3c62db7133754035d51f3bf9f1854523.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 The Spanish-American War (1898) Causes and Effects
The Spanish-American War (1898) Causes and Effects
 Spain’s Holdings/Prelude ► Spanish holdings at the end of 19 th Century § Philippines/Guam in Pacific § A few outposts in Africa § Cuba and Puerto Rico ► American Interest in Cuba § 1854 Ostend Manifesto
Spain’s Holdings/Prelude ► Spanish holdings at the end of 19 th Century § Philippines/Guam in Pacific § A few outposts in Africa § Cuba and Puerto Rico ► American Interest in Cuba § 1854 Ostend Manifesto
 Cuban Revolutions ► First War of Independence § 1868 -1878 ►Was a failure, but Cuba did manage to abolish slavery in 1886 § After emancipation, USA invests millions in sugar plantations ► Second War of Independence § Begins in 1895 ►Guerilla campaign ►Attempted to provoke the United States
Cuban Revolutions ► First War of Independence § 1868 -1878 ►Was a failure, but Cuba did manage to abolish slavery in 1886 § After emancipation, USA invests millions in sugar plantations ► Second War of Independence § Begins in 1895 ►Guerilla campaign ►Attempted to provoke the United States
 Important People ► Jose Marti (1853 -1895) § Organized 2 nd Cuban Revolution ► Valeriano Weyler § Spanish General ► William § § Randolph Hearst New York Journal “You furnish the pictures, I’ll furnish the war. ” ► Joseph Pulitzer § New York World
Important People ► Jose Marti (1853 -1895) § Organized 2 nd Cuban Revolution ► Valeriano Weyler § Spanish General ► William § § Randolph Hearst New York Journal “You furnish the pictures, I’ll furnish the war. ” ► Joseph Pulitzer § New York World
 American Interest ► Public opinion in the USA is split § Businesses Spanish § Other civilians Cubans ► Mc. Kinley takes office (1897) § Attempts Diplomatic solution ►Spain calls back Weyler ►Modifies concentration camps ►Spain offers Cuba limited self-government
American Interest ► Public opinion in the USA is split § Businesses Spanish § Other civilians Cubans ► Mc. Kinley takes office (1897) § Attempts Diplomatic solution ►Spain calls back Weyler ►Modifies concentration camps ►Spain offers Cuba limited self-government
