ce3d29f0ab2b1fdd3079d23ccfdd0269.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 The Significance of the Common European Framework for Teaching Modern Languages Today Jürgen Quetz Goethe-University Frankfurt am Main (Germany) Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
The Significance of the Common European Framework for Teaching Modern Languages Today Jürgen Quetz Goethe-University Frankfurt am Main (Germany) Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 Authors: Daniel Coste Brian North Joseph Sheils John L. M. Trim Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
Authors: Daniel Coste Brian North Joseph Sheils John L. M. Trim Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 The Common European Framework is … § one of the Council of Europe’s statements of language policy - of worldwide interest and influence § a model of competence § a help for planning FLT § an instrument to compare FLT concepts and materials, tests and qualifications Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
The Common European Framework is … § one of the Council of Europe’s statements of language policy - of worldwide interest and influence § a model of competence § a help for planning FLT § an instrument to compare FLT concepts and materials, tests and qualifications Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 The CEF is. . . • not a syllabus • not prescriptive • no manual for better language teaching Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
The CEF is. . . • not a syllabus • not prescriptive • no manual for better language teaching Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 © Hans-Jürgen Krumm Plurilingualism and Intercultural Competences as main political aims of the Co. E Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
© Hans-Jürgen Krumm Plurilingualism and Intercultural Competences as main political aims of the Co. E Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 plurilingual individuals multilingual societies CEF, Chapters 1 & 8 Consequences for FLT: (1) 1 + 2 (= mother tongue + 2 living modern languages in the school curriculum) (2) Intercultural Communicative Competence Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
plurilingual individuals multilingual societies CEF, Chapters 1 & 8 Consequences for FLT: (1) 1 + 2 (= mother tongue + 2 living modern languages in the school curriculum) (2) Intercultural Communicative Competence Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 The CEF as a model of competence CEF, Chapters 3 - 5 Language use, embracing language learning, comprises the actions performed by persons who. . . develop a range of competences, both general and in particular communicative language competences. They draw on the competences at their disposal in various contexts under various conditions and under various constraints to engage in language activities involving language processes to produce and/or receive texts. . . , activating those strategies which seem most appropriate for carrying out the tasks to be accomplished. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
