d45463b2d847f8b05304cb257452401b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 (The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey) TÜBİTAK and R&D M. Arif ADLI (Dr. Eng. ) Vice President TÜBİTAK 1 st Eurasian Silk Road Universities Convention, May 28 -31, 2010, Erzurum
(The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey) TÜBİTAK and R&D M. Arif ADLI (Dr. Eng. ) Vice President TÜBİTAK 1 st Eurasian Silk Road Universities Convention, May 28 -31, 2010, Erzurum
 TÜBİTAK The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey Established : 1963 Main Functions • Determining the ST and Innovation Policy of Turkey • Providing R&D Fundings, Grants and Fellowships • Conducting Research and Development Institutes (MRC, Space Inst. , Metrology Inst. , UEKAE, . . . ) TÜBİTAK’s budget: Approx. 900 mil. US$ R&D Funding: Approx. 470 mil. US $ 2
TÜBİTAK The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey Established : 1963 Main Functions • Determining the ST and Innovation Policy of Turkey • Providing R&D Fundings, Grants and Fellowships • Conducting Research and Development Institutes (MRC, Space Inst. , Metrology Inst. , UEKAE, . . . ) TÜBİTAK’s budget: Approx. 900 mil. US$ R&D Funding: Approx. 470 mil. US $ 2
 ST and Innovation Indicators for Turkey 2002 -2008 3
ST and Innovation Indicators for Turkey 2002 -2008 3
 Facts on TR for the year 2002 • R&D funds/human resources were not satisfactory – GERD : 0. 53% of GDP, (1. 2 Billion US$) – FTE : 24. 000 (Full Time Equivalent Researcher) • Sectoral distribution of R&D was unbalanced Sector 2002 (%) Academia 64 Industry 29 Public Institutions 9 No way to be competitive! Science and Technology Strategy was launched for (2005 -2010) : • Target 2013: GERD as percentage of GDP 2% (50% coming from industry) • Rapid increase in human resources (FTE Researcher) GERD: Gross Domestic Expenditure on Research and Development GDP : Gross Domestic Product • Target 2013 : FTE Researcher : 150 Thousand 4
Facts on TR for the year 2002 • R&D funds/human resources were not satisfactory – GERD : 0. 53% of GDP, (1. 2 Billion US$) – FTE : 24. 000 (Full Time Equivalent Researcher) • Sectoral distribution of R&D was unbalanced Sector 2002 (%) Academia 64 Industry 29 Public Institutions 9 No way to be competitive! Science and Technology Strategy was launched for (2005 -2010) : • Target 2013: GERD as percentage of GDP 2% (50% coming from industry) • Rapid increase in human resources (FTE Researcher) GERD: Gross Domestic Expenditure on Research and Development GDP : Gross Domestic Product • Target 2013 : FTE Researcher : 150 Thousand 4
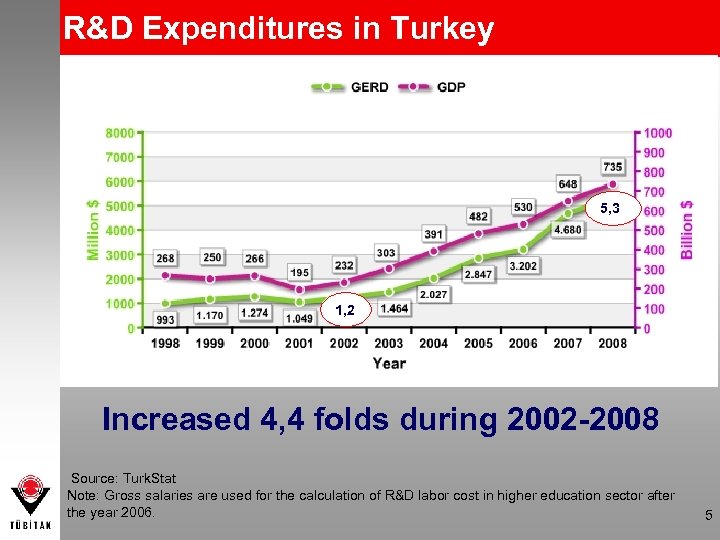 R&D Expenditures in Turkey 5, 3 1, 2 Increased 4, 4 folds during 2002 -2008 Source: Turk. Stat Note: Gross salaries are used for the calculation of R&D labor cost in higher education sector after the year 2006. 5
