c74cf66513252c1d7a66ec066755e8d3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72

The Roles of Light-harvesting Complex Binding Proteins in the assembly and disassembly of the Light-harvesting complex during chlorophyll starvation. Joshua William Kurz California State University, Long Beach

Overview • Introduction ∞ Chlorophyll - Photosystems - LHCs- CCH 1 - CCA 1 • Study goals • Materials & Methods ∞ Double mutants - Microarray - Western Blot • Results • Conclusions • Future Studies • References Cited

Introduction Arabidopsis thaliania • Member of the mustard (Brassicaceae) family.

Introduction Arabidopsis thaliania • Member of the mustard (Brassicaceae) family. • Small genome that has been nearly completely mapped.

Introduction Arabidopsis thaliania • Member of the mustard (Brassicaceae) family. • Small genome that has been nearly completely mapped. • Compact plant with a rapid life cycle and prolific seed production.
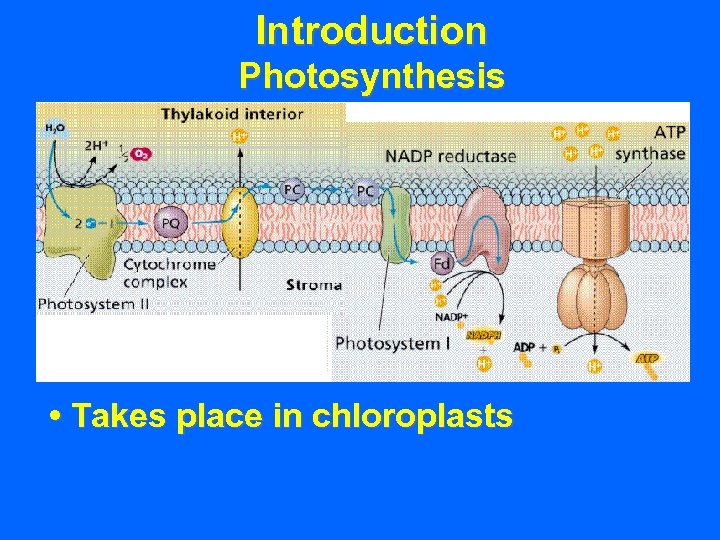
Introduction Photosynthesis • Takes place in chloroplasts
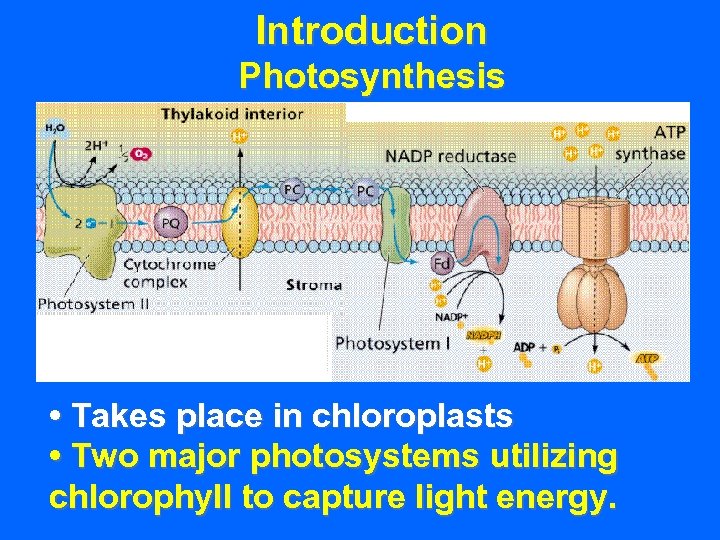
Introduction Photosynthesis • Takes place in chloroplasts • Two major photosystems utilizing chlorophyll to capture light energy.

Introduction Light Harvesting Complexes • Chlorophyll is also found in lightharvesting complexes (LHCs).

Introduction Light Harvesting Complexes • Chlorophyll is also found in lightharvesting complexes (LHCs). • LHCs encompass the photosystems.

