8d6d128f34ec29bbe73311edeb0b680c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 THE SELECT STATEMENT Purpose: designates a file and points to its physical location Syntax Definition: SELECT file-name-1 ASSIGN TO implementor-name-1 [ORGANIZATION IS LINE SEQUENTIAL] Examples: SELECT INPUT-FILE ASSIGN TO “lab 1. dat”. select input-file assign “lab 1. dat”. SELECT input-file ASSIGN “lab 1. dat” organization is line sequential. select INPUT-FILE assign to “lab 1. dat” organization line sequential. Select abcdefg ASSIGN ‘lab 1. dat’. Statement Syntax For Your Information The ASSIGN clause information is machine dependent • c: cobolprelabin. dat • /usr/class/cis 314/prelab/lab 1. dat • lab 1. dat No period on Syntax Defn - Why? ! Remember, the file-name-1 is the user-defined data name used on the FD associated with the physical file implementor-name-1 Starts in Area B 1 SELECT for every file your program accesses 1
THE SELECT STATEMENT Purpose: designates a file and points to its physical location Syntax Definition: SELECT file-name-1 ASSIGN TO implementor-name-1 [ORGANIZATION IS LINE SEQUENTIAL] Examples: SELECT INPUT-FILE ASSIGN TO “lab 1. dat”. select input-file assign “lab 1. dat”. SELECT input-file ASSIGN “lab 1. dat” organization is line sequential. select INPUT-FILE assign to “lab 1. dat” organization line sequential. Select abcdefg ASSIGN ‘lab 1. dat’. Statement Syntax For Your Information The ASSIGN clause information is machine dependent • c: cobolprelabin. dat • /usr/class/cis 314/prelab/lab 1. dat • lab 1. dat No period on Syntax Defn - Why? ! Remember, the file-name-1 is the user-defined data name used on the FD associated with the physical file implementor-name-1 Starts in Area B 1 SELECT for every file your program accesses 1
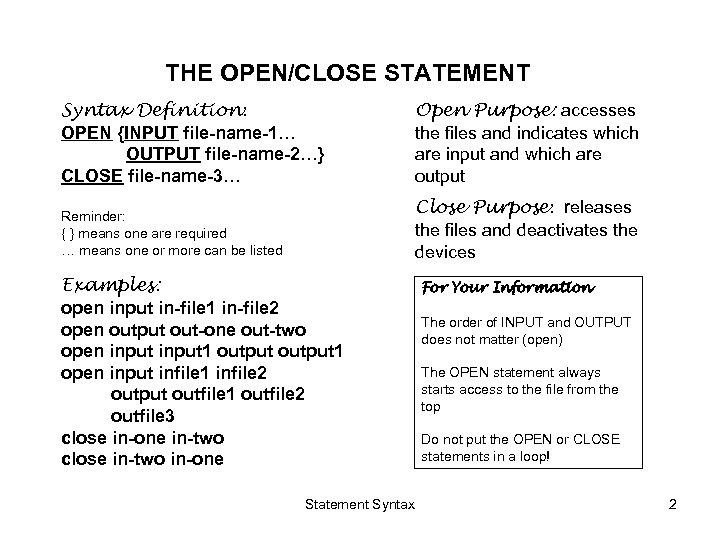 THE OPEN/CLOSE STATEMENT Syntax Definition: OPEN {INPUT file-name-1… OUTPUT file-name-2…} CLOSE file-name-3… Open Purpose: accesses the files and indicates which are input and which are output Reminder: { } means one are required … means one or more can be listed Close Purpose: releases the files and deactivates the devices Examples: open input in-file 1 in-file 2 open output out-one out-two open input 1 output 1 open input infile 1 infile 2 output outfile 1 outfile 2 outfile 3 close in-one in-two close in-two in-one Statement Syntax For Your Information The order of INPUT and OUTPUT does not matter (open) The OPEN statement always starts access to the file from the top Do not put the OPEN or CLOSE statements in a loop! 2
