THE SCOTTISH COURTS SYSTEM No Written Constitution UK



![CIVIL COURTS (i) COURT of SESSION [The Supreme Civil Court: sits in Edinburgh] CIVIL COURTS (i) COURT of SESSION [The Supreme Civil Court: sits in Edinburgh]](https://present5.com/presentacii-2/20171208\9566-the_scottish_courts_system.ppt\9566-the_scottish_courts_system_3.jpg)




9566-the_scottish_courts_system.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10
 THE SCOTTISH COURTS SYSTEM No Written Constitution UK Parliament Reserves Important Powers
THE SCOTTISH COURTS SYSTEM No Written Constitution UK Parliament Reserves Important Powers
 Courts within Scotland CIVIL COURT of SESSION Supreme civil court Sits in Edinburgh Maximum 26 judges (+part-time judges) SHERIFF COURT 49 ‘local’ courts in 6 areas (sheriffdoms) 142 sheriffs (+80 part-time) 6 sheriffs principal Functions: administration & appeals (cheaper & quicker than Court of Session) CRIMINAL HIGH COURT of JUSTICIARY Supreme criminal court Same judges as Court of Session SHERIFF COURT DISTRICT COURT In Glasgow, 3 stipendiary magistrates Otherwise, lay justices sit with legal assessor 2
Courts within Scotland CIVIL COURT of SESSION Supreme civil court Sits in Edinburgh Maximum 26 judges (+part-time judges) SHERIFF COURT 49 ‘local’ courts in 6 areas (sheriffdoms) 142 sheriffs (+80 part-time) 6 sheriffs principal Functions: administration & appeals (cheaper & quicker than Court of Session) CRIMINAL HIGH COURT of JUSTICIARY Supreme criminal court Same judges as Court of Session SHERIFF COURT DISTRICT COURT In Glasgow, 3 stipendiary magistrates Otherwise, lay justices sit with legal assessor 2
![>CIVIL COURTS (i) COURT of SESSION [The Supreme Civil Court: sits in Edinburgh] >CIVIL COURTS (i) COURT of SESSION [The Supreme Civil Court: sits in Edinburgh]](https://present5.com/presentacii-2/20171208\9566-the_scottish_courts_system.ppt\9566-the_scottish_courts_system_3.jpg) CIVIL COURTS (i) COURT of SESSION [The Supreme Civil Court: sits in Edinburgh] Outer House [Court of ‘First Instance’: one judge] Inner House [‘Divisions’ each comprising 3 senior judges sit as court of appeal, hearing appeals from the Outer House and from the Sheriff Court] Appeals from Inner House to Supreme Court of the United Kingdom Judgements of Inner House – on Fact & Law Judgements originating in Sheriff Court – on Law only 3
CIVIL COURTS (i) COURT of SESSION [The Supreme Civil Court: sits in Edinburgh] Outer House [Court of ‘First Instance’: one judge] Inner House [‘Divisions’ each comprising 3 senior judges sit as court of appeal, hearing appeals from the Outer House and from the Sheriff Court] Appeals from Inner House to Supreme Court of the United Kingdom Judgements of Inner House – on Fact & Law Judgements originating in Sheriff Court – on Law only 3
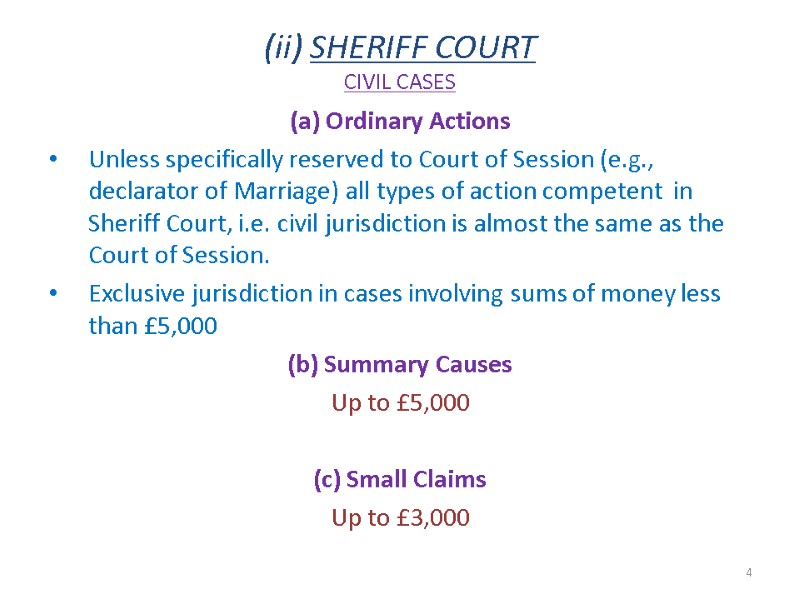
 (ii) SHERIFF COURT CIVIL CASES (a) Ordinary Actions Unless specifically reserved to Court of Session (e.g., declarator of Marriage) all types of action competent in Sheriff Court, i.e. civil jurisdiction is almost the same as the Court of Session. Exclusive jurisdiction in cases involving sums of money less than £5,000 (b) Summary Causes Up to £5,000 (c) Small Claims Up to £3,000 4
(ii) SHERIFF COURT CIVIL CASES (a) Ordinary Actions Unless specifically reserved to Court of Session (e.g., declarator of Marriage) all types of action competent in Sheriff Court, i.e. civil jurisdiction is almost the same as the Court of Session. Exclusive jurisdiction in cases involving sums of money less than £5,000 (b) Summary Causes Up to £5,000 (c) Small Claims Up to £3,000 4