 The de Lome Letter & the U. S. S. Maine ► Enrique Dupuy de Lome § Spanish minister to the United States ► The U. S. S. Maine § Sent to Cuba to evacuate Americans § February 15 th, 1898 explodes in Havana Harbor, 260+ KIA § Spanish and US investigations took place
The de Lome Letter & the U. S. S. Maine ► Enrique Dupuy de Lome § Spanish minister to the United States ► The U. S. S. Maine § Sent to Cuba to evacuate Americans § February 15 th, 1898 explodes in Havana Harbor, 260+ KIA § Spanish and US investigations took place


 Outcry for War ► USA sends Spain ultimatum § End concentration camps § Armistice with Cuban rebels ► Mc. Kinley wanted to avoid war at all cost § Public Outcry § Doubts about Spain § Personal political gain
Outcry for War ► USA sends Spain ultimatum § End concentration camps § Armistice with Cuban rebels ► Mc. Kinley wanted to avoid war at all cost § Public Outcry § Doubts about Spain § Personal political gain
 Mc. Kinley Asks for War ► April 11 th, 1898 § Mc. Kinley sends his war message to Congress § Urged armed intervention to free the oppressed Cubans ► Congress passes Teller Amendment § Cuba would be given their freedom after the US had overthrown Spanish ‘misrule’
Mc. Kinley Asks for War ► April 11 th, 1898 § Mc. Kinley sends his war message to Congress § Urged armed intervention to free the oppressed Cubans ► Congress passes Teller Amendment § Cuba would be given their freedom after the US had overthrown Spanish ‘misrule’
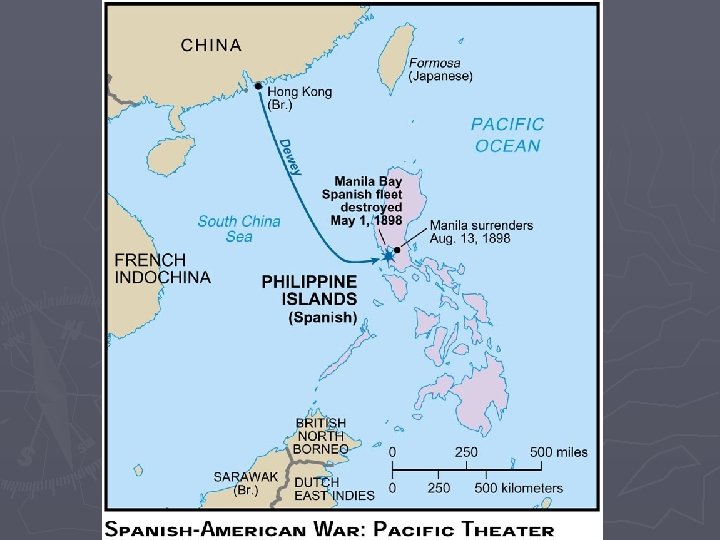
 War in the Pacific ► Spain expected first attack to be in Cuba ► American Pacific fleet steams to the Philippines § Strong steel navy (Mahan) § Led by Commodore George Dewey ► US fleet defeats Spanish fleet in Manila Bay on May 1 st, 1898
War in the Pacific ► Spain expected first attack to be in Cuba ► American Pacific fleet steams to the Philippines § Strong steel navy (Mahan) § Led by Commodore George Dewey ► US fleet defeats Spanish fleet in Manila Bay on May 1 st, 1898
 Poor Spain ► Spain loses Pacific fleet § 400 Sailors dead (Dewey = 0 casualties) ► Dewey becomes national hero § But could not invade Philippines with his sailors, was forced to wait for reinforcements ► European Imperialists protect interests in the Philippines, war with Germany avoided
