8da7c14418fd93699ba6a8d8a9c57f61.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 The Roman Circus and Amphitheatre
The Roman Circus and Amphitheatre
 Definitions circus: chariot race track amphitheatre: oval building for gladiatorial games, wild beast shows, etc.
Definitions circus: chariot race track amphitheatre: oval building for gladiatorial games, wild beast shows, etc.
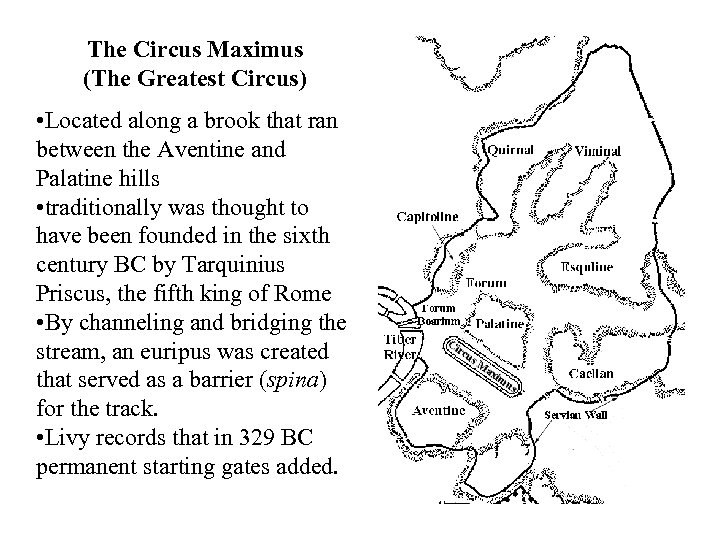 The Circus Maximus (The Greatest Circus) • Located along a brook that ran between the Aventine and Palatine hills • traditionally was thought to have been founded in the sixth century BC by Tarquinius Priscus, the fifth king of Rome • By channeling and bridging the stream, an euripus was created that served as a barrier (spina) for the track. • Livy records that in 329 BC permanent starting gates added.
The Circus Maximus (The Greatest Circus) • Located along a brook that ran between the Aventine and Palatine hills • traditionally was thought to have been founded in the sixth century BC by Tarquinius Priscus, the fifth king of Rome • By channeling and bridging the stream, an euripus was created that served as a barrier (spina) for the track. • Livy records that in 329 BC permanent starting gates added.
 History of the Circus Maximus • Starting gates rebuilt in 174 BC • Seven large wooden eggs set up between columns on the spina to indicate the completion of each lap. • Reconstruction by Julius Caesar (60 -44 B. C. )
History of the Circus Maximus • Starting gates rebuilt in 174 BC • Seven large wooden eggs set up between columns on the spina to indicate the completion of each lap. • Reconstruction by Julius Caesar (60 -44 B. C. )
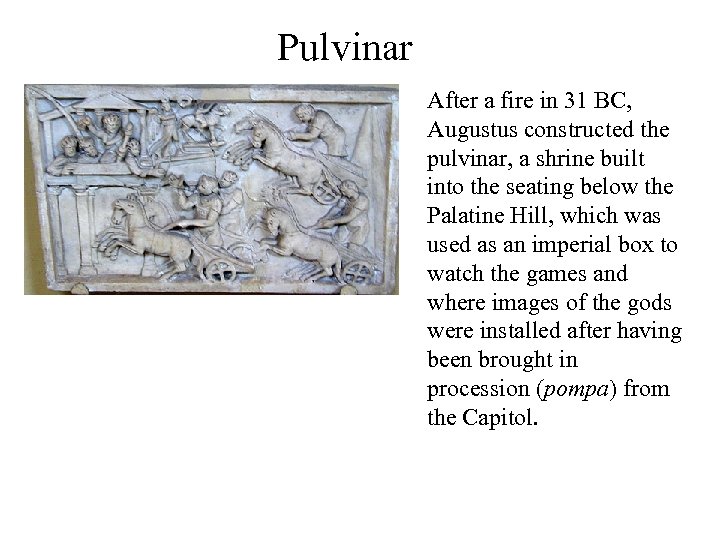 Pulvinar After a fire in 31 BC, Augustus constructed the pulvinar, a shrine built into the seating below the Palatine Hill, which was used as an imperial box to watch the games and where images of the gods were installed after having been brought in procession (pompa) from the Capitol.
Pulvinar After a fire in 31 BC, Augustus constructed the pulvinar, a shrine built into the seating below the Palatine Hill, which was used as an imperial box to watch the games and where images of the gods were installed after having been brought in procession (pompa) from the Capitol.
 Circus Maximus and the Palatine
Circus Maximus and the Palatine
 The Pulvinar Today
The Pulvinar Today
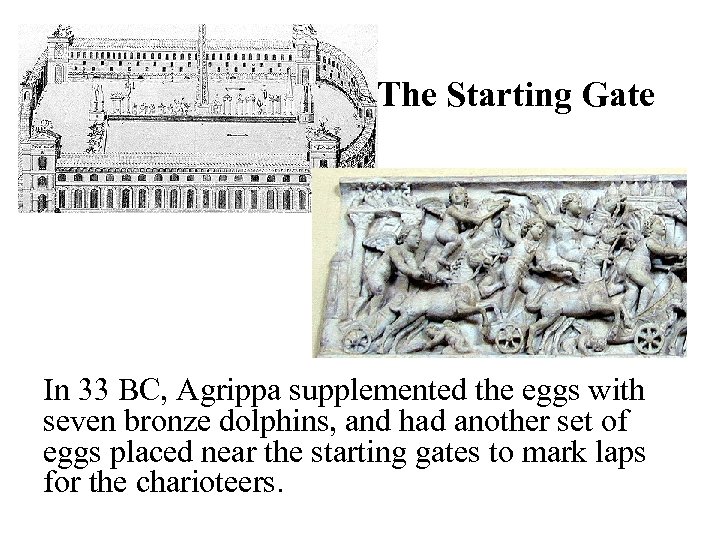 The Starting Gate In 33 BC, Agrippa supplemented the eggs with seven bronze dolphins, and had another set of eggs placed near the starting gates to mark laps for the charioteers.
