d8c4bea917e0dbbfaa7e6b975e74c2d4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

® The SIOP Model BUILDING BACKGROUND

Content Objectives We will: • Identify techniques for connecting students’ personal experiences, cultural background, and past learning to lesson concepts. • Explain the key elements of academic language.

Language Objectives We will: • Produce a variety of sentence types to analyze the language needed in a sociocultural context with a small group • Use an “I can” statement to describe how we will apply Building Background in our classes using our notes
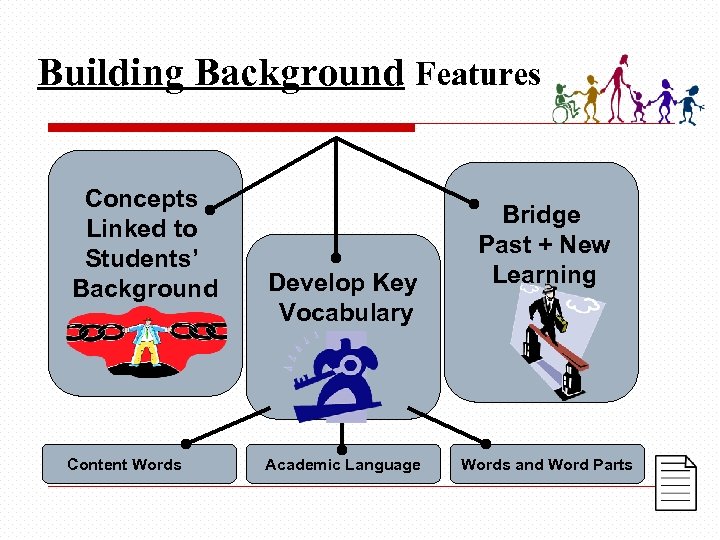
Building Background Features Concepts Linked to Students’ Background Content Words Develop Key Vocabulary Academic Language Bridge Past + New Learning Words and Word Parts
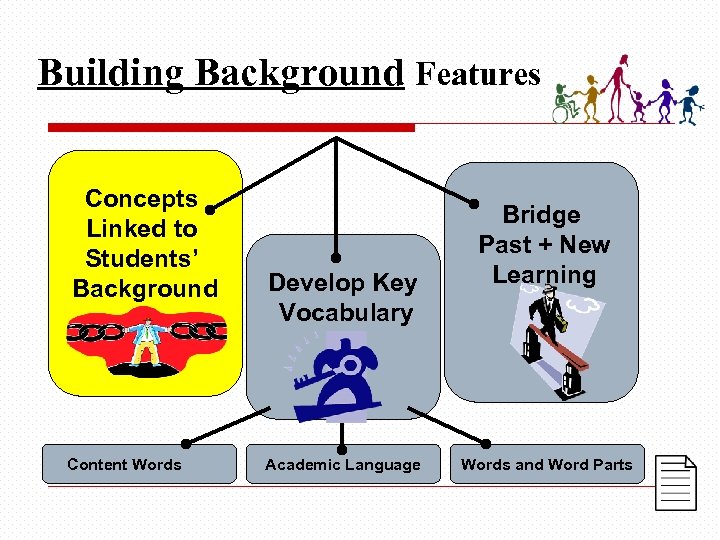
Building Background Features Concepts Linked to Students’ Background Content Words Develop Key Vocabulary Academic Language Bridge Past + New Learning Words and Word Parts

Concepts linked to students’ background experiences

Deep Culture vs. Surface Culture dress music food ting da concepts of time beliefs es ti amily f hea me lth & dic ine

Socioculturally Supportive Climate • How are we doing in creating a socioculturally supportive climate? • What can I do in my classroom? • Do I know about the different cultural backgrounds of my students?