The CEF as a model of competence CEF, Chapters 3 - 5 Language use, embracing language learning, comprises the actions performed by persons who. . . develop a range of competences, both general and in particular communicative language competences. They draw on the competences at their disposal in various contexts under various conditions and under various constraints to engage in language activities involving language processes to produce and/or receive texts. . . , activating those strategies which seem most appropriate for carrying out the tasks to be accomplished. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 Is the CEF like a ladder with equidistant steps? C 2 C 1 B 2 B 1 A 2 A 1 Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
Is the CEF like a ladder with equidistant steps? C 2 C 1 B 2 B 1 A 2 A 1 Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
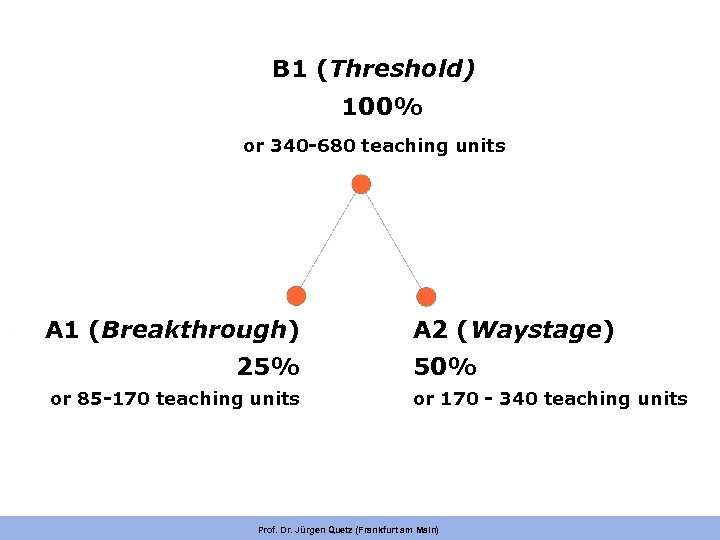 B 1 (Threshold) 100% or 340 -680 teaching units A 1 (Breakthrough) 25% or 85 -170 teaching units A 2 (Waystage) 50% or 170 - 340 teaching units Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
B 1 (Threshold) 100% or 340 -680 teaching units A 1 (Breakthrough) 25% or 85 -170 teaching units A 2 (Waystage) 50% or 170 - 340 teaching units Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 This 1 st dimension is used to define levels of § courses § course books & materials § tests and qualifications Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
This 1 st dimension is used to define levels of § courses § course books & materials § tests and qualifications Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
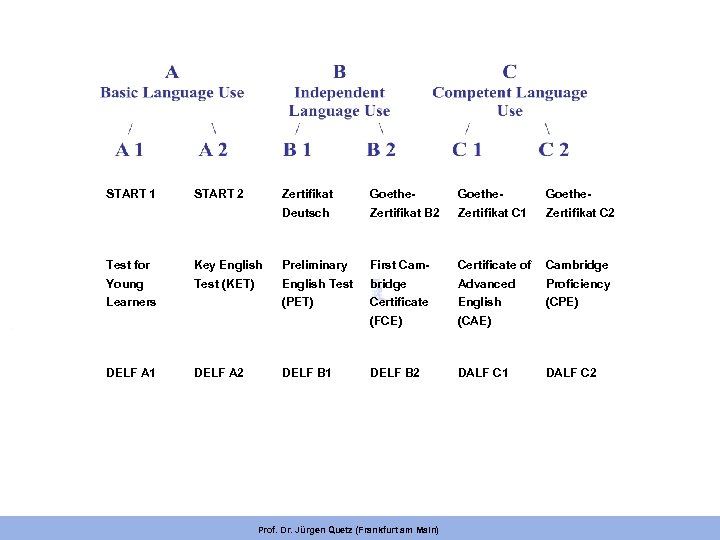 START 1 START 2 Zertifikat Goethe- Deutsch Zertifikat B 2 Zertifikat C 1 Zertifikat C 2 Test for Key English Preliminary First Cam- Certificate of Cambridge Young Test (KET) English Test bridge Advanced Proficiency (PET) Certificate English (CPE) (FCE) (CAE) DELF B 2 DALF C 1 Learners DELF A 1 DELF A 2 DELF B 1 Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main) DALF C 2
START 1 START 2 Zertifikat Goethe- Deutsch Zertifikat B 2 Zertifikat C 1 Zertifikat C 2 Test for Key English Preliminary First Cam- Certificate of Cambridge Young Test (KET) English Test bridge Advanced Proficiency (PET) Certificate English (CPE) (FCE) (CAE) DELF B 2 DALF C 1 Learners DELF A 1 DELF A 2 DELF B 1 Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main) DALF C 2
