a12ed2f1399eb706ba1a429a61b136ea.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

The Second Article The Executive Branch THE PRESIDENT and the Vice President

President • To be A pres: -35 yrs old • Live in US 14 yrs • Native Born • citizen Benefits pay 2001 move to $400, 000 • Travel and housing at the White house

Election and Term of Office • Every 4 years elected – Allowed two terms in office max 8 yrs – 22 amendments made twoterm limit legal 1951 – 10 yrs possible if VP takes over and then runs 2 more times • Our Pres– Franklin D Roosevelt first President 4 terms




Vice President • • -35 yrs old, live US 14 yrs, US Born Take office if President dies President over Senate Benefits Pay-today $198, 600 – Travel, housing • OUR VP-

Presidential Succession • -1947 -order in case of death-Vice President -Speaker of the House -President Pro Tempore the Senate -Secretary of State -see pg 359 • 1967 26 th amendment-If President can’t do the job then VP takes power • -New President chooses VP (both houses of Congress must approve) • -If President can’t do job for short time give power to VP

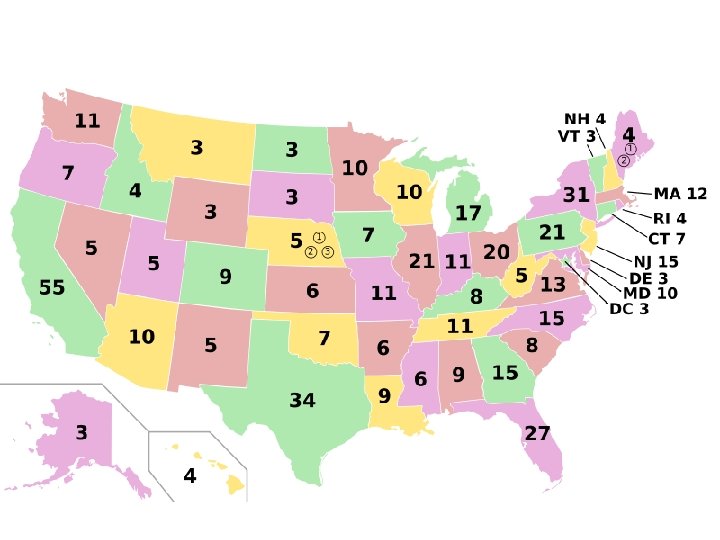
Election into office • In the past the person finish second in election chosen VP • 1804 12 th amendment- vote for Pres and VP together • Voted in by Electoral College PAST-Electoral college-group of officials chosen by each state to choose a President • People did not vote for president

Electoral College Today • Today 538 electors broken • Number based on the number of senators and representatives per State – Large populated states get more electors – The Electors vote based on how the state population voted – If candidate win state get all electors (CA 55) – Candidate must get 270 electoral votes to become president

3 problems with Electoral College 1. Popular vote winner not guaranteed to win elections – Popular vote – number of actual votes – Electoral -vote electoral votes based on states won • 2000 Al gore won popular vote but lost electoral vote • 2. Electors do not have to vote with popular vote(they nearly always do) • 3. House of representative will choose winner of neither gets 270 electoral votes
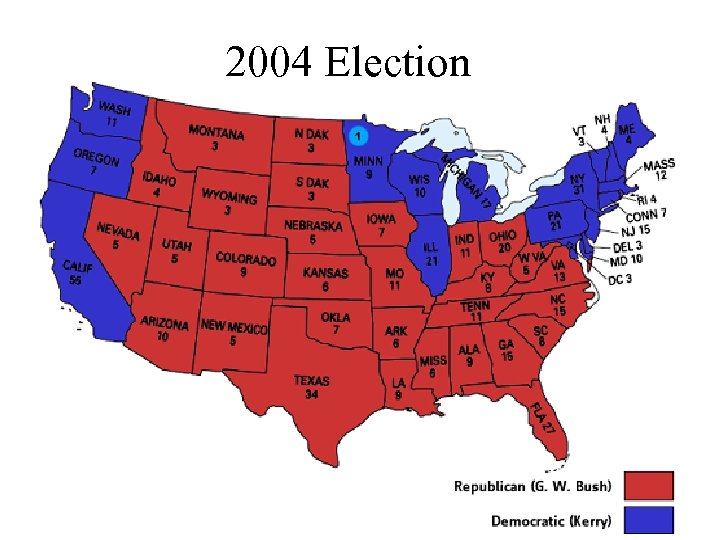
2004 Election

