4dbc929fd79944f6303a814f1cbaee77.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 The Spread of Islam 600 -1250 CE
The Spread of Islam 600 -1250 CE
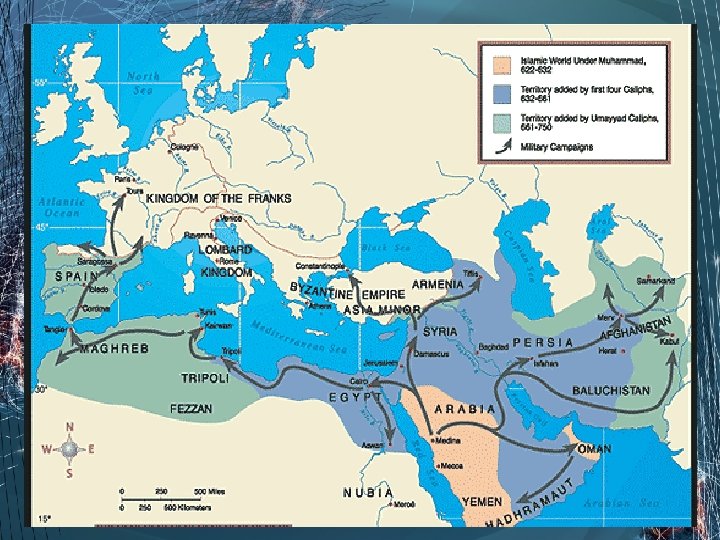
 Objectives • Assess the influence of geography on Islamic economic, social and political development, including the impact on conquest and trade. • Analyze historical turning points that affected the spread and influence of Islamic civilization, with emphasis on the Sunni. Shi’a division and the Battle of Tours.
Objectives • Assess the influence of geography on Islamic economic, social and political development, including the impact on conquest and trade. • Analyze historical turning points that affected the spread and influence of Islamic civilization, with emphasis on the Sunni. Shi’a division and the Battle of Tours.
 Big Ideas • In the first 3 centuries after Muhammad’s death, Muslim rule expanded rapidly; overcoming geographic barriers and facilitated by weakened political empires. • Political unity and the Arabic language facilitated trade and stimulated intellectual activity.
Big Ideas • In the first 3 centuries after Muhammad’s death, Muslim rule expanded rapidly; overcoming geographic barriers and facilitated by weakened political empires. • Political unity and the Arabic language facilitated trade and stimulated intellectual activity.
 Setting the Stage: Islamic Leadership Ø Overview ØUnlike many other religions, Muslims pray directly to Allah Ø Result ØRole of a religious leader (like a priest) is minimized.
Setting the Stage: Islamic Leadership Ø Overview ØUnlike many other religions, Muslims pray directly to Allah Ø Result ØRole of a religious leader (like a priest) is minimized.
 Setting the Stage: Islamic Worship Mosque – an Islamic house of worship
Setting the Stage: Islamic Worship Mosque – an Islamic house of worship
 Recall: The Hijrah & Medina Ø Muhammad and his followers left the city of Mecca after attacks in 622 AD Ø Hijrah: pilgrimage north to the city of Yathrib (Medina), 200 miles north of Mecca Ø There Muhammad became a political and religious leader and began to attract many followers Ø Over time people of Mecca unsuccessfully attempted to conquer Medina and put down Muhammad and his followers