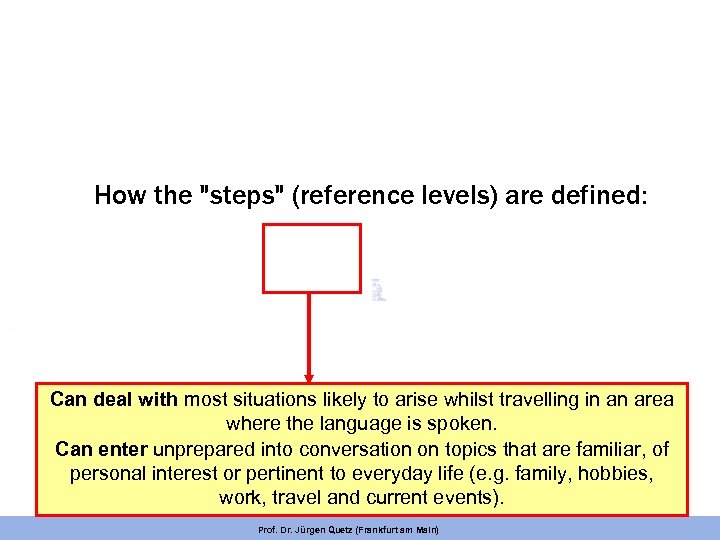 How the "steps" (reference levels) are defined: Can deal with most situations likely to arise whilst travelling in an area where the language is spoken. Can enter unprepared into conversation on topics that are familiar, of personal interest or pertinent to everyday life (e. g. family, hobbies, work, travel and current events). Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
How the "steps" (reference levels) are defined: Can deal with most situations likely to arise whilst travelling in an area where the language is spoken. Can enter unprepared into conversation on topics that are familiar, of personal interest or pertinent to everyday life (e. g. family, hobbies, work, travel and current events). Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
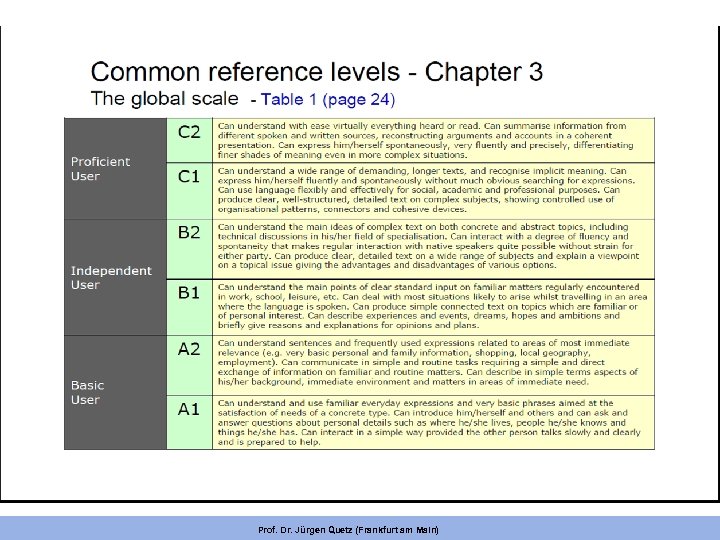
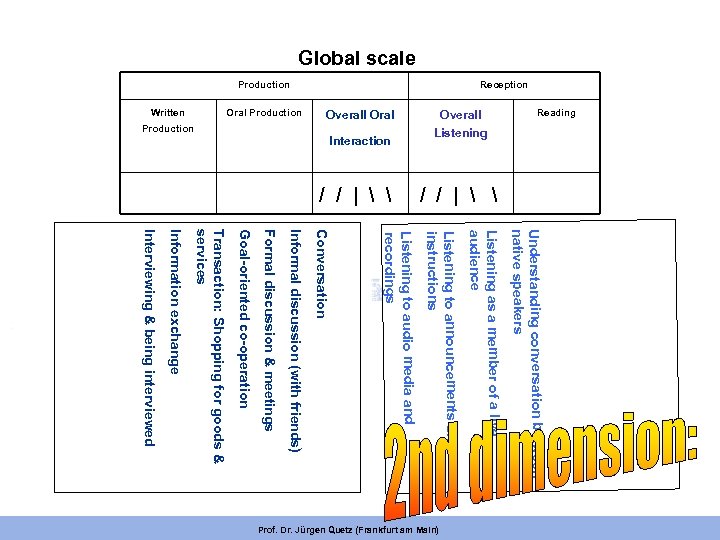 Global scale / | / / / | Understanding conversation between native speakers Listening as a member of a live audience Listening to announcements and instructions Listening to audio media and recordings Conversation Informal discussion (with friends) Formal discussion & meetings Goal-oriented co-operation Transaction: Shopping for goods & services Information exchange Interviewing & being interviewed Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main) Reading Overall Oral Production Written Listening Interaction Production Reception Production
Global scale / | / / / | Understanding conversation between native speakers Listening as a member of a live audience Listening to announcements and instructions Listening to audio media and recordings Conversation Informal discussion (with friends) Formal discussion & meetings Goal-oriented co-operation Transaction: Shopping for goods & services Information exchange Interviewing & being interviewed Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main) Reading Overall Oral Production Written Listening Interaction Production Reception Production
 Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
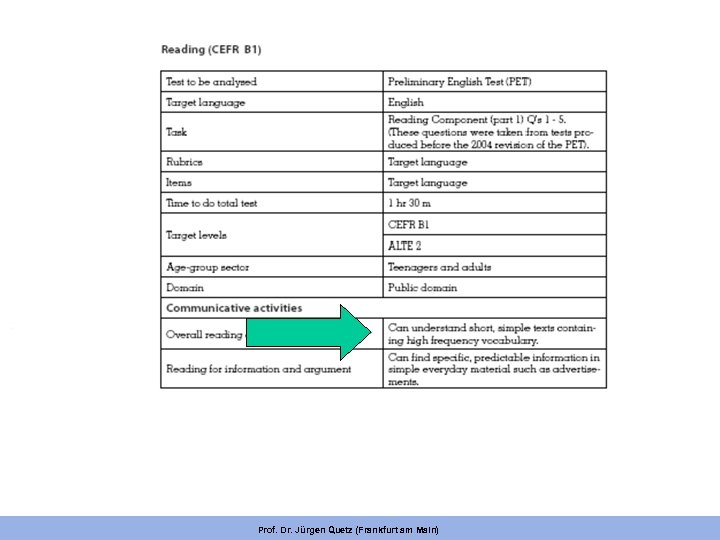
 READING (B 1) Look at the sign in each box on the left. Someone asks you what it means. Mark the letter next to the correct explanation – A, B, C or D – on your answer sheet. Example A B Get a free film with every one you buy. C One film free with each camera. D Films bought here are printed free. A You can buy tickets between 9 and 4 or just before the show begins. B The ticket office remains open for 15 minutes during each performance. C When there is a performance, tickets are not available after 4 o’clock. D Regency Cameras Buy two films and get one FREE Buy three films for the price of two. Tickets are on sale at the office until 15 minutes before the show starts. 1. Theatre Ticket Office Open every day 9 – 4 and for 15 minutes before each performance 2. A LEAVE THIS PARKING SPACE REE FOR EMERGENCY VEHICLES Visitors can park here if the space is empty. B Visitors can park here free in an emergency. C Visitors must not park their vehicles here. D Visitors do not need to pay to park here. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