2008

II President’s Major roles Chief Executive -Carry out Nations Laws

Passing Executive order • Executive order- rules or commands of President taken like a law • -Orders made during crisis when things need to be done quickly

• Appoint Officials- -Chooses who will be Supreme Court judges • -Ambassadors to other countries • -Cabinet- those help him make decisions • -Head of government agencies-CIA, FBI…

Chief Diplomat • President responsibility deal with other countries 2 powers • Appoint ambassador • -Send American representative to other countries • -Do not send ambassador to countries gain power illegally • -Ambassador check in with President issues of country

Make Treaty • -Treaty is an agreement between countries • -Senate must approve treaty • -Or executive agreement with leader of other country with out Senate

Commander in Chief • -Leader of Armed forces Navy, Army, Coast Guard, Marines, Air force • -Has power over all Generals- makes decision to attack or not

• War Powers Act 1973 • - President needs to tell Congress when troops are sent in • - Troops must be returned home after 60 days unless congress allows or declares war • Peace Time Role • - President can send troops to keep peace in other Countries • Use troops to keep order in the U. S.

The Cabinet • Executive Office -President on top below official help -Cabinet- group of officials help President make decisions

Cabinet-Group of advisers for President- • advise president on issues related to their department - not mentioned in the constitution • 15 leaders different departments (Areas)called Secretaries Secretary of Stateplans foreign policy

• -Treasury- money country has 1789 • -Defense- military 1789 • -Depatment of Justice- law enforcement 1870 • -Interior- problems inside country 1849 • -Agriculture- farming 1889 • -Commerce- trade of goods 1903 • -Labor- work force 1913 • Health and Human Services 1953

• -Housing and Urban Development- problems in cities 1965 • -Transportation- highways, Railroad, airlines 1966 • -Energy-oil, coal, electricity 1977 • -Education- schools advise and $$ 1979 • -Veterans Affairs- rights for military vets 1989 • -Homeland Securityprotecting country from outsiders 2002
III Foreign Policy and the Executive Office(President) -Foreign Policy- National plan for dealing with other countries.

4 Goals of Foreign Policy 1. National Security- Keep country safe from attack 2. International Trade- keeps trade with other countries -Keep economy (money) moving for Americans -Find places to sell American products and keep American Jobs 3. World peace- wars around world can hurt trade -Problems in Middle East affect oil prices 4. Promote democracy and Human rights around World -Set up Democratic gov in Iraq

American International trade

• . National Security Council-Safety of the country Make decisions on threats to country by groups or other countries • Oversee the CIA- gather information about other governments • Other Offices – Council of Economic Advisers-problems of employment, tax, inflation, & trade – Council on Environmental Quality - advise environment

Parts of Foreign policy Under President Executive Branch • -State Department, Defense Dept, CIA, National Security Council -President and congress share power • -Pres communicate other countries- only congress can declare war & control money for war

Treaties- agreement between Nations- President start, congress approve Executive agreement- agreement between 2 World Leaders – Between Pres Mex & US Ambassador official Representative to other country – Pres choose- Senate approve US gives money to help other countries – money to Colombia stop drug trade – Money to Iraq rebuild country

• Trade agreements Trade sanctions- punish other countries control trade with them – example- S Africa- slow trade with south Africa for racist laws 1980’s • Embargo- Not allow a group countries to trade with another – example- Cuba we do not buy or sell to Cuba

At any time IF military is needed present can send army for short Term problems • Sent army to Somalia (Africa) control a Revolution
a12ed2f1399eb706ba1a429a61b136ea.ppt