198aebf66f4245731e8d146bb321e33b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 The RT’s Role in Discharge Planning Al Heuer, Ph. D, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers SHRP
The RT’s Role in Discharge Planning Al Heuer, Ph. D, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers SHRP
 Major Learning Objectives Review why this is potentially important ! Discuss the indications/contraindications Summarize elements of a discharge plan Examine choices in alternate sites Describe RT equipment used in alternate sites Discuss discharge timelines Review major pitfalls & how to avoid them Provide additional resources
Major Learning Objectives Review why this is potentially important ! Discuss the indications/contraindications Summarize elements of a discharge plan Examine choices in alternate sites Describe RT equipment used in alternate sites Discuss discharge timelines Review major pitfalls & how to avoid them Provide additional resources
 Why is Proper Discharge Planning Important? - Patient Quality of Life – Tends to be better out of the hosptial Efficient use of Services-Keep them out of the Hospital Penalties for Short-term Readmissions under the Hospital Readmission Reduction Program (HRRP)
Why is Proper Discharge Planning Important? - Patient Quality of Life – Tends to be better out of the hosptial Efficient use of Services-Keep them out of the Hospital Penalties for Short-term Readmissions under the Hospital Readmission Reduction Program (HRRP)
 Why is Proper Discharge Planning Important? --Pay-for Performance – The Hospital Readmission Reduction Program (HRRP) ACA created the HRRP, which will reduce Medicare payment rates for hospitals with higher than expected readmission rates for specific conditions.
Why is Proper Discharge Planning Important? --Pay-for Performance – The Hospital Readmission Reduction Program (HRRP) ACA created the HRRP, which will reduce Medicare payment rates for hospitals with higher than expected readmission rates for specific conditions.
 Conditions Covered Under HRRP Initial 2013 Conditions 2015 Expansion COPD Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Heart Failure Pneumonia Coronary Bypass Surgery‐ Coronary Angioplasty Other Vascular Conditions
Conditions Covered Under HRRP Initial 2013 Conditions 2015 Expansion COPD Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Heart Failure Pneumonia Coronary Bypass Surgery‐ Coronary Angioplasty Other Vascular Conditions
 Shhh! Don’t Say “Frequent Flyer”!, HRRP Rewards Less Frequent Flying …and Here’s How! Patient is admitted but gets enrolled in a Re- admission Reduction Protocol Patient gets educated about their condition and the importance of adhering to their Tx. plan. Potential barrier to successful discharge are addressed and post discharge follow-up done. Patient stays out of the hospital. Better HRRP performance means more $ reimbursement to the hospital. More reimbursement means more $ for resources, including staff, equipment, etc.
Shhh! Don’t Say “Frequent Flyer”!, HRRP Rewards Less Frequent Flying …and Here’s How! Patient is admitted but gets enrolled in a Re- admission Reduction Protocol Patient gets educated about their condition and the importance of adhering to their Tx. plan. Potential barrier to successful discharge are addressed and post discharge follow-up done. Patient stays out of the hospital. Better HRRP performance means more $ reimbursement to the hospital. More reimbursement means more $ for resources, including staff, equipment, etc.