READING (B 1) Look at the sign in each box on the left. Someone asks you what it means. Mark the letter next to the correct explanation – A, B, C or D – on your answer sheet. Example A B Get a free film with every one you buy. C One film free with each camera. D Films bought here are printed free. A You can buy tickets between 9 and 4 or just before the show begins. B The ticket office remains open for 15 minutes during each performance. C When there is a performance, tickets are not available after 4 o’clock. D Regency Cameras Buy two films and get one FREE Buy three films for the price of two. Tickets are on sale at the office until 15 minutes before the show starts. 1. Theatre Ticket Office Open every day 9 – 4 and for 15 minutes before each performance 2. A LEAVE THIS PARKING SPACE REE FOR EMERGENCY VEHICLES Visitors can park here if the space is empty. B Visitors can park here free in an emergency. C Visitors must not park their vehicles here. D Visitors do not need to pay to park here. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 Also in Chapter 4 („ 2 nd Dimension“): Reception Strategies Planning Execution Evaluation Repair - Framing (selecting mental set, activating schemata, setting up expectations). - Identifying cues and inferring from them. - Hypothesis testing: matching cues to schemata. - Revising hypotheses. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
Also in Chapter 4 („ 2 nd Dimension“): Reception Strategies Planning Execution Evaluation Repair - Framing (selecting mental set, activating schemata, setting up expectations). - Identifying cues and inferring from them. - Hypothesis testing: matching cues to schemata. - Revising hypotheses. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 This 2 nd dimension is used to § describe communicative activities and strategies for courses & tests. . . § and the kind of language you need to carry out the activities; § it is the basis for test specifications in almost all modern testing systems. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