R&D Expenditures in Turkey 5, 3 1, 2 Increased 4, 4 folds during 2002 -2008 Source: Turk. Stat Note: Gross salaries are used for the calculation of R&D labor cost in higher education sector after the year 2006. 5
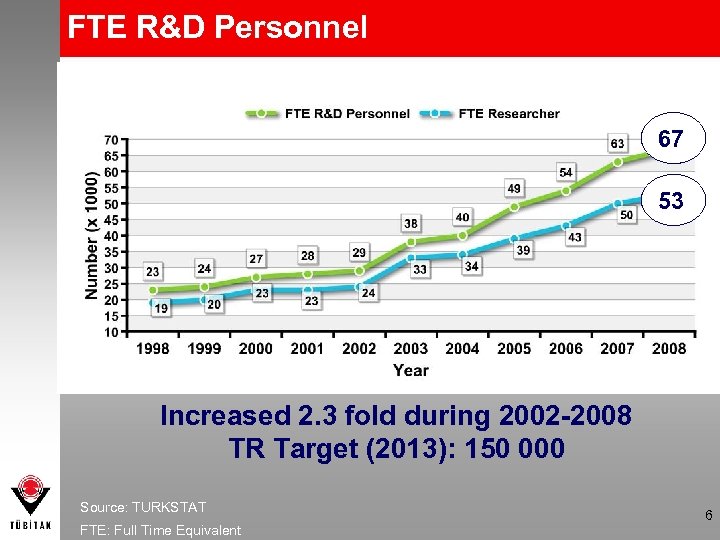 FTE R&D Personnel 67 53 Increased 2. 3 fold during 2002 -2008 TR Target (2013): 150 000 Source: TURKSTAT FTE: Full Time Equivalent 6
FTE R&D Personnel 67 53 Increased 2. 3 fold during 2002 -2008 TR Target (2013): 150 000 Source: TURKSTAT FTE: Full Time Equivalent 6
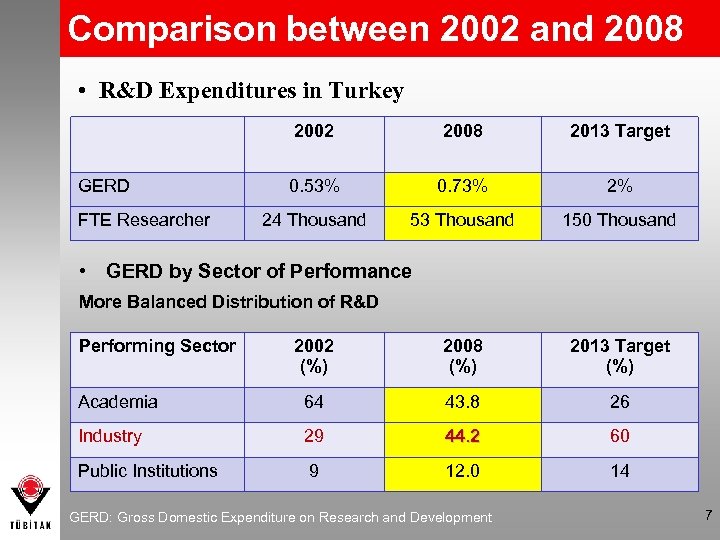 Comparison between 2002 and 2008 • R&D Expenditures in Turkey 2002 GERD FTE Researcher 2008 2013 Target 0. 53% 0. 73% 2% 24 Thousand 53 Thousand 150 Thousand • GERD by Sector of Performance More Balanced Distribution of R&D Performing Sector 2002 (%) 2008 (%) 2013 Target (%) Academia 64 43. 8 26 Industry 29 44. 2 60 Public Institutions 9 12. 0 14 GERD: Gross Domestic Expenditure on Research and Development 7
Comparison between 2002 and 2008 • R&D Expenditures in Turkey 2002 GERD FTE Researcher 2008 2013 Target 0. 53% 0. 73% 2% 24 Thousand 53 Thousand 150 Thousand • GERD by Sector of Performance More Balanced Distribution of R&D Performing Sector 2002 (%) 2008 (%) 2013 Target (%) Academia 64 43. 8 26 Industry 29 44. 2 60 Public Institutions 9 12. 0 14 GERD: Gross Domestic Expenditure on Research and Development 7
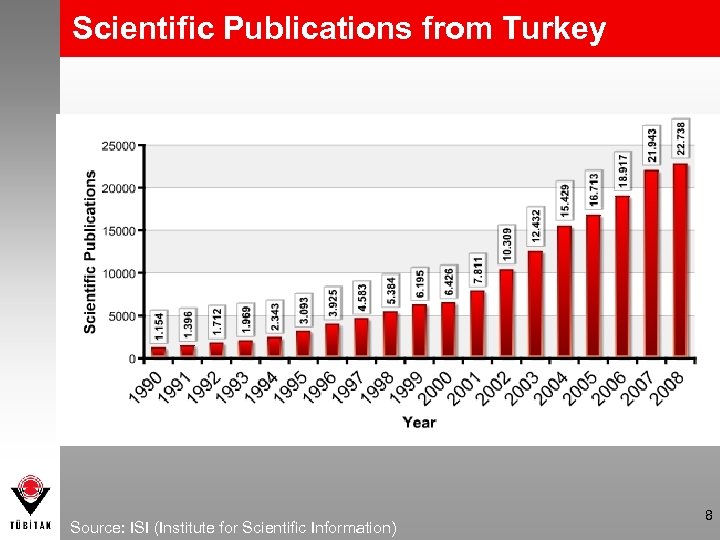 Scientific Publications from Turkey Source: ISI (Institute for Scientific Information) 8
Scientific Publications from Turkey Source: ISI (Institute for Scientific Information) 8
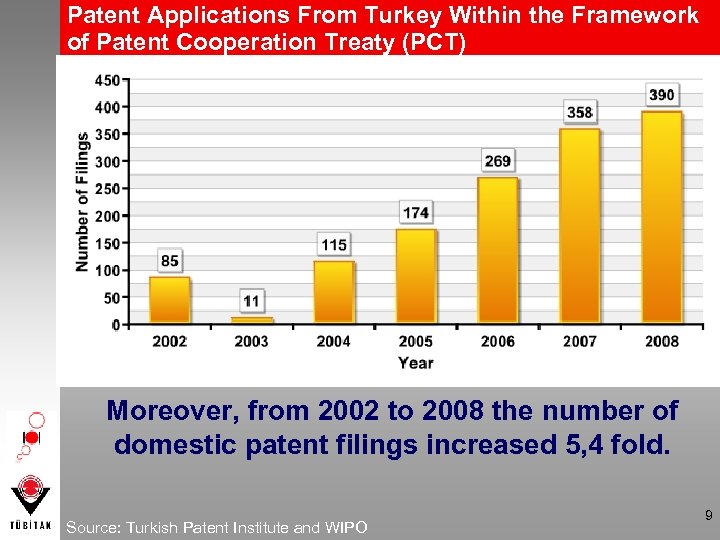 Patent Applications From Turkey Within the Framework of Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) Moreover, from 2002 to 2008 the number of domestic patent filings increased 5, 4 fold. Source: Turkish Patent Institute and WIPO 9
Patent Applications From Turkey Within the Framework of Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) Moreover, from 2002 to 2008 the number of domestic patent filings increased 5, 4 fold. Source: Turkish Patent Institute and WIPO 9
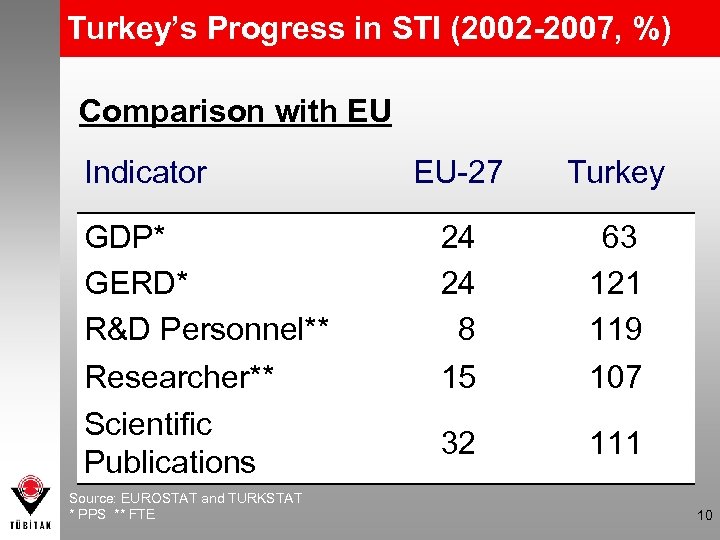 Turkey’s Progress in STI (2002 -2007, %) Comparison with EU Indicator GDP* GERD* R&D Personnel** Researcher** Scientific Publications Source: EUROSTAT and TURKSTAT * PPS ** FTE EU-27 Turkey 24 24 8 15 63 121 119 107 32 111 10
Turkey’s Progress in STI (2002 -2007, %) Comparison with EU Indicator GDP* GERD* R&D Personnel** Researcher** Scientific Publications Source: EUROSTAT and TURKSTAT * PPS ** FTE EU-27 Turkey 24 24 8 15 63 121 119 107 32 111 10
 From 2002 to 2007 Turkey outpaced • 2 countries regarding GERD; – Finland, Denmark • 6 countries regarding FTE R&D Personnel; – Finland, Denmark, Belgium, Austria, Greece, Romania • 5 countries regarding FTE Researchers; – Finland, Denmark, Belgium, Austria, The Netherlands • 4 countries regarding Scientific Publications; – Belgium, Poland, Taiwan, Israel 11