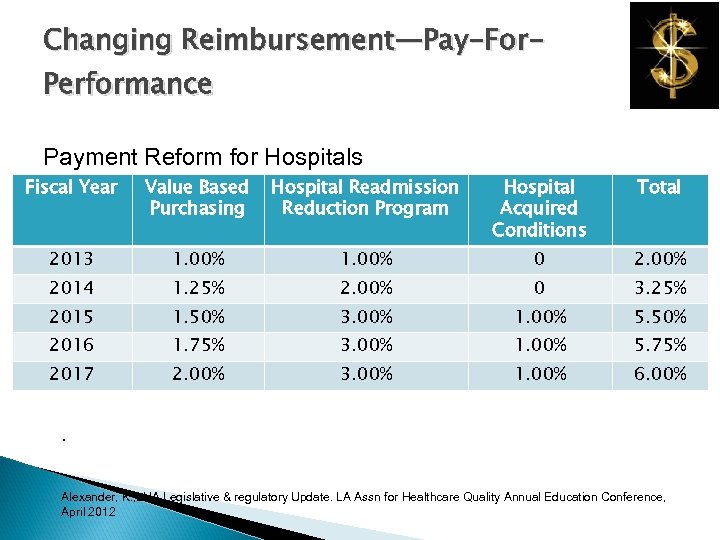 Changing Reimbursement—Pay-For. Performance Payment Reform for Hospitals Fiscal Year Value Based Purchasing Hospital Readmission Reduction Program Hospital Acquired Conditions Total 2013 1. 00% 0 2. 00% 2014 1. 25% 2. 00% 0 3. 25% 2015 1. 50% 3. 00% 1. 00% 5. 50% 2016 1. 75% 3. 00% 1. 00% 5. 75% 2017 2. 00% 3. 00% 1. 00% 6. 00% . Alexander, K. , LHA Legislative & regulatory Update. LA Assn for Healthcare Quality Annual Education Conference, April 2012
Changing Reimbursement—Pay-For. Performance Payment Reform for Hospitals Fiscal Year Value Based Purchasing Hospital Readmission Reduction Program Hospital Acquired Conditions Total 2013 1. 00% 0 2. 00% 2014 1. 25% 2. 00% 0 3. 25% 2015 1. 50% 3. 00% 1. 00% 5. 50% 2016 1. 75% 3. 00% 1. 00% 5. 75% 2017 2. 00% 3. 00% 1. 00% 6. 00% . Alexander, K. , LHA Legislative & regulatory Update. LA Assn for Healthcare Quality Annual Education Conference, April 2012
 Indications & Contraindications Indications: ◦ Stable clinical status—re-admission is unlikely e. g. , hemodynamics, nutrition No pending invasive medical procedures ◦ Willing & able (patient) and family/caregivers ◦ Health insurance coverage is in place ◦ Is the home (or other alternate site) suitable Barrier free Adjacency requirements (bedroom, near bath) Adequate electrical service, with back-up power Contraindications: ◦ Absence of the above
Indications & Contraindications Indications: ◦ Stable clinical status—re-admission is unlikely e. g. , hemodynamics, nutrition No pending invasive medical procedures ◦ Willing & able (patient) and family/caregivers ◦ Health insurance coverage is in place ◦ Is the home (or other alternate site) suitable Barrier free Adjacency requirements (bedroom, near bath) Adequate electrical service, with back-up power Contraindications: ◦ Absence of the above
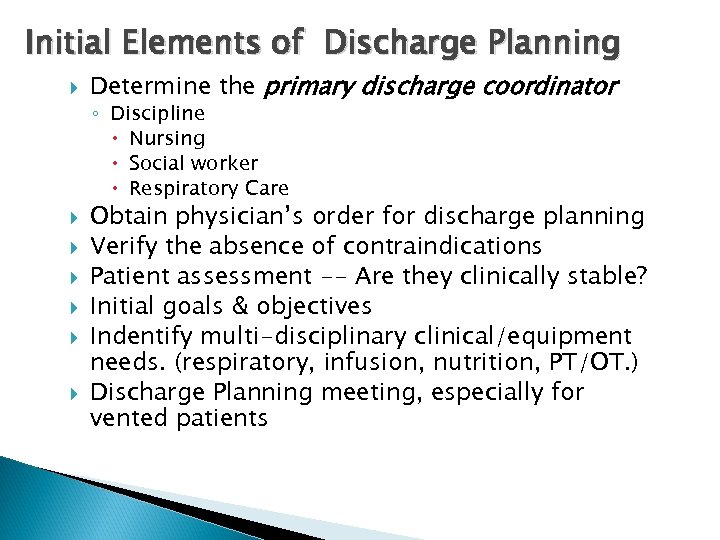 Initial Elements of Discharge Planning Determine the primary discharge coordinator ◦ Discipline Nursing Social worker Respiratory Care Obtain physician’s order for discharge planning Verify the absence of contraindications Patient assessment -- Are they clinically stable? Initial goals & objectives Indentify multi-disciplinary clinical/equipment needs. (respiratory, infusion, nutrition, PT/OT. ) Discharge Planning meeting, especially for vented patients
Initial Elements of Discharge Planning Determine the primary discharge coordinator ◦ Discipline Nursing Social worker Respiratory Care Obtain physician’s order for discharge planning Verify the absence of contraindications Patient assessment -- Are they clinically stable? Initial goals & objectives Indentify multi-disciplinary clinical/equipment needs. (respiratory, infusion, nutrition, PT/OT. ) Discharge Planning meeting, especially for vented patients
 Elements of the Discharge Planning (cont. ) Review insurance coverage and caveats Determine most appropriate clinical site Select specific facility or homecare company, with input from patient & insurer If homecare, ensure: ◦ Caregiver training ◦ Home inspection ◦ In-hospital vent trial (if appropriate) Document plan, including timelines & goals Review plan and modify as appropriate Obtain discharge order and execute plan Patient follow-up mechanism