THE OPEN/CLOSE STATEMENT Syntax Definition: OPEN {INPUT file-name-1… OUTPUT file-name-2…} CLOSE file-name-3… Open Purpose: accesses the files and indicates which are input and which are output Reminder: { } means one are required … means one or more can be listed Close Purpose: releases the files and deactivates the devices Examples: open input in-file 1 in-file 2 open output out-one out-two open input 1 output 1 open input infile 1 infile 2 output outfile 1 outfile 2 outfile 3 close in-one in-two close in-two in-one Statement Syntax For Your Information The order of INPUT and OUTPUT does not matter (open) The OPEN statement always starts access to the file from the top Do not put the OPEN or CLOSE statements in a loop! 2
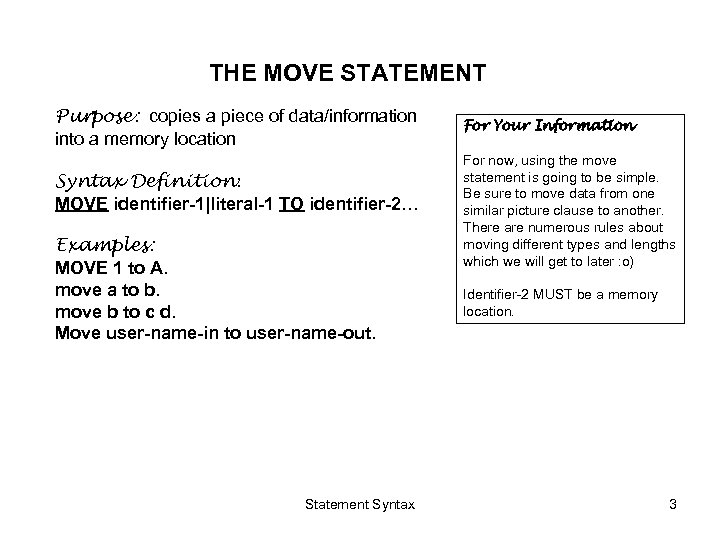 THE MOVE STATEMENT Purpose: copies a piece of data/information into a memory location Syntax Definition: MOVE identifier-1|literal-1 TO identifier-2… Examples: MOVE 1 to A. move a to b. move b to c d. Move user-name-in to user-name-out. Statement Syntax For Your Information For now, using the move statement is going to be simple. Be sure to move data from one similar picture clause to another. There are numerous rules about moving different types and lengths which we will get to later : o) Identifier-2 MUST be a memory location. 3
THE MOVE STATEMENT Purpose: copies a piece of data/information into a memory location Syntax Definition: MOVE identifier-1|literal-1 TO identifier-2… Examples: MOVE 1 to A. move a to b. move b to c d. Move user-name-in to user-name-out. Statement Syntax For Your Information For now, using the move statement is going to be simple. Be sure to move data from one similar picture clause to another. There are numerous rules about moving different types and lengths which we will get to later : o) Identifier-2 MUST be a memory location. 3
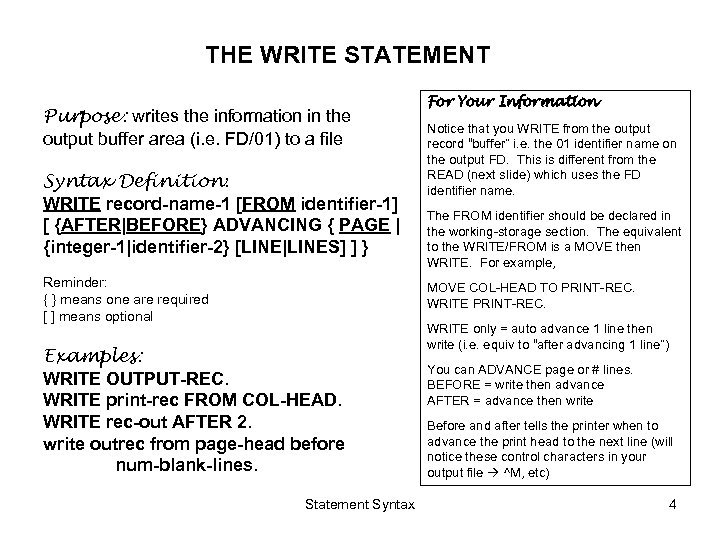 THE WRITE STATEMENT Purpose: writes the information in the output buffer area (i. e. FD/01) to a file Syntax Definition: WRITE record-name-1 [FROM identifier-1] [ {AFTER|BEFORE} ADVANCING { PAGE | {integer-1|identifier-2} [LINE|LINES] ] } Reminder: { } means one are required [ ] means optional For Your Information Notice that you WRITE from the output record “buffer” i. e. the 01 identifier name on the output FD. This is different from the READ (next slide) which uses the FD identifier name. The FROM identifier should be declared in the working-storage section. The equivalent to the WRITE/FROM is a MOVE then WRITE. For example, MOVE COL-HEAD TO PRINT-REC. WRITE PRINT-REC. Examples: WRITE OUTPUT-REC. WRITE print-rec FROM COL-HEAD. WRITE rec-out AFTER 2. write outrec from page-head before num-blank-lines. Statement Syntax WRITE only = auto advance 1 line then write (i. e. equiv to “after advancing 1 line”) You can ADVANCE page or # lines. BEFORE = write then advance AFTER = advance then write Before and after tells the printer when to advance the print head to the next line (will notice these control characters in your output file ^M, etc) 4