This 2 nd dimension is used to § describe communicative activities and strategies for courses & tests. . . § and the kind of language you need to carry out the activities; § it is the basis for test specifications in almost all modern testing systems. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 Canale und Swain (1981; 1983) Communicative Competence = linguistic competence (lexis, morphology, syntax, pronunciation, …) sociolinguistic competence (context adequate communication, awareness of rules of social interaction in a specific culture) discourse competence (e. g. produce a coherent spoken or written text) strategic competence (use of verbal and non-verbal strategies of communication in order to avoid break-down of communication) Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
Canale und Swain (1981; 1983) Communicative Competence = linguistic competence (lexis, morphology, syntax, pronunciation, …) sociolinguistic competence (context adequate communication, awareness of rules of social interaction in a specific culture) discourse competence (e. g. produce a coherent spoken or written text) strategic competence (use of verbal and non-verbal strategies of communication in order to avoid break-down of communication) Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
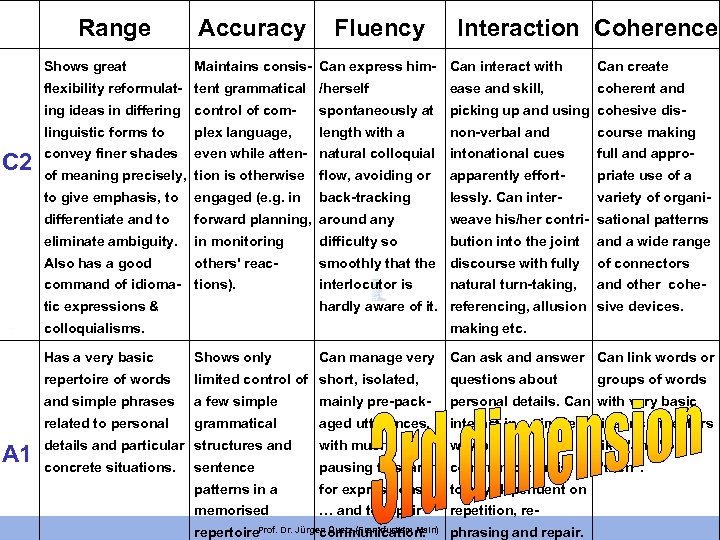 Range Shows great Accuracy Fluency Interaction Coherence Maintains consis- Can express him- Can interact with Can create flexibility reformulat- tent grammatical /herself ing ideas in differing control of com- spontaneously at picking up and using cohesive dis- linguistic forms to C 2 ease and skill, coherent and plex language, length with a non-verbal and course making convey finer shades even while atten- natural colloquial intonational cues full and appro- of meaning precisely, tion is otherwise flow, avoiding or apparently effort- priate use of a to give emphasis, to engaged (e. g. in back-tracking lessly. Can inter- variety of organi- differentiate and to forward planning, around any weave his/her contri- sational patterns eliminate ambiguity. in monitoring difficulty so bution into the joint Also has a good others' reac- smoothly that the discourse with fully of connectors command of idioma- tions). interlocutor is and other cohe- tic expressions & hardly aware of it. referencing, allusion sive devices. colloquialisms. natural turn-taking, and a wide range making etc. Has a very basic repertoire of words limited control of short, isolated, questions about and simple phrases a few simple mainly pre-pack- personal details. Can with very basic related to personal A 1 Shows only Can manage very Can ask and answer Can link words or grammatical aged utterances, interact in a simple linear connectors details and particular structures and with much way but like "and" or concrete situations. sentence pausing to search communication is patterns in a for expressions, totally dependent on memorised … and to repair repetition, re- repertoire. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main) phrasing and repair. communication. groups of words "then".