Recall: The Hijrah & Medina Ø Muhammad and his followers left the city of Mecca after attacks in 622 AD Ø Hijrah: pilgrimage north to the city of Yathrib (Medina), 200 miles north of Mecca Ø There Muhammad became a political and religious leader and began to attract many followers Ø Over time people of Mecca unsuccessfully attempted to conquer Medina and put down Muhammad and his followers
 Return to Mecca Ø In 630 CE Muhammad and 10, 000 of his followers marched to the outskirts of Mecca Ø City leaders surrendered and Muhammad and his followers entered the city in triumph Ø He destroyed idols in the Ka’aba and declared it a Muslim holy shrine Ø Muhammad died in 632 CE, leaving no political nor religious successor
Return to Mecca Ø In 630 CE Muhammad and 10, 000 of his followers marched to the outskirts of Mecca Ø City leaders surrendered and Muhammad and his followers entered the city in triumph Ø He destroyed idols in the Ka’aba and declared it a Muslim holy shrine Ø Muhammad died in 632 CE, leaving no political nor religious successor
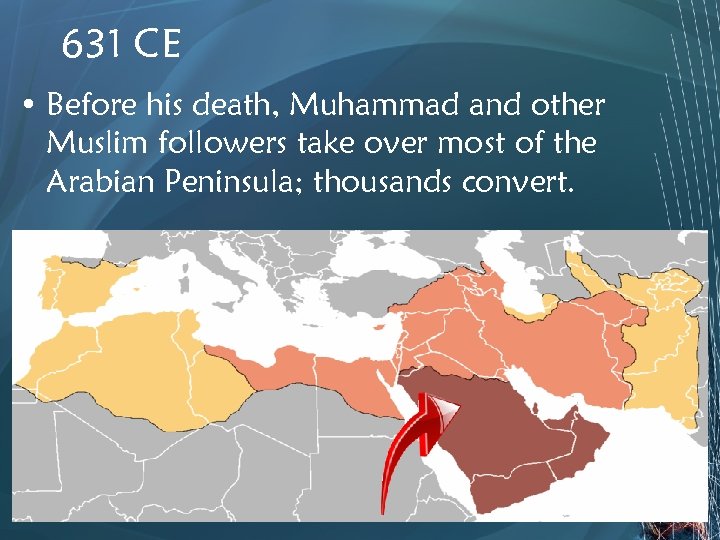 631 CE • Before his death, Muhammad and other Muslim followers take over most of the Arabian Peninsula; thousands convert.
631 CE • Before his death, Muhammad and other Muslim followers take over most of the Arabian Peninsula; thousands convert.
 After Muhammad Ø Four “Rightly Guided” Caliphs: 1. Abu-Bakr 2. Umar 3. Uthman 4. Ali Ø Caliph – a military/religious leader in the Muslim faith who uses the Quran and the Sunna to help rule. Literally means “successor” or “deputy” Ø 656: Uthman murdered, started a civil war with various groups struggling for power
After Muhammad Ø Four “Rightly Guided” Caliphs: 1. Abu-Bakr 2. Umar 3. Uthman 4. Ali Ø Caliph – a military/religious leader in the Muslim faith who uses the Quran and the Sunna to help rule. Literally means “successor” or “deputy” Ø 656: Uthman murdered, started a civil war with various groups struggling for power
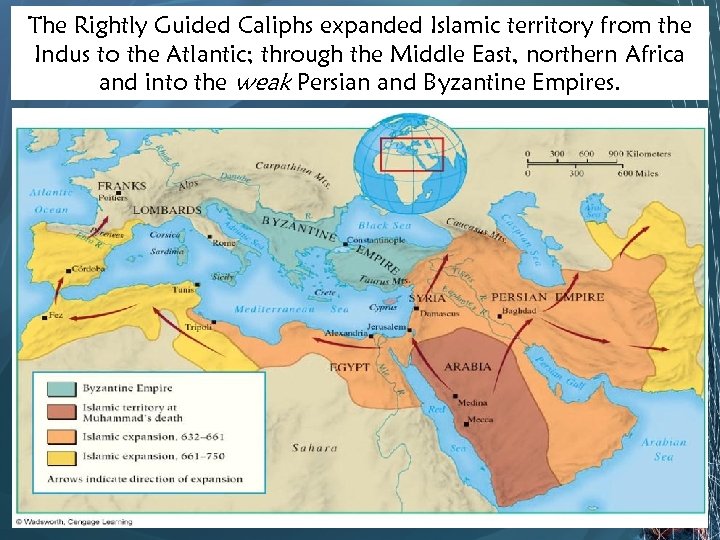 The Rightly Guided Caliphs expanded Islamic territory from the Indus to the Atlantic; through the Middle East, northern Africa and into the weak Persian and Byzantine Empires.