THE WRITE STATEMENT Purpose: writes the information in the output buffer area (i. e. FD/01) to a file Syntax Definition: WRITE record-name-1 [FROM identifier-1] [ {AFTER|BEFORE} ADVANCING { PAGE | {integer-1|identifier-2} [LINE|LINES] ] } Reminder: { } means one are required [ ] means optional For Your Information Notice that you WRITE from the output record “buffer” i. e. the 01 identifier name on the output FD. This is different from the READ (next slide) which uses the FD identifier name. The FROM identifier should be declared in the working-storage section. The equivalent to the WRITE/FROM is a MOVE then WRITE. For example, MOVE COL-HEAD TO PRINT-REC. WRITE PRINT-REC. Examples: WRITE OUTPUT-REC. WRITE print-rec FROM COL-HEAD. WRITE rec-out AFTER 2. write outrec from page-head before num-blank-lines. Statement Syntax WRITE only = auto advance 1 line then write (i. e. equiv to “after advancing 1 line”) You can ADVANCE page or # lines. BEFORE = write then advance AFTER = advance then write Before and after tells the printer when to advance the print head to the next line (will notice these control characters in your output file ^M, etc) 4
 THE READ STATEMENT Purpose: fills the input record buffer area with one record of information from the input file Syntax Definition: READ file-name-1 [ INTO identifier-1 ] AT END statement-1… [ NOT AT END statement-2… ] [END-READ] Examples: READ input-file at end move “Y” to eof. Read input-file into ws-work-area at end perform 999 -total-data. Read file-in-1 at end move “yes” to end-of file move “the end” to last-output close file-in END-READ For Your Information Notice that after the READ reserve word is the name of the FD, unlike the WRITE which uses the record-name (i. e. 01). The first period encountered will end the READ statement. The END-READ is called a scope terminator. Statement-1… will execute when the end of the file is reached Statement-2… will execute when you READ and the end of the file marker is not reached The INTO identifier should be declared in the working-storage section. The equivalent to the READ/INTO is a READ then MOVE. For example, READ input-file AT END… MOVE input-rec to ws-work-area. Statement Syntax 5
THE READ STATEMENT Purpose: fills the input record buffer area with one record of information from the input file Syntax Definition: READ file-name-1 [ INTO identifier-1 ] AT END statement-1… [ NOT AT END statement-2… ] [END-READ] Examples: READ input-file at end move “Y” to eof. Read input-file into ws-work-area at end perform 999 -total-data. Read file-in-1 at end move “yes” to end-of file move “the end” to last-output close file-in END-READ For Your Information Notice that after the READ reserve