Cultural Comparisons (Hofstede) • Individualist • Collectivist Geert Hostede Cultural Dimensions http: //www. geert-hofstede. com Hofstede, G (1986) 'Cultural differences in teaching and learning' International Journal of Intercultural Relations

Individualism │ │ │ │ │ Collectivism Hofstede’s Ratings USA Australia Great Britain Canada Italy France, Sweden Germany Israel Spain India Argentina, Japan Iran Arab countries Philippines Mexico East Africa Singapore, Thailand West Africa South Korea Costa Rica Indonesia, Pakistan Guatemala 91 90 89 80 76 71 67 54 51 48 46 41 38 32 30 27 20 20 18 15 14 6

Academic Differences MATH In some Latin American countries • Division may be done in a different way. • A period is used to indicate thousands, 3. 000 to indicate three thousand. • A comma is used to separate a decimal from a whole number 0, 5 instead of 0. 5

More Academic differences • Dates are written differently: 5/7/90 would mean July 5, 1990. • Days of the week and months of the year are not capitalized in Spanish. • Discourse patterns differ among cultures.

Do we know… 13

Political Cartoon

Political Cartoon • Think about a joke or a cartoon that you didn’t understand, such as a political cartoon. • Why was it confusing or not amusing? • What information might you have needed in order for it to make sense?
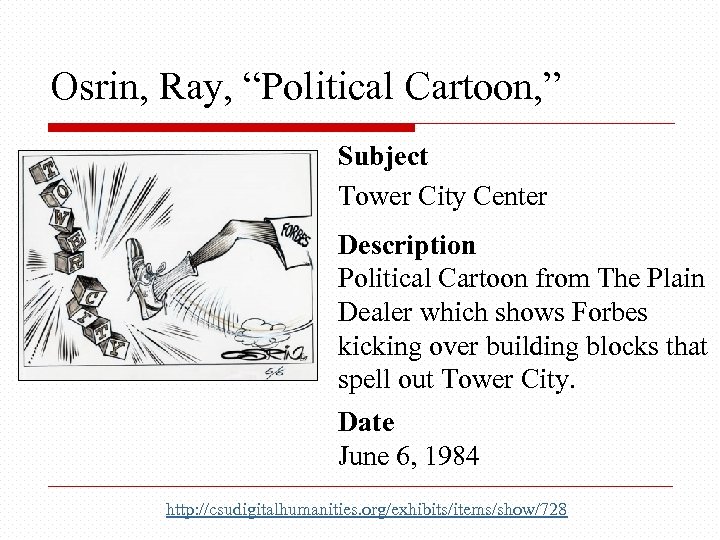
Osrin, Ray, “Political Cartoon, ” Subject Tower City Center Description Political Cartoon from The Plain Dealer which shows Forbes kicking over building blocks that spell out Tower City. Date June 6, 1984 http: //csudigitalhumanities. org/exhibits/items/show/728

If no link, Build Background Culturally embedded: • • • Political cartoons Ground Hog Day A day at the beach Cultural assumptions: e. g. Frosty the Snowman Fairy tales: e. g. Cinderella American history

Thinking about your classroom activities Consider: • Have students had an experience they can link? • Will the assignment or classroom activity bring up unpleasant associations? • Is the assignment culturally appropriate?

Social & Cultural Processes and Academic Language fish-bowl-download trussvillecityschools. com

Sociocultural Context http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=m. A 34 eny--P 4
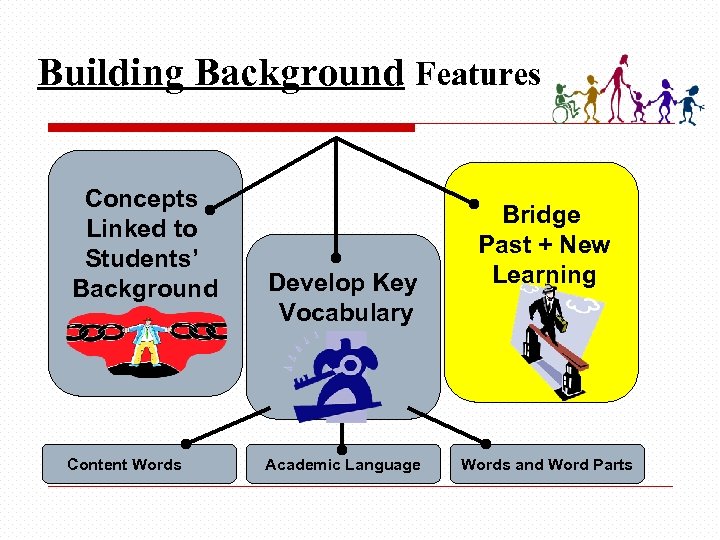
Building Background Features Concepts Linked to Students’ Background Content Words Develop Key Vocabulary Academic Language Bridge Past + New Learning Words and Word Parts