From 2002 to 2007 Turkey outpaced • 2 countries regarding GERD; – Finland, Denmark • 6 countries regarding FTE R&D Personnel; – Finland, Denmark, Belgium, Austria, Greece, Romania • 5 countries regarding FTE Researchers; – Finland, Denmark, Belgium, Austria, The Netherlands • 4 countries regarding Scientific Publications; – Belgium, Poland, Taiwan, Israel 11
 R&D Funds, Grants and Fellowships Provided by TÜBİTAK 12
R&D Funds, Grants and Fellowships Provided by TÜBİTAK 12
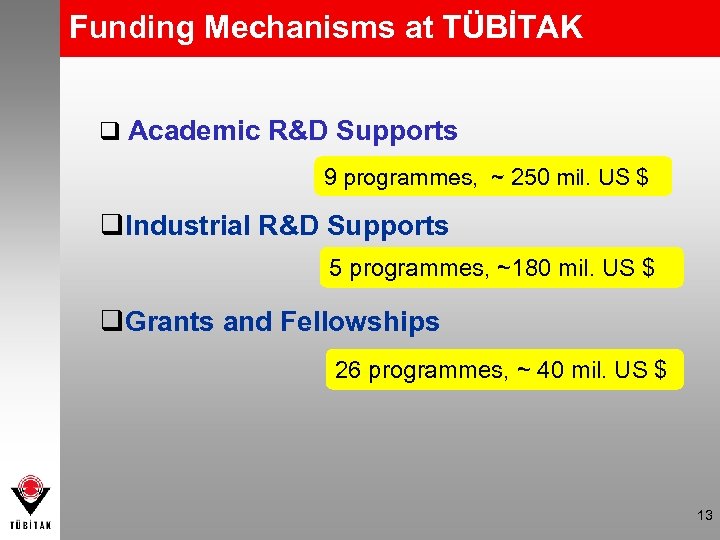 Funding Mechanisms at TÜBİTAK q Academic R&D Supports 9 programmes, ~ 250 mil. US $ q. Industrial R&D Supports 5 programmes, ~180 mil. US $ q. Grants and Fellowships 26 programmes, ~ 40 mil. US $ 13
Funding Mechanisms at TÜBİTAK q Academic R&D Supports 9 programmes, ~ 250 mil. US $ q. Industrial R&D Supports 5 programmes, ~180 mil. US $ q. Grants and Fellowships 26 programmes, ~ 40 mil. US $ 13
 ARDEB TÜBİTAK Academic R&D Supports • 9 Grant Committies • 9 support programmes • ~ 250 mil. US $ budget 14
ARDEB TÜBİTAK Academic R&D Supports • 9 Grant Committies • 9 support programmes • ~ 250 mil. US $ budget 14
 ARDEB – Funding Programs (8+1) The Support Programme for Scientific and Technological Research Projects (1002) Short-Term R&D Funding Programme (3501) National Young Researchers Career Development Programme (Career Programme) (1010) Global Researcher Programme (EVRENA) (1008) Patent Application Promotion and Support Programme ~ 100 mil. US $ (1001) (1011) The Programme for Participation in International Scientific Research Projects (UBAP) (1301) The Support Programme for the Initiative to Build Scientific and Technological Cooperation Networks and Platforms (İŞBAP) (2500) International Projects (Bilateral/multilateral) (1007) Support Programme for Research Projects of Public Institutions, Defense and Security ~ 150 mil. US $ 15
ARDEB – Funding Programs (8+1) The Support Programme for Scientific and Technological Research Projects (1002) Short-Term R&D Funding Programme (3501) National Young Researchers Career Development Programme (Career Programme) (1010) Global Researcher Programme (EVRENA) (1008) Patent Application Promotion and Support Programme ~ 100 mil. US $ (1001) (1011) The Programme for Participation in International Scientific Research Projects (UBAP) (1301) The Support Programme for the Initiative to Build Scientific and Technological Cooperation Networks and Platforms (İŞBAP) (2500) International Projects (Bilateral/multilateral) (1007) Support Programme for Research Projects of Public Institutions, Defense and Security ~ 150 mil. US $ 15
 Academic Research Funding Program Directorate Statistics 16
Academic Research Funding Program Directorate Statistics 16
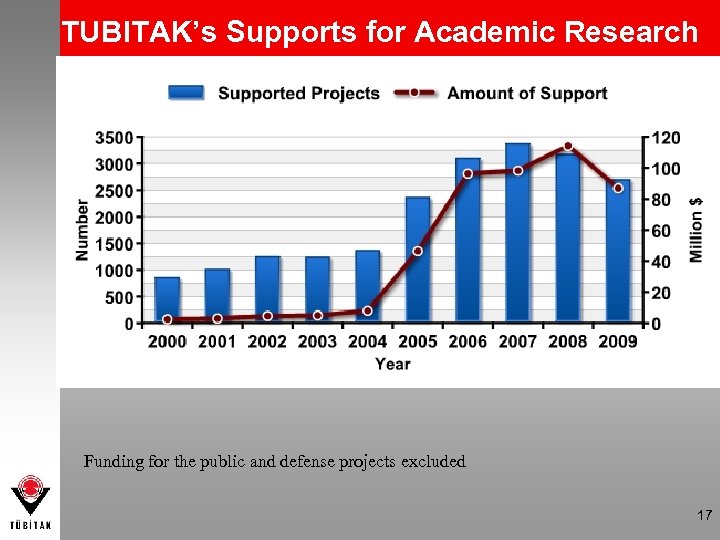 TUBITAK’s Supports for Academic Research Funding for the public and defense projects excluded 17