The Starting Gate In 33 BC, Agrippa supplemented the eggs with seven bronze dolphins, and had another set of eggs placed near the starting gates to mark laps for the charioteers.
 The Obelisk • The obelisk taken by Augustus from Heliopolis soon after the annexation of Egypt in 30 BC was the first to be brought to Rome. • In 10 BC, Augustus also erected it on the spina as a dedication to the Sun and monument of his conquest of Egypt.
The Obelisk • The obelisk taken by Augustus from Heliopolis soon after the annexation of Egypt in 30 BC was the first to be brought to Rome. • In 10 BC, Augustus also erected it on the spina as a dedication to the Sun and monument of his conquest of Egypt.
 Erecting the Obelisk
Erecting the Obelisk
 The Obelisk Today In 1587, it was excavated at the order of Pope Sixtus V and removed to its present site in the Piazza del Popolo.
The Obelisk Today In 1587, it was excavated at the order of Pope Sixtus V and removed to its present site in the Piazza del Popolo.
 Dionysus of Halicarnassus on the Circus Maximus • Dionysius of Halicarnassus described the Circus Maximus in 7 BC as "one of the most beautiful and admirable structures in Rome. " • It measured approximately 2, 035 feet in length and 460 feet in width and could seat 150, 000. • Outside, says Dionysius, "there are entrances and ascents for the spectators at every shop, so that the countless thousands of people