 (iii) SHERIFF COURT ADMINISTRATIVE CASES Fatal Accident Inquiries Licensing Appeals & other Summary Applications Child Protection Orders Children’s Referrals Bankruptcy Extradition [Designated sheriffs: Edinburgh only] Adults with Incapacity 5
(iii) SHERIFF COURT ADMINISTRATIVE CASES Fatal Accident Inquiries Licensing Appeals & other Summary Applications Child Protection Orders Children’s Referrals Bankruptcy Extradition [Designated sheriffs: Edinburgh only] Adults with Incapacity 5
 CRIMINAL COURTS HIGH COURT of JUSTICIARY (The supreme criminal court) Sits as Appeal Court in Edinburgh Sits as trials court ‘on circuit’ around Scotland Has exclusive jurisdiction to try: Murder Rape Treason All other crimes (including attempts to murder or rape) may be tried in the Sheriff Court One judge sits with a jury of 15 citizens 6
CRIMINAL COURTS HIGH COURT of JUSTICIARY (The supreme criminal court) Sits as Appeal Court in Edinburgh Sits as trials court ‘on circuit’ around Scotland Has exclusive jurisdiction to try: Murder Rape Treason All other crimes (including attempts to murder or rape) may be tried in the Sheriff Court One judge sits with a jury of 15 citizens 6
 HIGH COURT of JUSTICIARY (continued) Appeals From 1st instance cases in High Court of Justiciary & lower courts ‘Sifting’ process (1, then 2 judges) Appeals v. Sentence, 2 judges Appeals v Conviction, 3 or more judges 7
HIGH COURT of JUSTICIARY (continued) Appeals From 1st instance cases in High Court of Justiciary & lower courts ‘Sifting’ process (1, then 2 judges) Appeals v. Sentence, 2 judges Appeals v Conviction, 3 or more judges 7
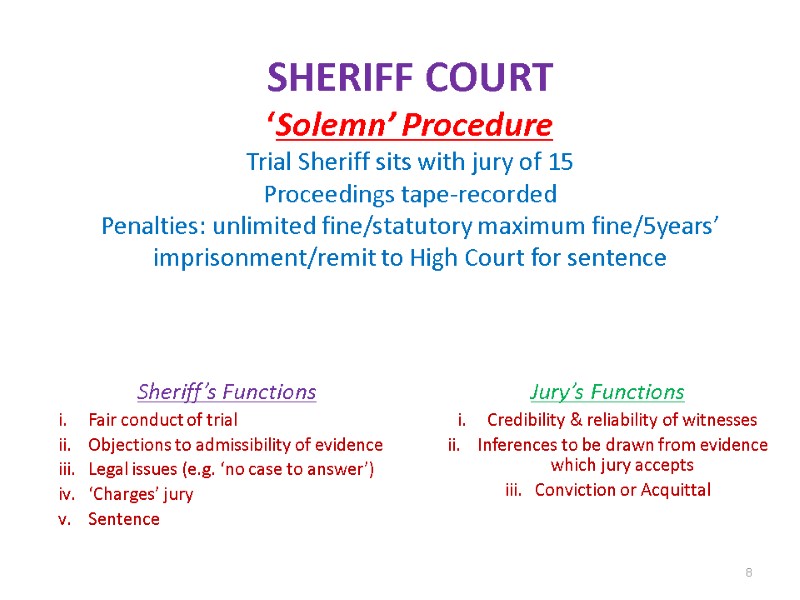
 SHERIFF COURT ‘Solemn’ Procedure Trial Sheriff sits with jury of 15 Proceedings tape-recorded Penalties: unlimited fine/statutory maximum fine/5years’ imprisonment/remit to High Court for sentence Sheriff’s Functions Fair conduct of trial Objections to admissibility of evidence Legal issues (e.g. ‘no case to answer’) ‘Charges’ jury Sentence Jury’s Functions Credibility & reliability of witnesses Inferences to be drawn from evidence which jury accepts Conviction or Acquittal 8
SHERIFF COURT ‘Solemn’ Procedure Trial Sheriff sits with jury of 15 Proceedings tape-recorded Penalties: unlimited fine/statutory maximum fine/5years’ imprisonment/remit to High Court for sentence Sheriff’s Functions Fair conduct of trial Objections to admissibility of evidence Legal issues (e.g. ‘no case to answer’) ‘Charges’ jury Sentence Jury’s Functions Credibility & reliability of witnesses Inferences to be drawn from evidence which jury accepts Conviction or Acquittal 8
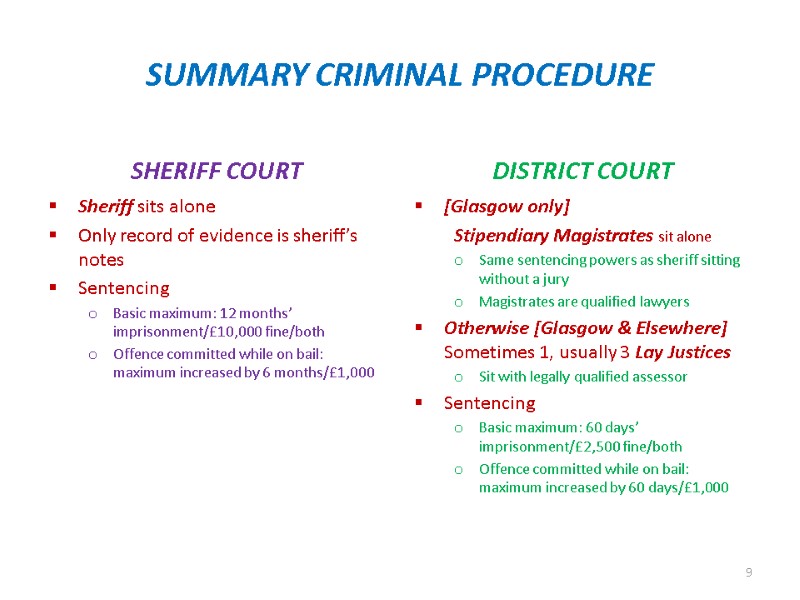
 SUMMARY CRIMINAL PROCEDURE SHERIFF COURT Sheriff sits alone Only record of evidence is sheriff’s notes Sentencing Basic maximum: 12 months’ imprisonment/£10,000 fine/both Offence committed while on bail: maximum increased by 6 months/£1,000 DISTRICT COURT [Glasgow only] Stipendiary Magistrates sit alone Same sentencing powers as sheriff sitting without a jury Magistrates are qualified lawyers Otherwise [Glasgow & Elsewhere] Sometimes 1, usually 3 Lay Justices Sit with legally qualified assessor Sentencing Basic maximum: 60 days’ imprisonment/£2,500 fine/both Offence committed while on bail: maximum increased by 60 days/£1,000 9