TUBITAK’s Supports for Academic Research Funding for the public and defense projects excluded 17
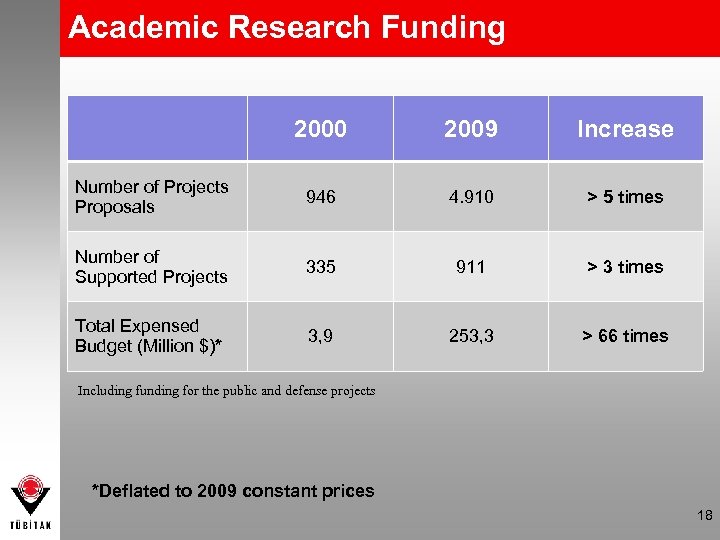 Academic Research Funding 2000 2009 Increase Number of Projects Proposals 946 4. 910 > 5 times Number of Supported Projects 335 911 > 3 times Total Expensed Budget (Million $)* 3, 9 253, 3 > 66 times Including funding for the public and defense projects *Deflated to 2009 constant prices 18
Academic Research Funding 2000 2009 Increase Number of Projects Proposals 946 4. 910 > 5 times Number of Supported Projects 335 911 > 3 times Total Expensed Budget (Million $)* 3, 9 253, 3 > 66 times Including funding for the public and defense projects *Deflated to 2009 constant prices 18
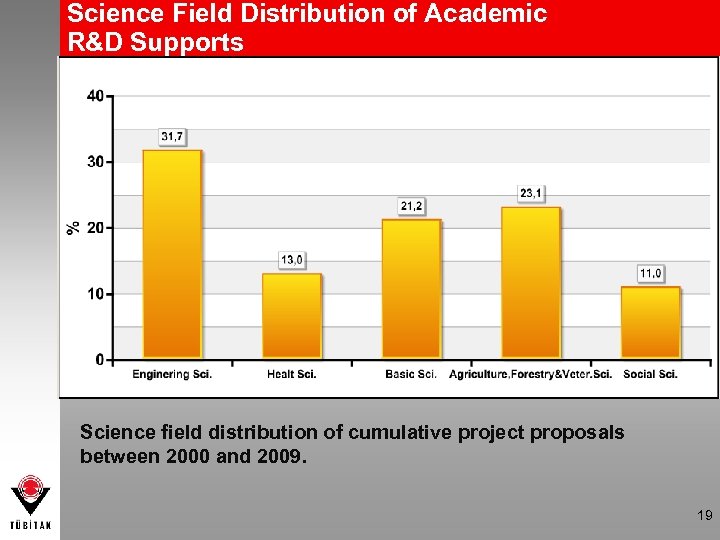 Science Field Distribution of Academic R&D Supports Science field distribution of cumulative project proposals between 2000 and 2009. 19
Science Field Distribution of Academic R&D Supports Science field distribution of cumulative project proposals between 2000 and 2009. 19
 TEYDEB Industrial R&D Supports • 5 Grant Committies • 5 support programmes • ~ 180 mil. US $ budget 20
TEYDEB Industrial R&D Supports • 5 Grant Committies • 5 support programmes • ~ 180 mil. US $ budget 20
 Technology & Innovation Grant Programmes (5) • (1501) Industrial R&D Projects Grant Programme • (1507) SME RDI (Research, Development & Innovation) Grant Programme • (1509) International Industrial R&D Projects Grant Programme • (1503) R&D Project Brokerage Events Grant Programme • (1508) Technoenterprise Grant Programme 21
Technology & Innovation Grant Programmes (5) • (1501) Industrial R&D Projects Grant Programme • (1507) SME RDI (Research, Development & Innovation) Grant Programme • (1509) International Industrial R&D Projects Grant Programme • (1503) R&D Project Brokerage Events Grant Programme • (1508) Technoenterprise Grant Programme 21
 Technology and Innovation Grant Programmes Directorate (TEYDEB) Statistics 22
Technology and Innovation Grant Programmes Directorate (TEYDEB) Statistics 22
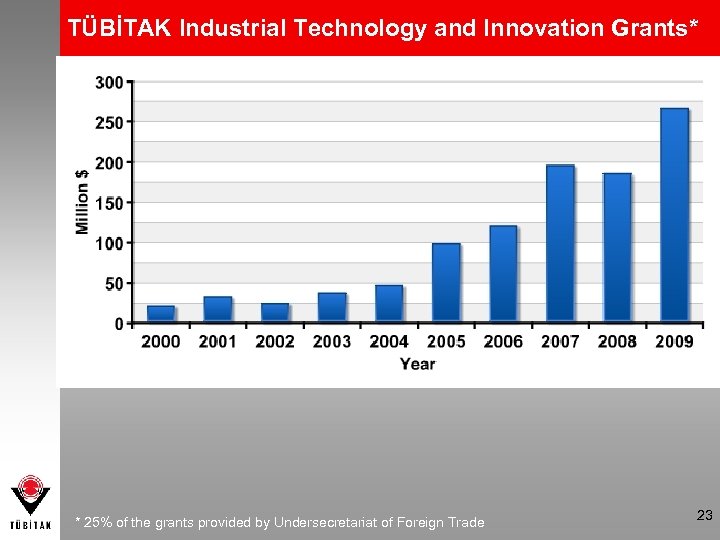 TÜBİTAK Industrial Technology and Innovation Grants* * 25% of the grants provided by Undersecretariat of Foreign Trade 23
TÜBİTAK Industrial Technology and Innovation Grants* * 25% of the grants provided by Undersecretariat of Foreign Trade 23
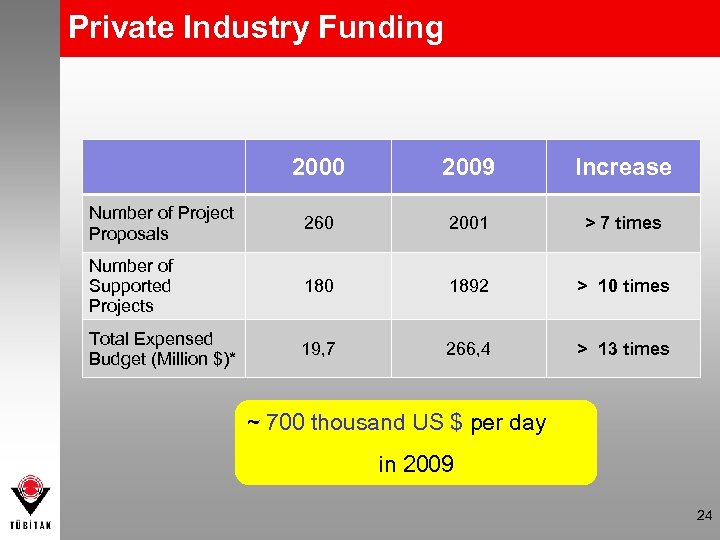 Private Industry Funding 2000 2009 Increase Number of Project Proposals 260 2001 > 7 times Number of Supported Projects 180 1892 > 10 times Total Expensed Budget (Million $)* 19, 7 266, 4 > 13 times ~ 700 thousand US $ per day in 2009 24
Private Industry Funding 2000 2009 Increase Number of Project Proposals 260 2001 > 7 times Number of Supported Projects 180 1892 > 10 times Total Expensed Budget (Million $)* 19, 7 266, 4 > 13 times ~ 700 thousand US $ per day in 2009 24