word is the name of the FD, unlike the WRITE which uses the record-name (i. e. 01). The first period encountered will end the READ statement. The END-READ is called a scope terminator. Statement-1… will execute when the end of the file is reached Statement-2… will execute when you READ and the end of the file marker is not reached The INTO identifier should be declared in the working-storage section. The equivalent to the READ/INTO is a READ then MOVE. For example, READ input-file AT END… MOVE input-rec to ws-work-area. Statement Syntax 5
 THE PERFORM STATEMENT Purpose: a sometimes loop, other times modular programming statement, that executes statement(s) sometimes based on a condition For Your Information TYPES: Single perform paragraph, Perform until, In-line perform (for both) Perform and perform until jump to the paragraph, execute the statements and come back to the perform statement before dropping to the next statement after the perform. Syntax Definition: PERFORM [paragraph-name-1] [ { THROUGH|THRU} paragraph-name-2 ] UNTIL condition-1 [END-PERFORM] Examples: PERFORM 500 -output-data. PERFORM 100 -read-data until eof = “Y”. perform until no-more-recs = “yes” read… move… write… end-perform If the UNTIL clause exists, the associated paragraph will execute if condition-1 is FALSE. If condition-1 is TRUE, the statements in the paragraph (or in line) will not be performed. *** This means that the condition will be checked first, then the paragraph executed If using the THRU option, the first paragraph must occur sequentially/physically prior to the second. All paragraphs in between are also executed Be careful of recursive-type (explain) and infinite loops be sure the condition eventually goes TRUE! Statement Syntax 6
THE PERFORM STATEMENT Purpose: a sometimes loop, other times modular programming statement, that executes statement(s) sometimes based on a condition For Your Information TYPES: Single perform paragraph, Perform until, In-line perform (for both) Perform and perform until jump to the paragraph, execute the statements and come back to the perform statement before dropping to the next statement after the perform. Syntax Definition: PERFORM [paragraph-name-1] [ { THROUGH|THRU} paragraph-name-2 ] UNTIL condition-1 [END-PERFORM] Examples: PERFORM 500 -output-data. PERFORM 100 -read-data until eof = “Y”. perform until no-more-recs = “yes” read… move… write… end-perform If the UNTIL clause exists, the associated paragraph will execute if condition-1 is FALSE. If condition-1 is TRUE, the statements in the paragraph (or in line) will not be performed. *** This means that the condition will be checked first, then the paragraph executed If using the THRU option, the first paragraph must occur sequentially/physically prior to the second. All paragraphs in between are also executed Be careful of recursive-type (explain) and infinite loops be sure the condition eventually goes TRUE! Statement Syntax 6