Poor Spain ► Spain loses Pacific fleet § 400 Sailors dead (Dewey = 0 casualties) ► Dewey becomes national hero § But could not invade Philippines with his sailors, was forced to wait for reinforcements ► European Imperialists protect interests in the Philippines, war with Germany avoided

 Fighting in the Philippines ► Dewey had the support of the Filipinos ► 11, 000+ American soldiers travel to the Philippines, join Filipino rebels § Filipinos led by Emilio Aguinaldo ► Capture Manila ► Total American losses in Philippines § 136 Casualties
Fighting in the Philippines ► Dewey had the support of the Filipinos ► 11, 000+ American soldiers travel to the Philippines, join Filipino rebels § Filipinos led by Emilio Aguinaldo ► Capture Manila ► Total American losses in Philippines § 136 Casualties
 The War in the Caribbean ► Blockade of Cuba § Demonstrated strength of new US Navy ► Army was very small § Relied on volunteers § Unsuited for tropical climate ► 17, 000 land in Cuba (June) § Four African American regiments § Calvary units (Rough Riders)
The War in the Caribbean ► Blockade of Cuba § Demonstrated strength of new US Navy ► Army was very small § Relied on volunteers § Unsuited for tropical climate ► 17, 000 land in Cuba (June) § Four African American regiments § Calvary units (Rough Riders)
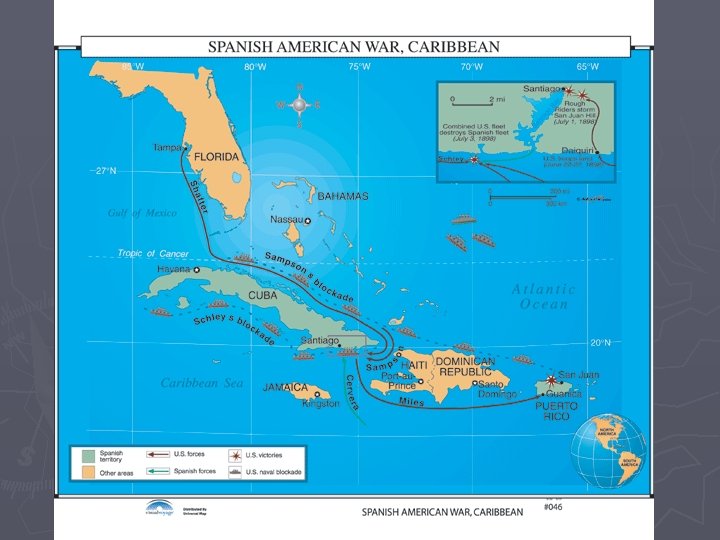
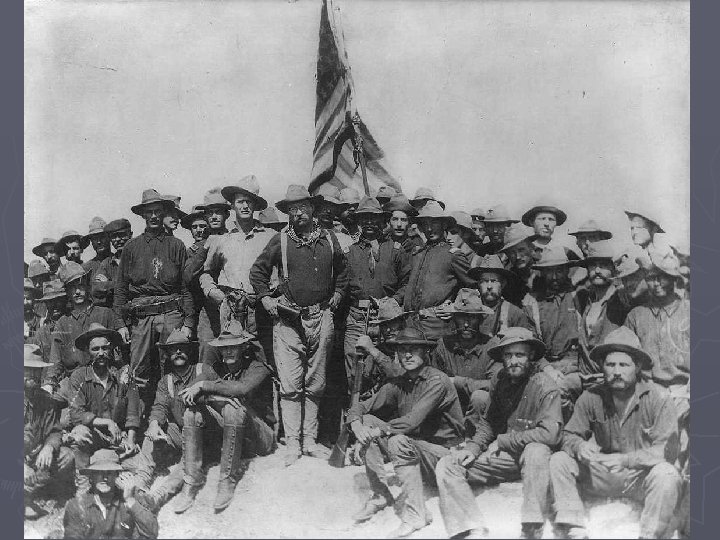
 Fighting in the Caribbean ► Shafer lands near Santiago § Little resistance ► Spanish were too unorganized, Santiago taken easily § Battle of Kettle/San Juan Hills (July 1) ► Puerto Rico (July 25) taken after destruction of Spanish fleet (July 3)
Fighting in the Caribbean ► Shafer lands near Santiago § Little resistance ► Spanish were too unorganized, Santiago taken easily § Battle of Kettle/San Juan Hills (July 1) ► Puerto Rico (July 25) taken after destruction of Spanish fleet (July 3)
 Treaty of Paris ► Armistice – August 12 th § “A splendid little war” ► Treaty approved Feb 6, 1899 § US gains ►Guam ►Puerto Rico ►Philippines sold for $20 Million § Manila taken the day after the armistice had been signed
Treaty of Paris ► Armistice – August 12 th § “A splendid little war” ► Treaty approved Feb 6, 1899 § US gains ►Guam ►Puerto Rico ►Philippines sold for $20 Million § Manila taken the day after the armistice had been signed