may enter and depart without inconvenience. " Inhabited by cooks, astrologers, and prostitutes, it was in this arcade of wooden shops (tabernae) that the disastrous fire of AD 64 broke out during the reign of Nero.
Dionysus of Halicarnassus on the Circus Maximus • Dionysius of Halicarnassus described the Circus Maximus in 7 BC as "one of the most beautiful and admirable structures in Rome. " • It measured approximately 2, 035 feet in length and 460 feet in width and could seat 150, 000. • Outside, says Dionysius, "there are entrances and ascents for the spectators at every shop, so that the countless thousands of people may enter and depart without inconvenience. " Inhabited by cooks, astrologers, and prostitutes, it was in this arcade of wooden shops (tabernae) that the disastrous fire of AD 64 broke out during the reign of Nero.
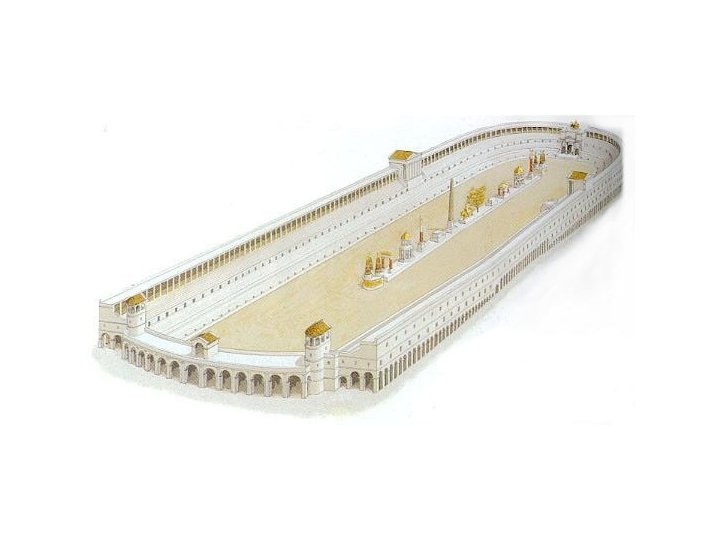

 The Circus Maximus Today
The Circus Maximus Today
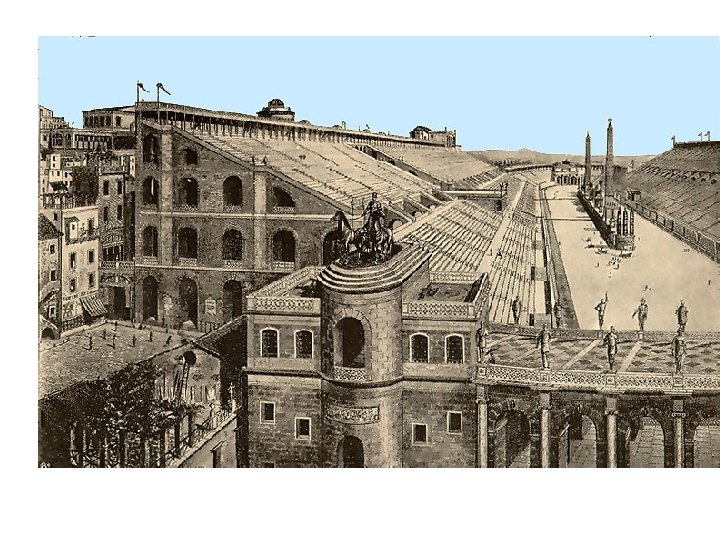

 East End of the Circus Maximus
East End of the Circus Maximus
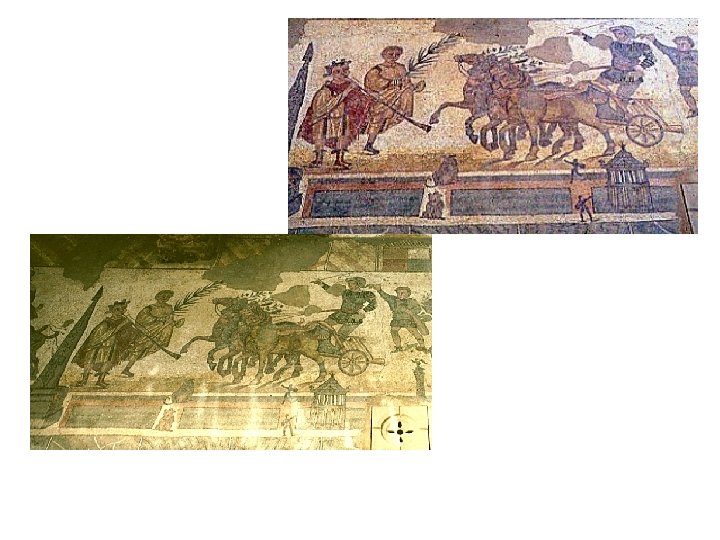
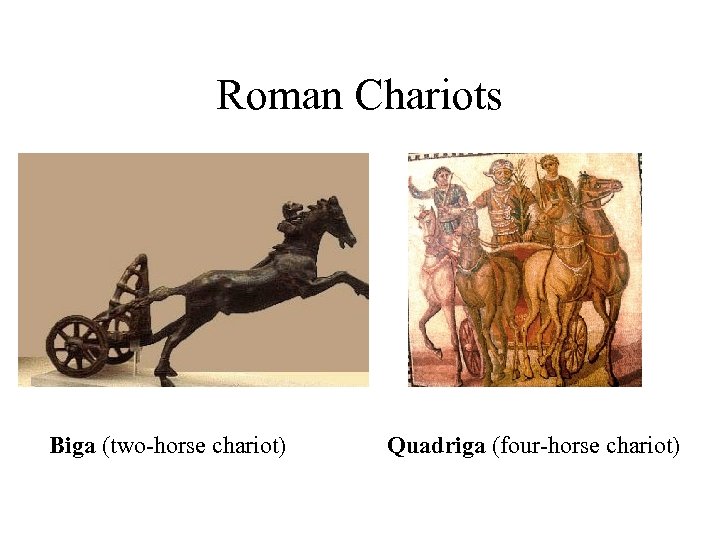 Roman Chariots Biga (two-horse chariot) Quadriga (four-horse chariot)
Roman Chariots Biga (two-horse chariot) Quadriga (four-horse chariot)
 Piazza Amerina Mosaic
Piazza Amerina Mosaic
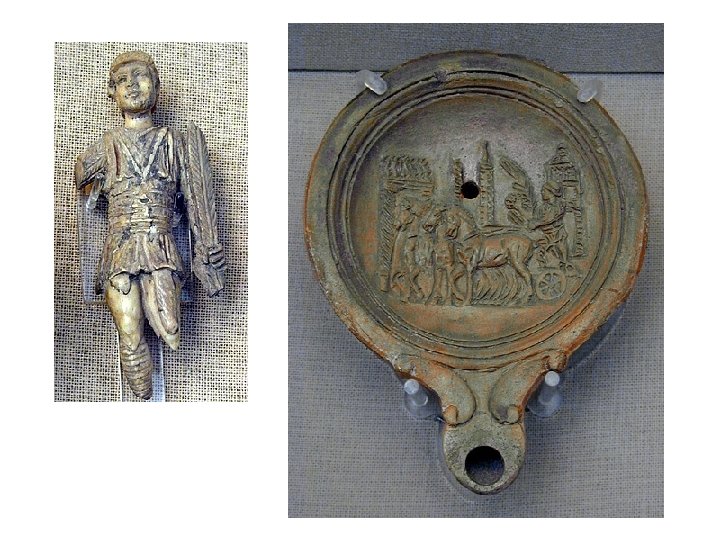


 Other Circuses in Rome Circus of Nero Circus of Maxentius