Range Shows great Accuracy Fluency Interaction Coherence Maintains consis- Can express him- Can interact with Can create flexibility reformulat- tent grammatical /herself ing ideas in differing control of com- spontaneously at picking up and using cohesive dis- linguistic forms to C 2 ease and skill, coherent and plex language, length with a non-verbal and course making convey finer shades even while atten- natural colloquial intonational cues full and appro- of meaning precisely, tion is otherwise flow, avoiding or apparently effort- priate use of a to give emphasis, to engaged (e. g. in back-tracking lessly. Can inter- variety of organi- differentiate and to forward planning, around any weave his/her contri- sational patterns eliminate ambiguity. in monitoring difficulty so bution into the joint Also has a good others' reac- smoothly that the discourse with fully of connectors command of idioma- tions). interlocutor is and other cohe- tic expressions & hardly aware of it. referencing, allusion sive devices. colloquialisms. natural turn-taking, and a wide range making etc. Has a very basic repertoire of words limited control of short, isolated, questions about and simple phrases a few simple mainly pre-pack- personal details. Can with very basic related to personal A 1 Shows only Can manage very Can ask and answer Can link words or grammatical aged utterances, interact in a simple linear connectors details and particular structures and with much way but like "and" or concrete situations. sentence pausing to search communication is patterns in a for expressions, totally dependent on memorised … and to repair repetition, re- repertoire. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main) phrasing and repair. communication. groups of words "then".
 ies rateg g st in plann tion pensa ir com pa g & re in onitor m es etenc mp tic co cy, . . . ) s lingui accura e, (rang ompetence t c exical tical compe ence l a es et etenc gramm gical comp p olo ic com g at phon pragm urn-takin & t ourse raction: t disc pmen e elo int tic dev thema ce heren co y fluenc Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
ies rateg g st in plann tion pensa ir com pa g & re in onitor m es etenc mp tic co cy, . . . ) s lingui accura e, (rang ompetence t c exical tical compe ence l a es et etenc gramm gical comp p olo ic com g at phon pragm urn-takin & t ourse raction: t disc pmen e elo int tic dev thema ce heren co y fluenc Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 This 3 rd dimension reflects traditional criteria for assessing language production and is also used to describe the "quality" of texts and text production Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
This 3 rd dimension reflects traditional criteria for assessing language production and is also used to describe the "quality" of texts and text production Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 Marking Criteria Oral Examination Criterion 1: Expression Assessment is based on the extent to which the language used (vocabulary and functional exponents) is appropriate to the task and the role relationship between the two candidates. Expression is: Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