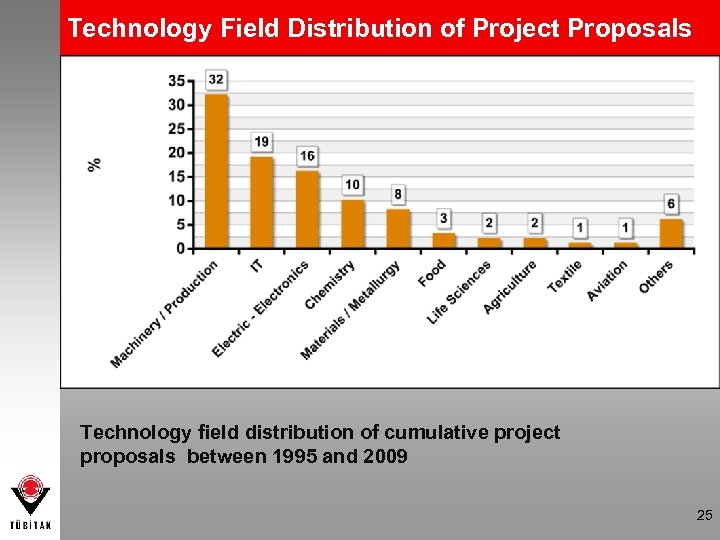 Technology Field Distribution of Project Proposals Technology field distribution of cumulative project proposals between 1995 and 2009 25
Technology Field Distribution of Project Proposals Technology field distribution of cumulative project proposals between 1995 and 2009 25
 BİDEB Grants and Fellowships • 26 grant or fellowship programmes • ~ 40 mil. US $ budget 26
BİDEB Grants and Fellowships • 26 grant or fellowship programmes • ~ 40 mil. US $ budget 26
 Scope of Grants • Science Olympiads and Project Contests • Scholarships for Graduate Students • Postdoctoral Fellowships • Scientific Meetings Grants • Scientific Exchange Fellowships • Scientific Meetings Participation Grants 26 different support programmes 27
Scope of Grants • Science Olympiads and Project Contests • Scholarships for Graduate Students • Postdoctoral Fellowships • Scientific Meetings Grants • Scientific Exchange Fellowships • Scientific Meetings Participation Grants 26 different support programmes 27
 Fellowship Programs for Foreigners • Ph. D Fellowship Program for Foreigners (2215) • Research Fellowship Program for Foreigners (2216) • Visiting Scientists Fellowship Program (2221) 28
Fellowship Programs for Foreigners • Ph. D Fellowship Program for Foreigners (2215) • Research Fellowship Program for Foreigners (2216) • Visiting Scientists Fellowship Program (2221) 28
 Department of Science Fellowships and Grant Programmes Statistics 29
Department of Science Fellowships and Grant Programmes Statistics 29
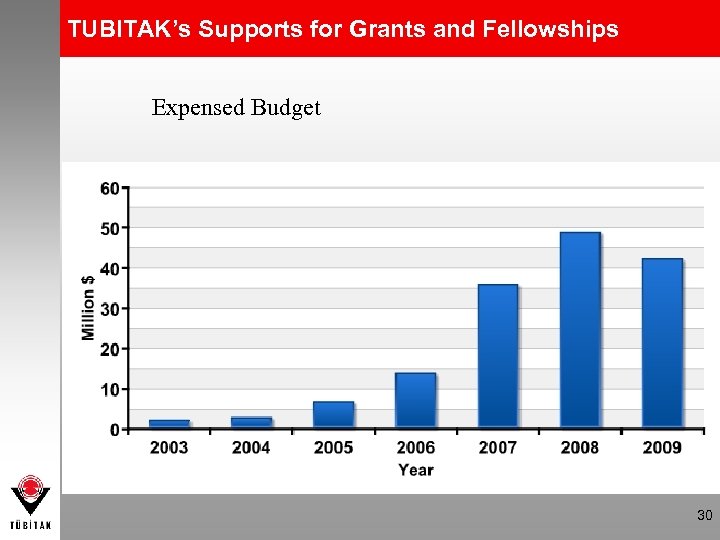 TUBITAK’s Supports for Grants and Fellowships Expensed Budget 30
TUBITAK’s Supports for Grants and Fellowships Expensed Budget 30
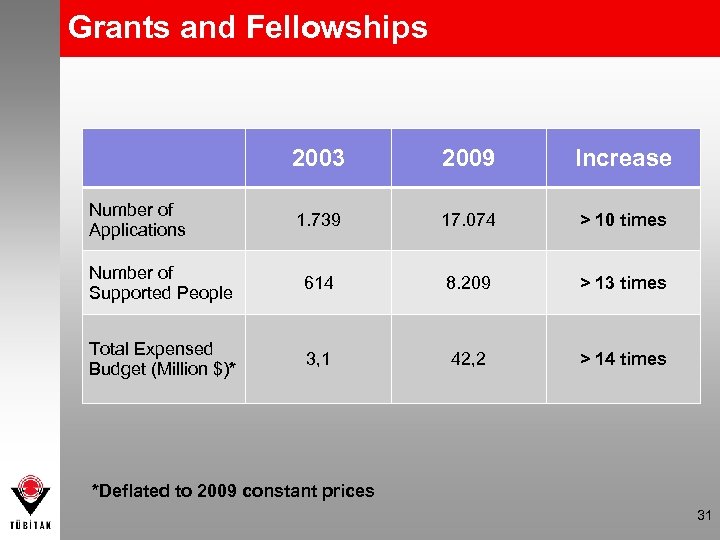 Grants and Fellowships 2003 2009 Increase 1. 739 17. 074 > 10 times Number of Supported People 614 8. 209 > 13 times Total Expensed Budget (Million $)* 3, 1 42, 2 > 14 times Number of Applications *Deflated to 2009 constant prices 31
Grants and Fellowships 2003 2009 Increase 1. 739 17. 074 > 10 times Number of Supported People 614 8. 209 > 13 times Total Expensed Budget (Million $)* 3, 1 42, 2 > 14 times Number of Applications *Deflated to 2009 constant prices 31
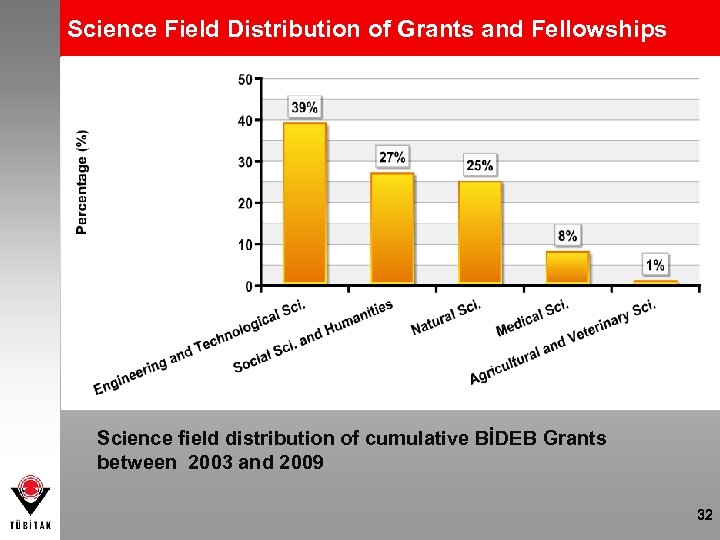 Science Field Distribution of Grants and Fellowships Science field distribution of cumulative BİDEB Grants between 2003 and 2009 32
Science Field Distribution of Grants and Fellowships Science field distribution of cumulative BİDEB Grants between 2003 and 2009 32
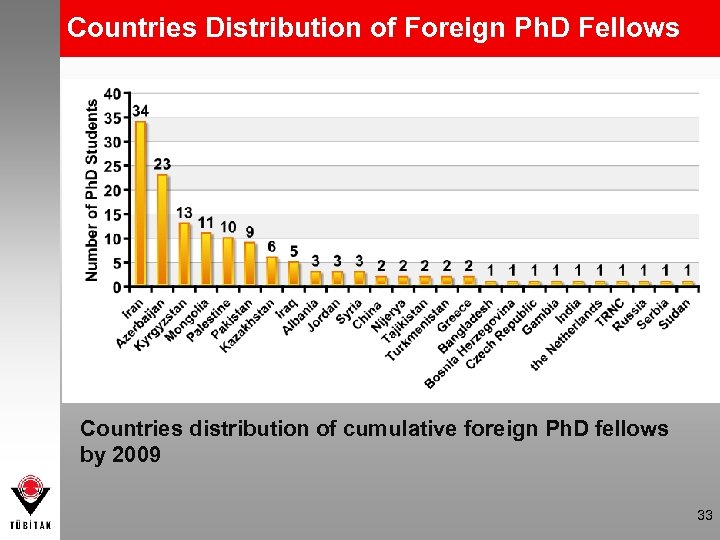 Countries Distribution of Foreign Ph. D Fellows Countries distribution of cumulative foreign Ph. D fellows by 2009 33
Countries Distribution of Foreign Ph. D Fellows Countries distribution of cumulative foreign Ph. D fellows by 2009 33
 MRC Research at TÜBİTAK RESEARCH INSTITUTES at TÜBİTAK 34
MRC Research at TÜBİTAK RESEARCH INSTITUTES at TÜBİTAK 34
