCO, Inc.
Benefits l Integration and analysis infrastructures can support a heterogeneous information model § Provides a way to manage the complexity of operating in more than one market § Analysis applications can span markets q l Unified risk management for entire utility Vendors can more readily deliver products off the shelf using a single code base that can be applied to different markets § The larger the code base (total lines of code that need to be maintained) the greater the cost of software Software is more adaptable to change l These factors lower costs and reduce risk for utilities l 7 © Copyright 2005 SISCO, Inc.
Conclusions l Architecture and software must be developed to support heterogeneous models § White paper under development – new rev will be produced if preliminary buy in achieved in WG 16. § Move to support OWL in TC 57 § WG 16 would need to do the additional modeling required § Change from a fixed information model to a flexible one will require significant development by vendors l 8 Need to get buy in from industry on this approach before we attempt to standardized © Copyright 2005 SISCO, Inc.
282cff7a2ccaee4e218c8cac8e6b7760.ppt