How Can We Bridge Past Learning to New Concepts? SIOP says be… • Explicit • Intentionally planned • Do a brief review of prior lesson
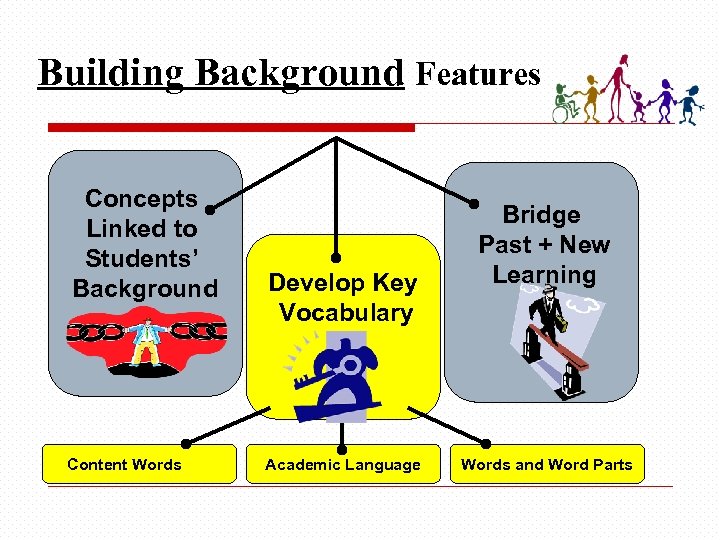
Building Background Features Concepts Linked to Students’ Background Content Words Develop Key Vocabulary Academic Language Bridge Past + New Learning Words and Word Parts
Determining Key Vocabulary • The SIOP Model • Common Core State Standards http: //mediasite. k 12. hi. us/HIDOE/Viewer/? peid=d 0 a 7 b 57 e 02 df 43 eebcd 625 e 390 c 0826 e 1 d • WIDA
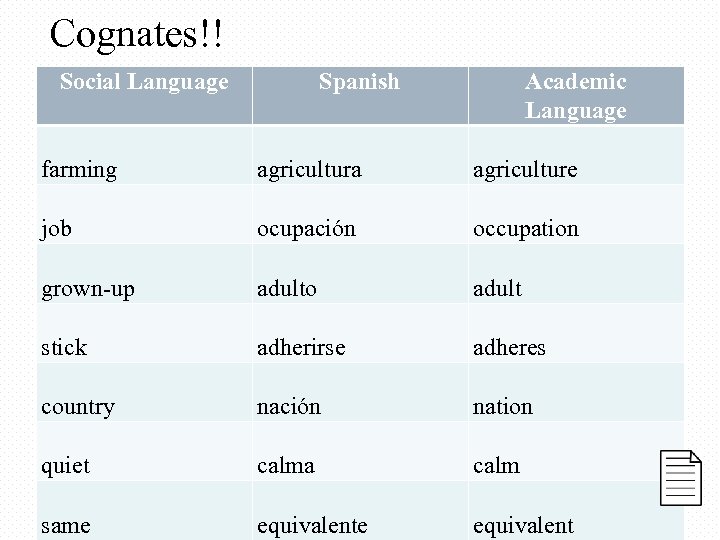
Cognates!! Social Language Spanish Academic Language farming agricultura agriculture job ocupación occupation grown-up adulto adult stick adherirse adheres country nación nation quiet calma calm same equivalent