Introduction Light Harvesting Complexes • Chlorophyll is also found in lightharvesting complexes (LHCs). • LHCs encompass the photosystems. • Provide supplemental pigments for greater light-harvesting efficiency.

Introduction Light Harvesting Complexes • Chlorophyll is also found in lightharvesting complexes (LHCs). • LHCs encompass the photosystems. • Provide supplemental pigments for greater light-harvesting efficiency. • LHCs actually contain up to 80% of the chlorophyll mass for the entire photosystem.

Introduction Light Harvesting Complexes • Chlorophyll is also found in lightharvesting complexes (LHCs). • LHCs encompass the photosystems. • Provide supplemental pigments for greater light-harvesting efficiency. • LHCs actually contain up to 80% of the chlorophyll mass for the entire photosystem. • The LHC is assembled and disassembled in response to changes in light levels.
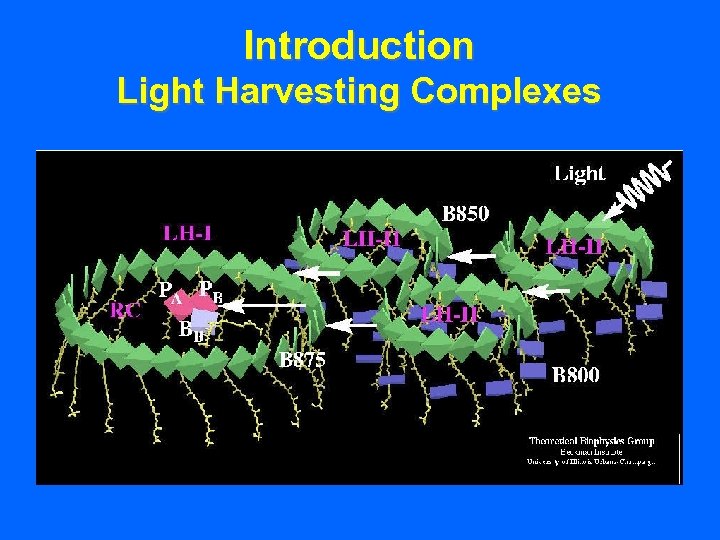
Introduction Light Harvesting Complexes

Introduction LHCBs • Light Harvesting Complex Building Proteins.

Introduction LHCBs • Light Harvesting Complex Building Proteins. • Incorporate, assemble and disassemble LHC.

Introduction LHCBs • Light Harvesting Complex Building Proteins. • Incorporate, assemble and disassemble LHC. • Encoded by nuclear genes, and are regulated through a DNA promoter site.

Introduction LHCBs • Light Harvesting Complex Building Proteins. • Incorporate, assemble and disassemble LHC. • Encoded by nuclear genes, and are regulated through a DNA promoter site. • Are stable only when bound with chlorophyl and imparts stability to chlorophyl.

Introduction LHCBs • Light Harvesting Complex Building Proteins. • Incorporate, assemble and disassemble LHC. • Encoded by nuclear genes, and are regulated through a DNA promoter site. • Are stable only when bound with chlorophyl and imparts stability to chlorophyl. • Must be fast acting or both are degraded.

Introduction LHCBs • Light Harvesting Complex Building Proteins. • Incorporate, assemble and disassemble LHC. • Encoded by nuclear genes, and are regulated through a DNA promoter site. • Are stable only when bound with chlorophyl and imparts stability to chlorophyl. • Must be fast acting or both are degraded. • Six identified LHCB genes: lhcb 1, Lhcb 2, Lhcb 3, etc….

Introduction LHCBs • Light Harvesting Complex Building Proteins. • Incorporate, assemble and disassemble LHC. • Encoded by nuclear genes, and are regulated through a DNA promoter site. • Are stable only when bound with chlorophyl and imparts stability to chlorophyl. • Must be fast acting or both are degraded. • Six identified LHCB genes: lhcb 1, Lhcb 2, Lhcb 3, etc…. • Specific LHCB roles are unclear.

Introduction CCH 1 • Conditional chlorina (cch 1) discovered by Dr. Judith Brusslan.