The Rightly Guided Caliphs expanded Islamic territory from the Indus to the Atlantic; through the Middle East, northern Africa and into the weak Persian and Byzantine Empires.
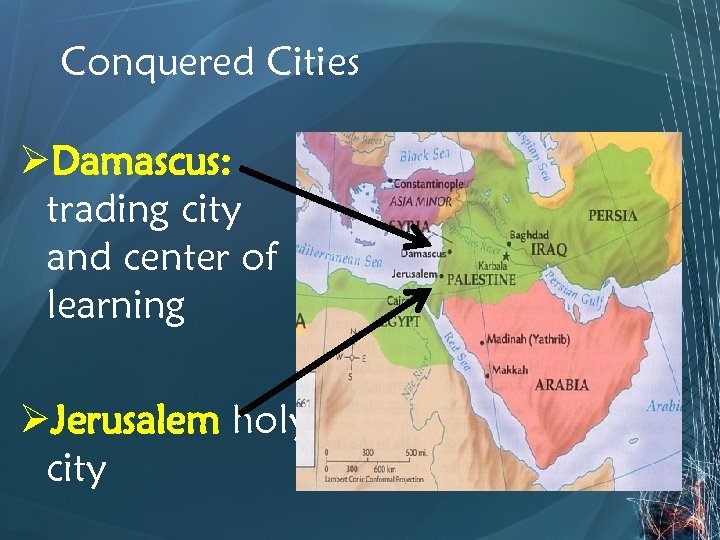 Conquered Cities ØDamascus: trading city and center of learning ØJerusalem holy city
Conquered Cities ØDamascus: trading city and center of learning ØJerusalem holy city
 Essential Question Ø How did geography impact the spread of Islam?
Essential Question Ø How did geography impact the spread of Islam?
 The Spread of Islamic Influence: Trade/Travel Ø Spread quickly along trade routes from Mecca to Medina Ø Reasons for appeal ØSimple, direct message ØEquality of all believers ØBased on oral traditions – did not need to be literate
The Spread of Islamic Influence: Trade/Travel Ø Spread quickly along trade routes from Mecca to Medina Ø Reasons for appeal ØSimple, direct message ØEquality of all believers ØBased on oral traditions – did not need to be literate
 The Spread of Islamic Influence: Conquest ØThe Byzantine and Persian Empires (Iran) had been weakened by decades of war.
The Spread of Islamic Influence: Conquest ØThe Byzantine and Persian Empires (Iran) had been weakened by decades of war.
 The Spread of Islamic Influence: Conquest Ø Mohammed declared a Jihad (“struggle”) against non-believers, which motivated Arab armies to conquer other lands. Ø They believed that if they died in a Jihad, then they would be guaranteed a place in paradise.
The Spread of Islamic Influence: Conquest Ø Mohammed declared a Jihad (“struggle”) against non-believers, which motivated Arab armies to conquer other lands. Ø They believed that if they died in a Jihad, then they would be guaranteed a place in paradise.
 The Spread of Islamic Influence: Conquest Ø Muslims saw the victories in terms of Jihad. A sign of support from God, which made them more willing to fight. Ø In conquered lands, polytheists were forced to convert, but monotheists were given an option: Ø Lose lands and pay protection tax.
The Spread of Islamic Influence: Conquest Ø Muslims saw the victories in terms of Jihad. A sign of support from God, which made them more willing to fight. Ø In conquered lands, polytheists were forced to convert, but monotheists were given an option: Ø Lose lands and pay protection tax.
 The Spread of Islamic Influence: Conquest ØWhy did most Polytheists willingly convert? (Hint: Think Christianity!)
The Spread of Islamic Influence: Conquest ØWhy did most Polytheists willingly convert? (Hint: Think Christianity!)
 The Spread of Islamic Influence Ø Through Trade and Conquest, Arabs were able to construct a relatively huge empire in a very short amount of time. ØWhy was this such a great feat? (Hint: Think Geography!)
The Spread of Islamic Influence Ø Through Trade and Conquest, Arabs were able to construct a relatively huge empire in a very short amount of time. ØWhy was this such a great feat? (Hint: Think Geography!)