Word Parts: Roots and Affixes How can we help students learn vocabulary? prefix + root + suffix
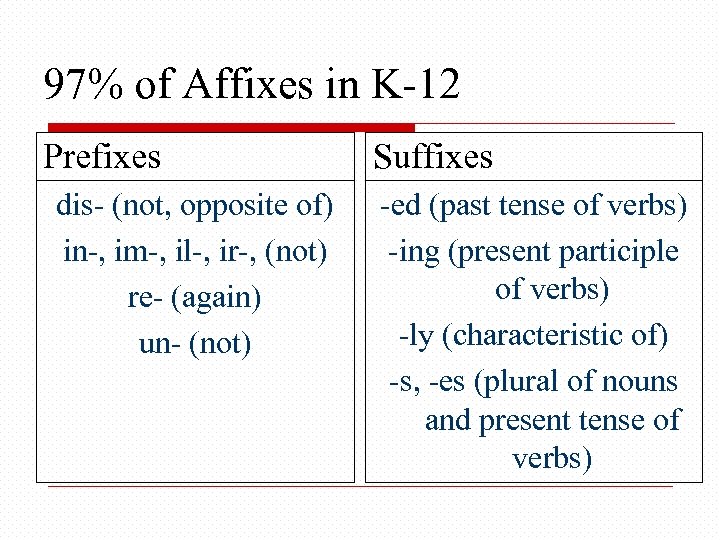
97% of Affixes in K-12 Prefixes dis- (not, opposite of) in-, im-, il-, ir-, (not) re- (again) un- (not) Suffixes -ed (past tense of verbs) -ing (present participle of verbs) -ly (characteristic of) -s, -es (plural of nouns and present tense of verbs)

Tiers of Language Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 3
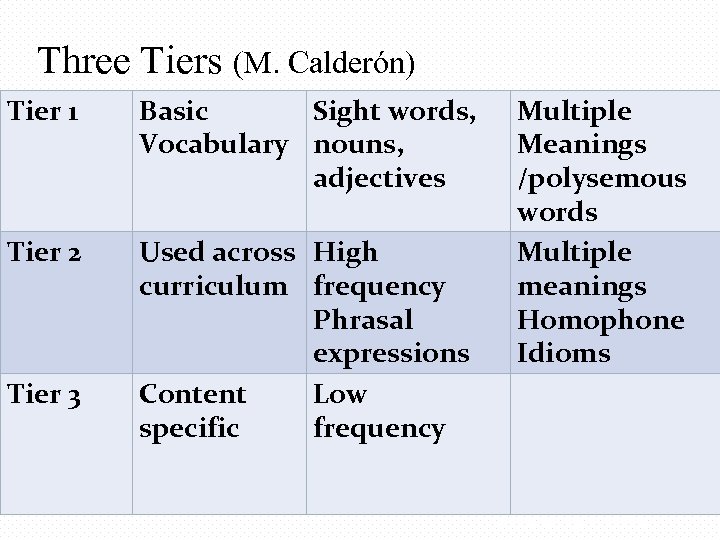
Three Tiers (M. Calderón) Tier 1 Basic Sight words, Vocabulary nouns, adjectives Tier 2 Used across High curriculum frequency Phrasal expressions Content Low specific frequency Tier 3 Multiple Meanings /polysemous words Multiple meanings Homophone Idioms Emphasize key vocabulary
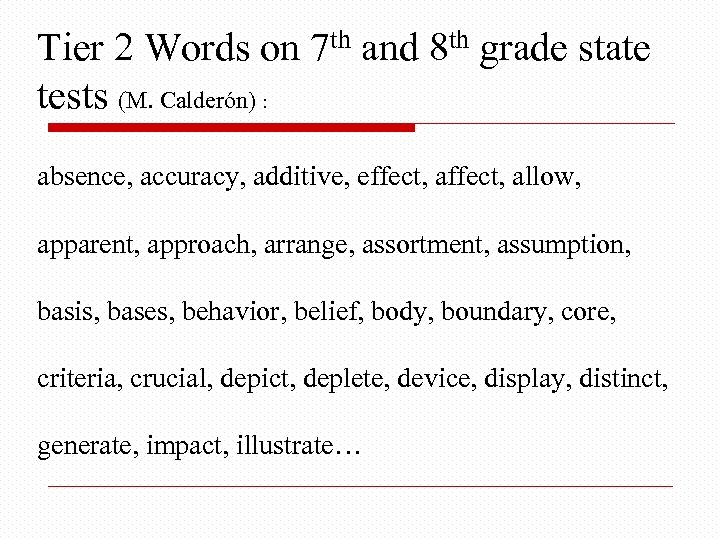
Tier 2 Words on 7 th and 8 th grade state tests (M. Calderón) : absence, accuracy, additive, effect, allow, apparent, approach, arrange, assortment, assumption, basis, bases, behavior, belief, body, boundary, core, criteria, crucial, depict, deplete, device, display, distinct, generate, impact, illustrate…