 Research at TÜBİTAK Research Institutes are publicly funded legal entities, wishing to increase their total income through publicprivate collaborations; especially in the form of partnerships with industry. 35
Research at TÜBİTAK Research Institutes are publicly funded legal entities, wishing to increase their total income through publicprivate collaborations; especially in the form of partnerships with industry. 35
 Research at TÜBİTAK Research Center and Institutes • 10 R&D Institutes • 4 R&D Support Units • 1 Technological Free Zone 2009 Research Expenditures : ~290 Million $ Total Number of Researchers : 2. 656 (Permanent Personnel: 1874, Project personnel: 782) 36
Research at TÜBİTAK Research Center and Institutes • 10 R&D Institutes • 4 R&D Support Units • 1 Technological Free Zone 2009 Research Expenditures : ~290 Million $ Total Number of Researchers : 2. 656 (Permanent Personnel: 1874, Project personnel: 782) 36
 Marmara Research Center (6 Institutes) Food Institute The LARGEST research center in Turkey, leading the S&T in their professions and conducting R&D projects in 7 different areas to meet the customer satisfaction. Energy Institute Earth and Marine Sciences Institute Genetic Engineering and Bio. Technology Institute Materials Institute Chemistry Institute 37
Marmara Research Center (6 Institutes) Food Institute The LARGEST research center in Turkey, leading the S&T in their professions and conducting R&D projects in 7 different areas to meet the customer satisfaction. Energy Institute Earth and Marine Sciences Institute Genetic Engineering and Bio. Technology Institute Materials Institute Chemistry Institute 37
 National Metrology Institute (UME) UME mainly aims to: • Establishing a national measurement system • Providing services to the laboratories in terms of calibration, training, consultancy and other mechanisms. 38
National Metrology Institute (UME) UME mainly aims to: • Establishing a national measurement system • Providing services to the laboratories in terms of calibration, training, consultancy and other mechanisms. 38
 TÜBİTAK National Electronics & Cryptology Research Institute Research Areas • Information Security • Microelectronics • Optoelectronics • Electronic Warfare • Digital Signature Certification Authority 39
TÜBİTAK National Electronics & Cryptology Research Institute Research Areas • Information Security • Microelectronics • Optoelectronics • Electronic Warfare • Digital Signature Certification Authority 39
 Defense Industries R&D Institute (SAGE) The Institute is engaged in research on; • composite solid fuels, • rocket engine design, • missile aerodynamics and flight mechanics, • materials, mechanical design methods, • electro-optics and defence support systems and control systems. 40