Other Circuses in Rome Circus of Nero Circus of Maxentius
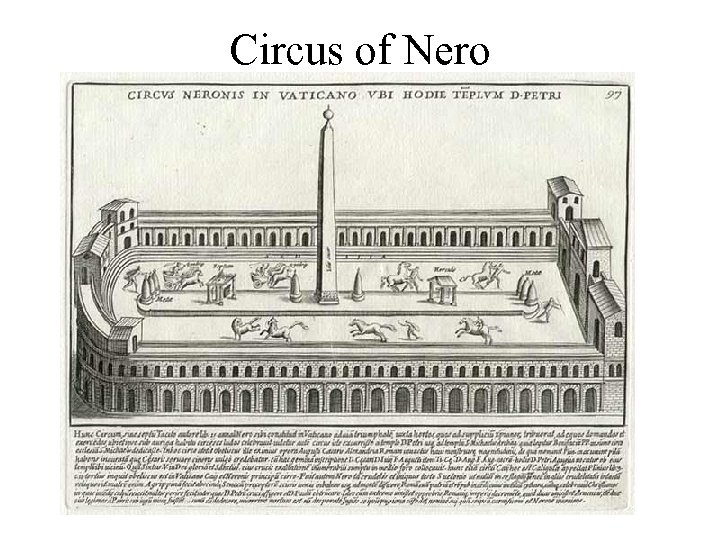 Circus of Nero
Circus of Nero
 Circus of Nero Today
Circus of Nero Today
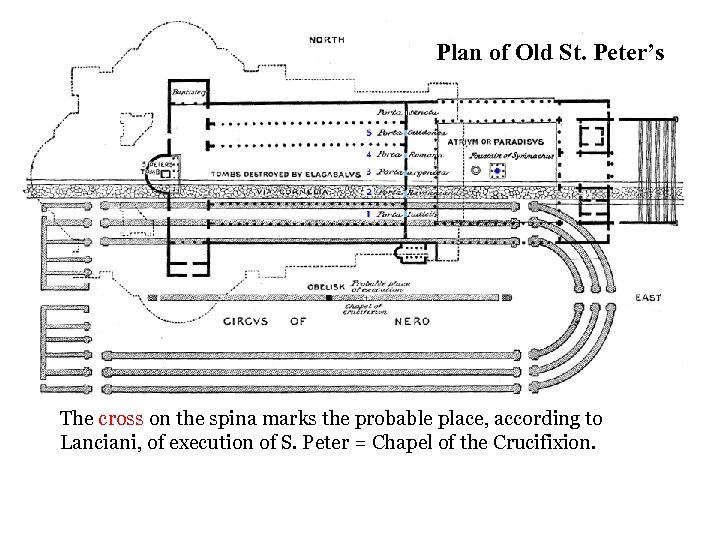 Plan of Old St. Peter’s The cross on the spina marks the probable place, according to Lanciani, of execution of S. Peter = Chapel of the Crucifixion.
Plan of Old St. Peter’s The cross on the spina marks the probable place, according to Lanciani, of execution of S. Peter = Chapel of the Crucifixion.
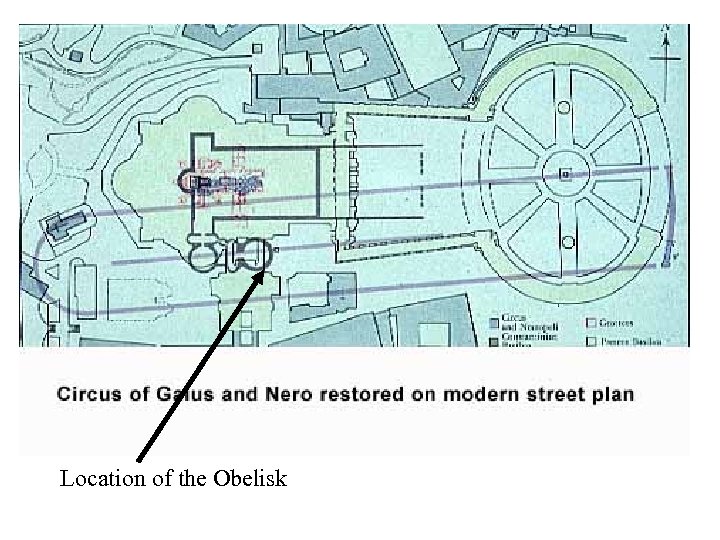 Location of the Obelisk
Location of the Obelisk
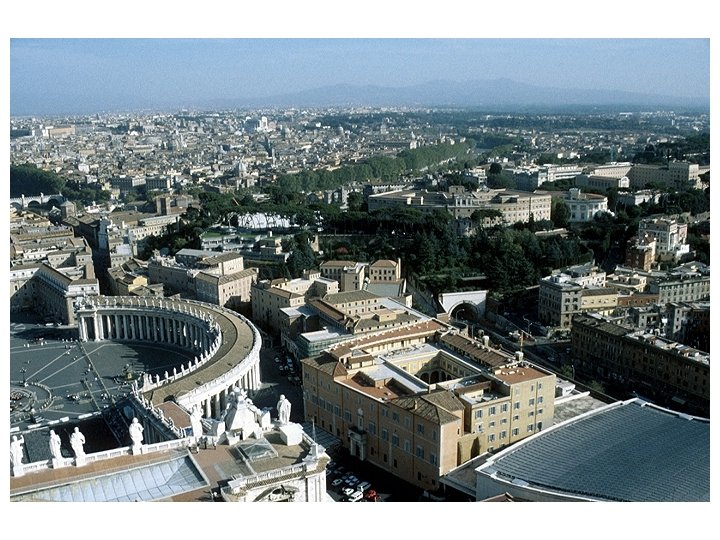


 Obelisk of Nero’s Circus • Possibly quarried at Aswan in the reign of Nebkaure Amenemhet II (B. C. 19 th Century), and erected at the pylon of the Temple of the Sun in Heliopolis. • Erected at the Julian Forum in Alexandria by the order of Octavianus (the first Roman Emperor Augustus [reigned B. C. 27 - A. D. 14]) • In A. D. 37 (40? ), then Roman Emperor Caligula transported it to Rome, and erected it in the Caligula Circus (later the Nero Circus (Circus Gai et Neronis), or the Vatican Circus). • The time elapsed. . . , then Pope Sixtus V [reigned 1585 -1590] directed the obelisk to be reerected at the center of the colonnaded square, so -called St. Peter's Square in 1586, in front of the "new" Basilica of St. Peter, which was under construction at that time.