Elements of the Discharge Planning (cont. ) Review insurance coverage and caveats Determine most appropriate clinical site Select specific facility or homecare company, with input from patient & insurer If homecare, ensure: ◦ Caregiver training ◦ Home inspection ◦ In-hospital vent trial (if appropriate) Document plan, including timelines & goals Review plan and modify as appropriate Obtain discharge order and execute plan Patient follow-up mechanism
 Pre-Discharge Medical Record Review Chart Review: ◦ MD’s orders: Discharge planning order ◦ Progress notes: Have they made sufficient progress? Pending invasive procedures/surgeries? ◦ Labs/X-rays: Serial CBCs, cultures, CXRs ◦ Special limitations/needs ◦ Therapy: Current Resp. Therapy Supp’l O 2 Bronchodilators ◦ Otherapy PT, OT, Nursing
Pre-Discharge Medical Record Review Chart Review: ◦ MD’s orders: Discharge planning order ◦ Progress notes: Have they made sufficient progress? Pending invasive procedures/surgeries? ◦ Labs/X-rays: Serial CBCs, cultures, CXRs ◦ Special limitations/needs ◦ Therapy: Current Resp. Therapy Supp’l O 2 Bronchodilators ◦ Otherapy PT, OT, Nursing
 Pre-Discharge Patient Assessment Overall appearance Psycho-social Issues Vital signs Breath sounds SPO 2/ABG Overall clinical stability Ambulation Tolerance for ADLs
Pre-Discharge Patient Assessment Overall appearance Psycho-social Issues Vital signs Breath sounds SPO 2/ABG Overall clinical stability Ambulation Tolerance for ADLs
 Common Alternate Site Conditions COPD Restrictive Disorders ◦ Pul. Fibrosis, Sarcoidosis, CF, TB, Lung CA Cardiovascular Conditions -- CHF, Post MI Other Conditions ◦ OSA ◦ BPD ◦ Periodic breathing
Common Alternate Site Conditions COPD Restrictive Disorders ◦ Pul. Fibrosis, Sarcoidosis, CF, TB, Lung CA Cardiovascular Conditions -- CHF, Post MI Other Conditions ◦ OSA ◦ BPD ◦ Periodic breathing
 Discharge Planning Team—Ideally Multidisciplinary & Collaborative Patient/Caregiver Case Manager (In-house & Ins. /HMO Rep) MD RN (In-hospital & Post-Discharge) RCP Social Worker DME Provider Other Appropriate Disciplines (PT, OT, etc. )
Discharge Planning Team—Ideally Multidisciplinary & Collaborative Patient/Caregiver Case Manager (In-house & Ins. /HMO Rep) MD RN (In-hospital & Post-Discharge) RCP Social Worker DME Provider Other Appropriate Disciplines (PT, OT, etc. )
 Team Duties: Continuity of Care & ADLs Any deal killers for the discharge? ? ? Patient assessment and follow-up Review pt’s psychosocial status Health insurance issues Patient/caregiver education Plan, coordinate and evaluate care Determine and provide equipment needs Using community resources (meals, transp. ) Vocational training and job placement
Team Duties: Continuity of Care & ADLs Any deal killers for the discharge? ? ? Patient assessment and follow-up Review pt’s psychosocial status Health insurance issues Patient/caregiver education Plan, coordinate and evaluate care Determine and provide equipment needs Using community resources (meals, transp. ) Vocational training and job placement