Introduction CCH 1 • Conditional chlorina (cch 1) discovered by Dr. Judith Brusslan. • Chlorophyll levels near that of wild-type at low light intensity.

Introduction CCH 1 • Conditional chlorina (cch 1) discovered by Dr. Judith Brusslan. • Chlorophyll levels near that of wild-type at low light intensity. • Pale yellow-green phenotype in cch 1 mutant at moderate light intensity; otherwise viable & acclimates to chlorophyll deficiency.
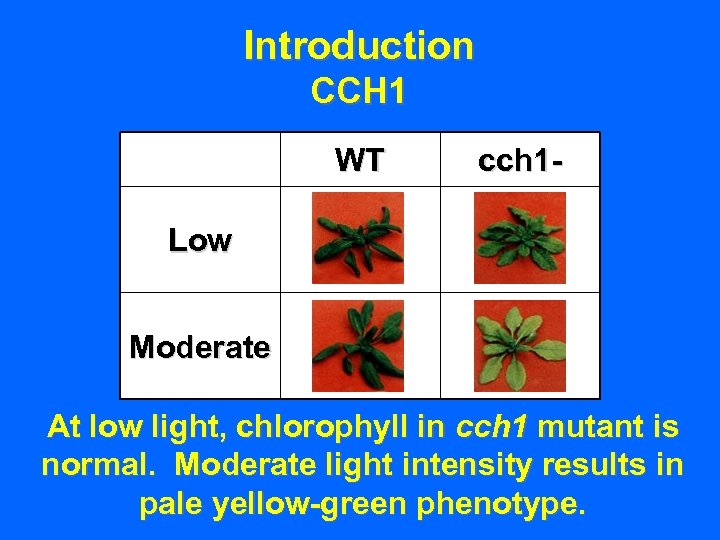
Introduction CCH 1 WT cch 1 - Low Moderate At low light, chlorophyll in cch 1 mutant is normal. Moderate light intensity results in pale yellow-green phenotype.

Introduction CCH 1 (cont’d) • Point mutation alters a sub-unit of the Mgchelatase enzyme that catalyzes a final intermediate in chlorophyll a biosynthesis.
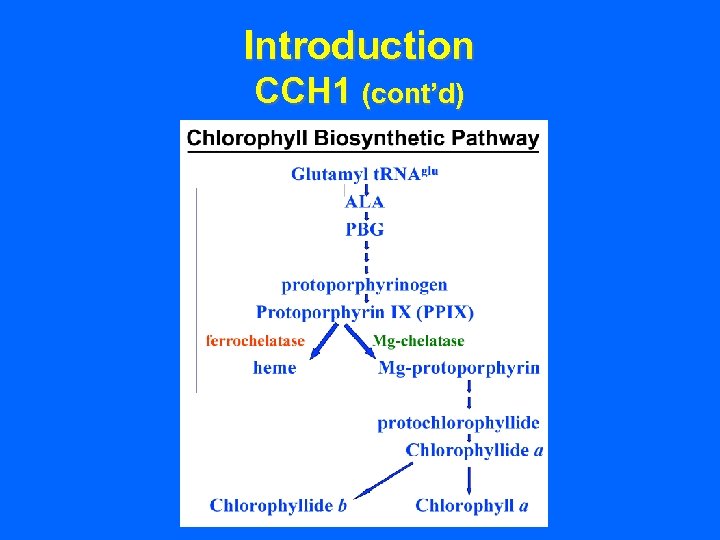
Introduction CCH 1 (cont’d)
Introduction CCH 1 (cont’d) • Point mutation alters a sub-unit of the Mgchelatase enzyme that catalyzes a final intermediate in chlorophyll a biosynthesis. • Decreased chlorophyll levels shown to lead to decreased levels of all six LHCBs.
Introduction CCH 1 (cont’d) • Point mutation alters a sub-unit of the Mgchelatase enzyme that catalyzes a final intermediate in chlorophyll a biosynthesis. • Decreased chlorophyll levels shown to lead to decreased levels of all six LHCBs. • The related Light Harvesting Complexes (LHC) are disassembled in an unknown process because they are unstable when they are not bound to chlorophyll.