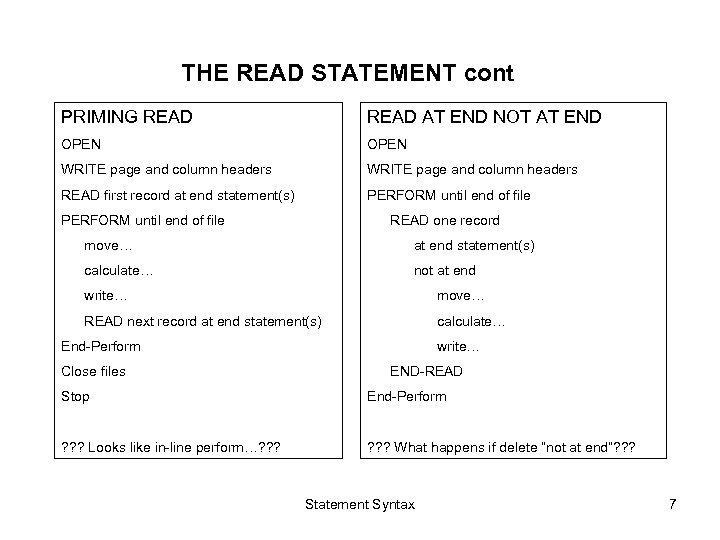 THE READ STATEMENT cont PRIMING READ AT END NOT AT END OPEN WRITE page and column headers READ first record at end statement(s) PERFORM until end of file READ one record move… at end statement(s) calculate… not at end write… move… READ next record at end statement(s) calculate… End-Perform Close files write… END-READ Stop End-Perform ? ? ? Looks like in-line perform…? ? ? ? What happens if delete “not at end”? ? ? Statement Syntax 7
THE READ STATEMENT cont PRIMING READ AT END NOT AT END OPEN WRITE page and column headers READ first record at end statement(s) PERFORM until end of file READ one record move… at end statement(s) calculate… not at end write… move… READ next record at end statement(s) calculate… End-Perform Close files write… END-READ Stop End-Perform ? ? ? Looks like in-line perform…? ? ? ? What happens if delete “not at end”? ? ? Statement Syntax 7
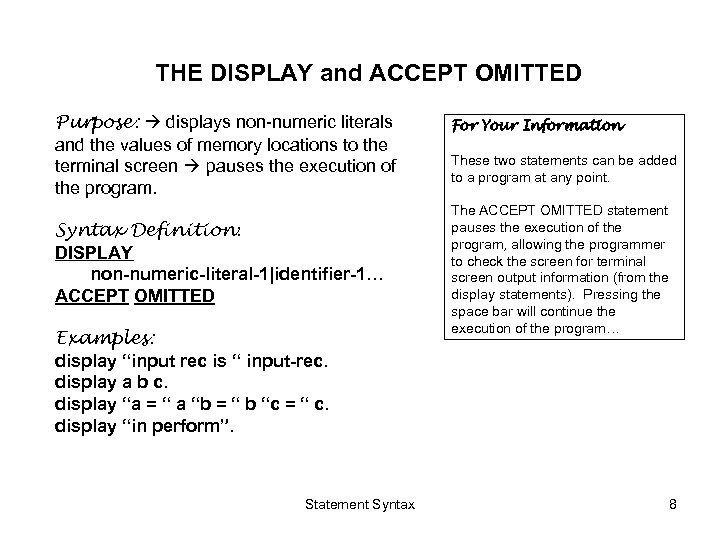 THE DISPLAY and ACCEPT OMITTED Purpose: displays non-numeric literals and the values of memory locations to the terminal screen pauses the execution of the program. Syntax Definition: DISPLAY non-numeric-literal-1|identifier-1… ACCEPT OMITTED Examples: display “input rec is “ input-rec. display a b c. display “a = “ a “b = “ b “c = “ c. display “in perform”. Statement Syntax For Your Information These two statements can be added to a program at any point. The ACCEPT OMITTED statement pauses the execution of the program, allowing the programmer to check the screen for terminal screen output information (from the display statements). Pressing the space bar will continue the execution of the program… 8
THE DISPLAY and ACCEPT OMITTED Purpose: displays non-numeric literals and the values of memory locations to the terminal screen pauses the execution of the program. Syntax Definition: DISPLAY non-numeric-literal-1|identifier-1… ACCEPT OMITTED Examples: display “input rec is “ input-rec. display a b c. display “a = “ a “b = “ b “c = “ c. display “in perform”. Statement Syntax For Your Information These two statements can be added to a program at any point. The ACCEPT OMITTED statement pauses the execution of the program, allowing the programmer to check the screen for terminal screen output information (from the display statements). Pressing the space bar will continue the execution of the program… 8
 THE STOP RUN STATEMENT Purpose: terminates the execution of the program Syntax Definition: STOP RUN. Examples: Not applicable : o) For Your Information This statement should be the last logical statement that your program executes. Not to be confused with the last physical statement of your program. Statement Syntax 9