Defense Industries R&D Institute (SAGE) The Institute is engaged in research on; • composite solid fuels, • rocket engine design, • missile aerodynamics and flight mechanics, • materials, mechanical design methods, • electro-optics and defence support systems and control systems. 40
 TÜBİTAK Space Technologies Research Institute Research Areas – Space Technologies; Remote Sensing; Power Electronics; Power Quality Monitoring; Power Electronics 250 Employees : Researchers 68%; Technical Support Staff 16%; Administrative Staff 16% 41
TÜBİTAK Space Technologies Research Institute Research Areas – Space Technologies; Remote Sensing; Power Electronics; Power Quality Monitoring; Power Electronics 250 Employees : Researchers 68%; Technical Support Staff 16%; Administrative Staff 16% 41
 INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION 42
INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION 42
 INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION Bilateral Cooperation joint projects, scientific meetings/workshops, expert exchanges, scientific visits etc. are financially supported Multilateral Cooperation Turkey participates actively in the European research programmes as well as regional organisations and international organisations Participation of the Turkish scientists to the activities organised by these organisations is supported or monitored by TÜBİTAK. Cooperation with European Union – FP 7 informing, encouraging and preparing the Turkish scientific and technological research community towards participation in the FP 7. 43
INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION Bilateral Cooperation joint projects, scientific meetings/workshops, expert exchanges, scientific visits etc. are financially supported Multilateral Cooperation Turkey participates actively in the European research programmes as well as regional organisations and international organisations Participation of the Turkish scientists to the activities organised by these organisations is supported or monitored by TÜBİTAK. Cooperation with European Union – FP 7 informing, encouraging and preparing the Turkish scientific and technological research community towards participation in the FP 7. 43
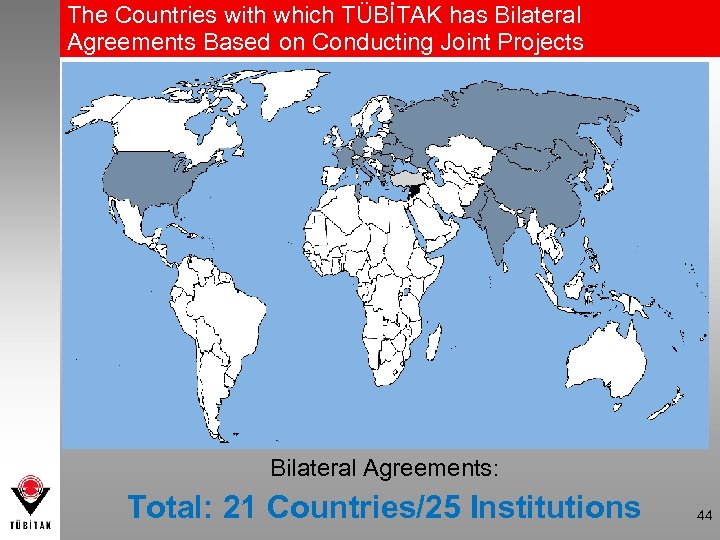 The Countries with which TÜBİTAK has Bilateral Agreements Based on Conducting Joint Projects Bilateral Agreements: Total: 21 Countries/25 Institutions 44
The Countries with which TÜBİTAK has Bilateral Agreements Based on Conducting Joint Projects Bilateral Agreements: Total: 21 Countries/25 Institutions 44