 Essential Question Ø What were some major historical turning points that marked the spread and influence of Islamic civilization?
Essential Question Ø What were some major historical turning points that marked the spread and influence of Islamic civilization?
 Growing Unrest Ø Ali, Muhammad’s cousin and son-in-law, the last Rightly Guided Caliph, elected to power. Ø Mu’awiyah, Governor of Syria, questions Ali’s authority to rule. Ø Ali assassinated, with him, so too left the elective system of choosing a caliph Ø Umayyads – came to power, moved Muslim capital from Medina to Damascus
Growing Unrest Ø Ali, Muhammad’s cousin and son-in-law, the last Rightly Guided Caliph, elected to power. Ø Mu’awiyah, Governor of Syria, questions Ali’s authority to rule. Ø Ali assassinated, with him, so too left the elective system of choosing a caliph Ø Umayyads – came to power, moved Muslim capital from Medina to Damascus
 Sunni/Shi’a Split Ø Majority of Muslims accepted Umayyads’ rule Ø Minority group believed the caliph needed to be a descendant of the Prophet – Shi’a: meant the “party” of Ali – Caliph should be descendant of Muhammad – Sunni: those who did not resist rule of Umayyads, meant followers of Muhammad’s example – Caliph should be chosen by Muslim leaders
Sunni/Shi’a Split Ø Majority of Muslims accepted Umayyads’ rule Ø Minority group believed the caliph needed to be a descendant of the Prophet – Shi’a: meant the “party” of Ali – Caliph should be descendant of Muhammad – Sunni: those who did not resist rule of Umayyads, meant followers of Muhammad’s example – Caliph should be chosen by Muslim leaders
 People Profile: Sunni Muslims • The majority group (80%) • Caliph chosen by Muslim leaders • Believe that the descendants of any of the four caliphs can become a leader in the faith as long as they were religious, knowledgeable and well-liked. • Sunna means “in the tradition of the prophet. ” – Believed that Mohammed wanted the community to choose the leader.
People Profile: Sunni Muslims • The majority group (80%) • Caliph chosen by Muslim leaders • Believe that the descendants of any of the four caliphs can become a leader in the faith as long as they were religious, knowledgeable and well-liked. • Sunna means “in the tradition of the prophet. ” – Believed that Mohammed wanted the community to choose the leader.
 People Profile: Shi’a Muslims • The minority group • Much stricter beliefs • Believe that the leaders should only be direct descendants of Muhammad and the final caliph (Ali). • Shi’a call Muhammad’s successors Imams (worship leaders of a mosque and the Muslim community. Considered to be divinely appointed, sinless, infallible successors of Muhammad).
People Profile: Shi’a Muslims • The minority group • Much stricter beliefs • Believe that the leaders should only be direct descendants of Muhammad and the final caliph (Ali). • Shi’a call Muhammad’s successors Imams (worship leaders of a mosque and the Muslim community. Considered to be divinely appointed, sinless, infallible successors of Muhammad).
 Schism still exists to this day; Shiites live in Iran, western Afghanistan, & sections of Iraq 25
Schism still exists to this day; Shiites live in Iran, western Afghanistan, & sections of Iraq 25
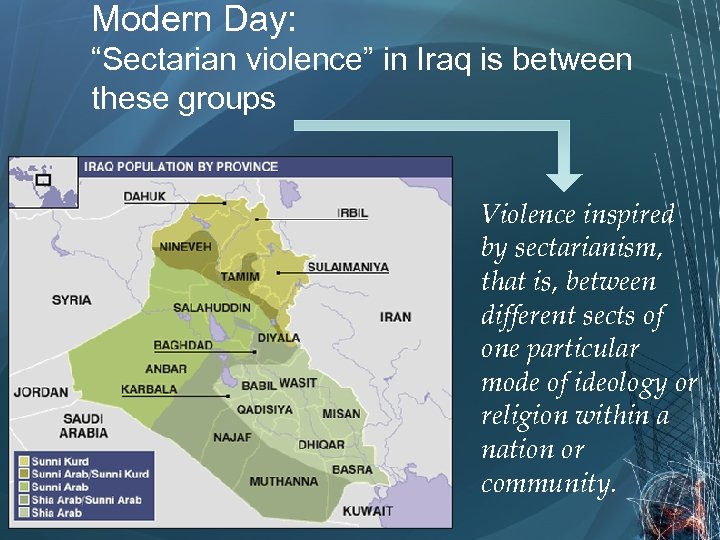 Modern Day: “Sectarian violence” in Iraq is between these groups Violence inspired by sectarianism, that is, between different sects of one particular mode of ideology or religion within a nation or community.