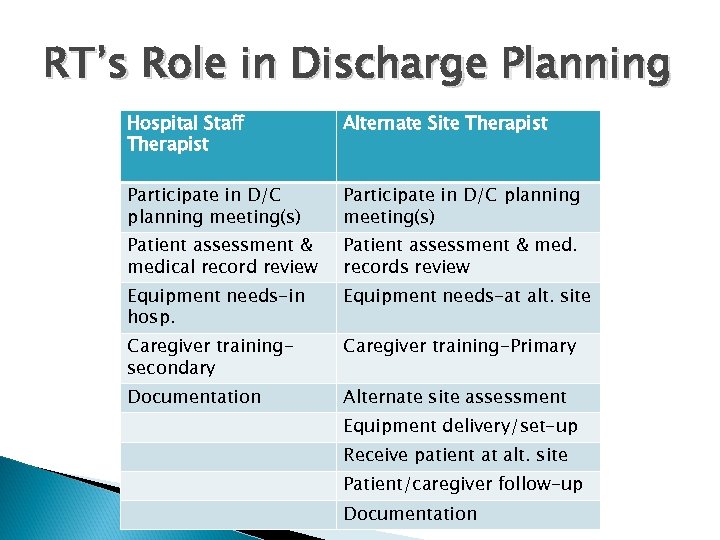 RT’s Role in Discharge Planning Hospital Staff Therapist Alternate Site Therapist Participate in D/C planning meeting(s) Patient assessment & medical record review Patient assessment & med. records review Equipment needs-in hosp. Equipment needs-at alt. site Caregiver trainingsecondary Caregiver training-Primary Documentation Alternate site assessment Equipment delivery/set-up Receive patient at alt. site Patient/caregiver follow-up Documentation
RT’s Role in Discharge Planning Hospital Staff Therapist Alternate Site Therapist Participate in D/C planning meeting(s) Patient assessment & medical record review Patient assessment & med. records review Equipment needs-in hosp. Equipment needs-at alt. site Caregiver trainingsecondary Caregiver training-Primary Documentation Alternate site assessment Equipment delivery/set-up Receive patient at alt. site Patient/caregiver follow-up Documentation
 Determining the Appropriate Alternate Site Collaborative: Patient, caregiver, interdisciplinary team, insurance co. , facility/home care company The category (home vs SNF) is a function of: Medical complexity of patient…in relation to facility’s or homecare company’s ability to meet such needs… For ethical/legal reasons, the patient &/or family should participate in the choice of home care company or facility.
Determining the Appropriate Alternate Site Collaborative: Patient, caregiver, interdisciplinary team, insurance co. , facility/home care company The category (home vs SNF) is a function of: Medical complexity of patient…in relation to facility’s or homecare company’s ability to meet such needs… For ethical/legal reasons, the patient &/or family should participate in the choice of home care company or facility.
 Non-Acute Care Alternatives Short-term Rehab—Interim step to another alternate site. To increase ADLs SNF—Longer term, not medically complex Long-term Acute Care Hospitals (LTACs) ◦ If need to be seen by an MD daily ◦ More complex medical needs which may be met outside acute care hospital Home—The emphasis of this presentation Hospice-Terminally ill patients
Non-Acute Care Alternatives Short-term Rehab—Interim step to another alternate site. To increase ADLs SNF—Longer term, not medically complex Long-term Acute Care Hospitals (LTACs) ◦ If need to be seen by an MD daily ◦ More complex medical needs which may be met outside acute care hospital Home—The emphasis of this presentation Hospice-Terminally ill patients
 Short-term Rehab Care Generally Less than 60 Days (per Medicare Guidelines) Indicated if underlying condition is improved but Pt needs significant rehabilitation due to extensive convalescence. ◦ e. g. : Extensive stay in the ICU. Modalities: Resp. therapy, PT, OT, nursing Often, Patient goes home or to long-term facility after rehab.
Short-term Rehab Care Generally Less than 60 Days (per Medicare Guidelines) Indicated if underlying condition is improved but Pt needs significant rehabilitation due to extensive convalescence. ◦ e. g. : Extensive stay in the ICU. Modalities: Resp. therapy, PT, OT, nursing Often, Patient goes home or to long-term facility after rehab.
 Alternative to Homecare--Long. Term & Subacute Home care contraindicated. ◦ Pt. Can’t perform self-care, insufficient caregiver support ◦ Pt. is still somewhat unstable ◦ Inappropriate home setting Patient needs 24 -hour medical supervision. Patient requires relatively intensive level of support services.