 The Institutions with which TÜBİTAK has Bilateral Agreements Based on Conducting Joint Projects • • BELARUS – National Academy of Sciences • of Belarus • BULGARIA – Academy of Sciences of MONGOLIA – Academy of Sciences PAKISTAN – Ministry of Science and • • • CHINA – Ministry of Science and Technology GERMANY – DFG (Deutsche • ROMANIA – ANSC (National Authority for Bulgaria Forchungsgemeinschaft) – BMBF (Ministry of Education and Research) • GREECE – GSRT (General Secretariat for • FRANCE – CNRS (Centre National de la Research and Technology) Recherche) – Ministry of Foreign Affairs • INDIA – CSIR (Council of Scientific and • ITALY – CNR (Consiglio Nazionale delle Industrial Research) Ricerche) – Ministry of Foreign Affairs • HUNGARY – National Research and • MACEDONIA – Ministry of Education and Technology Office (NKTH) Science Technology Scientific Research) RUSSIAN FEDERATION – Russian Foundation for Basic. Research (RFBR) • • SLOVAKIA – Academy of Sciences SLOVENIA – Ministry of Higher • SOUTH KOREA – KRF (Korea Research • • SYRIA – Ministry of Higher Education – to be launched TUNISIA – Ministry of Higher Education, • UKRAINE – NASU (Academy of Sciences) Education, Science and Technology Foundation) Scientific Research and Technology – Ministry of Education and Science • • USA – NSF (National Science Foundation) Total: 21 Countries/25 45 Institutions
The Institutions with which TÜBİTAK has Bilateral Agreements Based on Conducting Joint Projects • • BELARUS – National Academy of Sciences • of Belarus • BULGARIA – Academy of Sciences of MONGOLIA – Academy of Sciences PAKISTAN – Ministry of Science and • • • CHINA – Ministry of Science and Technology GERMANY – DFG (Deutsche • ROMANIA – ANSC (National Authority for Bulgaria Forchungsgemeinschaft) – BMBF (Ministry of Education and Research) • GREECE – GSRT (General Secretariat for • FRANCE – CNRS (Centre National de la Research and Technology) Recherche) – Ministry of Foreign Affairs • INDIA – CSIR (Council of Scientific and • ITALY – CNR (Consiglio Nazionale delle Industrial Research) Ricerche) – Ministry of Foreign Affairs • HUNGARY – National Research and • MACEDONIA – Ministry of Education and Technology Office (NKTH) Science Technology Scientific Research) RUSSIAN FEDERATION – Russian Foundation for Basic. Research (RFBR) • • SLOVAKIA – Academy of Sciences SLOVENIA – Ministry of Higher • SOUTH KOREA – KRF (Korea Research • • SYRIA – Ministry of Higher Education – to be launched TUNISIA – Ministry of Higher Education, • UKRAINE – NASU (Academy of Sciences) Education, Science and Technology Foundation) Scientific Research and Technology – Ministry of Education and Science • • USA – NSF (National Science Foundation) Total: 21 Countries/25 45 Institutions
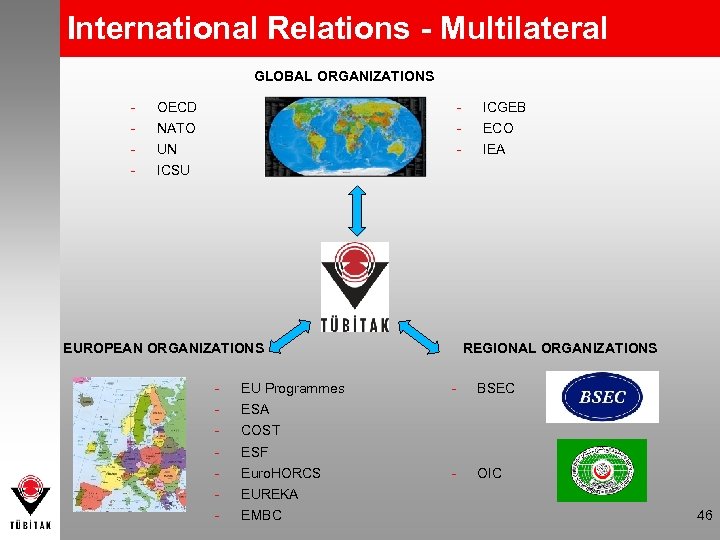 International Relations - Multilateral GLOBAL ORGANIZATIONS - - OECD NATO UN ICGEB ECO IEA ICSU EUROPEAN ORGANIZATIONS - EU Programmes REGIONAL ORGANIZATIONS - BSEC - OIC ESA COST ESF Euro. HORCS EUREKA EMBC 46
International Relations - Multilateral GLOBAL ORGANIZATIONS - - OECD NATO UN ICGEB ECO IEA ICSU EUROPEAN ORGANIZATIONS - EU Programmes REGIONAL ORGANIZATIONS - BSEC - OIC ESA COST ESF Euro. HORCS EUREKA EMBC 46
 TÜBİTAK Thank You… www. tubitak. gov. tr 47
TÜBİTAK Thank You… www. tubitak. gov. tr 47