Modern Day: “Sectarian violence” in Iraq is between these groups Violence inspired by sectarianism, that is, between different sects of one particular mode of ideology or religion within a nation or community.
 The first dynasty following the era of the Rightly Guided Caliphs came from the Umayyad family Sunni’s supported the Umayyad Dynasty Shi’a’s viewed the Umayyad caliphs as illegitimate leaders.
The first dynasty following the era of the Rightly Guided Caliphs came from the Umayyad family Sunni’s supported the Umayyad Dynasty Shi’a’s viewed the Umayyad caliphs as illegitimate leaders.
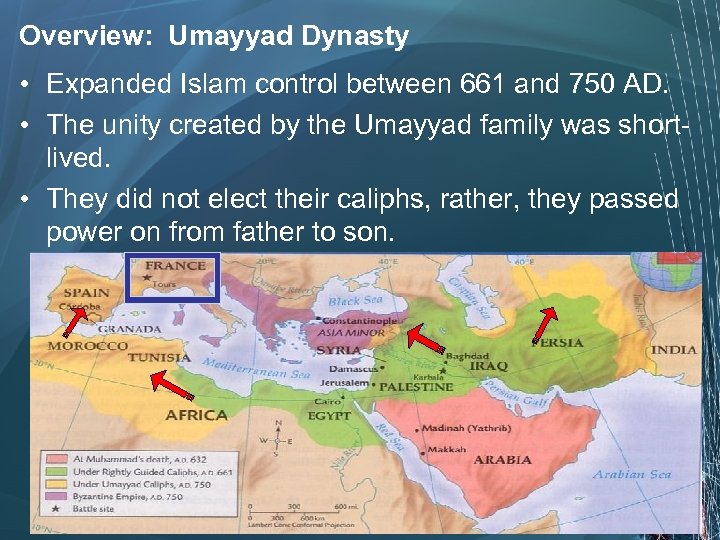 Overview: Umayyad Dynasty • Expanded Islam control between 661 and 750 AD. • The unity created by the Umayyad family was shortlived. • They did not elect their caliphs, rather, they passed power on from father to son.
Overview: Umayyad Dynasty • Expanded Islam control between 661 and 750 AD. • The unity created by the Umayyad family was shortlived. • They did not elect their caliphs, rather, they passed power on from father to son.
 Umayyad Accomplishments Moved the capital of Islam to Damascus, Syria. The Great Mosque 29
Umayyad Accomplishments Moved the capital of Islam to Damascus, Syria. The Great Mosque 29
 Umayyad Accomplishments • Established a common currency, called the dinar, which became the most commonly used coin in the world.
Umayyad Accomplishments • Established a common currency, called the dinar, which became the most commonly used coin in the world.
 Umayyad Accomplishments • Made Arabic the official language of all Muslim areas. • Impact: The Arabic language was needed to read the Koran, so it spread Islam and facilitated trade across Islamic lands.
Umayyad Accomplishments • Made Arabic the official language of all Muslim areas. • Impact: The Arabic language was needed to read the Koran, so it spread Islam and facilitated trade across Islamic lands.