Obelisk of Nero’s Circus • Possibly quarried at Aswan in the reign of Nebkaure Amenemhet II (B. C. 19 th Century), and erected at the pylon of the Temple of the Sun in Heliopolis. • Erected at the Julian Forum in Alexandria by the order of Octavianus (the first Roman Emperor Augustus [reigned B. C. 27 - A. D. 14]) • In A. D. 37 (40? ), then Roman Emperor Caligula transported it to Rome, and erected it in the Caligula Circus (later the Nero Circus (Circus Gai et Neronis), or the Vatican Circus). • The time elapsed. . . , then Pope Sixtus V [reigned 1585 -1590] directed the obelisk to be reerected at the center of the colonnaded square, so -called St. Peter's Square in 1586, in front of the "new" Basilica of St. Peter, which was under construction at that time.
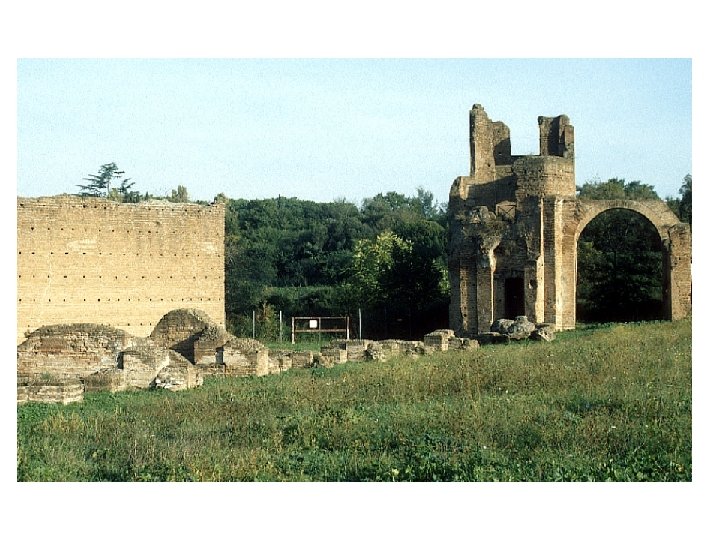
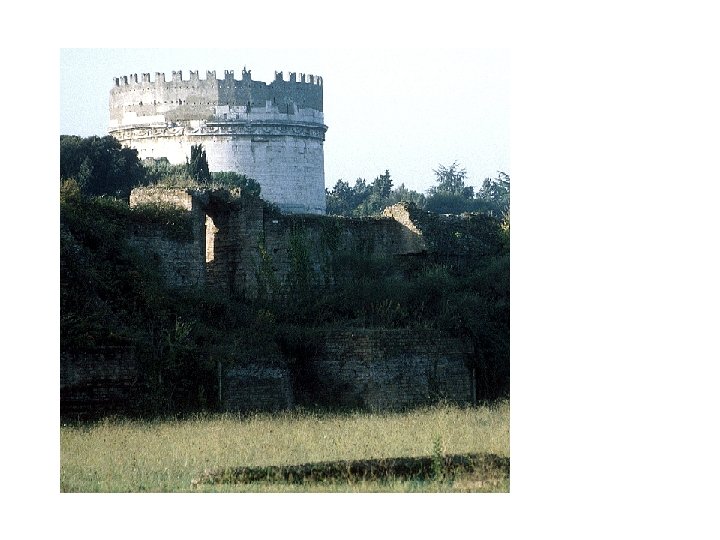
 Circus of Maxentius The Circus of Maxentius, built at the beginning of the fourth century near the Via Appia. It is the best preserved of all Roman circuses. It was 513 meters long and 91 meters wide, and held some 10, 000 people.
Circus of Maxentius The Circus of Maxentius, built at the beginning of the fourth century near the Via Appia. It is the best preserved of all Roman circuses. It was 513 meters long and 91 meters wide, and held some 10, 000 people.
 Model
Model


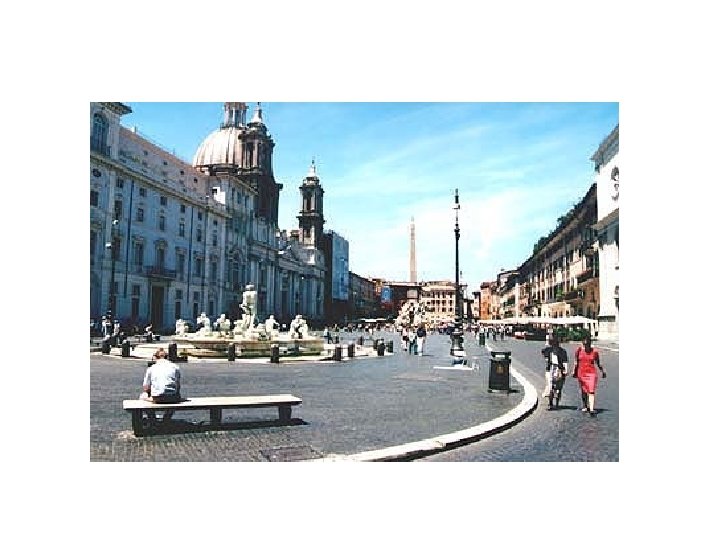
 The Obelisk • Created at Aswan (Upper Egypt, 640 km south of Cairo) by the order of Roman Emperor Domitianus for his accession of Domitianus in A. D. 81. • Carried to Rome and erected between the Serapeum Temple • Maxentius [reigned 306 -312] moved it to the Circo di Massenzio. • At some unknown date, the obelisk was toppled and broken into a few pieces. • Finally, in 17 th Century, Pope Innocentius X [reigned 1644 -1655] decided to re-erect it in Piazza Navona in commemoration of his election. Because he had lived in the building which faces the Piazza Navona.