SUMMARY CRIMINAL PROCEDURE SHERIFF COURT Sheriff sits alone Only record of evidence is sheriff’s notes Sentencing Basic maximum: 12 months’ imprisonment/£10,000 fine/both Offence committed while on bail: maximum increased by 6 months/£1,000 DISTRICT COURT [Glasgow only] Stipendiary Magistrates sit alone Same sentencing powers as sheriff sitting without a jury Magistrates are qualified lawyers Otherwise [Glasgow & Elsewhere] Sometimes 1, usually 3 Lay Justices Sit with legally qualified assessor Sentencing Basic maximum: 60 days’ imprisonment/£2,500 fine/both Offence committed while on bail: maximum increased by 60 days/£1,000 9
 Courts & Other bodies Outside Scotland which may have Jurisdiction in Scottish Matters The Court of Justice of the Communities (European Community Law: Sits in Luxembourg) Where an issue involving European Treaties arises in domestic court, a direction of the ECJ must be sought, OR Any existing decision of the ECJ on the same issue must be followed Scottish court may apply to ECJ for a ‘preliminary ruling’ on a question of EC law which the court considers is ‘necessary to enable it to give judgement’ (2) The European Court of Human Rights (Sits in Strasbourg) The Scotland Act 1998, S.98 & Sch.6: An individual claiming to be the victim of a breach of a right under the European Convention on Human Rights may bring the alleged breach before the EC of HR after all domestic remedies have been exhausted An individual who asserts that he is the victim of such a breach may raise the issue [a ‘devolution issue’] in proceedings before a Scottish Court Judgements on ‘devolution issues’ (in civil and criminal cases) may be appealed to the Scottish supreme courts and to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council The Human Rights Act 1998: So far as it is possible to do so, primary and secondary legislation must be read & given effect in a way which is compatible with the Convention rights (3) The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (Sits in London) 10
Courts & Other bodies Outside Scotland which may have Jurisdiction in Scottish Matters The Court of Justice of the Communities (European Community Law: Sits in Luxembourg) Where an issue involving European Treaties arises in domestic court, a direction of the ECJ must be sought, OR Any existing decision of the ECJ on the same issue must be followed Scottish court may apply to ECJ for a ‘preliminary ruling’ on a question of EC law which the court considers is ‘necessary to enable it to give judgement’ (2) The European Court of Human Rights (Sits in Strasbourg) The Scotland Act 1998, S.98 & Sch.6: An individual claiming to be the victim of a breach of a right under the European Convention on Human Rights may bring the alleged breach before the EC of HR after all domestic remedies have been exhausted An individual who asserts that he is the victim of such a breach may raise the issue [a ‘devolution issue’] in proceedings before a Scottish Court Judgements on ‘devolution issues’ (in civil and criminal cases) may be appealed to the Scottish supreme courts and to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council The Human Rights Act 1998: So far as it is possible to do so, primary and secondary legislation must be read & given effect in a way which is compatible with the Convention rights (3) The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (Sits in London) 10