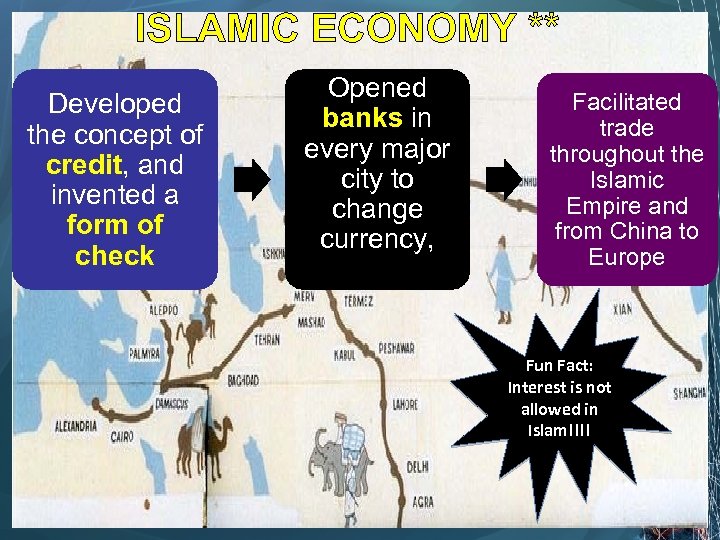 ISLAMIC ECONOMY ** Developed the concept of credit, and invented a form of check Opened banks in every major city to change currency, Facilitated trade throughout the Islamic Empire and from China to Europe Fun Fact: Interest is not allowed in Islam!!!!
ISLAMIC ECONOMY ** Developed the concept of credit, and invented a form of check Opened banks in every major city to change currency, Facilitated trade throughout the Islamic Empire and from China to Europe Fun Fact: Interest is not allowed in Islam!!!!
 Cultural & Scientific Milestones Ø Education – Elementary education for both sexes – Universities (“House of Wisdom”) and libraries Ø Preserved Greek, Roman, Persian, Indian learning by translating ancient texts Ø Spread Arabic numerals from India, including the concept of zero (Replaced Roman numerals) Ø Algebra (Al-Khwarizmi) (“al-jabr”) Ø Astronomy: Astrolabe, earth’s rotation & circumference. Ø Medicine: doctor licensing, hospitals, ERs
Cultural & Scientific Milestones Ø Education – Elementary education for both sexes – Universities (“House of Wisdom”) and libraries Ø Preserved Greek, Roman, Persian, Indian learning by translating ancient texts Ø Spread Arabic numerals from India, including the concept of zero (Replaced Roman numerals) Ø Algebra (Al-Khwarizmi) (“al-jabr”) Ø Astronomy: Astrolabe, earth’s rotation & circumference. Ø Medicine: doctor licensing, hospitals, ERs
 Islamic Literature ** Ø A Thousand One Arabian Nights – A collection of stories and folk tales – “Aladdin’s Wonderful Lamp” was one of the stories.
Islamic Literature ** Ø A Thousand One Arabian Nights – A collection of stories and folk tales – “Aladdin’s Wonderful Lamp” was one of the stories.
 Cultural Milestones Ø Architecture: adopted arches, aqueducts from Rome and domes, mosaics from Byzantine. Ø ** Minarets – Tower from which prayer calls are made Ø ** Islamic artists also used geometric shapes to make intricate patterns.
Cultural Milestones Ø Architecture: adopted arches, aqueducts from Rome and domes, mosaics from Byzantine. Ø ** Minarets – Tower from which prayer calls are made Ø ** Islamic artists also used geometric shapes to make intricate patterns.
 Cultural Milestones Ø Religious art – Didn’t show God, humans – Arabesque – Calligraphy This bird’s body is composed of words of faith in calligraphy.
Cultural Milestones Ø Religious art – Didn’t show God, humans – Arabesque – Calligraphy This bird’s body is composed of words of faith in calligraphy.
 Muslim Society Ø Absorbed/blended many cultures and traditions Ø Some social mobility –improve rank through religious, scholarly, military achievements Ø A form of slavery common – Not based on race – Among earliest converts – Treated with equality and respect – Muslims not enslaved – Children of slaves who convert are freed – Females who marry masters freed – Slaves can buy freedom
Muslim Society Ø Absorbed/blended many cultures and traditions Ø Some social mobility –improve rank through religious, scholarly, military achievements Ø A form of slavery common – Not based on race – Among earliest converts – Treated with equality and respect – Muslims not enslaved – Children of slaves who convert are freed – Females who marry masters freed – Slaves can buy freedom
 732 CE Outcome of the Battle of Tours – King Charles Martel defeated the Muslim army at the Battle of Tours (modern France). 38
732 CE Outcome of the Battle of Tours – King Charles Martel defeated the Muslim army at the Battle of Tours (modern France). 38
 Impact of the Battle of Tours • The battle of Tours finally stalled the expansion of Islam; preventing most of Europe from converting • Spain remained under Muslim control until 1492.