Introduction CCA 1 • Circadian Clock-Associated (CCA 1).

Introduction CCA 1 • Circadian Clock-Associated (CCA 1). • Participates in phytochrome control and circadian regulation.
Introduction CCA 1 • Circadian Clock-Associated (CCA 1). • Participates in phytochrome control and circadian regulation. • CCA 1 null mutation identified and cloned.
Introduction CCA 1 • Circadian Clock-Associated (CCA 1). • Participates in phytochrome control and circadian regulation. • CCA 1 null mutation identified and cloned. • cca 1 gene product required DNA promoter of Lhcb 1.
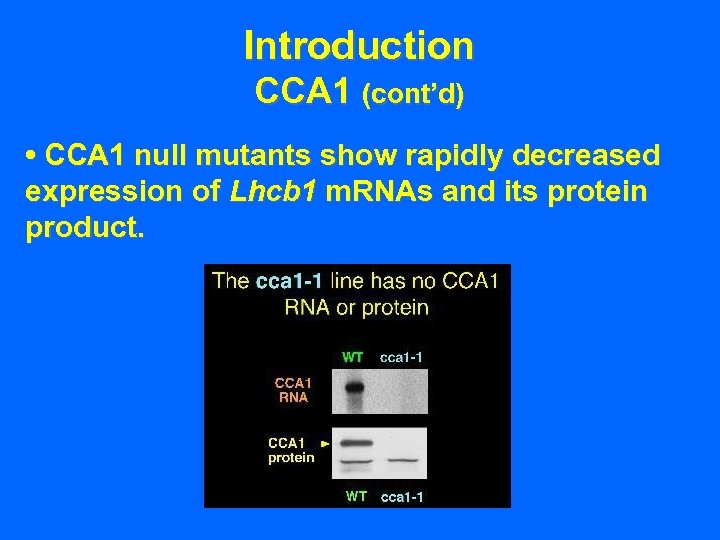
Introduction CCA 1 (cont’d) • CCA 1 null mutants show rapidly decreased expression of Lhcb 1 m. RNAs and its protein product.
Introduction CCA 1 (cont’d) • CCA 1 null mutants show rapidly decreased expression of Lhcb 1 m. RNAs and its protein product. • No change in the chlorophyll phenotype of the plants.
Introduction CCA 1 (cont’d) • CCA 1 null mutants show rapidly decreased expression of Lhcb 1 m. RNAs and its protein product. • No change in the chlorophyll phenotype of the plants. • Suggests that the cca 1 gene product participates in the assembly of the LHC.

Study Goals • Cch 1 mutants over express cca 1, sometimes at levels four times greater than in wild type plants.

Study Goals • Cch 1 mutants over express cca 1, sometimes at levels four times greater than in wild type plants. • Suspected to be a response to chlorophyll-a starvation to minimize LHC assembly and isolate chlorophyll-a incorporation to photosystem assembly.

Study Goals • Cch 1 mutants over express cca 1, sometimes at levels four times greater than in wild type plants. • Suspected to be a response to chlorophyll-a starvation to minimize LHC assembly and isolate chlorophyll-a incorporation to photosystem assembly. • While LHCB 1 is abundant in cch 1 mutants, the other LHCBs are degraded (disassembly of LHC).

Study Goals • Cch 1 mutants over express cca 1, sometimes at levels four times greater than in wild type plants. • Suspected to be a response to chlorophyll-a starvation to minimize LHC assembly and isolate chlorophyll-a incorporation to photosystem assembly. • While LHCB 1 is abundant in cch 1 mutants, the other LHCBs are degraded (disassembly of LHC). • Hypothesize double mutant cch 1 -/cca 1 - will provide insight into the role of cca 1 in the assembly or disassembly of LHCs.

Study Goals • Designed to explain the up regulation of cca 1 and, subsequently, lhcb 1 when cch 1 is simultaneously under expressed.

