 The Scientific Method • Universal approach to solving scientific problems
The Scientific Method • Universal approach to solving scientific problems
 Observations • Make sure your observations are Quantitative. § Something you can count • NOT Qualitative § Feelings, relative measurements
Observations • Make sure your observations are Quantitative. § Something you can count • NOT Qualitative § Feelings, relative measurements
 Give me an example of quantitative observation of this picture of the cast of House M. D.
Give me an example of quantitative observation of this picture of the cast of House M. D.
 Constructing an Experiment • Tests ONLY 1 variable at a time • Independent Variable § What you change in the experiment • Dependent Variable § What change because of the independent Variable § What you measure • Controls (constants) controlled variables § What stays the same in the whole experiment
Constructing an Experiment • Tests ONLY 1 variable at a time • Independent Variable § What you change in the experiment • Dependent Variable § What change because of the independent Variable § What you measure • Controls (constants) controlled variables § What stays the same in the whole experiment
 2 Groups in an Experiment 1. Control Group § The group that you do nothing new to 2. Experimental Group § § The group with the independent variable The group you change
2 Groups in an Experiment 1. Control Group § The group that you do nothing new to 2. Experimental Group § § The group with the independent variable The group you change
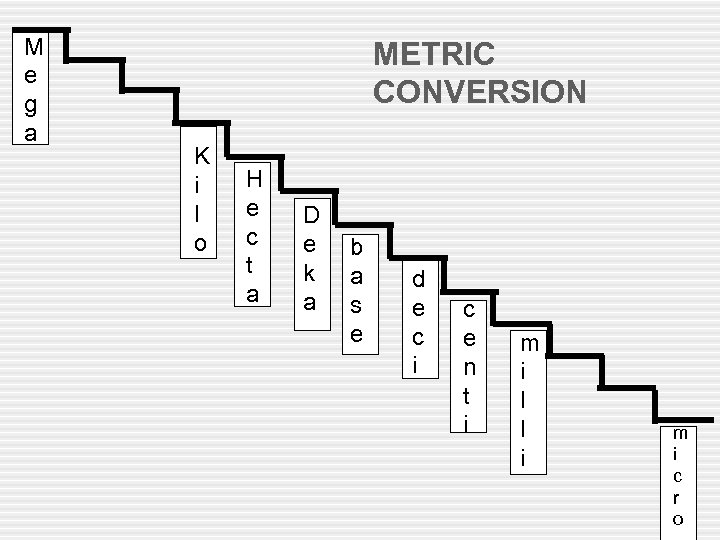 M e g a METRIC CONVERSION K i l o H e c t a D e k a b a s e d e c i c e n t i m i l l i m i c r o
M e g a METRIC CONVERSION K i l o H e c t a D e k a b a s e d e c i c e n t i m i l l i m i c r o
 Giga-1, 000, 000 Mega-1, 000, 000 Kilo-1, 000 Heca-100 Deca-10 Base-1 Deci-0. 1 Centi-0. 01 SI UNITS SI = Système International d'unités International System of Units Milli-0. 001 Micro-0. 0000001 Nano-0. 000001
Giga-1, 000, 000 Mega-1, 000, 000 Kilo-1, 000 Heca-100 Deca-10 Base-1 Deci-0. 1 Centi-0. 01 SI UNITS SI = Système International d'unités International System of Units Milli-0. 001 Micro-0. 0000001 Nano-0. 000001
 SI UNITS cont… • Length = meters (m) § Metric Ruler • Volume = liters (L) § Graduated Cylinder • Weight = grams (g) § Triple Beam/ Electronic Balance • Temperature = Celsius (C°) § Thermometer
SI UNITS cont… • Length = meters (m) § Metric Ruler • Volume = liters (L) § Graduated Cylinder • Weight = grams (g) § Triple Beam/ Electronic Balance • Temperature = Celsius (C°) § Thermometer
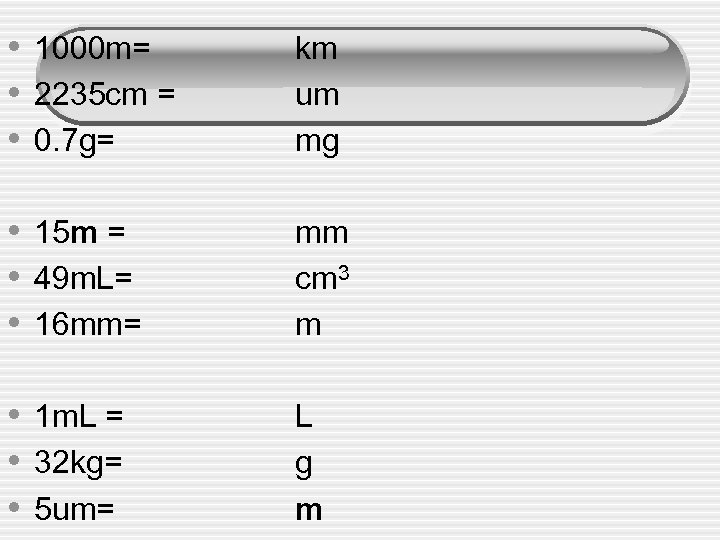 • 1000 m= • 2235 cm = • 0. 7 g= km um mg • 15 m = • 49 m. L= • 16 mm= mm cm 3 m • 1 m. L = • 32 kg= • 5 um= L g m
• 1000 m= • 2235 cm = • 0. 7 g= km um mg • 15 m = • 49 m. L= • 16 mm= mm cm 3 m • 1 m. L = • 32 kg= • 5 um= L g m