Alternative to Homecare--Long. Term & Subacute Home care contraindicated. ◦ Pt. Can’t perform self-care, insufficient caregiver support ◦ Pt. is still somewhat unstable ◦ Inappropriate home setting Patient needs 24 -hour medical supervision. Patient requires relatively intensive level of support services.
 Home Care is Often, the Site of Choice: Patient is stable -- No longer requires acute or sub-acute levels of care ◦ Initial reason for hospitalization is resolved Patient/caregiver -- Can properly administer treatment and routine care. Insurance company approval--Home care tends to be most cost effective Appropriate home environment -- For safe and effective delivery of care, confirmed via a pre-discharge home safety check. Hospice Care -- End of life palliative homecare
Home Care is Often, the Site of Choice: Patient is stable -- No longer requires acute or sub-acute levels of care ◦ Initial reason for hospitalization is resolved Patient/caregiver -- Can properly administer treatment and routine care. Insurance company approval--Home care tends to be most cost effective Appropriate home environment -- For safe and effective delivery of care, confirmed via a pre-discharge home safety check. Hospice Care -- End of life palliative homecare
 Common Alternative Site & Home Care Equipment Respiratory: ◦ Oxygen -- Concentrator, Liquid, conserving device ◦ Aerosol Therapy Large Volume--Tacheostomy Pts. Small Volume--COPD & Asthma CPT -- CF & Bronchiectasis Nasal CPAP -- OSA Bipap -- OSA, Neuromuscular DX Ventilators—Invasive/non-invasive Apnea monitor Disposables: trach tubes, O 2 devices, circuits, suction Non-respiratory: Beds, wheelchairs, lifts. ◦ ◦ ◦
Common Alternative Site & Home Care Equipment Respiratory: ◦ Oxygen -- Concentrator, Liquid, conserving device ◦ Aerosol Therapy Large Volume--Tacheostomy Pts. Small Volume--COPD & Asthma CPT -- CF & Bronchiectasis Nasal CPAP -- OSA Bipap -- OSA, Neuromuscular DX Ventilators—Invasive/non-invasive Apnea monitor Disposables: trach tubes, O 2 devices, circuits, suction Non-respiratory: Beds, wheelchairs, lifts. ◦ ◦ ◦
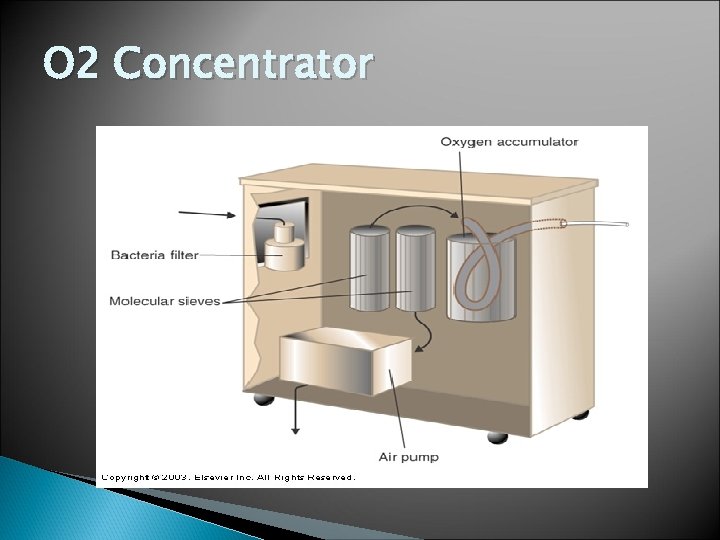 O 2 Concentrator
O 2 Concentrator
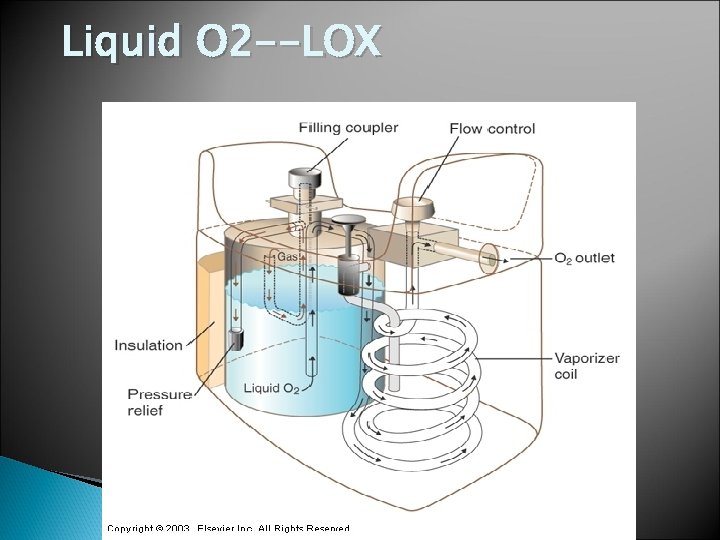 Liquid O 2 --LOX
Liquid O 2 --LOX