Study Goals • Designed to explain the up regulation of cca 1 and, subsequently, lhcb 1 when cch 1 is simultaneously under expressed. • We will quantify the expression of lhcb 2, lhcb 3, lhcb 4, lhcb 5, and lhcb 6 to identify the role of these genes in response to the down regulation of lhcb 1.

Study Goals • Designed to explain the up regulation of cca 1 and, subsequently, lhcb 1 when cch 1 is simultaneously under expressed. • We will quantify the expression of lhcb 2, lhcb 3, lhcb 4, lhcb 5, and lhcb 6 to identify the role of these genes in response to the down regulation of lhcb 1. • If the results of this study support our hypothesis, they will suggest that LHCB 1 is involved in LHC disassembly.

Methods • Bred and selected for Arabidopsis cch 1 -, cca 1 - double mutants using cch 1 mutant homozygote in parental generation.
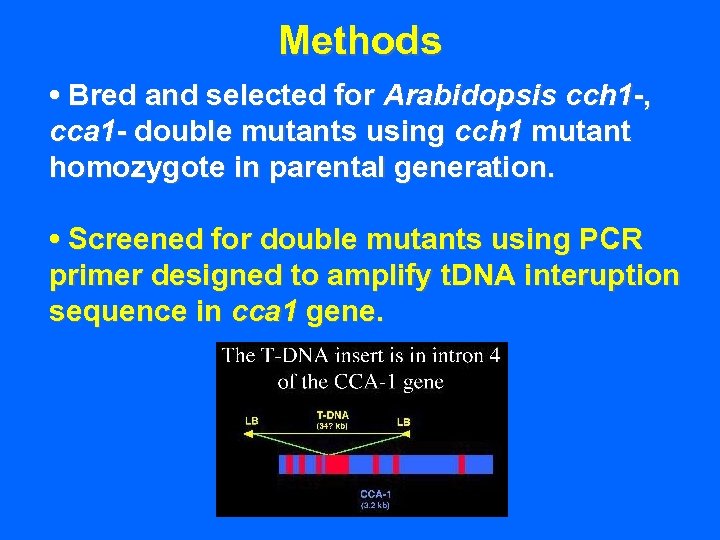
Methods • Bred and selected for Arabidopsis cch 1 -, cca 1 - double mutants using cch 1 mutant homozygote in parental generation. • Screened for double mutants using PCR primer designed to amplify t. DNA interuption sequence in cca 1 gene.