The Obelisk • Created at Aswan (Upper Egypt, 640 km south of Cairo) by the order of Roman Emperor Domitianus for his accession of Domitianus in A. D. 81. • Carried to Rome and erected between the Serapeum Temple • Maxentius [reigned 306 -312] moved it to the Circo di Massenzio. • At some unknown date, the obelisk was toppled and broken into a few pieces. • Finally, in 17 th Century, Pope Innocentius X [reigned 1644 -1655] decided to re-erect it in Piazza Navona in commemoration of his election. Because he had lived in the building which faces the Piazza Navona.
 Stadium of Domitian • Built by Domitian in the Campus Martius for athletic contests • Used for several years for gladiatorial combats after the Colosseum was damaged by fire in 217. • Arcades were occupied by brothels • Restored by Alexander Severus, and sometimes called in the Middle Ages circus Alexandri
Stadium of Domitian • Built by Domitian in the Campus Martius for athletic contests • Used for several years for gladiatorial combats after the Colosseum was damaged by fire in 217. • Arcades were occupied by brothels • Restored by Alexander Severus, and sometimes called in the Middle Ages circus Alexandri

 Remains of the Entrance
Remains of the Entrance
 Piazza Navonna • Seats for about 15, 000 spectators • According to the legend, S. Agnes met a martyr's death in the brothels in the arcades of this stadium, and in her honour a church was built in the ninth century in the middle of the cavea on the west side, which was afterwards known as S. Agnese in Agone or de Cryptis Agonis • The Piazza Navona, the largest in the city, now called officially Circo Agonale, preserves almost exactly the shape and size of the stadium. The piazza itself corresponds closely with the arena, the length of which seems to have been about 250 metres, and the surrounding buildings stand on the ruins of the cavea. • Under the church of S. Agnese remains of brick and concrete walls, travertine pilasters and the seats of the cavea are still to be seen, and other traces have been found beneath the existing buildings at other points. For excavations in the sixteenth century, see LS ii. 228‑ 231; iii. 224‑ 225; iv. 190; LR 498‑ 500; HJ 592‑ 594.
Piazza Navonna • Seats for about 15, 000 spectators • According to the legend, S. Agnes met a martyr's death in the brothels in the arcades of this stadium, and in her honour a church was built in the ninth century in the middle of the cavea on the west side, which was afterwards known as S. Agnese in Agone or de Cryptis Agonis • The Piazza Navona, the largest in the city, now called officially Circo Agonale, preserves almost exactly the shape and size of the stadium. The piazza itself corresponds closely with the arena, the length of which seems to have been about 250 metres, and the surrounding buildings stand on the ruins of the cavea. • Under the church of S. Agnese remains of brick and concrete walls, travertine pilasters and the seats of the cavea are still to be seen, and other traces have been found beneath the existing buildings at other points. For excavations in the sixteenth century, see LS ii. 228‑ 231; iii. 224‑ 225; iv. 190; LR 498‑ 500; HJ 592‑ 594.