 Bi. PAP for NPPV (Respironics Bi. PAP Synchrony)
Bi. PAP for NPPV (Respironics Bi. PAP Synchrony)
 Volume Ventilators
Volume Ventilators
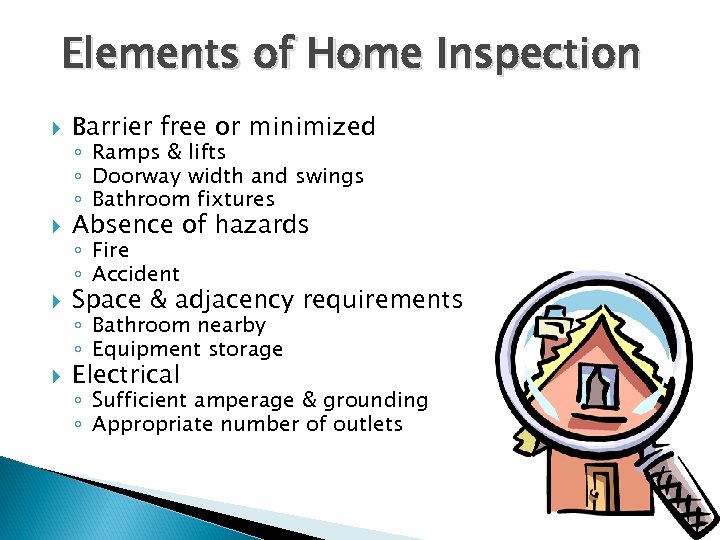 Elements of Home Inspection Barrier free or minimized Absence of hazards Space & adjacency requirements Electrical ◦ Ramps & lifts ◦ Doorway width and swings ◦ Bathroom fixtures ◦ Fire ◦ Accident ◦ Bathroom nearby ◦ Equipment storage ◦ Sufficient amperage & grounding ◦ Appropriate number of outlets
Elements of Home Inspection Barrier free or minimized Absence of hazards Space & adjacency requirements Electrical ◦ Ramps & lifts ◦ Doorway width and swings ◦ Bathroom fixtures ◦ Fire ◦ Accident ◦ Bathroom nearby ◦ Equipment storage ◦ Sufficient amperage & grounding ◦ Appropriate number of outlets
 Patient/Caregiver Education Essentials Know your material!!! Assess your audience & learning environment Don’t use technical lingo Set realistic learning objectives & don’t overload audience Use varied teaching methods ◦ Written material ◦ Hands-on demo Give examples, reinforce & repeat!!! Keep audience involved & encourage questions Provide written and ongoing (website) resources Provide for language translation Evaluate extent of learning (e. g. , return demonstration) Obtain learner feedback Revise and refine as necessary
Patient/Caregiver Education Essentials Know your material!!! Assess your audience & learning environment Don’t use technical lingo Set realistic learning objectives & don’t overload audience Use varied teaching methods ◦ Written material ◦ Hands-on demo Give examples, reinforce & repeat!!! Keep audience involved & encourage questions Provide written and ongoing (website) resources Provide for language translation Evaluate extent of learning (e. g. , return demonstration) Obtain learner feedback Revise and refine as necessary
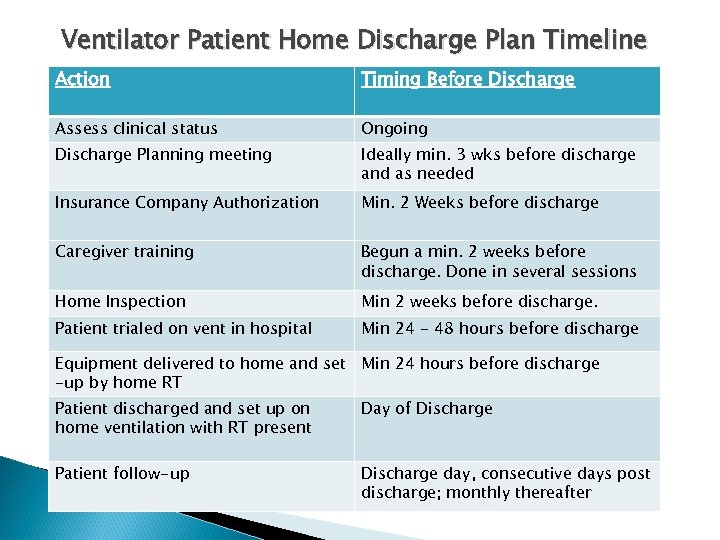 Ventilator Patient Home Discharge Plan Timeline Action Timing Before Discharge Assess clinical status Ongoing Discharge Planning meeting Ideally min. 3 wks before discharge and as needed Insurance Company Authorization Min. 2 Weeks before discharge Caregiver training Begun a min. 2 weeks before discharge. Done in several sessions Home Inspection Min 2 weeks before discharge. Patient trialed on vent in hospital Min 24 - 48 hours before discharge Equipment delivered to home and set Min 24 hours before discharge -up by home RT Patient discharged and set up on home ventilation with RT present Day of Discharge Patient follow-up Discharge day, consecutive days post discharge; monthly thereafter