Methods • Bred and selected for Arabidopsis cch 1 -, cca 1 - double mutants using cch 1 mutant homozygote in parental generation. • Screened for double mutants using PCR primer designed to amplify t. DNA interuption sequence in cca 1 gene. • Expose double mutants to low and moderate light intensities.
Methods • Made observations of resulting phenotypes and quantified total chlorophyll using dimethylformamide(DMF) and Spectrophotometric analyisis.
Methods • Made observations of resulting phenotypes and quantified total chlorophyll using dimethylformamide(DMF) and Spectrophotometric analyisis. • Quantified LHCB levels in double mutants using Western blot analysis.
Methods • Made observations of resulting phenotypes and quantified total chlorophyll using dimethylformamide(DMF) and Spectrophotometric analyisis. • Quantified LHCB levels in double mutants using Western blot analysis. • Quantified lhcb gene expression using Microarray analysis.
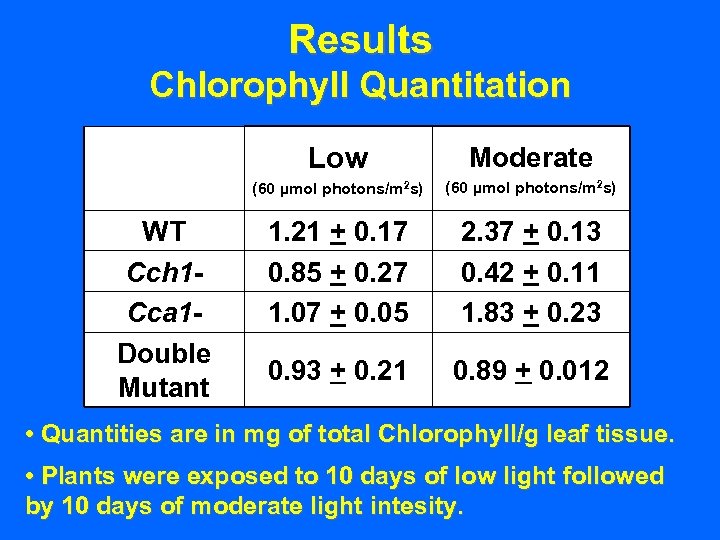