 The Flavian Amphitheatre • Begun by the founder of the Flavian dynasty, Vespasian • Reached the top of the second level before his death in AD 79 • His son and successor Titus added the third and fourth levels and celebrated the dedication of the enlarged structure in AD 80 • Further minor additions were made by Titus's brother and successor Domitian • Later restoration work, especially in the 3 rd century • The exterior dimensions of the wall are 188 m length, 15 m breadth, circumference 527 m and height 50 m HEIGHT: 48. 5 m DATE: ca. AD 70 -80
The Flavian Amphitheatre • Begun by the founder of the Flavian dynasty, Vespasian • Reached the top of the second level before his death in AD 79 • His son and successor Titus added the third and fourth levels and celebrated the dedication of the enlarged structure in AD 80 • Further minor additions were made by Titus's brother and successor Domitian • Later restoration work, especially in the 3 rd century • The exterior dimensions of the wall are 188 m length, 15 m breadth, circumference 527 m and height 50 m HEIGHT: 48. 5 m DATE: ca. AD 70 -80
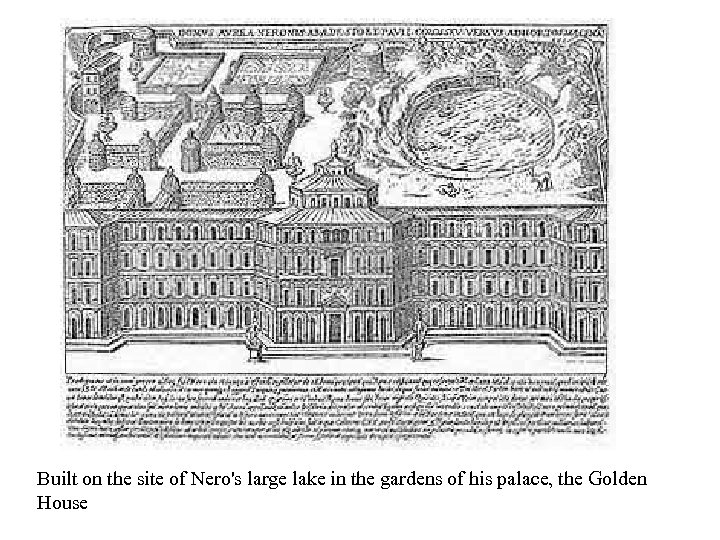 Built on the site of Nero's large lake in the gardens of his palace, the Golden House
Built on the site of Nero's large lake in the gardens of his palace, the Golden House
 The Colosseum
The Colosseum
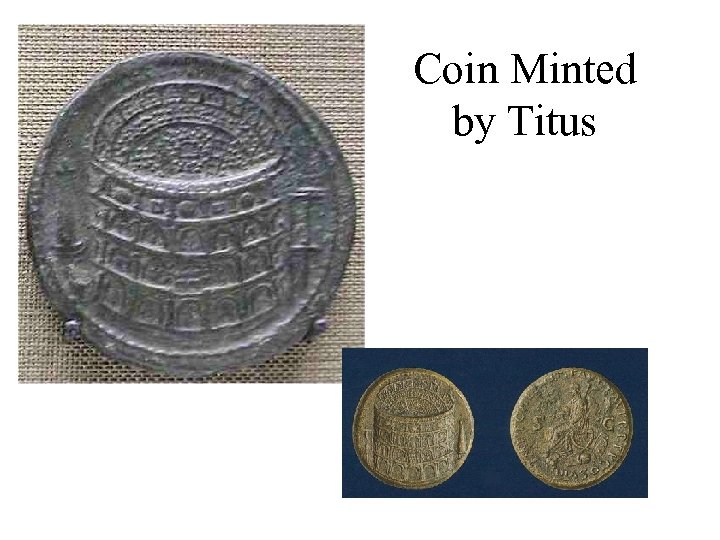 Coin Minted by Titus
Coin Minted by Titus
 The Facade • Exterior decorated with a facade of engaged columns and pilasters that serve no structural purpose • Half-columns of the first three levels from the ground floor upwards display the Greek architectural orders: • 1. Doric (with a cushion-like capital-piece above the actual column) • 2. Ionic (with spiralling volutes at the capital) • 3. Corinthian (with a capital in the form of acanthus leaves) • The top storey has Corinthian pilasters.
The Facade • Exterior decorated with a facade of engaged columns and pilasters that serve no structural purpose • Half-columns of the first three levels from the ground floor upwards display the Greek architectural orders: • 1. Doric (with a cushion-like capital-piece above the actual column) • 2. Ionic (with spiralling volutes at the capital) • 3. Corinthian (with a capital in the form of acanthus leaves) • The top storey has Corinthian pilasters.
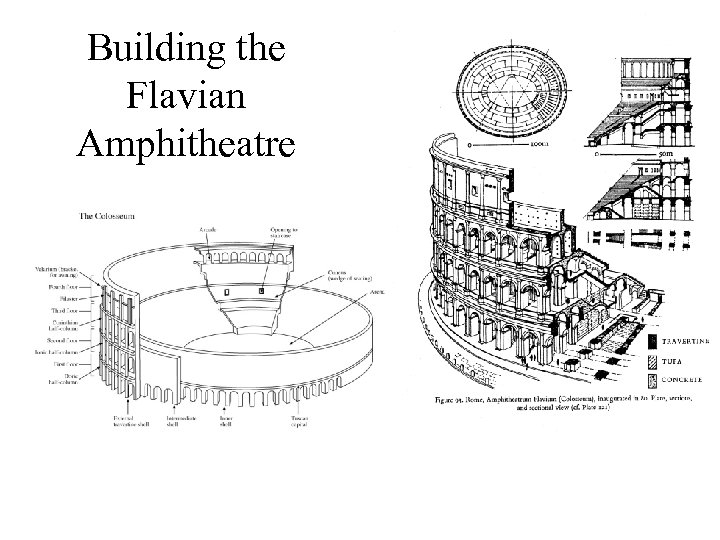 Building the Flavian Amphitheatre
Building the Flavian Amphitheatre
 The Arena The floor of the elliptical arena (86 m x 54 m) was presumably made of wood, covered with sand for the gladiatorial combats and wild beast fights.
The Arena The floor of the elliptical arena (86 m x 54 m) was presumably made of wood, covered with sand for the gladiatorial combats and wild beast fights.