THE STOP RUN STATEMENT Purpose: terminates the execution of the program Syntax Definition: STOP RUN. Examples: Not applicable : o) For Your Information This statement should be the last logical statement that your program executes. Not to be confused with the last physical statement of your program. Statement Syntax 9
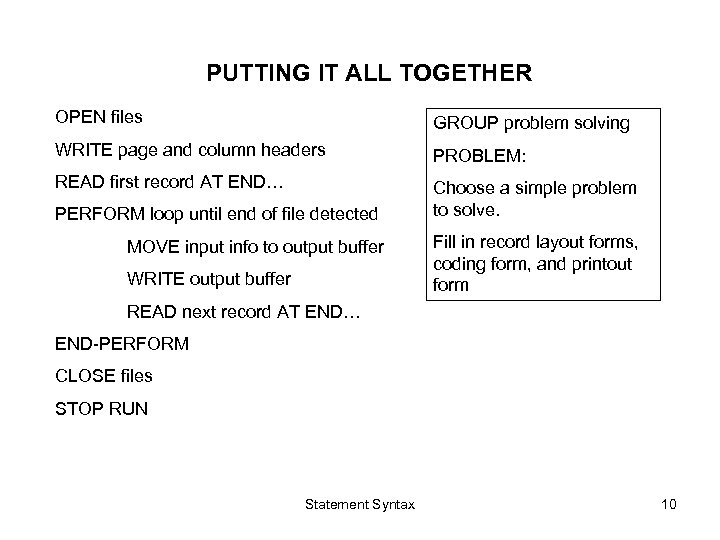 PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER OPEN files GROUP problem solving WRITE page and column headers PROBLEM: READ first record AT END… Choose a simple problem to solve. PERFORM loop until end of file detected MOVE input info to output buffer WRITE output buffer Fill in record layout forms, coding form, and printout form READ next record AT END… END-PERFORM CLOSE files STOP RUN Statement Syntax 10
PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER OPEN files GROUP problem solving WRITE page and column headers PROBLEM: READ first record AT END… Choose a simple problem to solve. PERFORM loop until end of file detected MOVE input info to output buffer WRITE output buffer Fill in record layout forms, coding form, and printout form READ next record AT END… END-PERFORM CLOSE files STOP RUN Statement Syntax 10
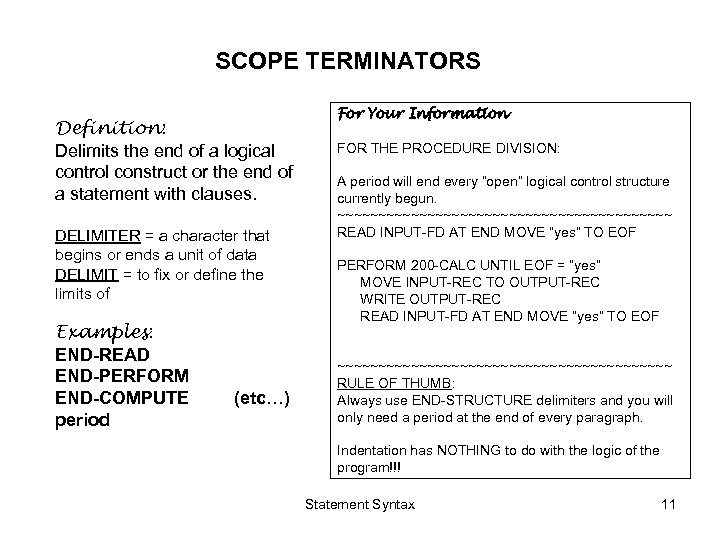 SCOPE TERMINATORS Definition: Delimits the end of a logical control construct or the end of a statement with clauses. DELIMITER = a character that begins or ends a unit of data DELIMIT = to fix or define the limits of Examples: END-READ END-PERFORM END-COMPUTE period (etc…) For Your Information FOR THE PROCEDURE DIVISION: A period will end every “open” logical control structure currently begun. ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ READ INPUT-FD AT END MOVE “yes” TO EOF PERFORM 200 -CALC UNTIL EOF = “yes” MOVE INPUT-REC TO OUTPUT-REC WRITE OUTPUT-REC READ INPUT-FD AT END MOVE “yes” TO EOF ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ RULE OF THUMB: Always use END-STRUCTURE delimiters and you will only need a period at the end of every paragraph. Indentation has NOTHING to do with the logic of the program!!! Statement Syntax 11
SCOPE TERMINATORS Definition: Delimits the end of a logical control construct or the end of a statement with clauses. DELIMITER = a character that begins or ends a unit of data DELIMIT = to fix or define the limits of Examples: END-READ END-PERFORM END-COMPUTE period (etc…) For Your Information FOR THE PROCEDURE DIVISION: A period will end every “open” logical control structure currently begun. ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ READ INPUT-FD AT END MOVE “yes” TO EOF PERFORM 200 -CALC UNTIL EOF = “yes” MOVE INPUT-REC TO OUTPUT-REC WRITE OUTPUT-REC READ INPUT-FD AT END MOVE “yes” TO EOF ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ RULE OF THUMB: Always use END-STRUCTURE delimiters and you will only need a period at the end of every paragraph. Indentation has NOTHING to do with the logic of the program!!! Statement Syntax 11