Results Chlorophyll Quantitation Low (60 µmol photons/m 2 s) WT Cch 1 Cca 1 Double Mutant Moderate (60 µmol photons/m 2 s) 1. 21 + 0. 17 0. 85 + 0. 27 1. 07 + 0. 05 2. 37 + 0. 13 0. 42 + 0. 11 1. 83 + 0. 23 0. 93 + 0. 21 0. 89 + 0. 012 • Quantities are in mg of total Chlorophyll/g leaf tissue. • Plants were exposed to 10 days of low light followed by 10 days of moderate light intesity.
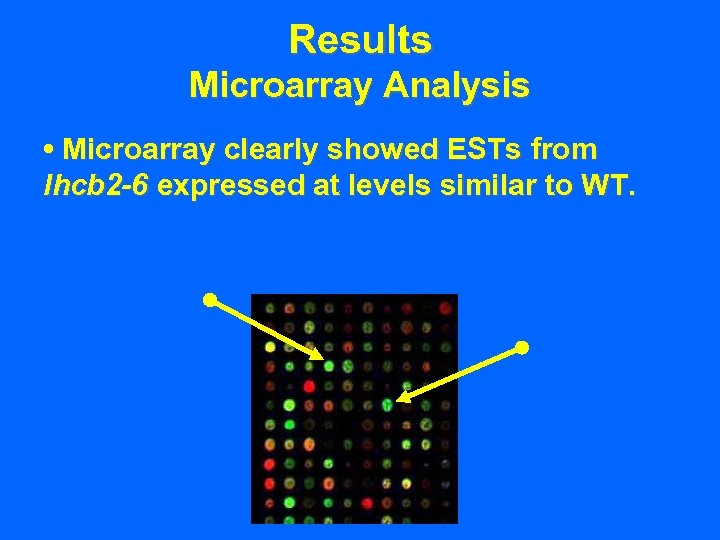
Results Microarray Analysis • Microarray clearly showed ESTs from lhcb 2 -6 expressed at levels similar to WT.
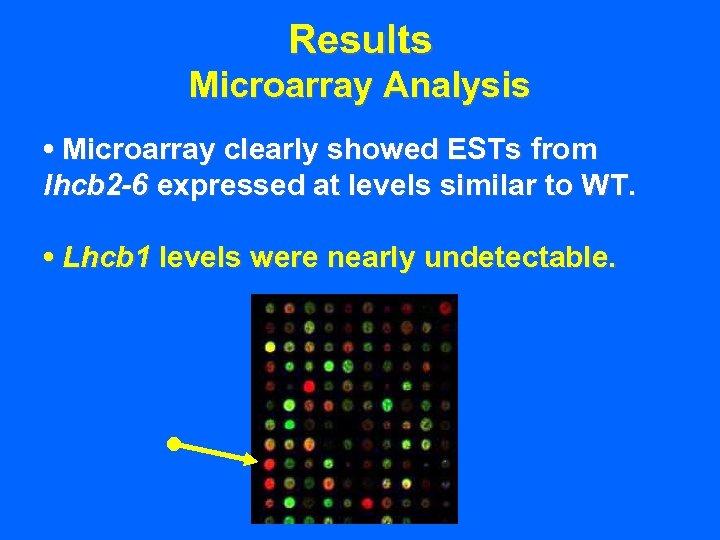
Results Microarray Analysis • Microarray clearly showed ESTs from lhcb 2 -6 expressed at levels similar to WT. • Lhcb 1 levels were nearly undetectable.
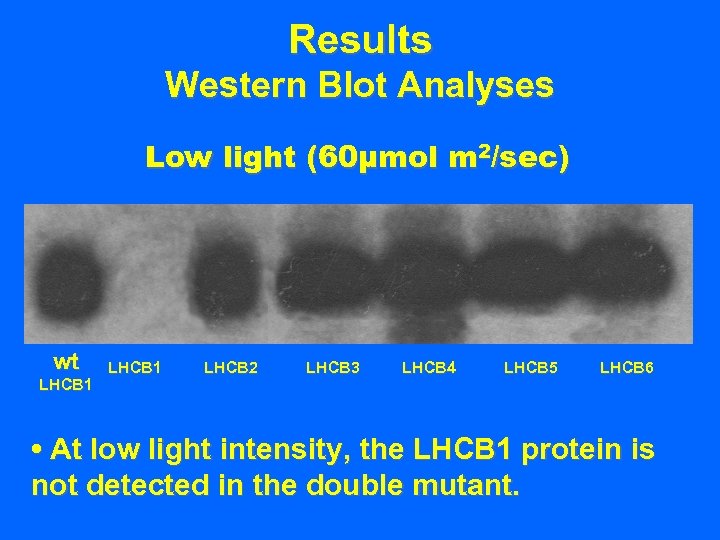
Results Western Blot Analyses Low light (60µmol m 2/sec) wt LHCB 1 LHCB 2 LHCB 3 LHCB 4 LHCB 5 LHCB 6 • At low light intensity, the LHCB 1 protein is not detected in the double mutant.
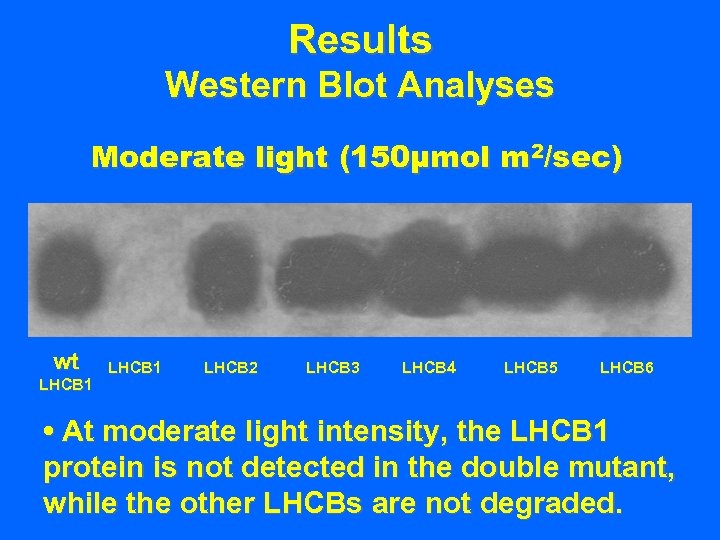
Results Western Blot Analyses Moderate light (150µmol m 2/sec) wt LHCB 1 LHCB 2 LHCB 3 LHCB 4 LHCB 5 LHCB 6 • At moderate light intensity, the LHCB 1 protein is not detected in the double mutant, while the other LHCBs are not degraded.