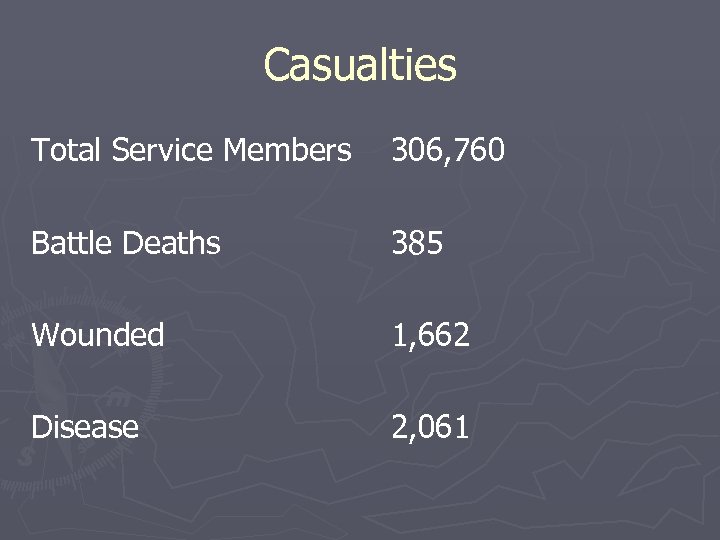 Casualties Total Service Members 306, 760 Battle Deaths 385 Wounded 1, 662 Disease 2, 061
Casualties Total Service Members 306, 760 Battle Deaths 385 Wounded 1, 662 Disease 2, 061
 Puerto Rico and Cuba ► Foraker Act – Puerto Rico (1900) § Ended military rule in PR and set up a civil gov § PR granted U. S. citizenship in 1917 ► Platt Amendment – Cuba (1901) § Cuba could not make treaties that might limit its independence or permit a foreign power to control any part of its territory § The US reserved the right to intervene in Cuba § Cuba was not to go into debt § The US could buy or lease land on the island for naval stations and refueling stations
Puerto Rico and Cuba ► Foraker Act – Puerto Rico (1900) § Ended military rule in PR and set up a civil gov § PR granted U. S. citizenship in 1917 ► Platt Amendment – Cuba (1901) § Cuba could not make treaties that might limit its independence or permit a foreign power to control any part of its territory § The US reserved the right to intervene in Cuba § Cuba was not to go into debt § The US could buy or lease land on the island for naval stations and refueling stations
 The Philippines ► The US assumes similar role as Spanish § Philippines = gateway to China/East Asia ► Filipinos rise in revolt § Led by Emilio Aguinaldo ► 70, 000 US troops sent to put down rebellion § Lasts 3 years, cost $400 million ► US sets up government similar to PR § Philippines gain independence July 1, 1946
The Philippines ► The US assumes similar role as Spanish § Philippines = gateway to China/East Asia ► Filipinos rise in revolt § Led by Emilio Aguinaldo ► 70, 000 US troops sent to put down rebellion § Lasts 3 years, cost $400 million ► US sets up government similar to PR § Philippines gain independence July 1, 1946

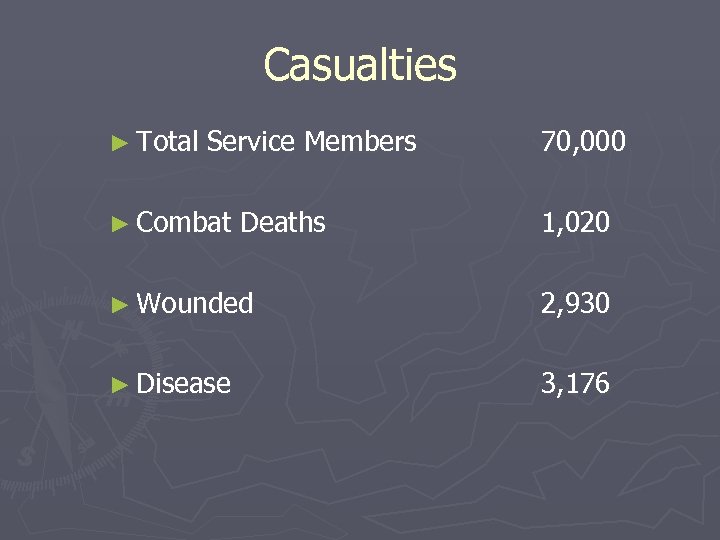 Casualties ► Total Service Members ► Combat Deaths 70, 000 1, 020 ► Wounded 2, 930 ► Disease 3, 176
Casualties ► Total Service Members ► Combat Deaths 70, 000 1, 020 ► Wounded 2, 930 ► Disease 3, 176
 Impact of the War ► Emergence of the U. S. as a great power § Industrial § Military ► Naval Power ► U. S. move toward Imperialism ► First “Media War”
Impact of the War ► Emergence of the U. S. as a great power § Industrial § Military ► Naval Power ► U. S. move toward Imperialism ► First “Media War”