Tier 2 words on 11 th and 12 th grade state tests (M. Calderón) : vary, underlying, albeit, solely, successive, denote, crucial, oddly, analogous, compiled, oddly, whereby, notwithstanding, forthcoming, ultimately, assume, coincide, hence, widespread, implicit…

Multiple Meanings / Polysemous Words Moises http: //youtu. be/I 6 Y 0 HAj. LKYI

Idioms and Sayings “It’s raining cats and dogs out there!” “Don’t count your chickens before they hatch” “You need to get your ducks in a row” “He talks out of both sides of his mouth!” ___________________________ 33

The “Student’s” Voice Margarita Calderón A Queen’s Wish One gray winter day the elderly queen summoned all her grandchildren to the castle. “I have been fortunate to have lived a long life, ” she said. “But in time your generation will rule the country. You must work persistently to help the people and take care of the land. “We will always work hard, ” the children replied. “You must also be faithful to your brothers and sisters, no matter what, ” the queen said. Calderón & Associates

Activity • Underline the words you think are simple (Tier 1) • Circle the words you think are more difficult (Tier 2) • Put a rectangle around the words that you think are the key vocabulary (Tier 3)
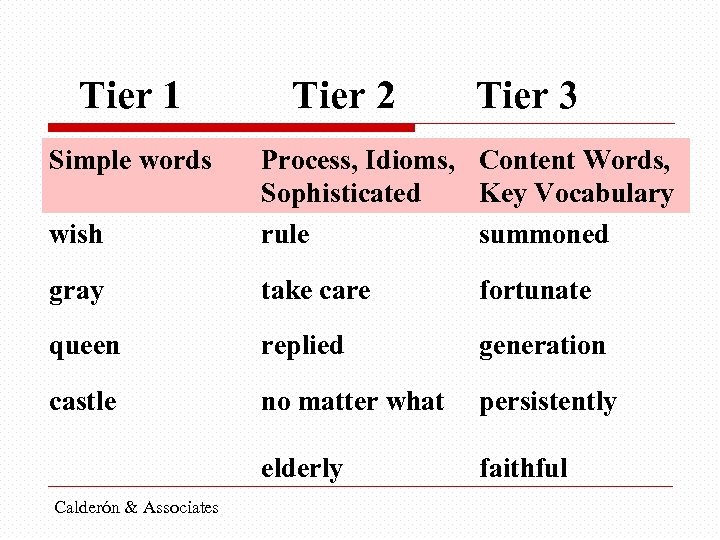
Tier 1 Simple words Tier 2 Tier 3 wish Process, Idioms, Content Words, Sophisticated Key Vocabulary rule summoned gray take care fortunate queen replied generation castle no matter what persistently elderly faithful Calderón & Associates

What Can I Use Right Away to Help My ELLs?

Sample SIOP Lesson Plan

Owning Building Background Continue to write a lesson plan you can use including the features of Building Background • Concepts linked to students’ backgrounds • Links between past learning and new learning • Develop key vocabulary

Content Objectives How did we: • Identify techniques for connecting students’ personal experiences, cultural background, and past learning to lesson concepts. • Explain the key elements of academic language.

Language Objectives How did we: • Produce a variety of sentence types to analyze the language needed in a sociocultural context with a small group • Use an “I can” statement to describe how we will apply Building Background in our classes using our notes
d8c4bea917e0dbbfaa7e6b975e74c2d4.ppt