Conclusions • Chlorophyll levels in double mutants are characteristic of cch 1 mutants, inducing chlorophyll starvation.

Conclusions • Chlorophyll levels in double mutants are characteristic of cch 1 mutants, inducing chlorophyll starvation. • Plants respond to cch 1 mutant chlorophyll starvation by upregulation of cca 1.
Conclusions • Chlorophyll levels in double mutants are characteristic of cch 1 mutants, inducing chlorophyll starvation. • Plants respond to cch 1 mutant chlorophyll starvation by upregulation of cca 1. • CCA 1 is a transcription promoter of lhcb 1.
Conclusions • Chlorophyll levels in double mutants are characteristic of cch 1 mutants, inducing chlorophyll starvation. • Plants respond to cch 1 mutant chlorophyll starvation by upregulation of cca 1. • CCA 1 is a transcription promoter of lhcb 1. • Double mutants for cch 1 and cca 1 could not respond to chlorophyll starvation by upregulation cca 1 to disassemble LHCs.

Conclusions • Disassembly of LHCs increases the efficient incorporation of chlorophyll into the Photosystem complexes.

Conclusions • Disassembly of LHCs increases the efficient incorporation of chlorophyll into the Photosystem complexes. • The inability to upregulate cca 1 resulted in the persistence of LHCBs 2 through 6 while LHCB 1 was undetected.

Conclusions • Disassembly of LHCs increases the efficient incorporation of chlorophyll into the Photosystem complexes. • The inability to upregulate cca 1 resulted in the persistence of LHCBs 2 through 6 while LHCB 1 was undetected. • LHCB 1 is involved in the disassembly of the LHC, ultimately resulting in the degradation of LHCB 2 through 6.

Future Studies • Disseminate the roles of the other LHCBs through knockout experiments, creating null mutants for LHCBs 2 through 6, with and without active LHCB 1.

Future Studies • Disseminate the roles of the other LHCBs through knockout experiments, creating null mutants for LHCBs 2 through 6, with and without active LHCB 1. • Rescue therapy of double cca 1 and cch 1 mutants with exogenous CCA 1 and LHCB, independently.
Future Studies • Disseminate the roles of the other LHCBs through knockout experiments, creating null mutants for LHCBs 2 through 6, with and without active LHCB 1. • Rescue therapy of double cca 1 and cch 1 mutants with exogenous CCA 1 and LHCB, independently. • Knockout experiments of Photosystem Binding proteins in LHCB null mutants.

Acknowledgements • Dr. Judith Brusslan

Acknowledgements • Dr. Judith Brusslan • Dr. Andrew “Zed” Mason

Acknowledgements • Dr. Judith Brusslan • Dr. Andrew “Zed” Mason • Dr. James Archie

Acknowledgements • Dr. Judith Brusslan • Dr. Andrew “Zed” Mason • Dr. James Archie • Brian Thorson

Acknowledgements • Dr. Judith Brusslan • Dr. Andrew “Zed” Mason • Dr. James Archie • Brian Thorson • Siggi Von Gesjen

Acknowledgements • Dr. Judith Brusslan • Dr. Andrew “Zed” Mason • Dr. James Archie • Brian Thorson • Siggi Von Gesjen • Howard Hughes Medical Institute

References 1. Meyerowitz, E. M. 1984. A pretty comprehensive overview of Arabidopsology. CSHL Press , New York, USA 2. Campbell, N. A. 1999. Biology: 5 th Ed. Addison. Wessley, Philidelphia, PA 3. Morashige, D. T. and Thornber, J. P. 1992. Identification and analysis of a barley c. DNA clone encoding the 31 k. D LHC Iia apoprotein of the light-harvesting complex of PSII. Plant Physiology 98: 238 -245 4. Paulsen, H. 1995. Invited review; chlorophyll a/b binding proteins. Photochemistry and Photobiology 62(3): 367 -382

References (cont’d) 5. Bennet, J. 1981. Biosynthesis of the lightharvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. European Journal of Biochemistry 118: 61 -70 6. Brusslan, J. A. , Linford, A. S. , Espineda, C. E. 1999. The at. CAO gene. Encoding chlorophyll a oxygenase, is required for Chl b synthesis in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 96(18): 10507 -11 7. Green, R. M. , Tobin, E. M. 1999 Loss of CCA protein 1 in arabidopsis results in altered clock regulated gene expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 96(7): 4176 -79

References (cont’d) 8. Green, B. R. , 1988. Mini-Review: The chlorophyll-protein complexes of higher plant photosynthetic membrane. Photosynthesis Research 15: 3 -32 9. Wang, Z. Y. et al. , 1997. A myb-related transcription factor is involved in the Phytochrome regulation of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 9(4): 491 -507 10. Tobin, E. M. , Wang Z. Y. 1997. Constitutive expression of the CCA 1 protein disrupts circadian rhythm and suppresses its own expression. Cell 93(7): 1207 -1217
c74cf66513252c1d7a66ec066755e8d3.ppt