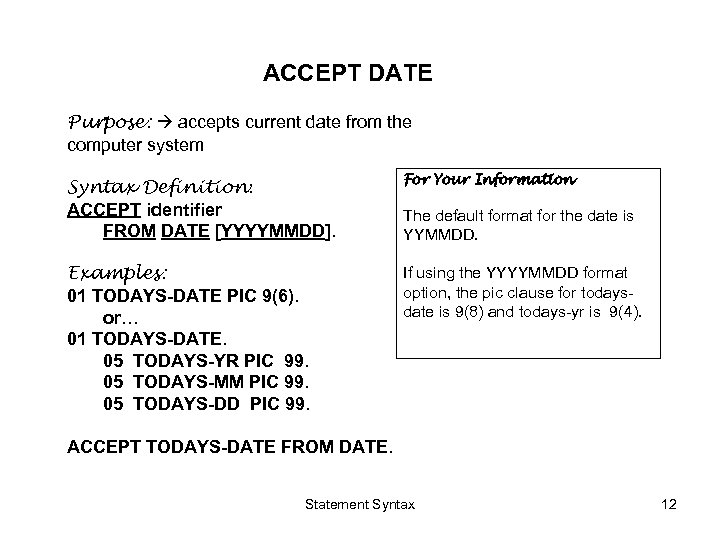 ACCEPT DATE Purpose: accepts current date from the computer system Syntax Definition: ACCEPT identifier FROM DATE [YYYYMMDD]. For Your Information Examples: 01 TODAYS-DATE PIC 9(6). or… 01 TODAYS-DATE. 05 TODAYS-YR PIC 99. 05 TODAYS-MM PIC 99. 05 TODAYS-DD PIC 99. If using the YYYYMMDD format option, the pic clause for todaysdate is 9(8) and todays-yr is 9(4). The default format for the date is YYMMDD. ACCEPT TODAYS-DATE FROM DATE. Statement Syntax 12
ACCEPT DATE Purpose: accepts current date from the computer system Syntax Definition: ACCEPT identifier FROM DATE [YYYYMMDD]. For Your Information Examples: 01 TODAYS-DATE PIC 9(6). or… 01 TODAYS-DATE. 05 TODAYS-YR PIC 99. 05 TODAYS-MM PIC 99. 05 TODAYS-DD PIC 99. If using the YYYYMMDD format option, the pic clause for todaysdate is 9(8) and todays-yr is 9(4). The default format for the date is YYMMDD. ACCEPT TODAYS-DATE FROM DATE. Statement Syntax 12
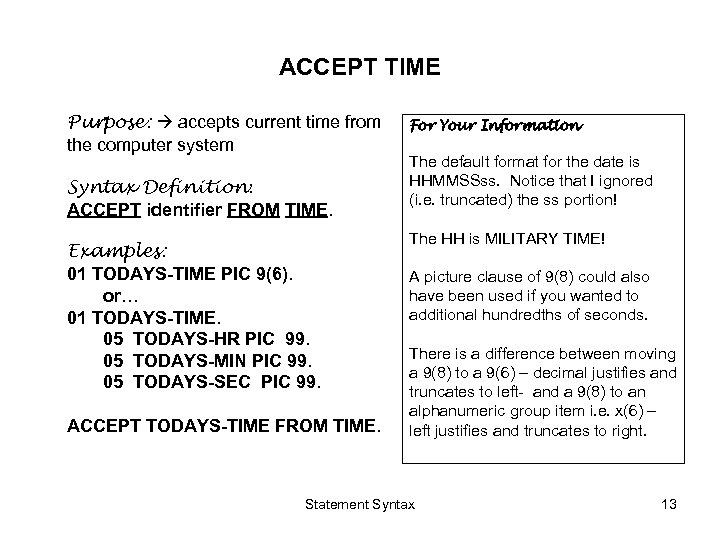 ACCEPT TIME Purpose: accepts current time from the computer system Syntax Definition: ACCEPT identifier FROM TIME. Examples: 01 TODAYS-TIME PIC 9(6). or… 01 TODAYS-TIME. 05 TODAYS-HR PIC 99. 05 TODAYS-MIN PIC 99. 05 TODAYS-SEC PIC 99. ACCEPT TODAYS-TIME FROM TIME. For Your Information The default format for the date is HHMMSSss. Notice that I ignored (i. e. truncated) the ss portion! The HH is MILITARY TIME! A picture clause of 9(8) could also have been used if you wanted to additional hundredths of seconds. There is a difference between moving a 9(8) to a 9(6) – decimal justifies and truncates to left- and a 9(8) to an alphanumeric group item i. e. x(6) – left justifies and truncates to right. Statement Syntax 13
ACCEPT TIME Purpose: accepts current time from the computer system Syntax Definition: ACCEPT identifier FROM TIME. Examples: 01 TODAYS-TIME PIC 9(6). or… 01 TODAYS-TIME. 05 TODAYS-HR PIC 99. 05 TODAYS-MIN PIC 99. 05 TODAYS-SEC PIC 99. ACCEPT TODAYS-TIME FROM TIME. For Your Information The default format for the date is HHMMSSss. Notice that I ignored (i. e. truncated) the ss portion! The HH is MILITARY TIME! A picture clause of 9(8) could also have been used if you wanted to additional hundredths of seconds. There is a difference between moving a 9(8) to a 9(6) – decimal justifies and truncates to left- and a 9(8) to an alphanumeric group item i. e. x(6) – left justifies and truncates to right. Statement Syntax 13