Marking Criteria Oral Examination Criterion 1: Expression Assessment is based on the extent to which the language used (vocabulary and functional exponents) is appropriate to the task and the role relationship between the two candidates. Expression is: Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
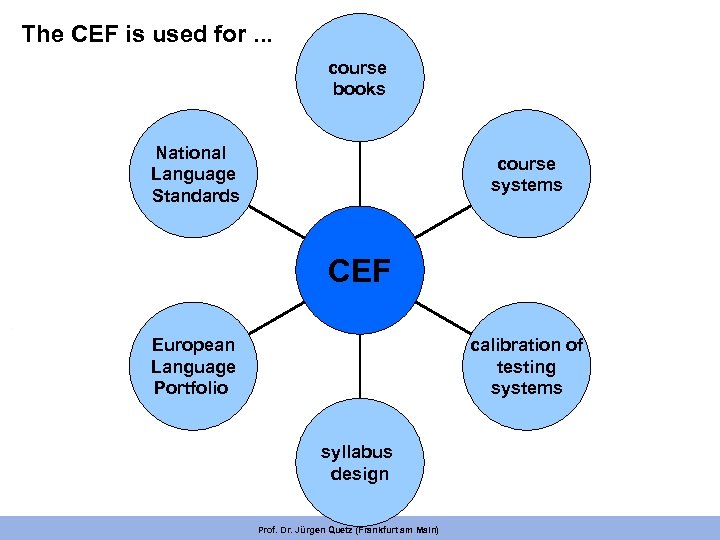 The CEF is used for. . . course books National Language Standards course systems CEF European Language Portfolio calibration of testing systems syllabus design Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
The CEF is used for. . . course books National Language Standards course systems CEF European Language Portfolio calibration of testing systems syllabus design Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
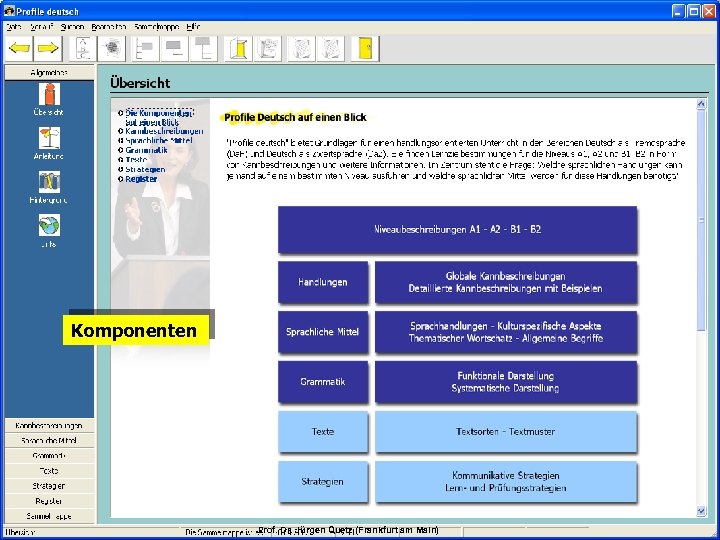 Die Komponenten Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
Die Komponenten Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 Ge. R descriptor Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
Ge. R descriptor Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 • The CEF is by far the most important and most influential document of language policy in Europe. • It is used in all member countries of the EU (and far beyond - even in Asia). • It has been translated into almost 40 languages (including Korean & Japanese). • It serves as a guideline for most innovations in the field of FLT. • There is a wealth of teaching material with transparent levels defined according to the CEF. • It is used for defining cut-off points for entry examinations for European countries (Test. Da. F, Goethe exams). • Even ETS has felt it necessary to relate TOEIC / TOEFL tests to the CEF system (to protect their chances on the European market). Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
• The CEF is by far the most important and most influential document of language policy in Europe. • It is used in all member countries of the EU (and far beyond - even in Asia). • It has been translated into almost 40 languages (including Korean & Japanese). • It serves as a guideline for most innovations in the field of FLT. • There is a wealth of teaching material with transparent levels defined according to the CEF. • It is used for defining cut-off points for entry examinations for European countries (Test. Da. F, Goethe exams). • Even ETS has felt it necessary to relate TOEIC / TOEFL tests to the CEF system (to protect their chances on the European market). Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
 CEF and methodology task-based approach focus on language activities (listening, reading, speaking, writing), not so much on formal knowledge: "Teach the language, not about the language. " Practice of these activities in classroom tasks, through project work (e. g. Airport project), use of media to get authentic texts into the classroom and take learners beyond the classroom. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)
CEF and methodology task-based approach focus on language activities (listening, reading, speaking, writing), not so much on formal knowledge: "Teach the language, not about the language. " Practice of these activities in classroom tasks, through project work (e. g. Airport project), use of media to get authentic texts into the classroom and take learners beyond the classroom. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Quetz (Frankfurt am Main)