Ventilator Patient Home Discharge Plan Timeline Action Timing Before Discharge Assess clinical status Ongoing Discharge Planning meeting Ideally min. 3 wks before discharge and as needed Insurance Company Authorization Min. 2 Weeks before discharge Caregiver training Begun a min. 2 weeks before discharge. Done in several sessions Home Inspection Min 2 weeks before discharge. Patient trialed on vent in hospital Min 24 - 48 hours before discharge Equipment delivered to home and set Min 24 hours before discharge -up by home RT Patient discharged and set up on home ventilation with RT present Day of Discharge Patient follow-up Discharge day, consecutive days post discharge; monthly thereafter
 The Written Discharge Plan Physician of record and order Patient diagnosis and current clinical status Patient equipment and clinical needs Goals & objectives Time Line with tentative discharge date Schedule of key activities, ◦ Who’s responsible for what ◦ Target dates Educational materials & training assessment tools Funding source and limits
The Written Discharge Plan Physician of record and order Patient diagnosis and current clinical status Patient equipment and clinical needs Goals & objectives Time Line with tentative discharge date Schedule of key activities, ◦ Who’s responsible for what ◦ Target dates Educational materials & training assessment tools Funding source and limits
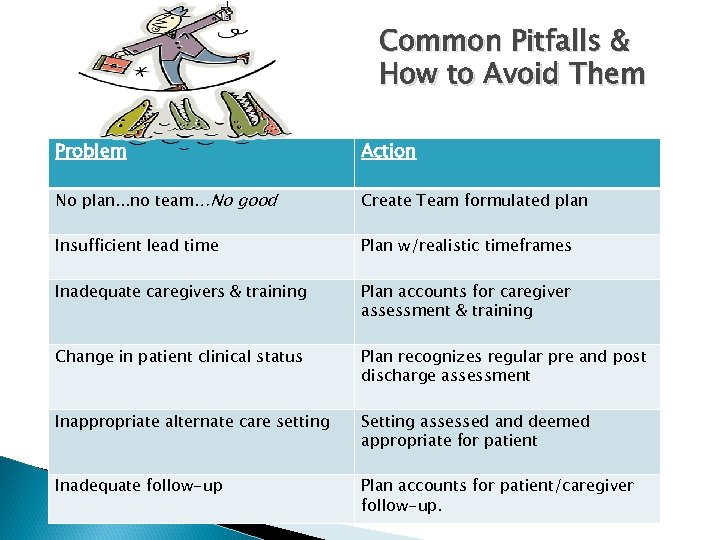 Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them Problem Action No plan. . . no team…No good Create Team formulated plan Insufficient lead time Plan w/realistic timeframes Inadequate caregivers & training Plan accounts for caregiver assessment & training Change in patient clinical status Plan recognizes regular pre and post discharge assessment Inappropriate alternate care setting Setting assessed and deemed appropriate for patient Inadequate follow-up Plan accounts for patient/caregiver follow-up.
Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them Problem Action No plan. . . no team…No good Create Team formulated plan Insufficient lead time Plan w/realistic timeframes Inadequate caregivers & training Plan accounts for caregiver assessment & training Change in patient clinical status Plan recognizes regular pre and post discharge assessment Inappropriate alternate care setting Setting assessed and deemed appropriate for patient Inadequate follow-up Plan accounts for patient/caregiver follow-up.
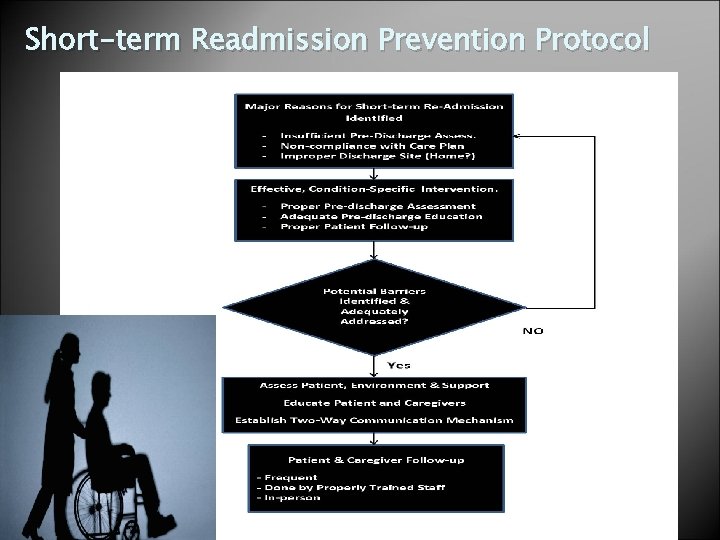 Short-term Readmission Prevention Protocol
Short-term Readmission Prevention Protocol
 Outcome Assessment —Was the Discharge Successful? ◦ Was the patient received at the new site without complications? ◦ Treatment/Progress goals being met & documented (e. g. , trach collar trial, increased ADL tolerance) ◦ Patient the patient clinically stable ◦ Customer/patient is satisfied (via P. G. survey) ◦ No short-term readmission to hospital!!! ◦ If Hospice -- Patient comfort & dignity
Outcome Assessment —Was the Discharge Successful? ◦ Was the patient received at the new site without complications? ◦ Treatment/Progress goals being met & documented (e. g. , trach collar trial, increased ADL tolerance) ◦ Patient the patient clinically stable ◦ Customer/patient is satisfied (via P. G. survey) ◦ No short-term readmission to hospital!!! ◦ If Hospice -- Patient comfort & dignity
 Additional Resources AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines (related to discharge planning and respiratory therapy in alternate sites). Butler, TJ, Laboratory Exercises for Competency in Respiratory Care, ed 3, 2013. Oakes, D; Wyka, K & Wyka, K, Oakes Respiratory Home Care - An On-Site Reference Guide, 2012. Kacmarek, RM, Stoller, J & Heuer AJ, Egan’s Fundamentals of Respiratory Care, ed 11 th ed, 2016. Heuer, AJ & Scanlan, CL, Clinical Assessment in Respiratory Care, ed 7, 2014
Additional Resources AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines (related to discharge planning and respiratory therapy in alternate sites). Butler, TJ, Laboratory Exercises for Competency in Respiratory Care, ed 3, 2013. Oakes, D; Wyka, K & Wyka, K, Oakes Respiratory Home Care - An On-Site Reference Guide, 2012. Kacmarek, RM, Stoller, J & Heuer AJ, Egan’s Fundamentals of Respiratory Care, ed 11 th ed, 2016. Heuer, AJ & Scanlan, CL, Clinical Assessment in Respiratory Care, ed 7, 2014