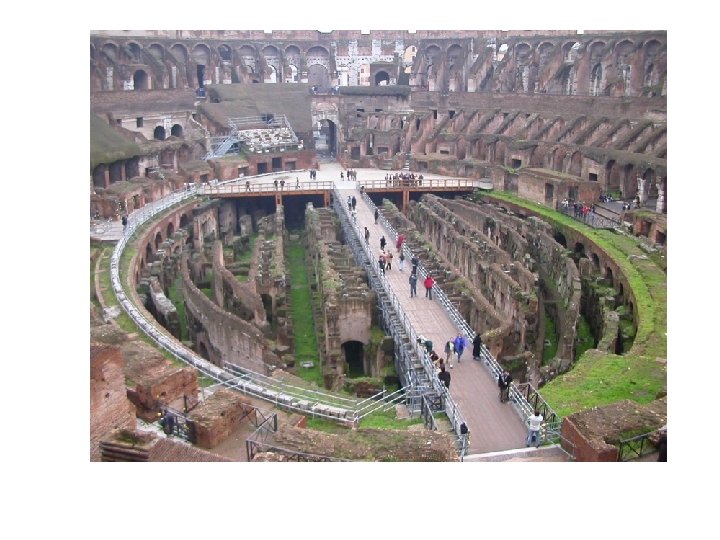

 • Provision had to be made for the drainage of the site through a sewer before any construction could begin • Natural flow of water through the excavated hollow was useful for the staging of mock naval battles in the arena • The substructure goes down 6. 08 m to a brick pavement excavated to reveal the remains of dens for wild beasts, elevators and other devices
• Provision had to be made for the drainage of the site through a sewer before any construction could begin • Natural flow of water through the excavated hollow was useful for the staging of mock naval battles in the arena • The substructure goes down 6. 08 m to a brick pavement excavated to reveal the remains of dens for wild beasts, elevators and other devices
 Seats • For the spectators' protection against wild beast attacks a fence surrounded the fighting area • Behind this and on a platform about 4 m above the arena was the podium for distinguished spectators, particularly city officials. • Above this is the cavea, where most of the seating was placed, consisting of two main sections • 20 rows of marble seats (visible in the center)
Seats • For the spectators' protection against wild beast attacks a fence surrounded the fighting area • Behind this and on a platform about 4 m above the arena was the podium for distinguished spectators, particularly city officials. • Above this is the cavea, where most of the seating was placed, consisting of two main sections • 20 rows of marble seats (visible in the center)
 Velarium velarium: fabric canopy provided relief from sun
Velarium velarium: fabric canopy provided relief from sun
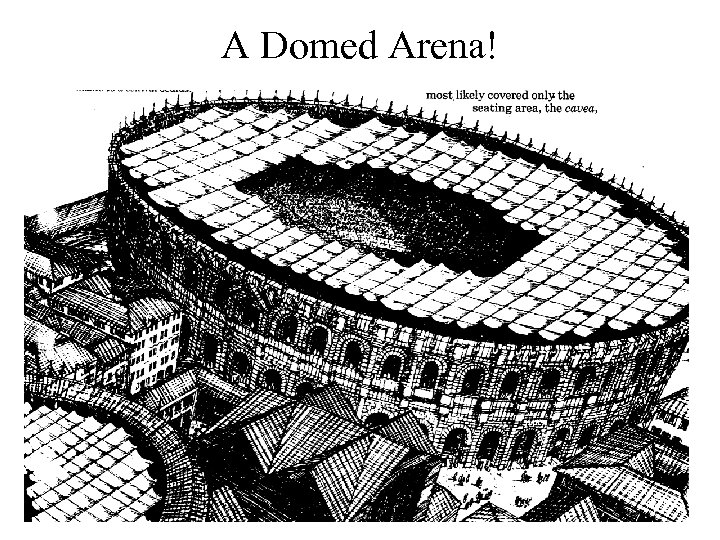 A Domed Arena!
A Domed Arena!
 Venerable Bede (c. 673 -735) While the Colosseum stands, Rome shall stand; when the Colosseum falls, Rome shall fall; when Rome falls, the world shall fall.
Venerable Bede (c. 673 -735) While the Colosseum stands, Rome shall stand; when the Colosseum falls, Rome shall fall; when Rome falls, the world shall fall.
 Amphitheatres in the Roman World Spread all over the empire there were more than 200 large and countless small amphitheatres, of which almost half are situated in Italy. Arles (S France), ca 80, outer: 136 by 107 m, arena: 69 by 38 m El Djem (Tunisia), ca 230. outer: 149 by 124 m, length arena: 65 m Leptis Magna (Libya), ca 60, outer 100 by 80 m Nîmes (France), ca 80, outer: 132 by 101 m, arena: 69 by 38 m. Pompeji (Italy), ca 80 BC, outer: 135 by 104 m Rome (Italy), 70 -80, outer: 188 by 156 m, arena: 80 bu 54 m
Amphitheatres in the Roman World Spread all over the empire there were more than 200 large and countless small amphitheatres, of which almost half are situated in Italy. Arles (S France), ca 80, outer: 136 by 107 m, arena: 69 by 38 m El Djem (Tunisia), ca 230. outer: 149 by 124 m, length arena: 65 m Leptis Magna (Libya), ca 60, outer 100 by 80 m Nîmes (France), ca 80, outer: 132 by 101 m, arena: 69 by 38 m. Pompeji (Italy), ca 80 BC, outer: 135 by 104 m Rome (Italy), 70 -80, outer: 188 by 156 m, arena: 80 bu 54 m
 Arles (S France), ca 80, outer: 136 by 107 m, arena: 69 by 38 m
Arles (S France), ca 80, outer: 136 by 107 m, arena: 69 by 38 m
 Nimes (France), ca 80, outer: 132 by 101 m, arena: 69 by 38 m
Nimes (France), ca 80, outer: 132 by 101 m, arena: 69 by 38 m
 Pompeii (Italy), ca 80 BC, outer: 135 by 104 m This is the oldest amphitheatre and was built in 80 BC. Held 12, 000 spectators.
Pompeii (Italy), ca 80 BC, outer: 135 by 104 m This is the oldest amphitheatre and was built in 80 BC. Held 12, 000 spectators.
 Riot in Pompeii 59 A. D.
Riot in Pompeii 59 A. D.
 El Djem (Tunisia), ca 230. outer: 149 by 124 m, length arena: 65 m
El Djem (Tunisia), ca 230. outer: 149 by 124 m, length arena: 65 m
 Leptis Magna (Libya), ca 60, outer 100 by 80 m
Leptis Magna (Libya), ca 60, outer 100 by 80 m