Impact of the Battle of Tours • The battle of Tours finally stalled the expansion of Islam; preventing most of Europe from converting • Spain remained under Muslim control until 1492.
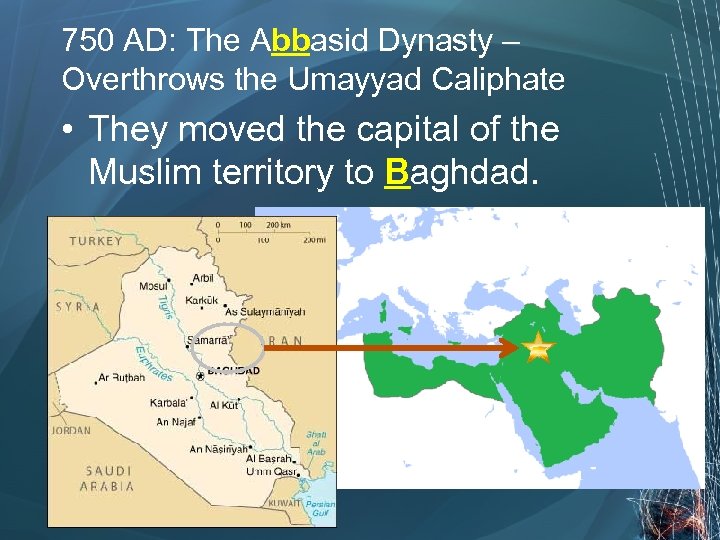 750 AD: The Abbasid Dynasty – Overthrows the Umayyad Caliphate • They moved the capital of the Muslim territory to Baghdad.
750 AD: The Abbasid Dynasty – Overthrows the Umayyad Caliphate • They moved the capital of the Muslim territory to Baghdad.
 41 A New Capital: Baghdad ØBaghdad became a center of learning and trade until it was conquered by the Mongols in 1258 AD.
41 A New Capital: Baghdad ØBaghdad became a center of learning and trade until it was conquered by the Mongols in 1258 AD.
 Thinking Chronologically ØMajor historical turning points of Islamic civilization: – 611 AD: Death of Ali: Sunni-Shi’a division – 634 AD: Muslim conquest of Damascus – 637 AD: Muslim conquest of Jerusalem – 732 AD: Muslim defeat at the Battle of Tours – 762 AD: Islamic capital moved to Baghdad – 1258 AD: Fall of Baghdad to the Mongols
Thinking Chronologically ØMajor historical turning points of Islamic civilization: – 611 AD: Death of Ali: Sunni-Shi’a division – 634 AD: Muslim conquest of Damascus – 637 AD: Muslim conquest of Jerusalem – 732 AD: Muslim defeat at the Battle of Tours – 762 AD: Islamic capital moved to Baghdad – 1258 AD: Fall of Baghdad to the Mongols
 Today, countries with the Largest Muslim Population 1. Indonesia 183, 000 6. Iran 62, 000 2. Pakistan 134, 000 7. Egypt 59, 000 3. India 121, 000 8. Nigeria 53, 000 4. Bangladesh 114, 000 9. Algeria 31, 000 66, 000 10. Morocco 29, 000 5. Turkey *Arabs make up only 20% of the total Muslim population of the world.
Today, countries with the Largest Muslim Population 1. Indonesia 183, 000 6. Iran 62, 000 2. Pakistan 134, 000 7. Egypt 59, 000 3. India 121, 000 8. Nigeria 53, 000 4. Bangladesh 114, 000 9. Algeria 31, 000 66, 000 10. Morocco 29, 000 5. Turkey *Arabs make up only 20% of the total Muslim population of the world.


